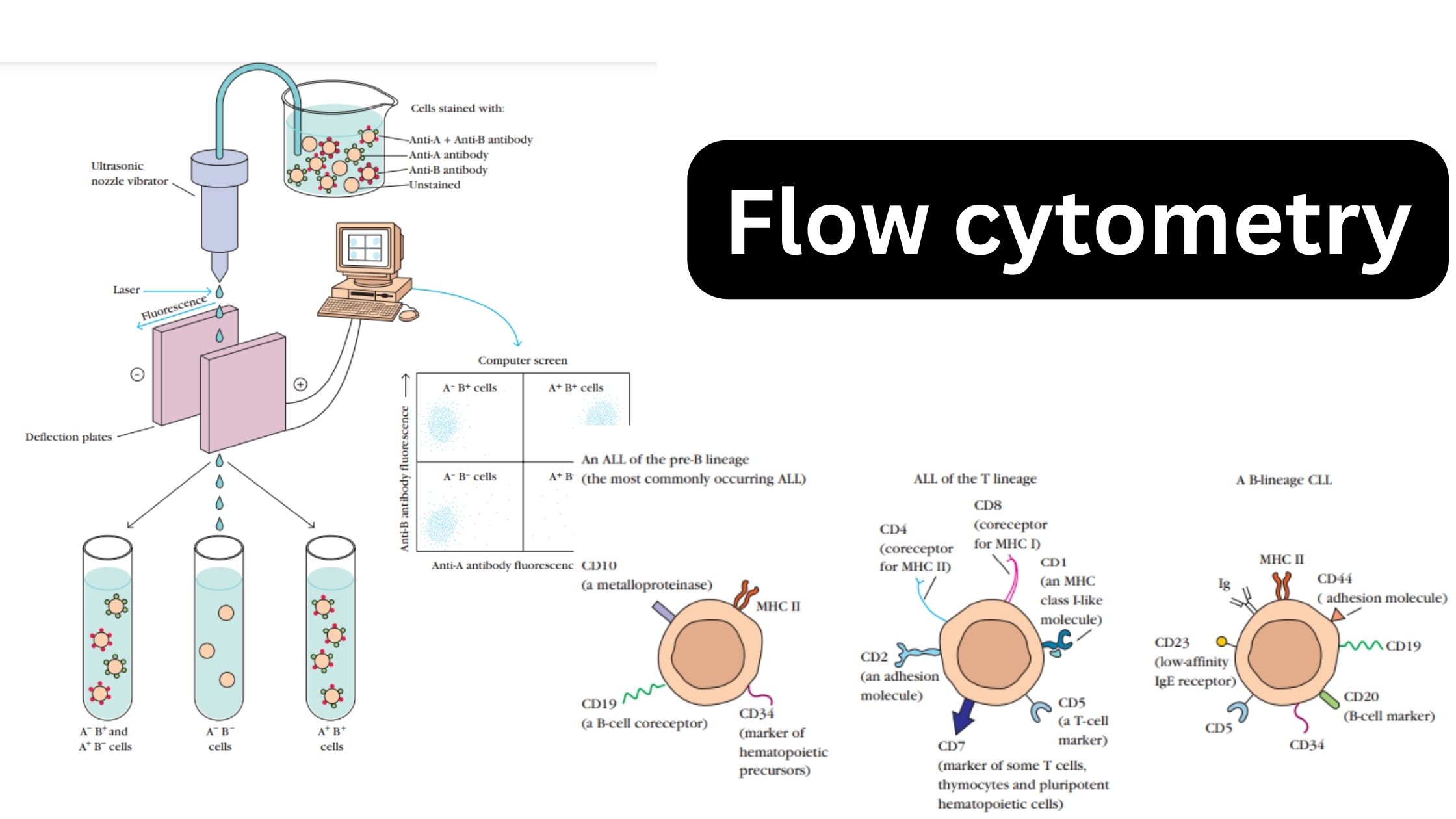
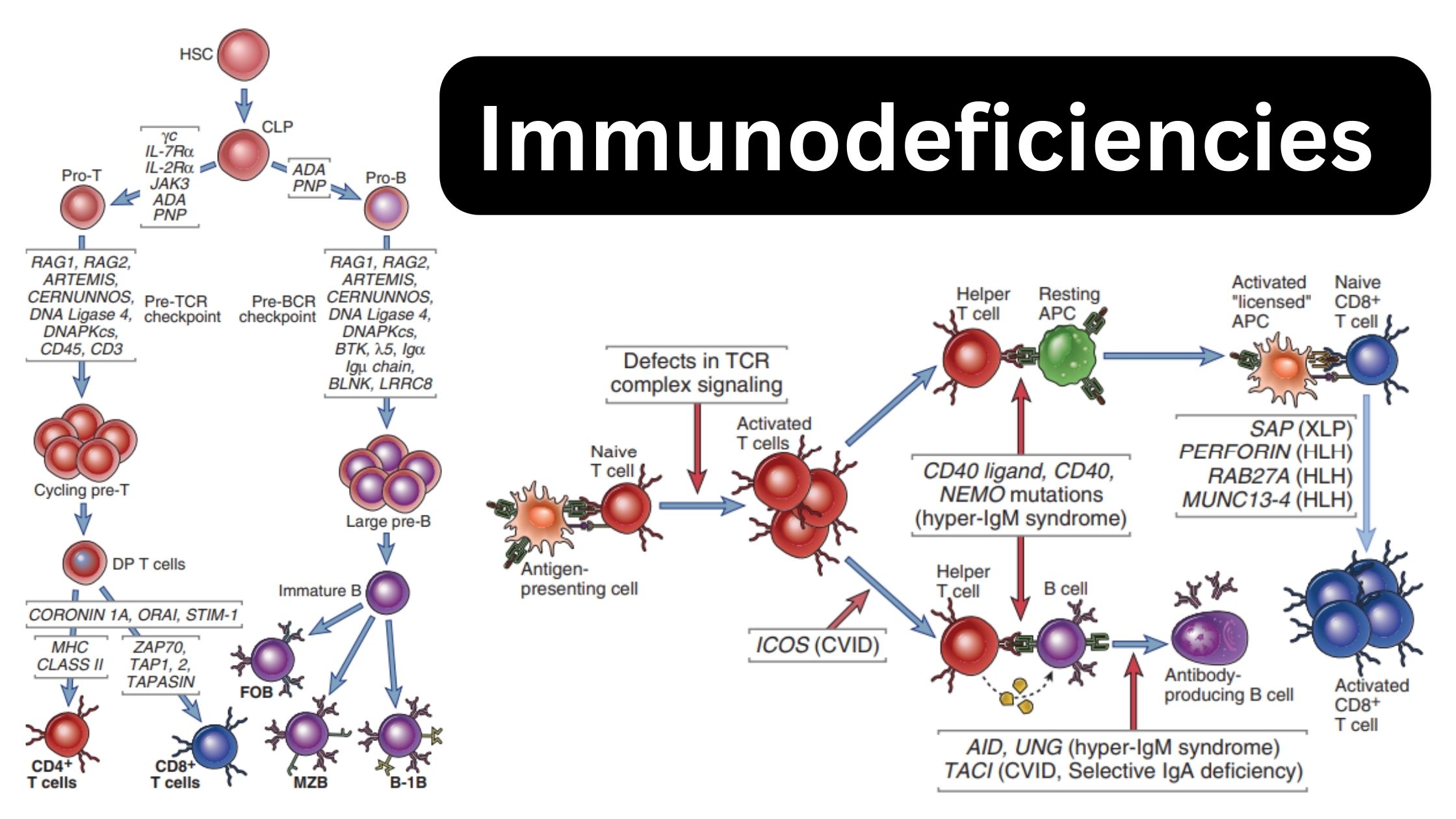
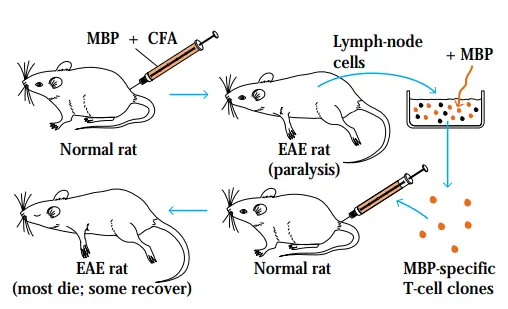
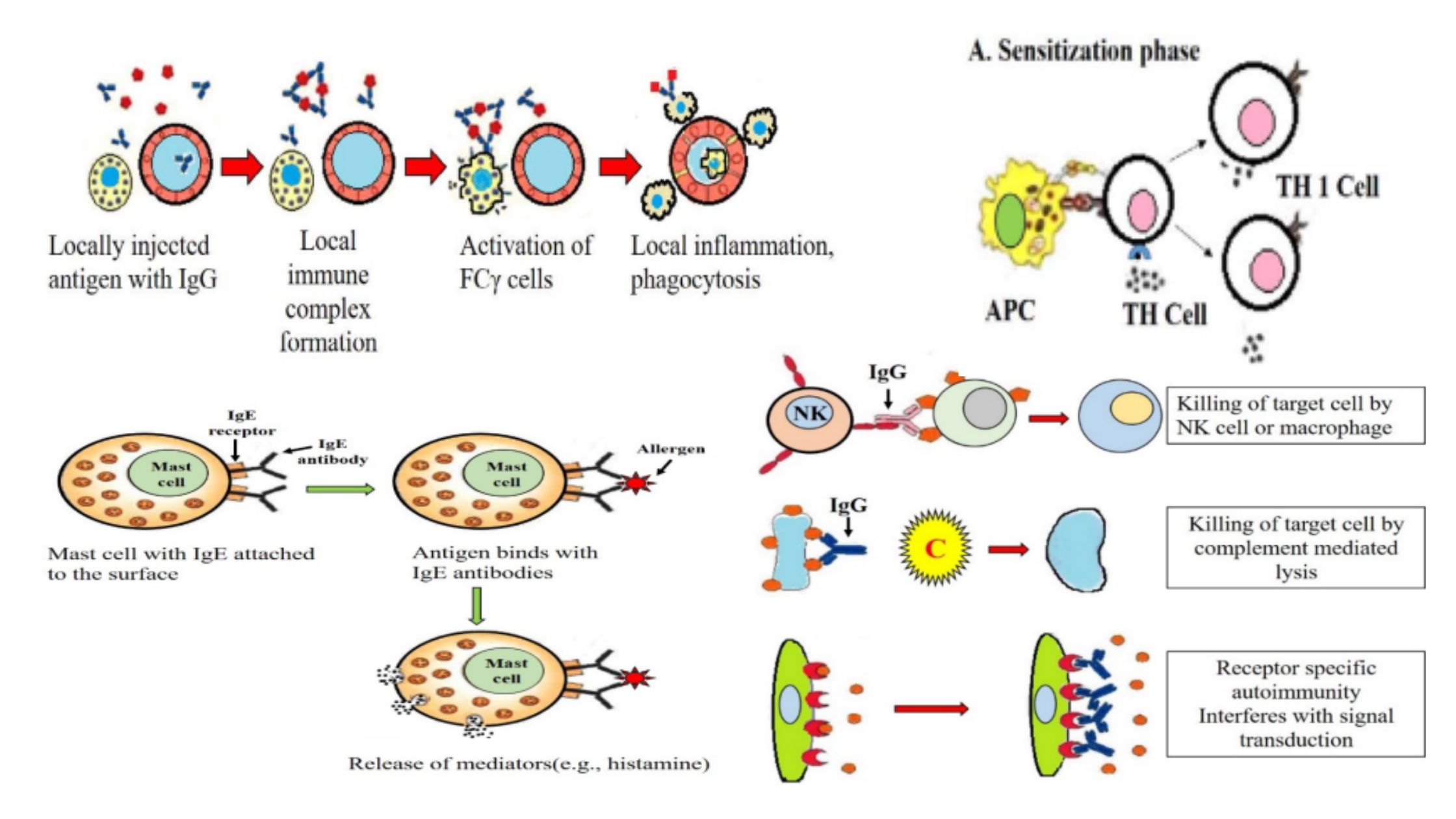
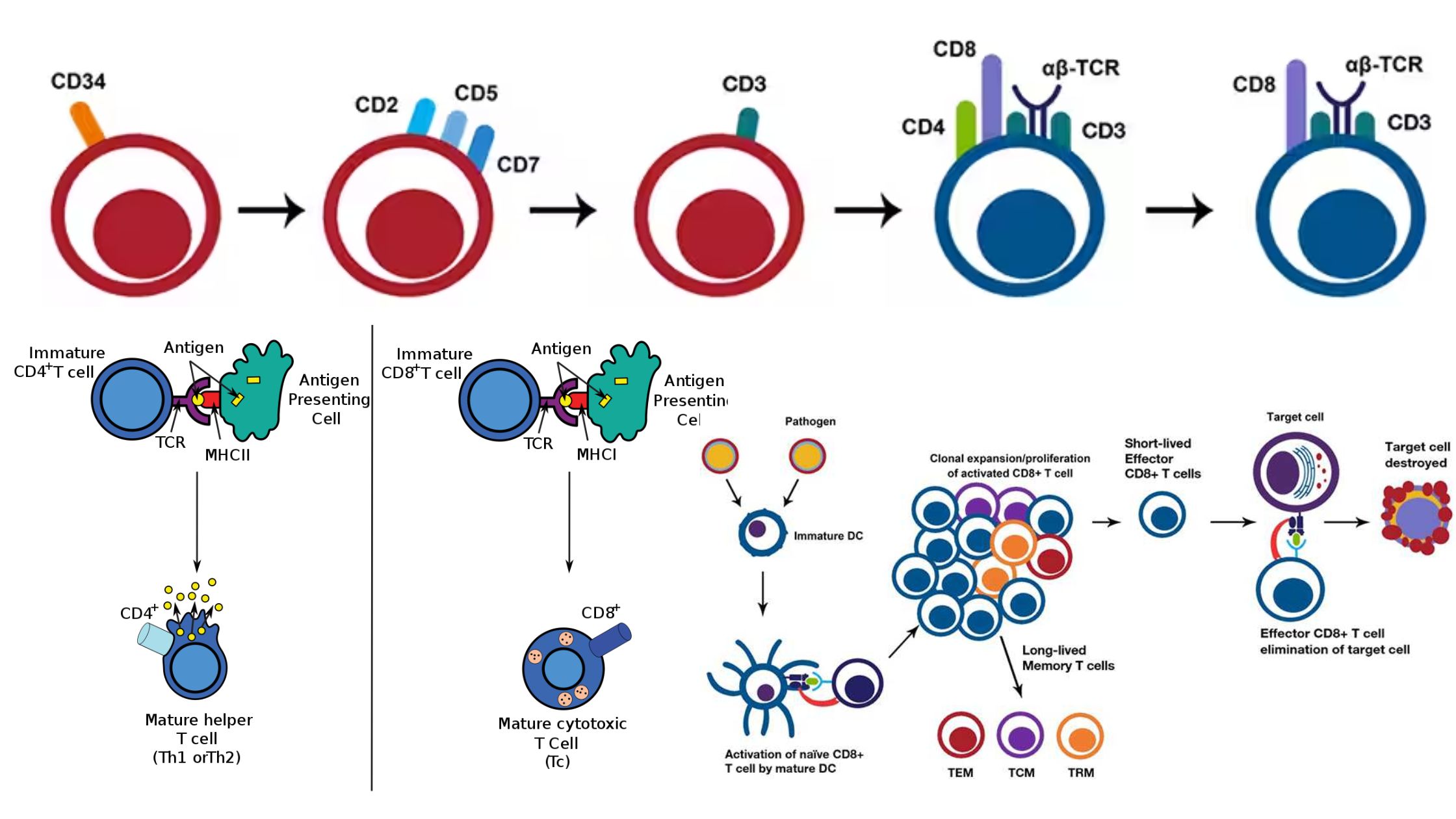
Flow Cytometry – Principle, Process, Uses
What is Flow cytometry? Flow cytometry Instrumentation Flow cytometry Principle Information Obtained from Flow cytometry The flow cytometer has various clinical and scientific applications. The determination of the type and amount of white blood cells in blood samples is a typical clinical application. By treating properly processed blood samples with a fluorescently tagged antibody and … Read more