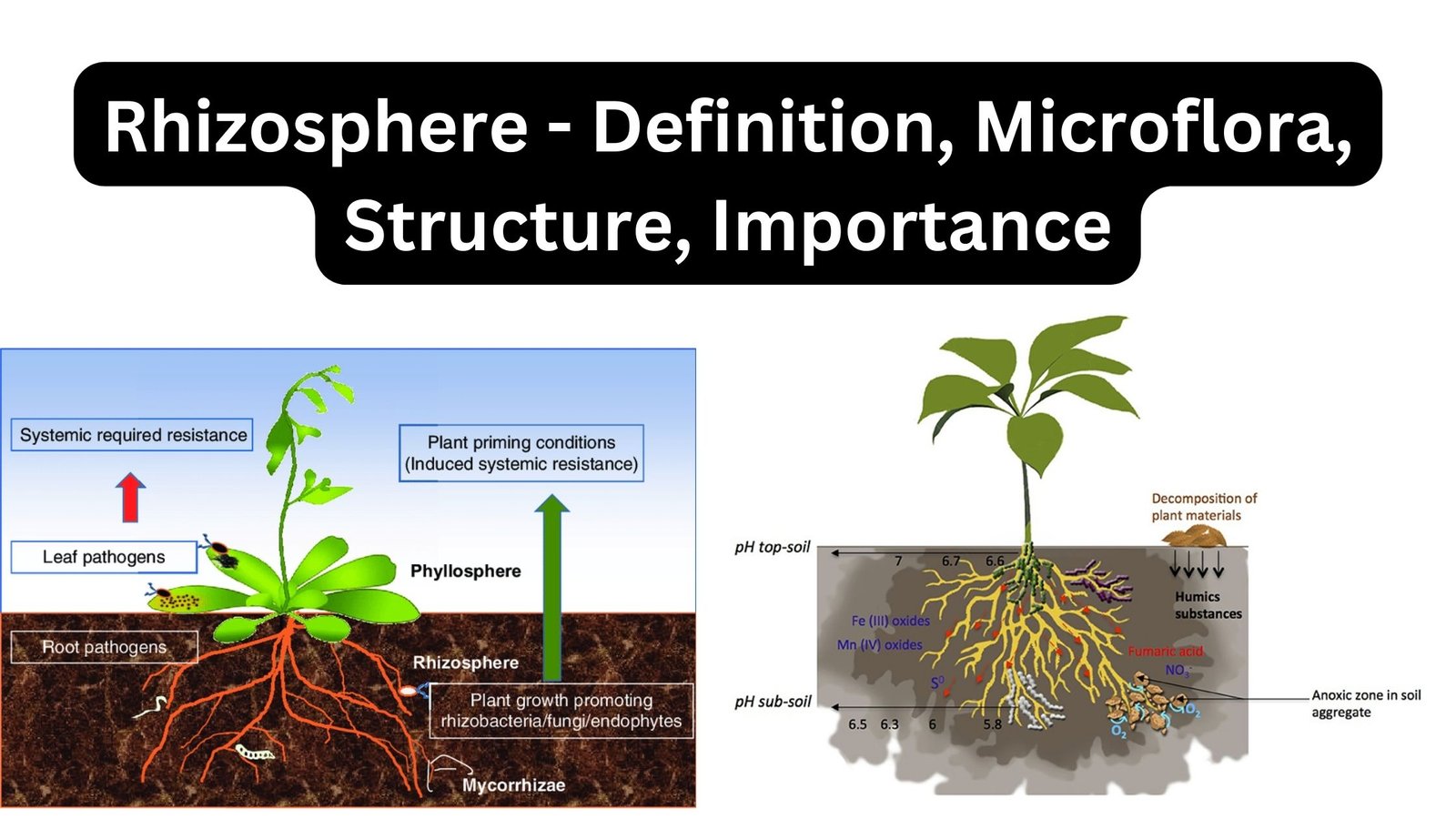
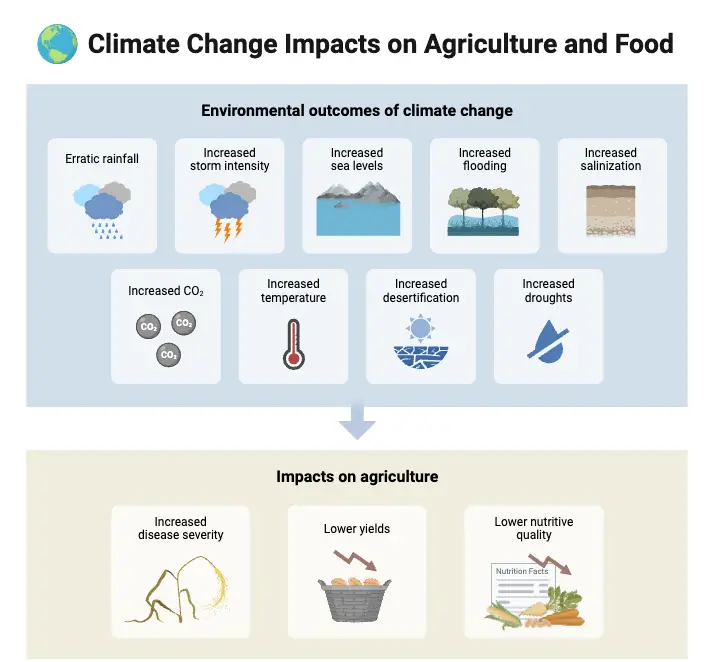
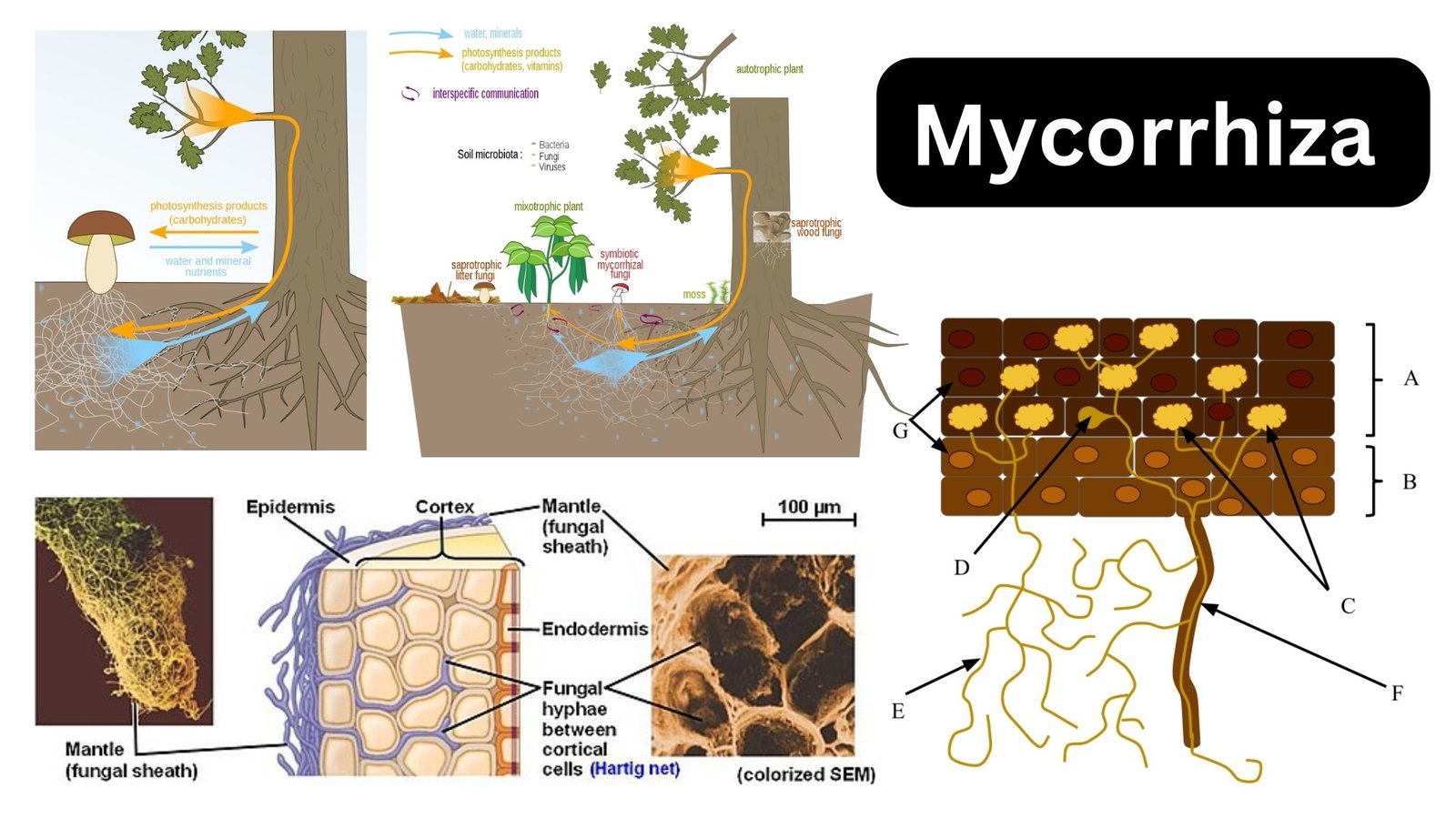
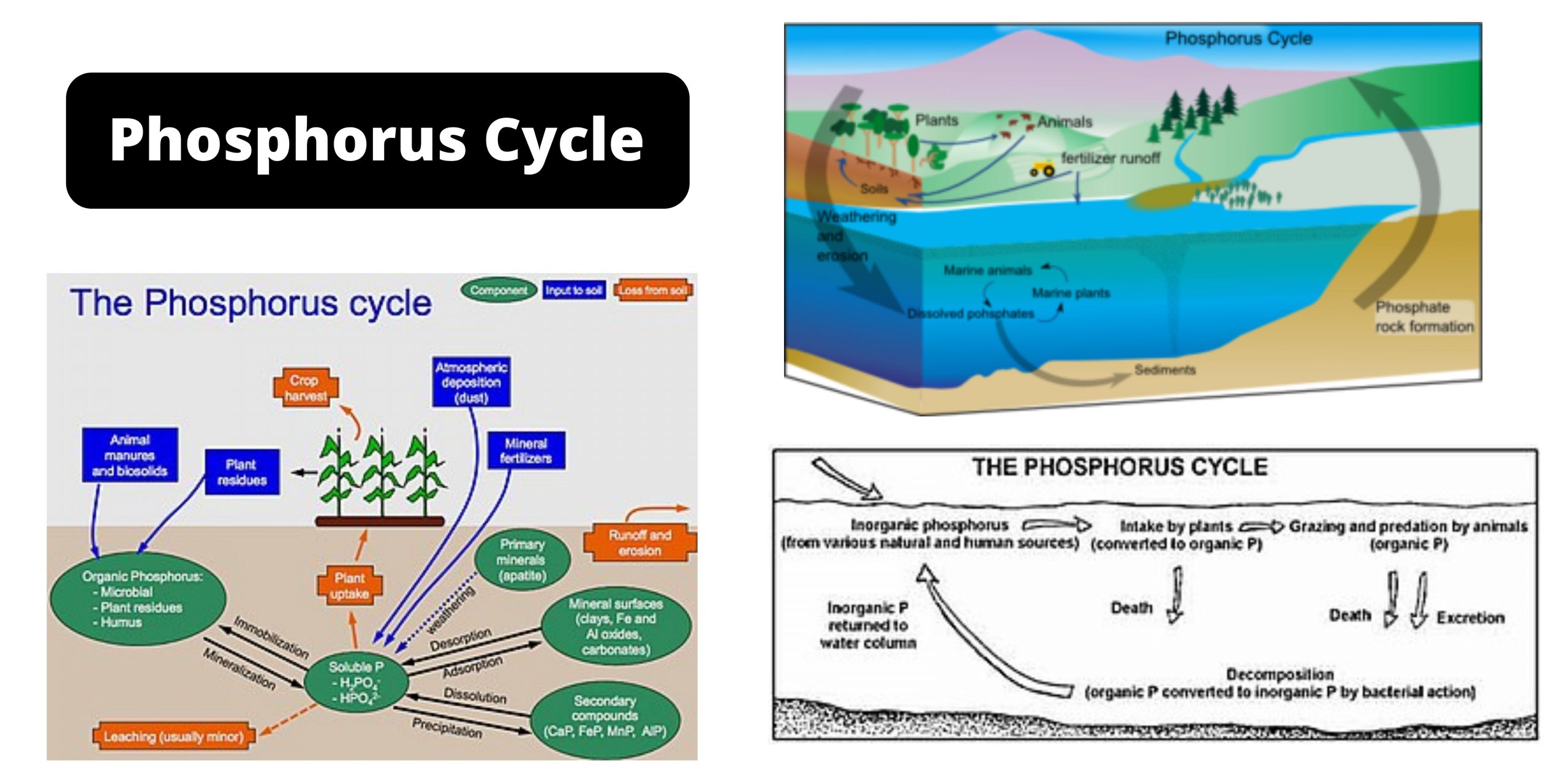
Biodiversity Hotspots – Definition, Criteria, Importance, Examples
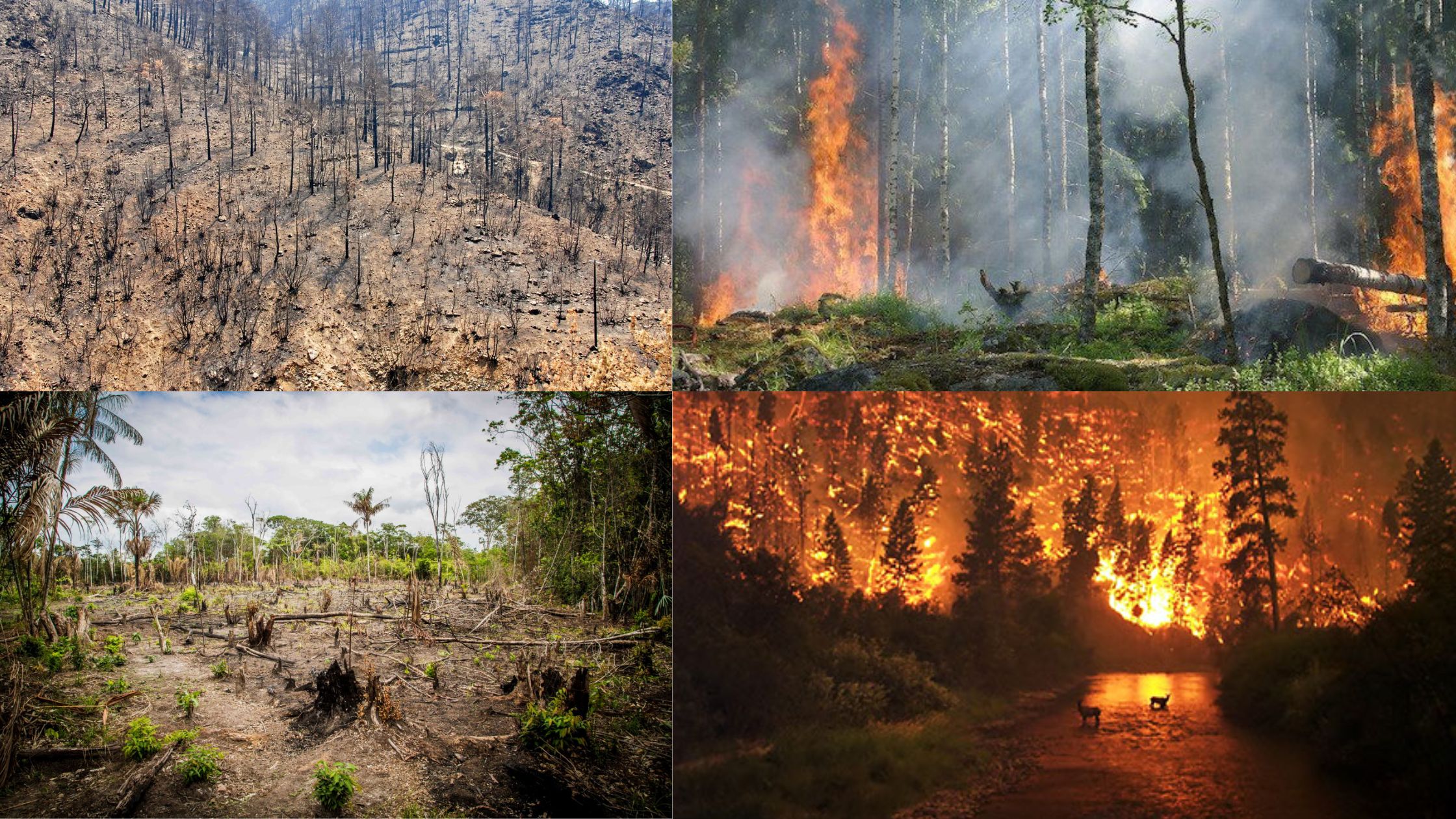
Biodiversity hotspots are regions packed with an extraordinary variety of plant and animal life found nowhere else on Earth—but they’re also in serious trouble. To qualify as a hotspot, an area must have at least 1,500 unique plant species and have already lost over 70% of its original natural habitat due to human activities like … Read more