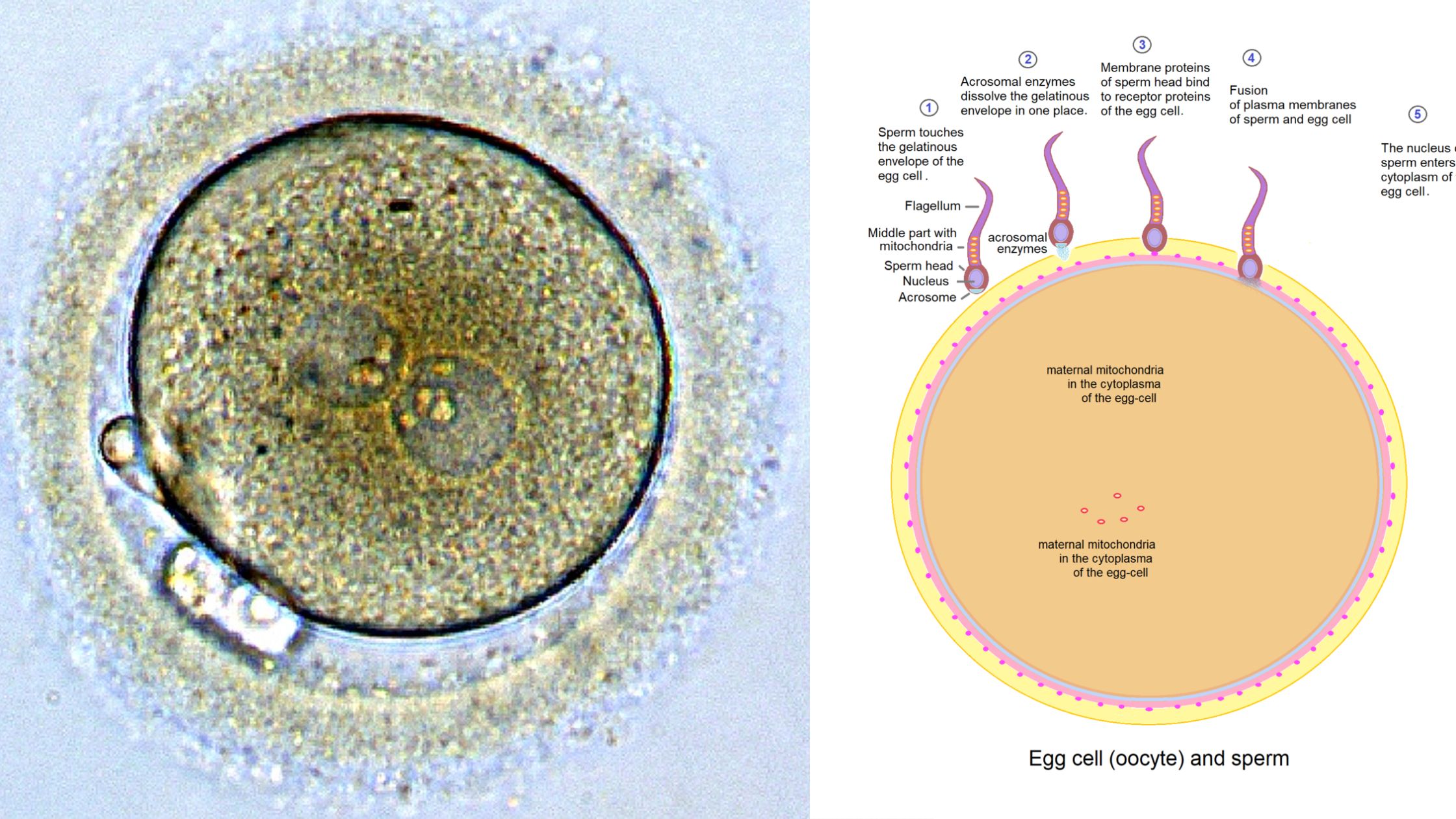
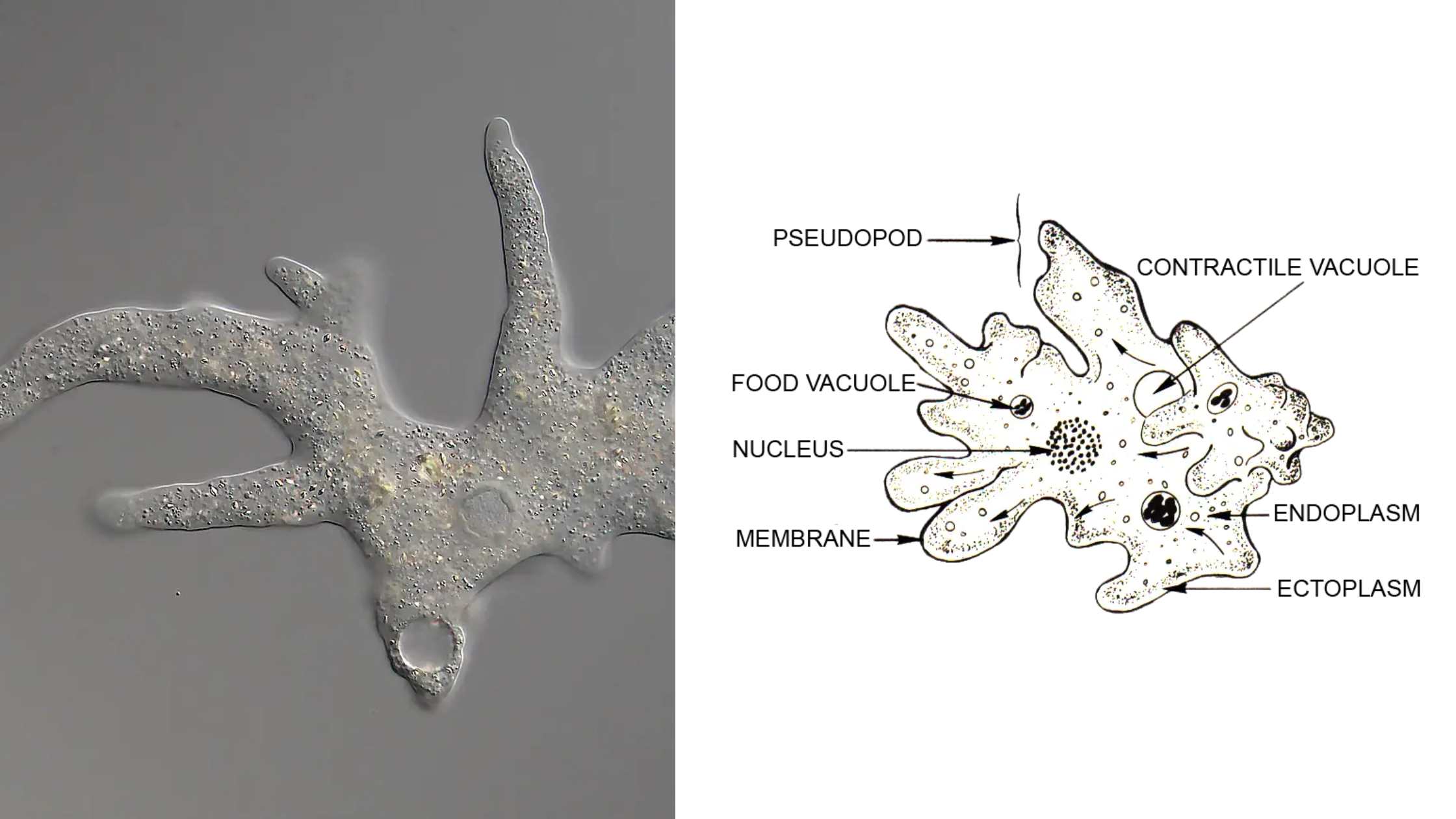
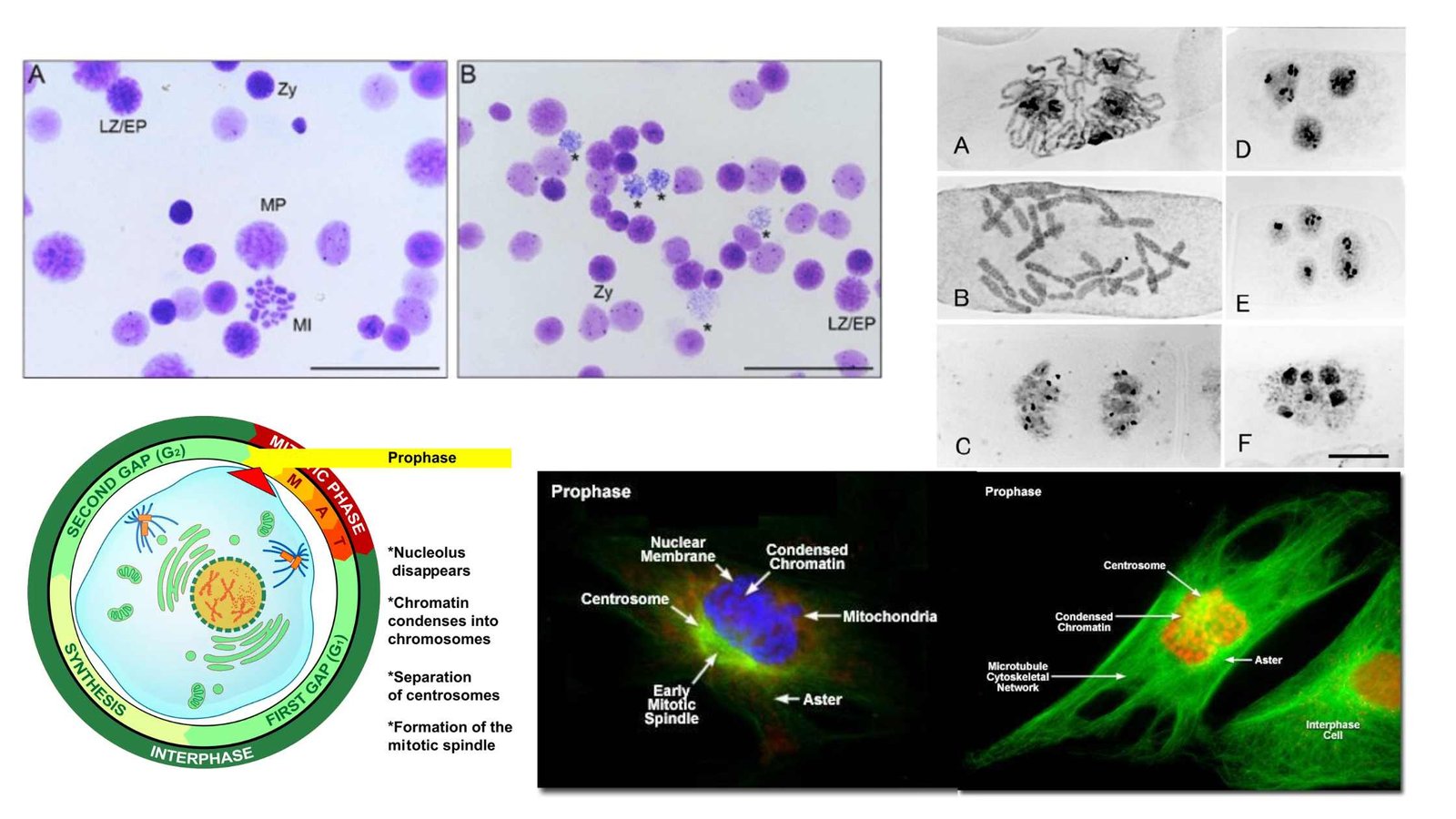
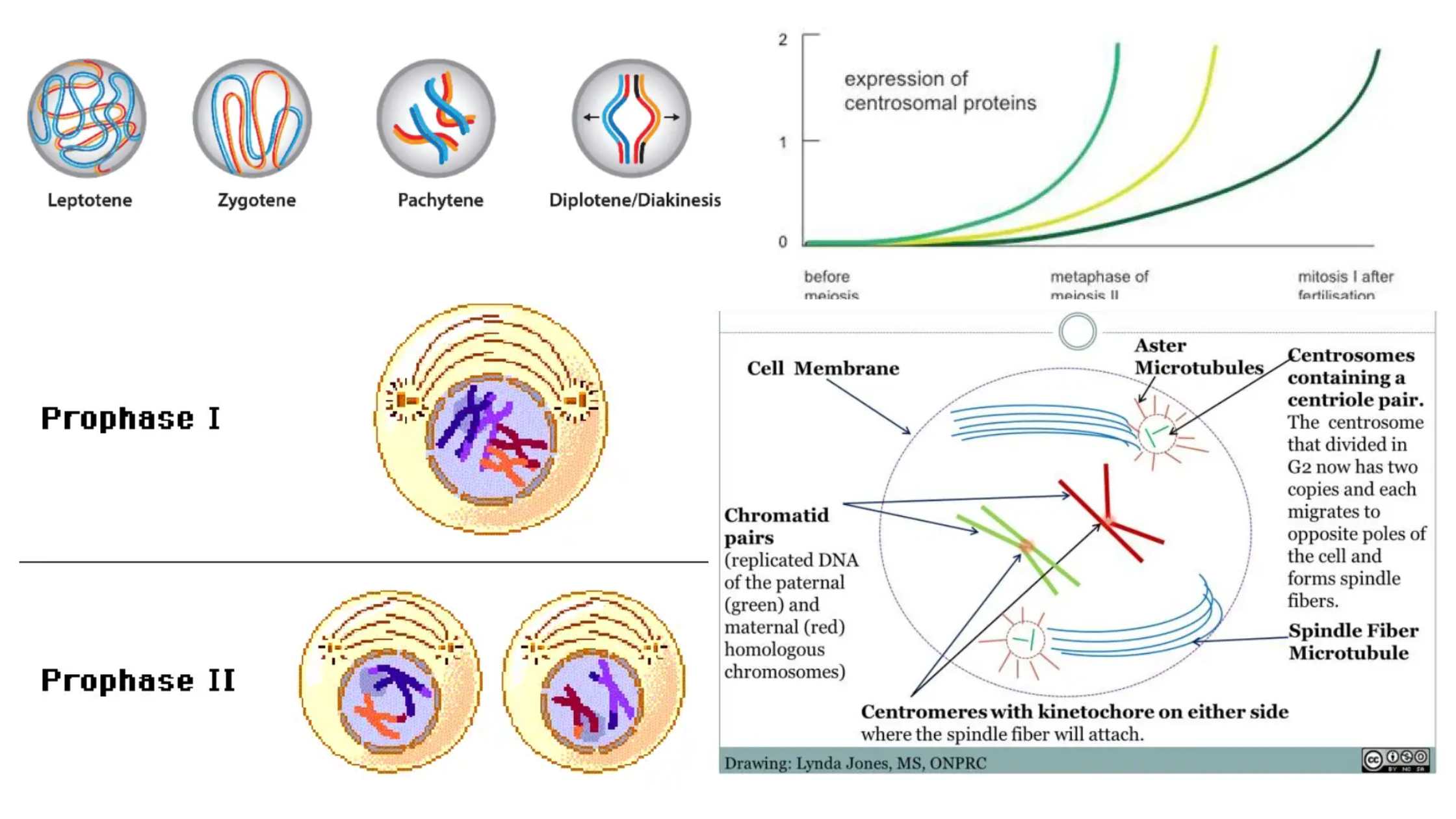
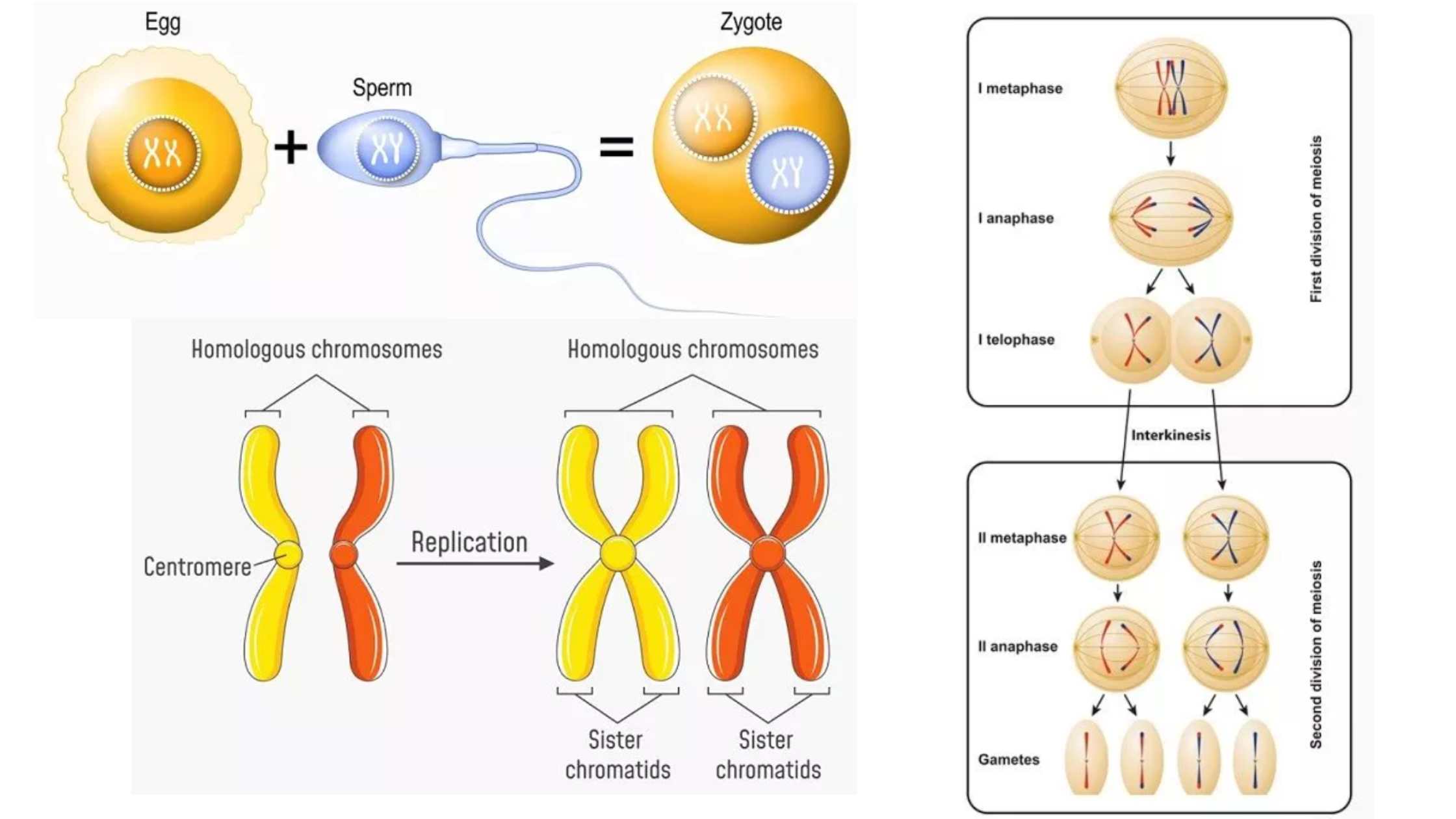
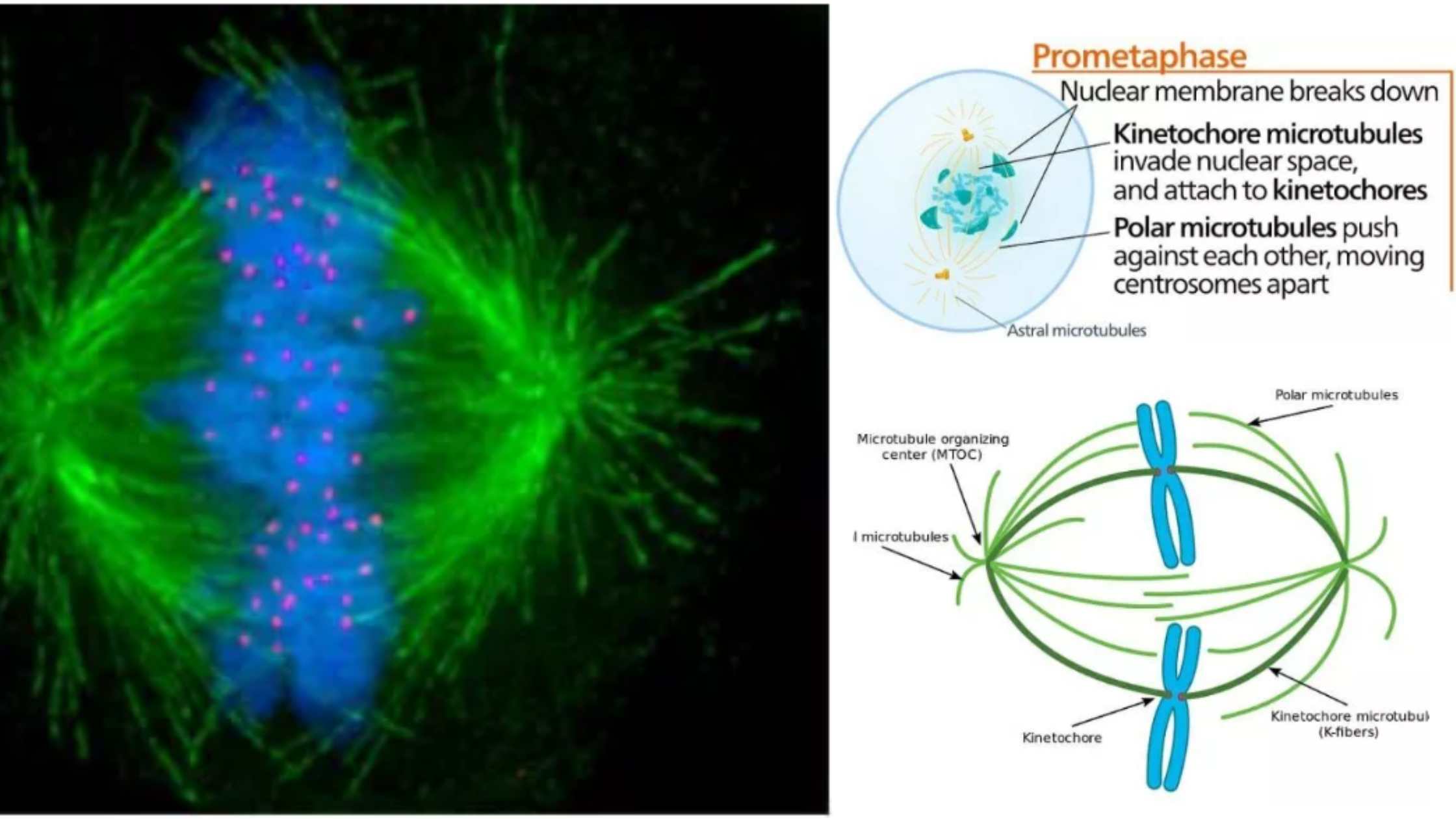
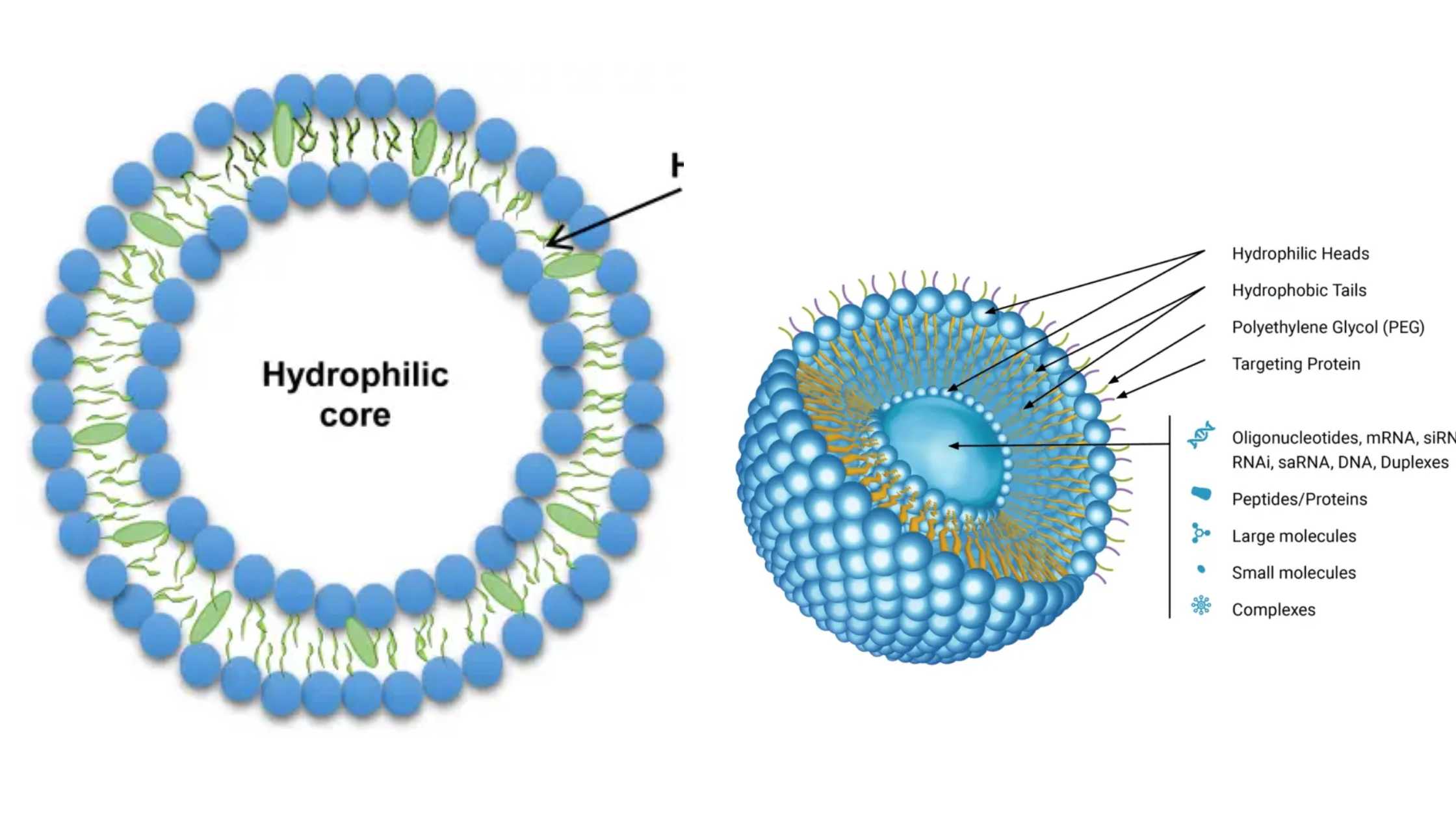
Zygote – Definition, Formation, Development, Example
What is a Zygote? A zygote is a crucial concept in biology, representing the very first stage of a new organism’s development following the fertilization event. The term “zygote” (pronounced /ˈzaɪˌɡoʊt/) originates from the Ancient Greek word ζυγωτός (zygōtós), meaning ‘joined’ or ‘yoked,’ derived from ζυγοῦν (zygoun), which means ‘to join’ or ‘to yoke’. This … Read more