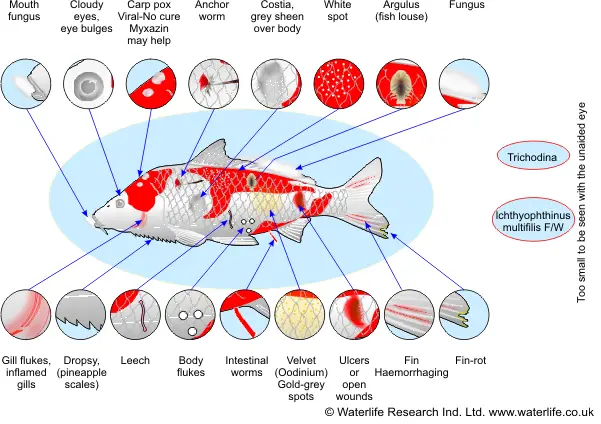
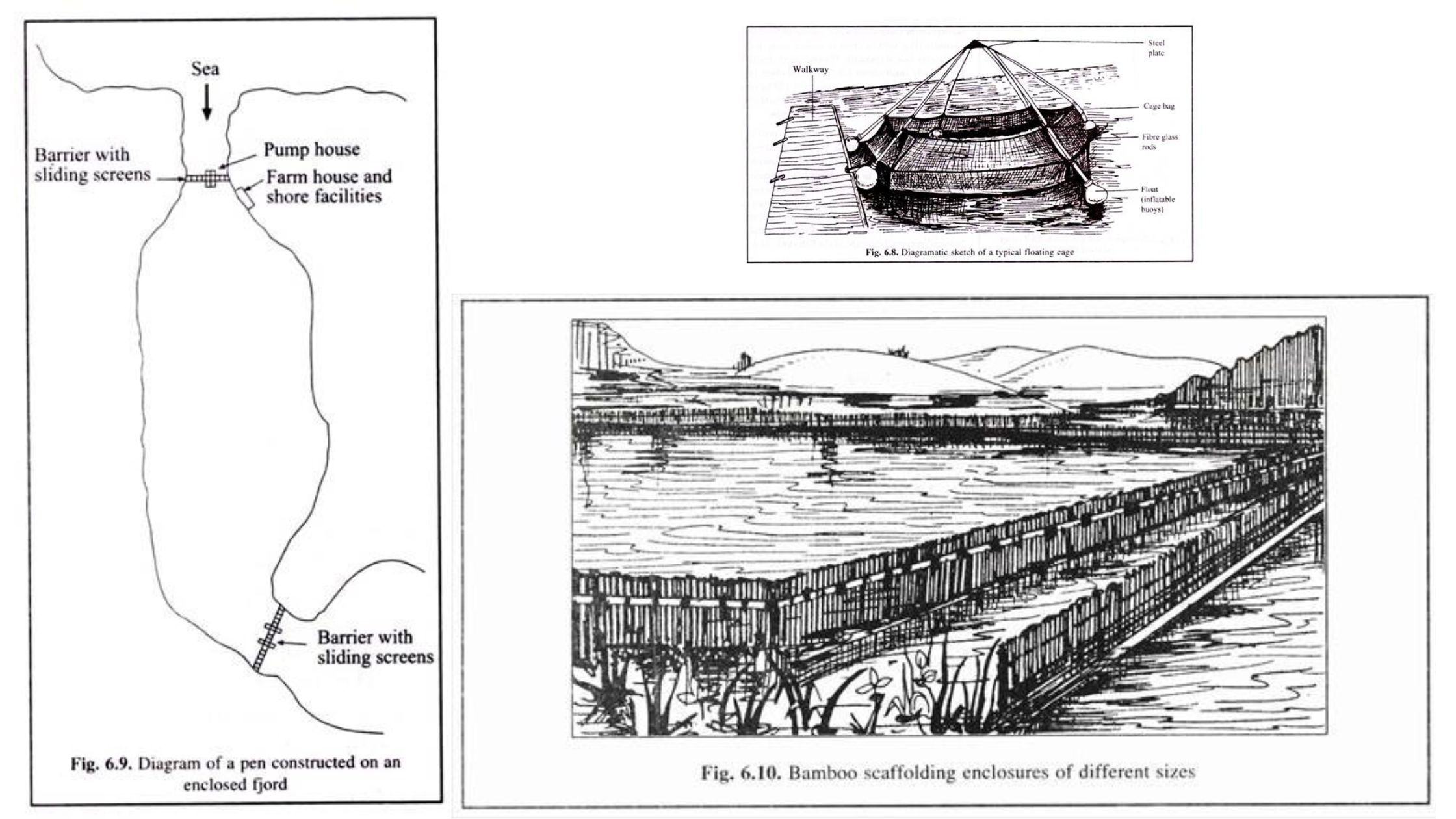
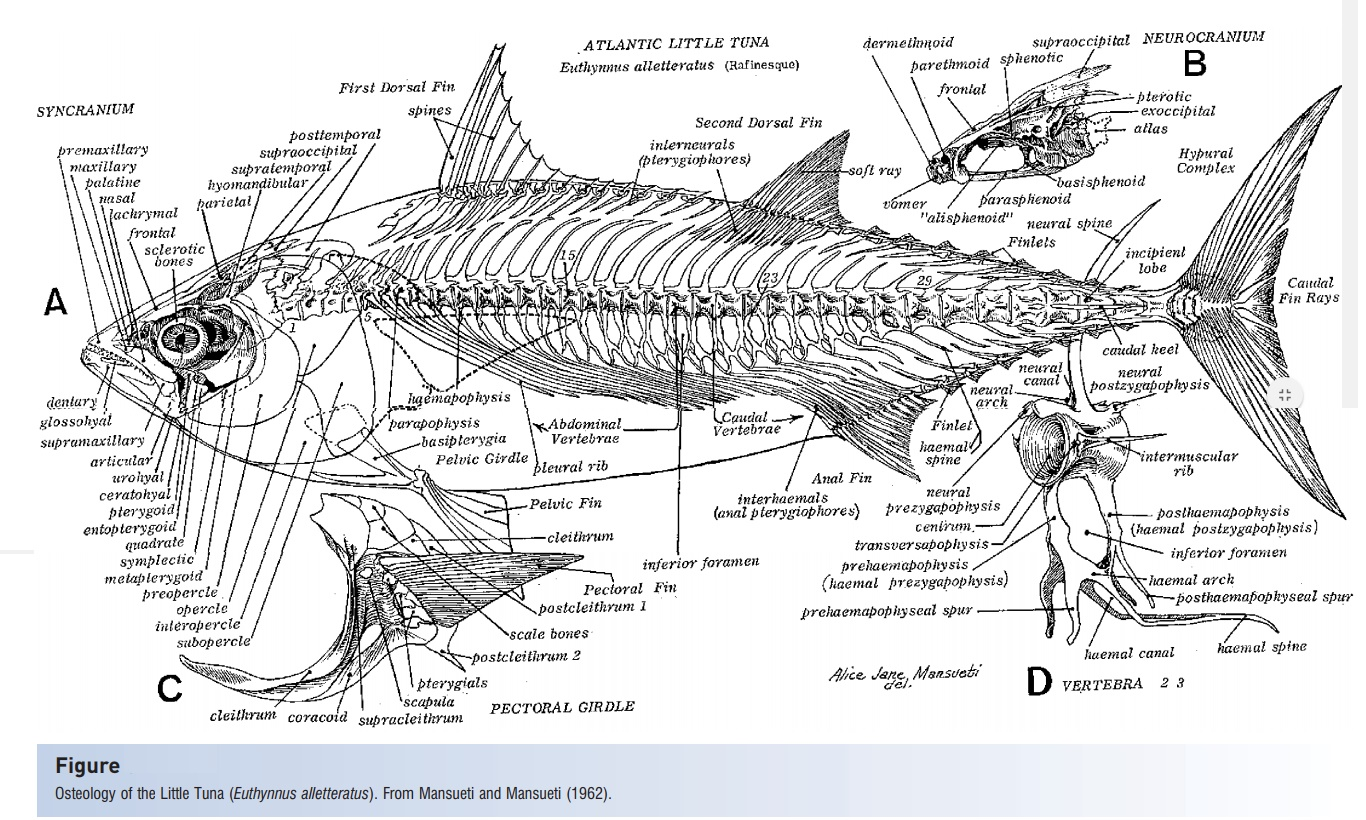
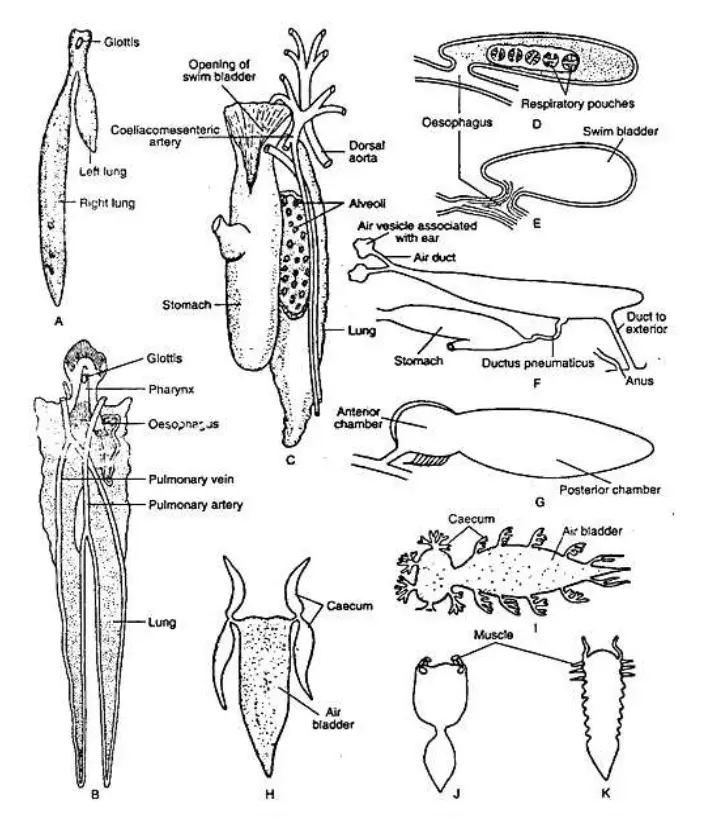
Composite Fish Culture – Definition, Steps, Advantages
What is Composite Fish Culture? Steps in Composite Fish Culture 1. Site selection Site selection is a critical aspect of aquaculture that significantly influences the success of fish farming operations. Choosing an appropriate site requires a comprehensive evaluation of various factors that can affect fish health, growth, and overall productivity. The process can be categorized … Read more