Bead Homogenizer | Bead Mill Homogenizers – Principle, Uses
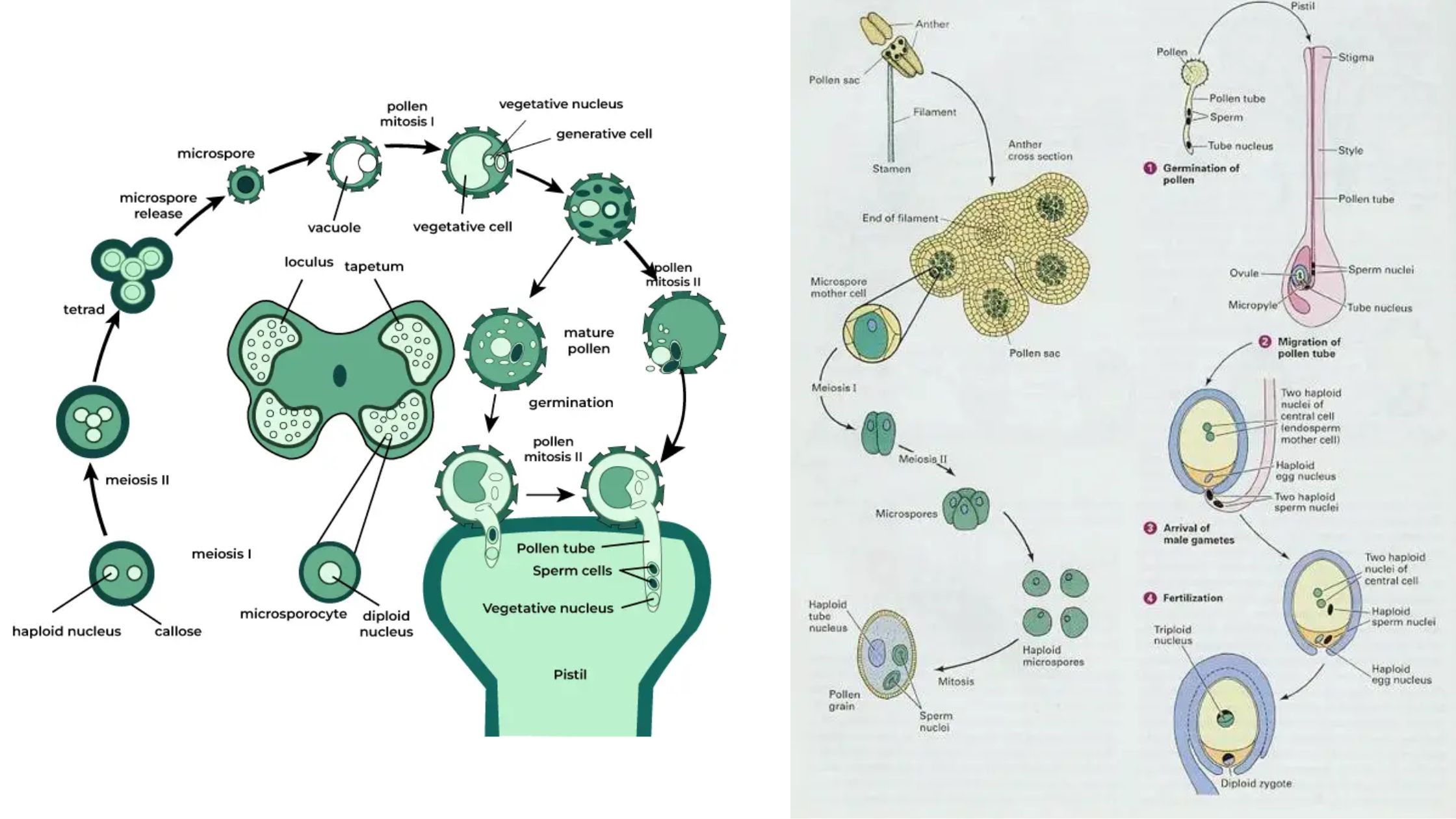
What Is a Bead Mill Homogenizer (Bead Homogenizer)? Principle of Bead Mill Homogenizer Parts of Bead Mill Homogenizer A bead mill homogenizer, also known as a bead mill or a bead agitator, typically consists of the following parts: Operating Procedure of Bead Mill Homogenizer Advantages of Bead Mill Homogenizer Limitations of Bead Mill Homogenizer