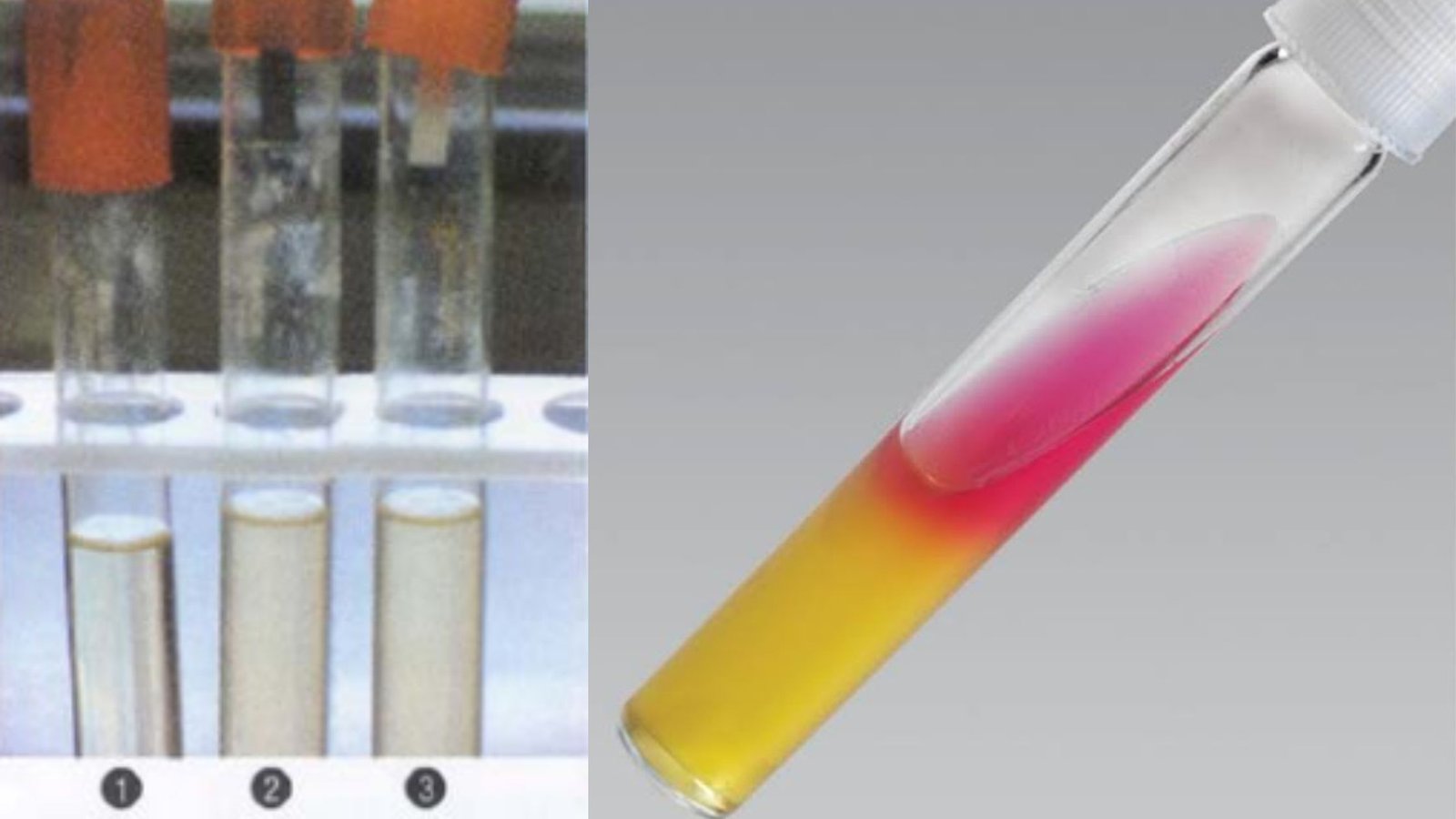
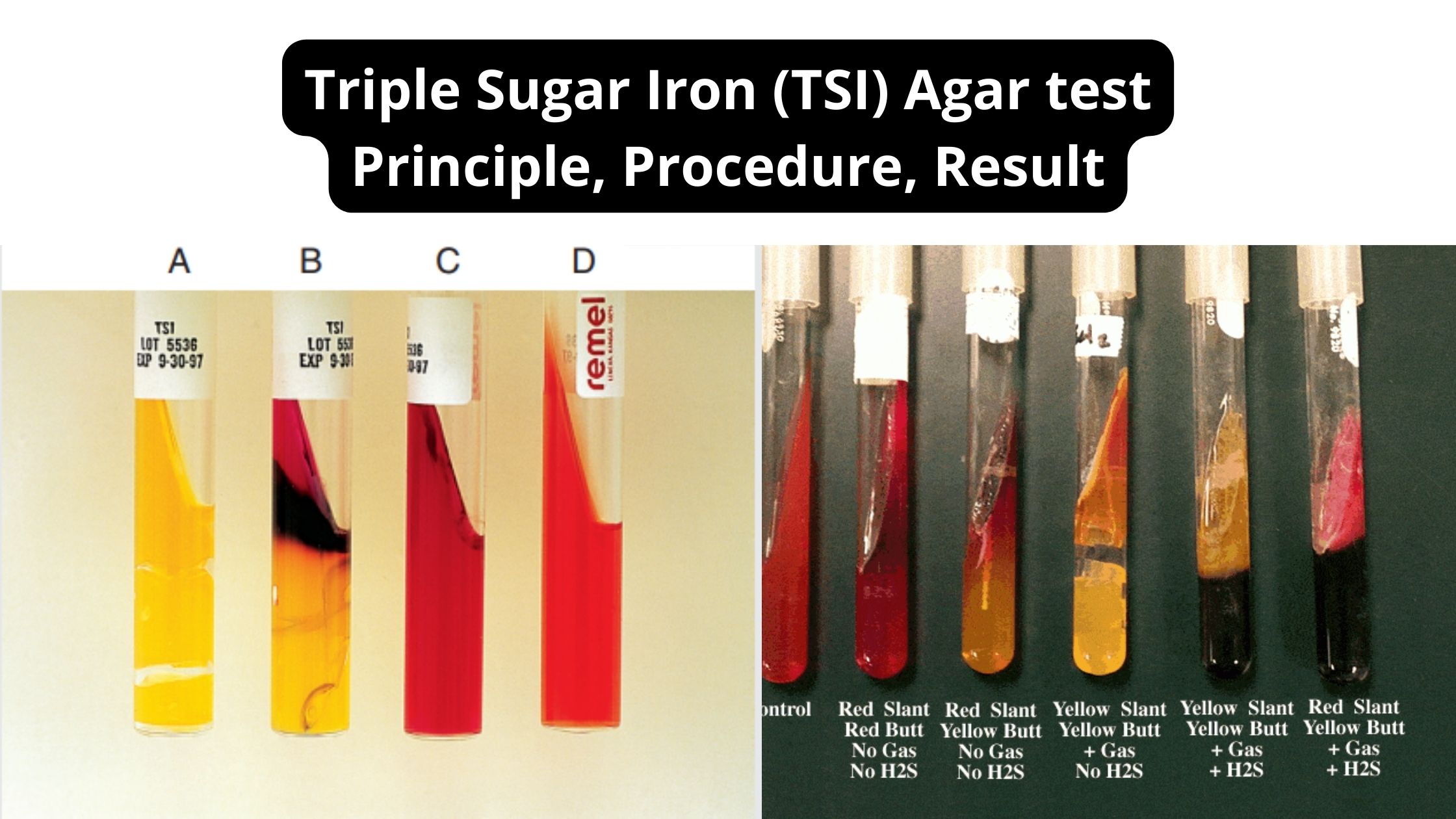
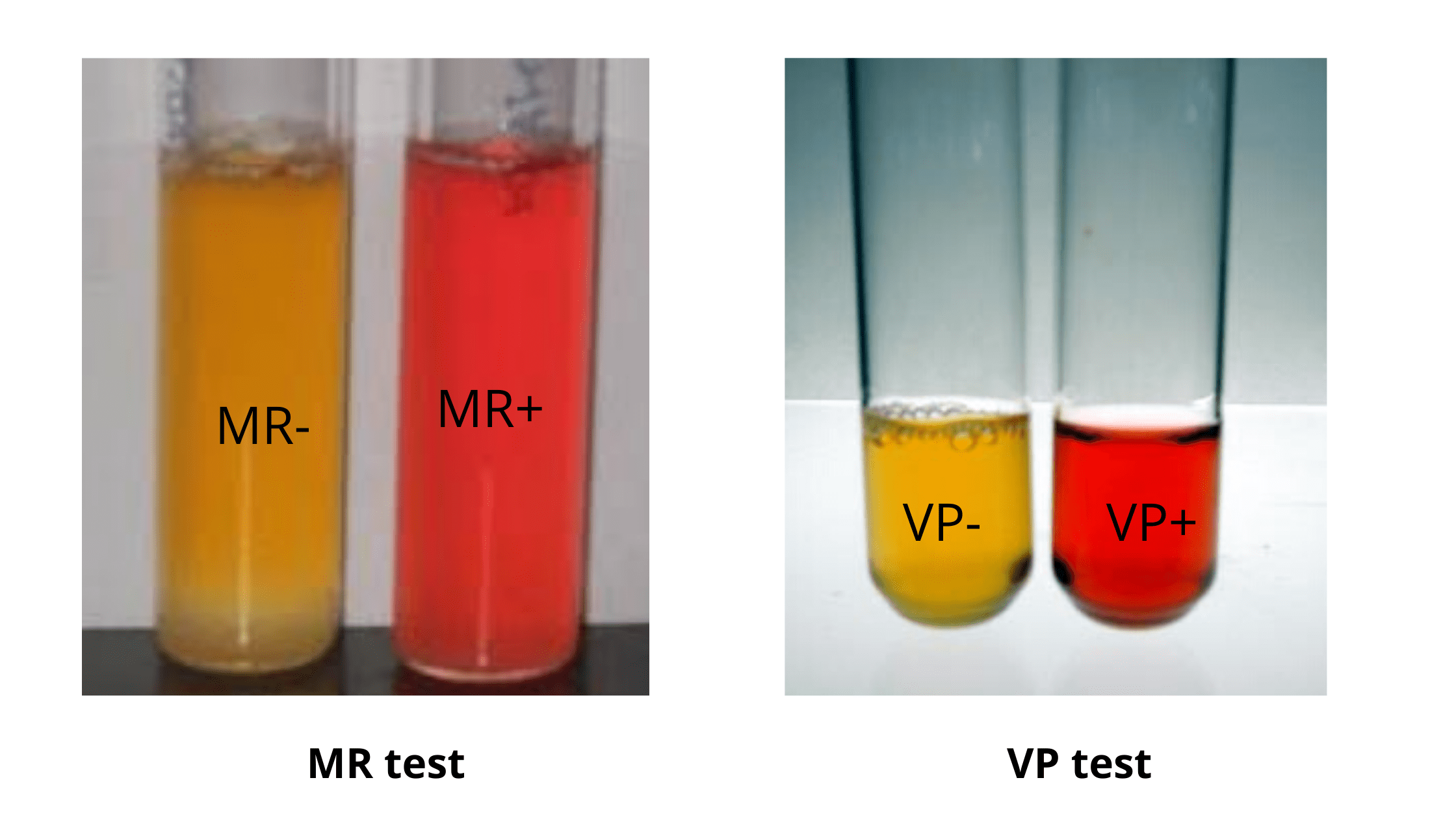
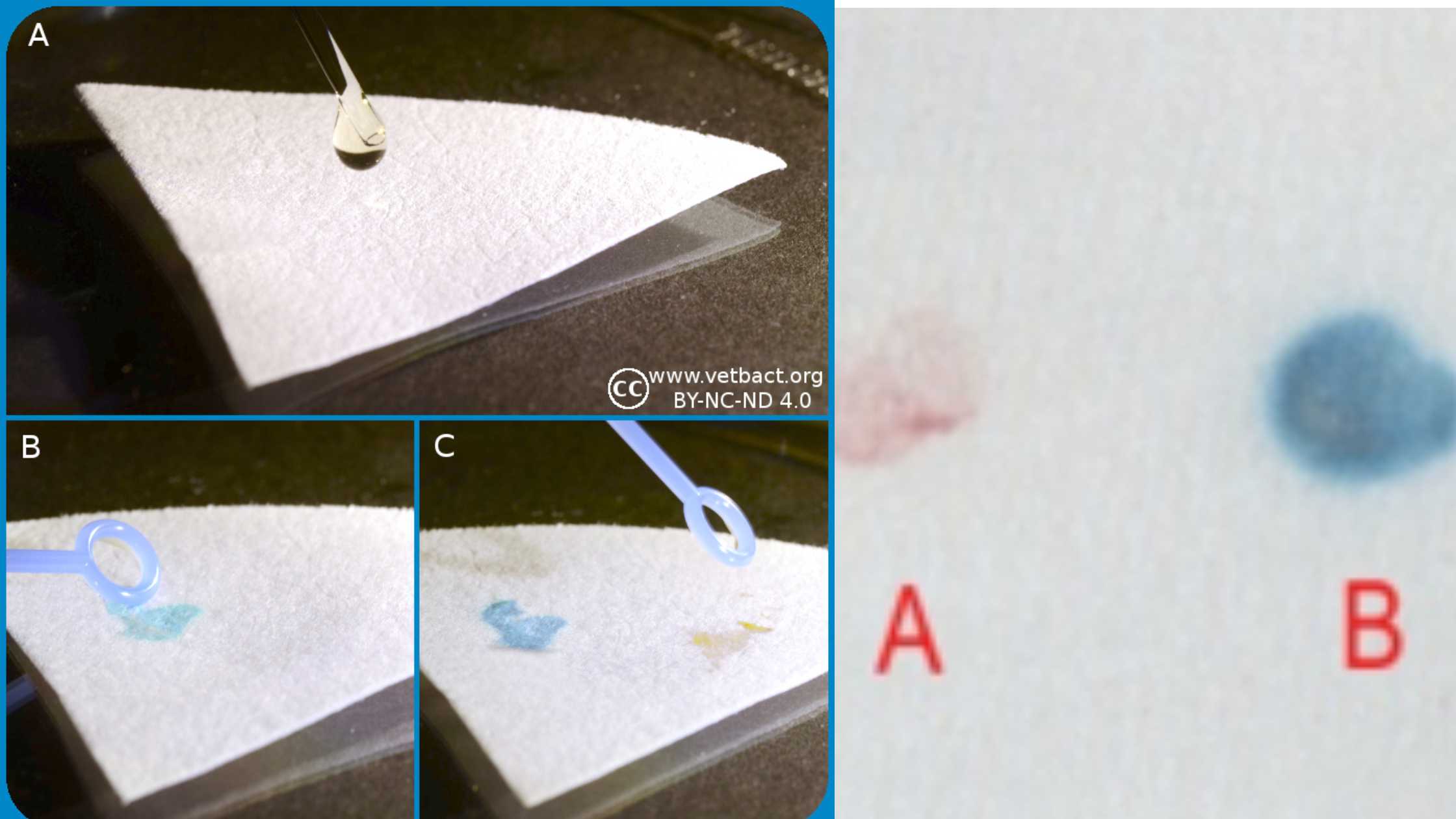
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Test – Principle, Procedure, Result
What is Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Test? Hydrogen sulfide (H S)-producing bacteria Principle of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Test Objective of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Test Media for the detection of Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) Commonly used media for detecting hydrogen sulphide generation, sulphur sources, and sulphide indicators include the following: Media Sulfur source H₂S indicator Bismuth sulfite Peptones … Read more