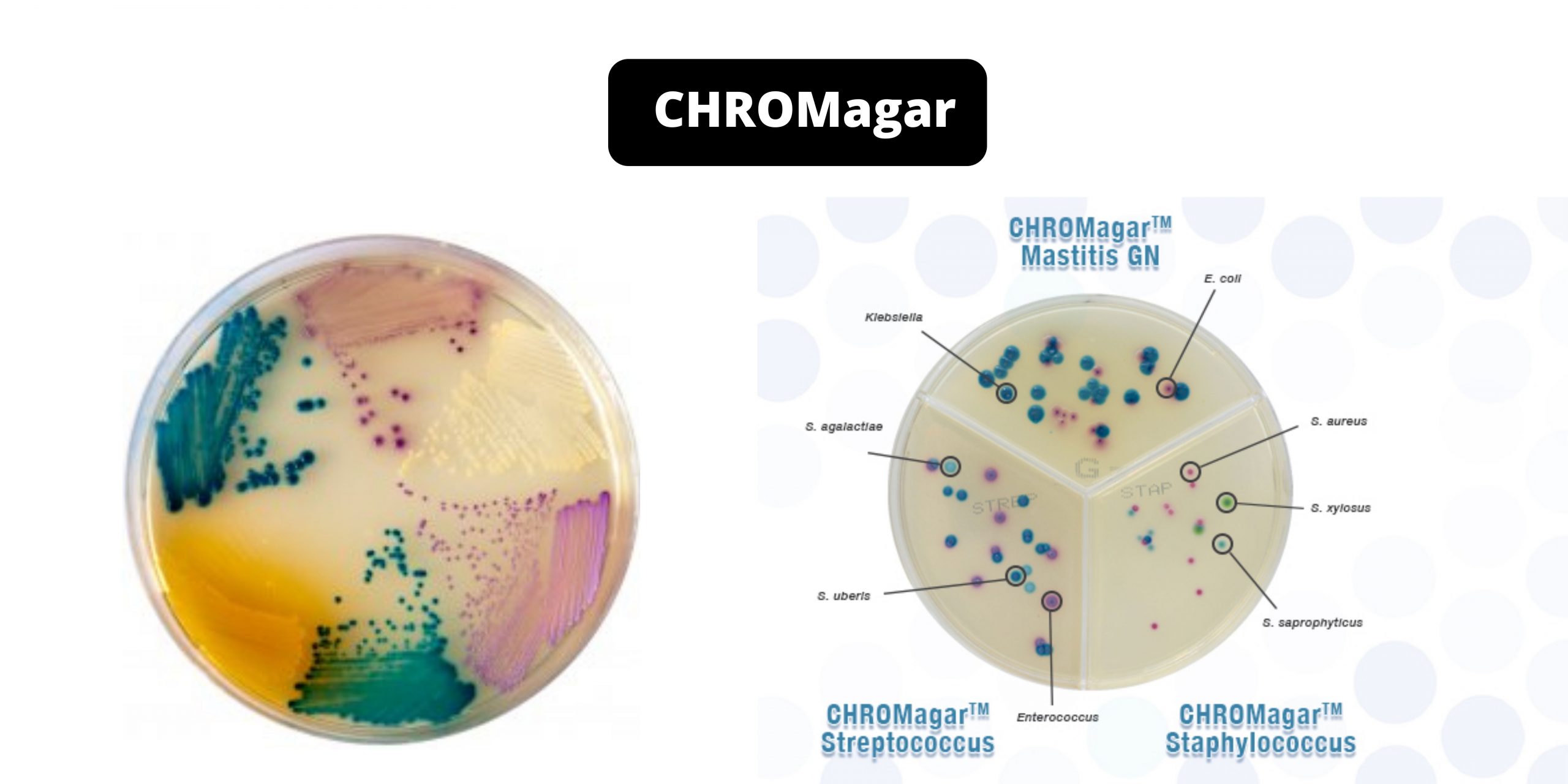
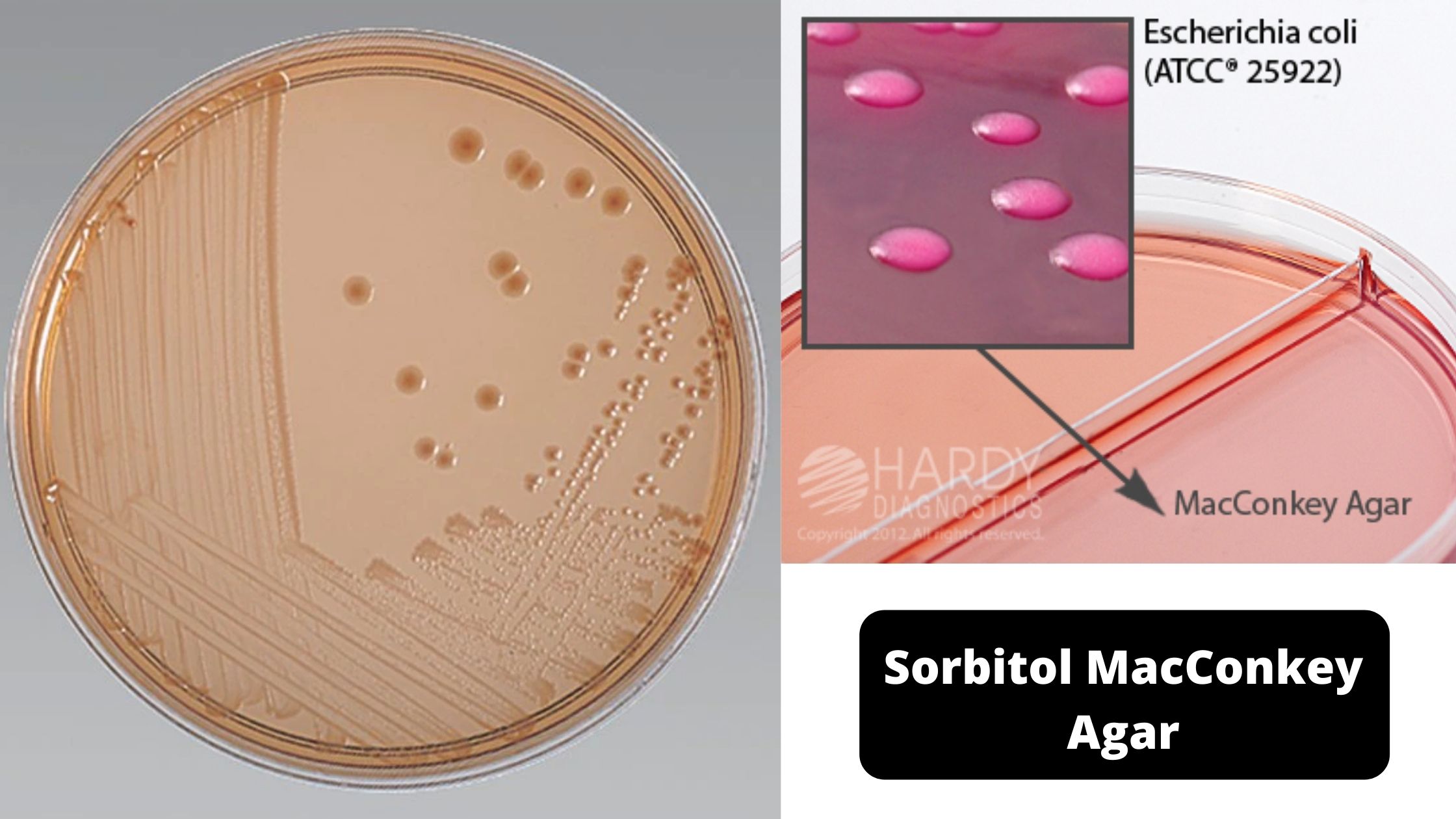
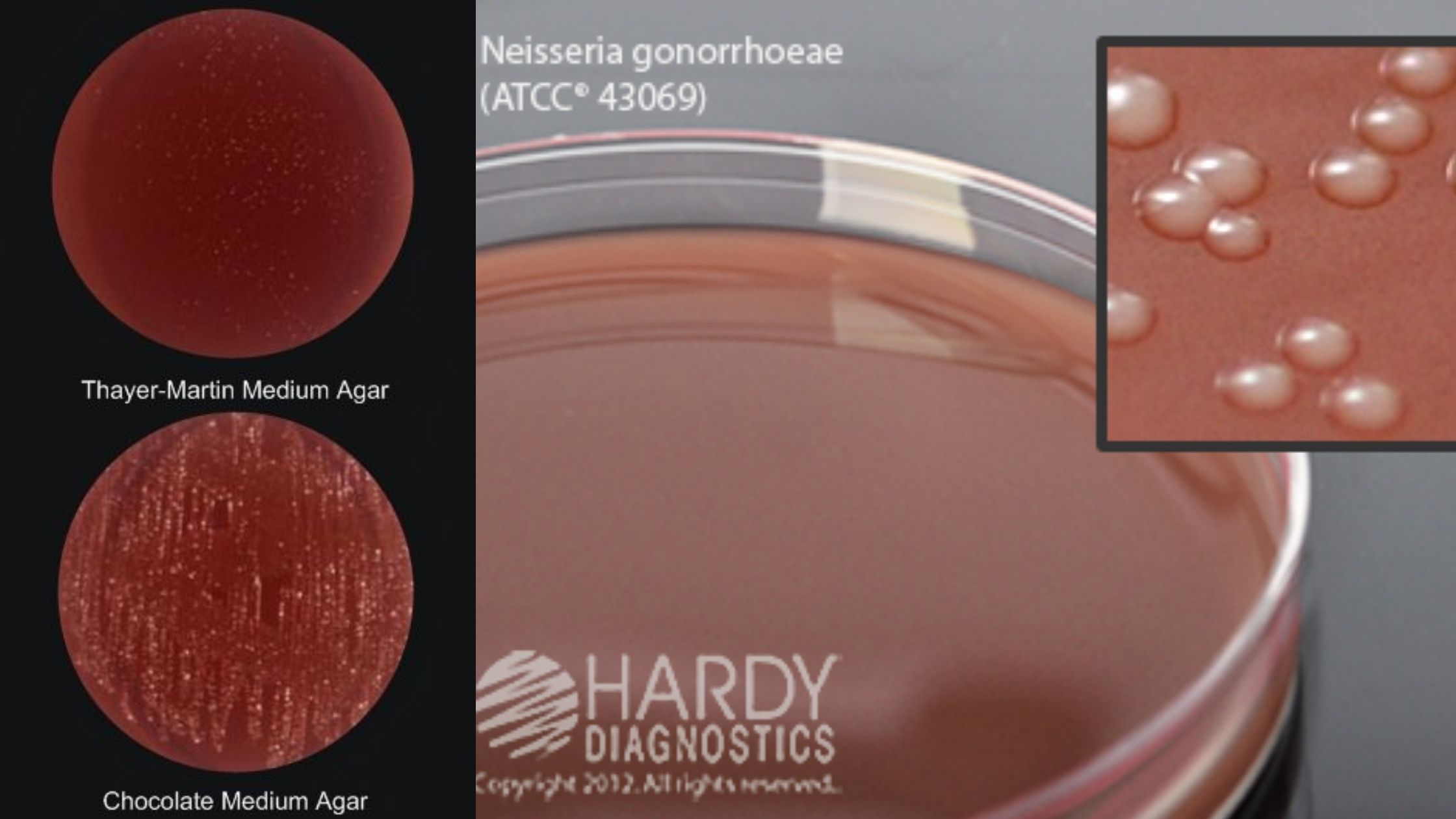
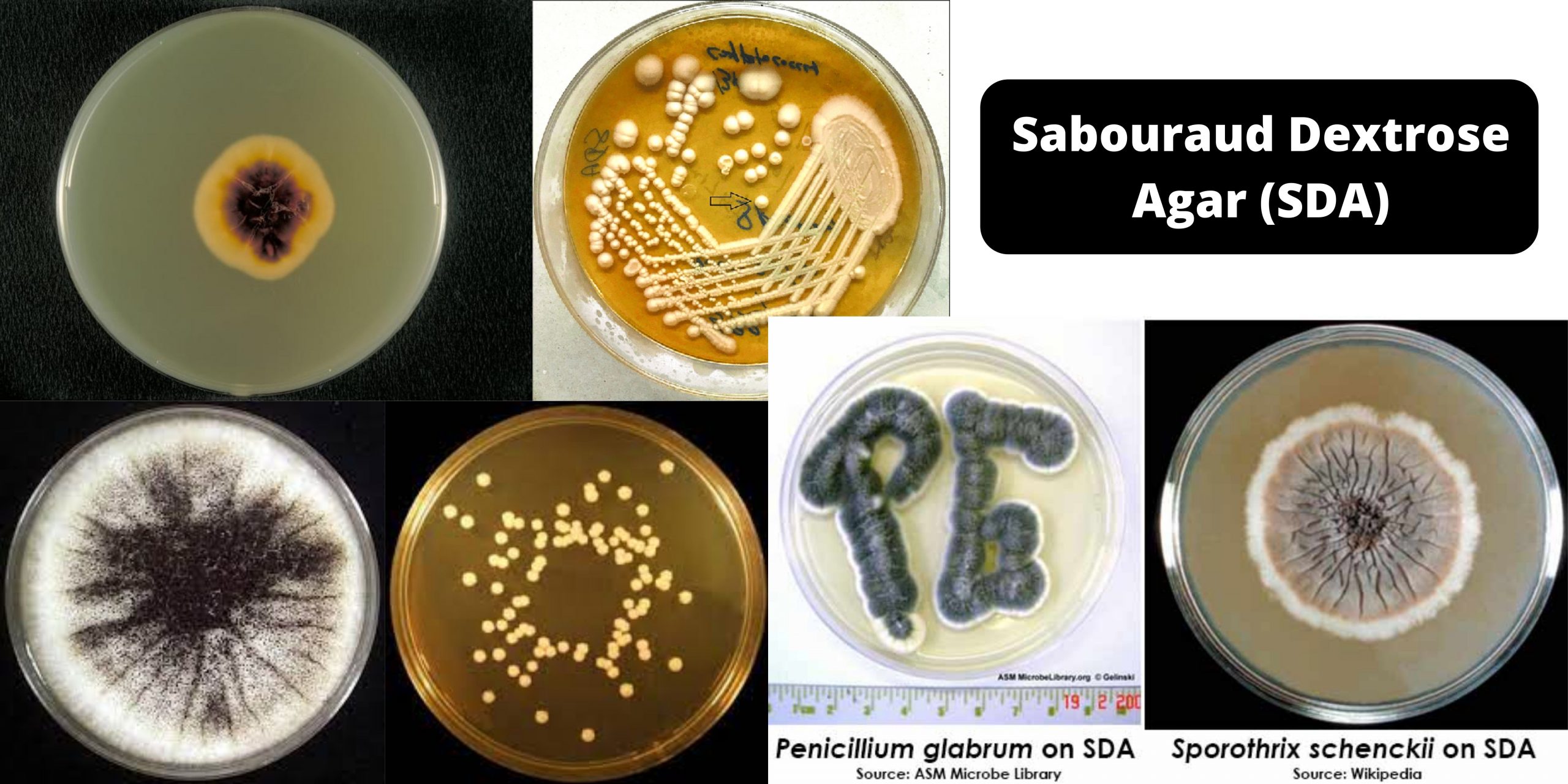
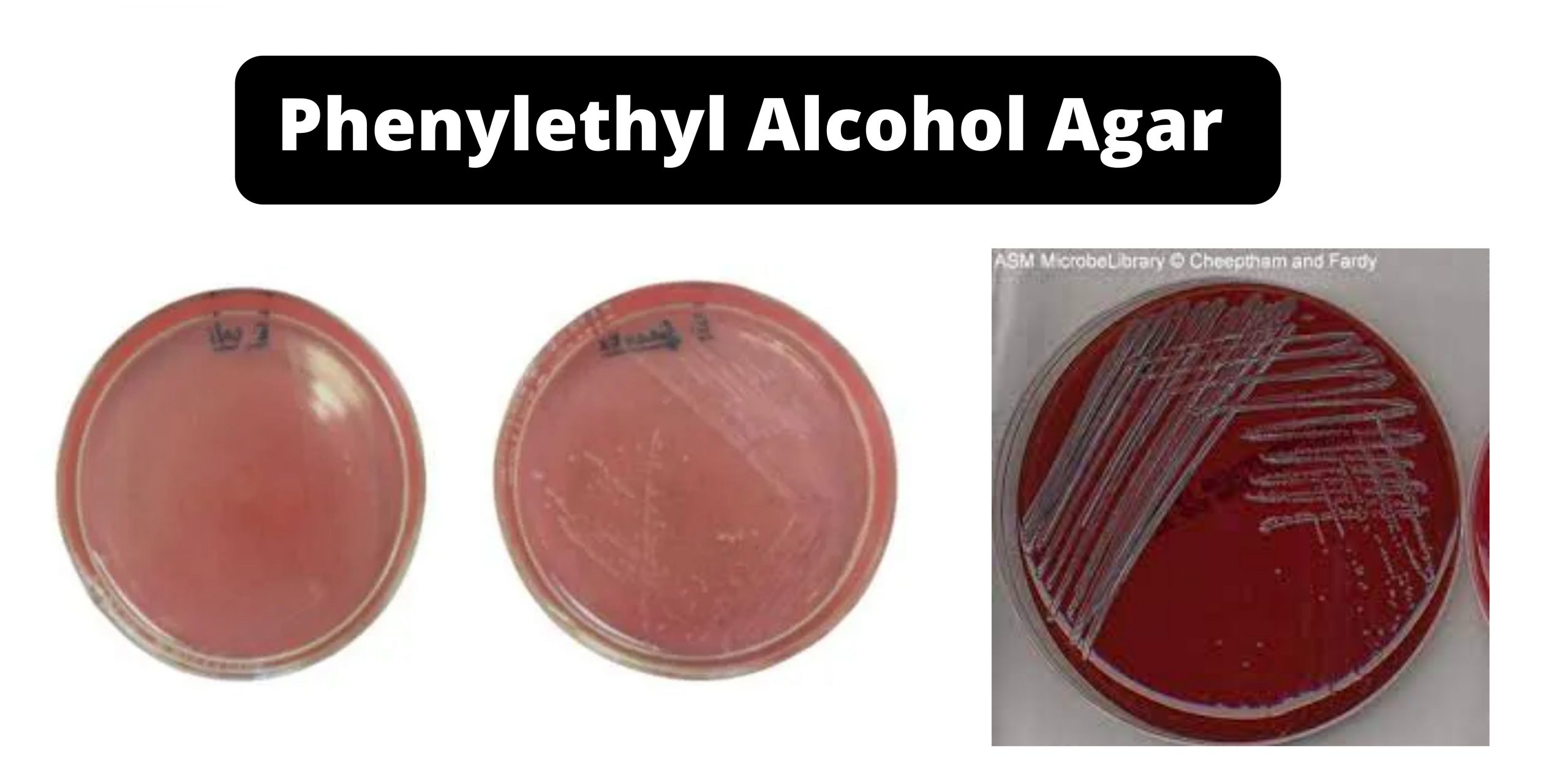
CHROMagar – Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
In 1979, Dr. A. Rambach invented and patented the first chromogenic medium for E.coli detection. This technology uses a color-based differentiation technique. It uses soluble colorless molecules, also known as chromogens. They are composed of a substrate that targets a specific enzyme activity and a chromophore. The chromophore can be released when the enzyme of the target organism cleaves the colorless, chromogenic conjugate.