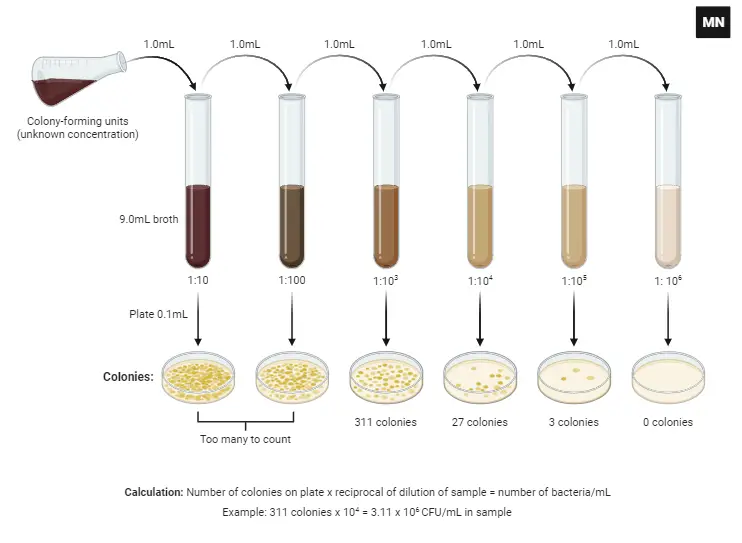
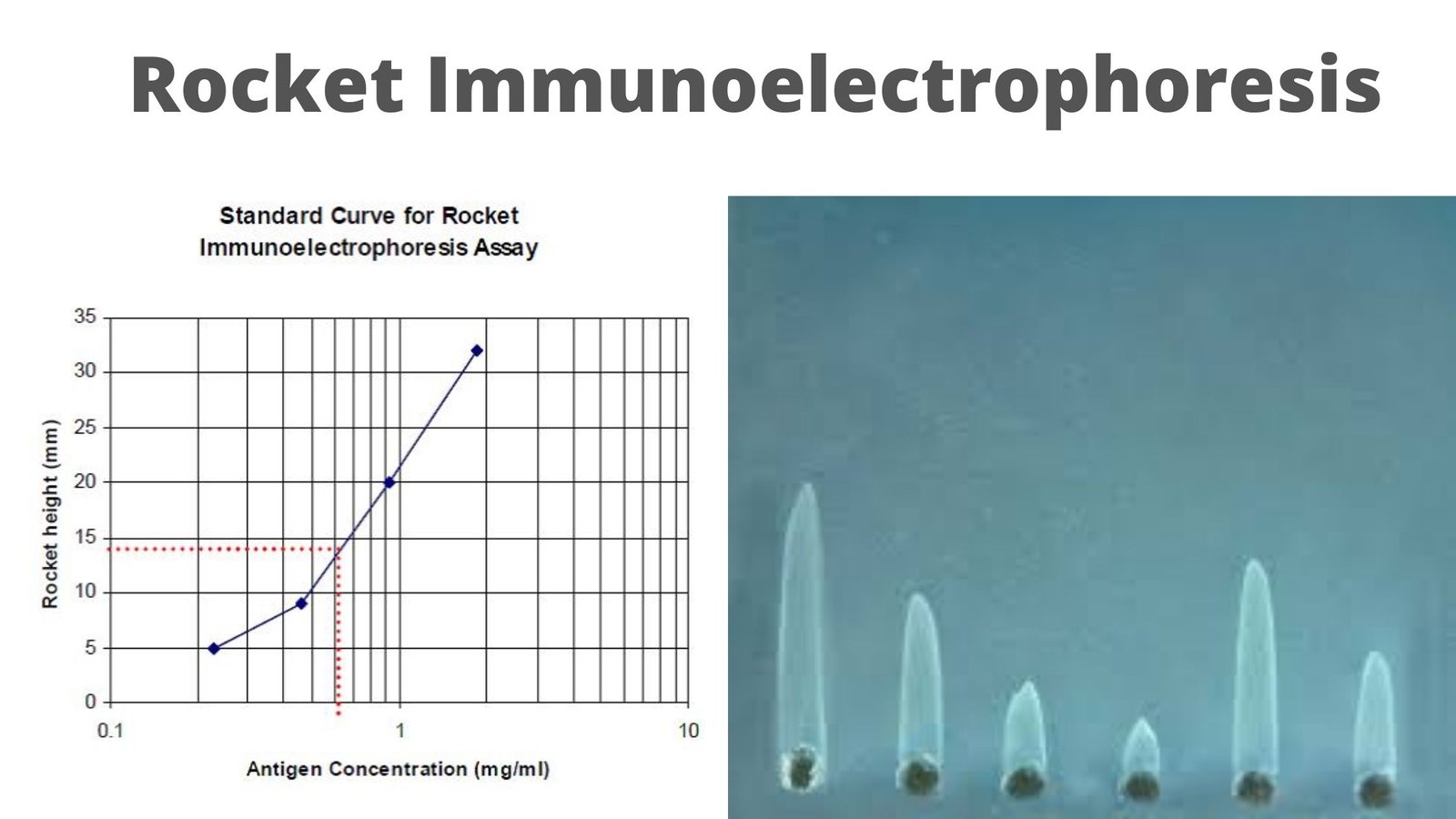
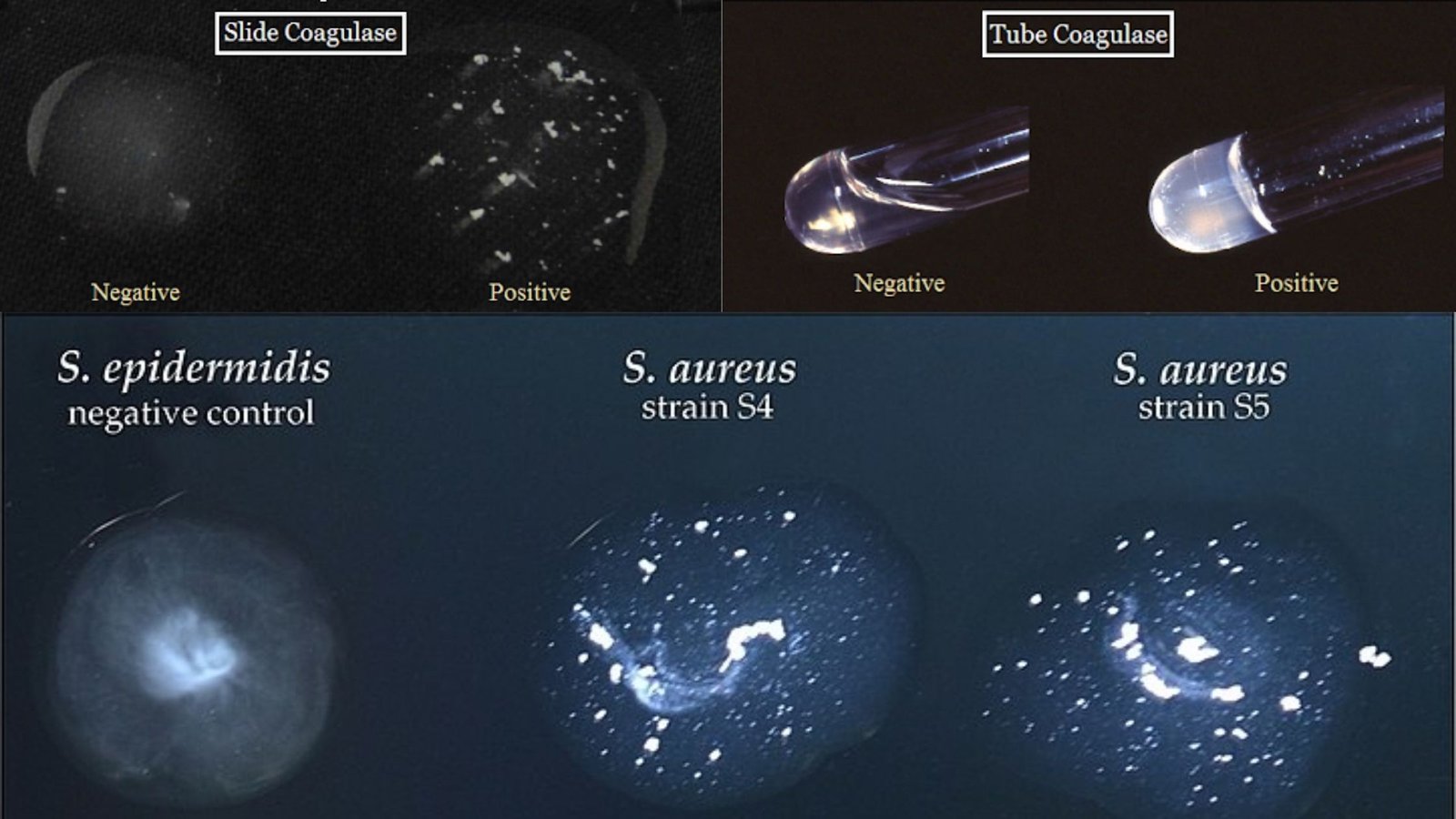
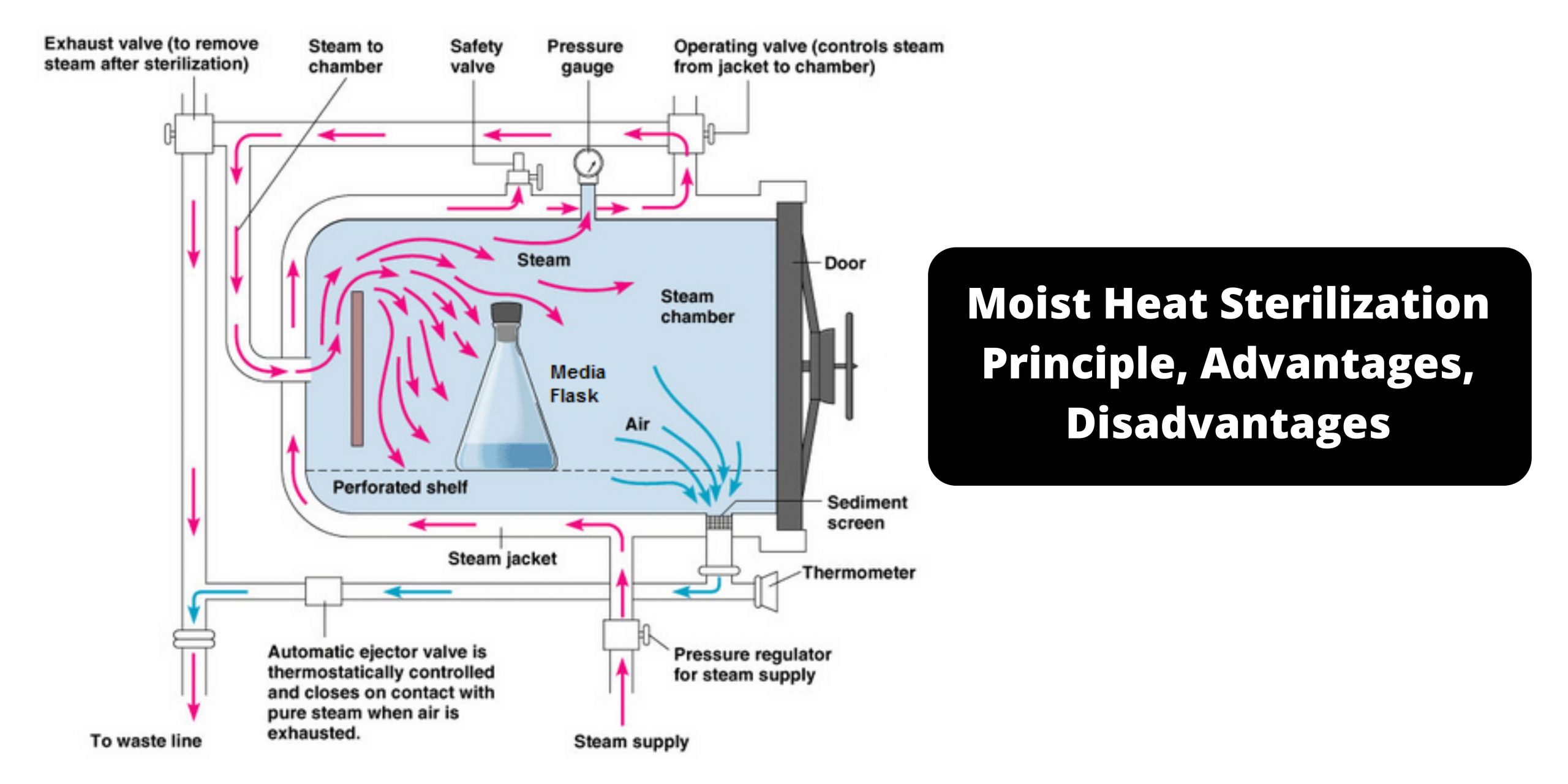
Filtration – Definition, Mechanisms, Types, Examples, Application
What is Filtration? Filtration is utilised to separate a dispersion based on particle size. The filtered mixture is put to an appropriate porous material filter. Particles smaller than the filter’s pores can pass through and enter the filtrate, while larger particles are retained on the filter’s surface. Filtration is a process that is used to … Read more