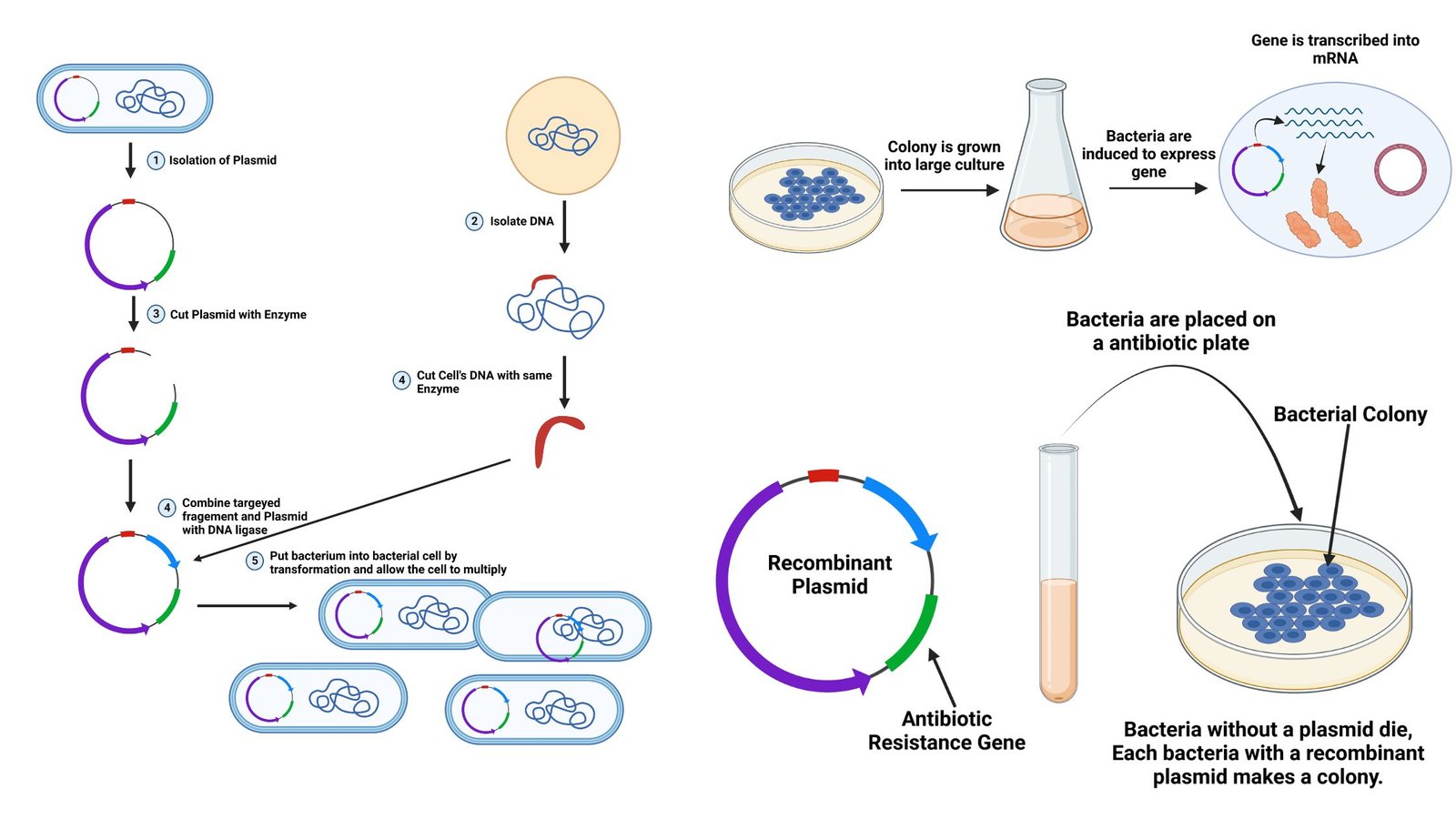
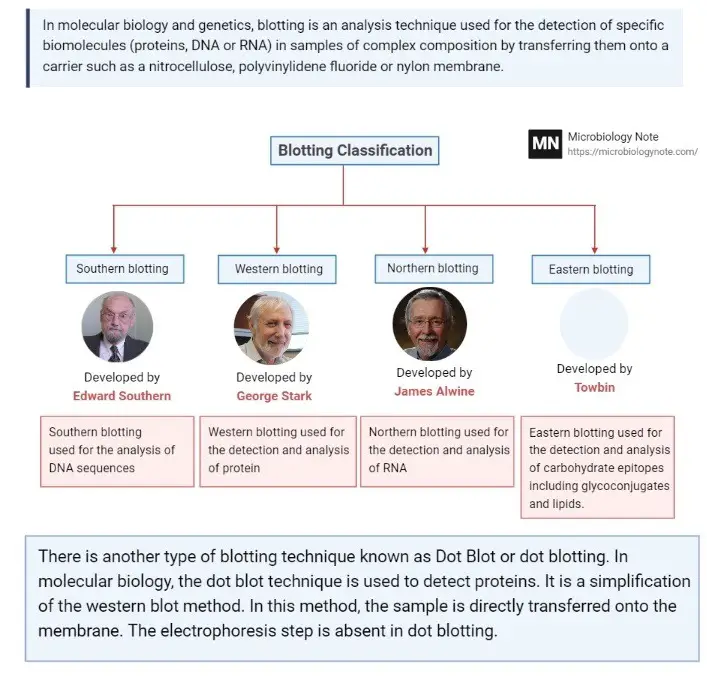
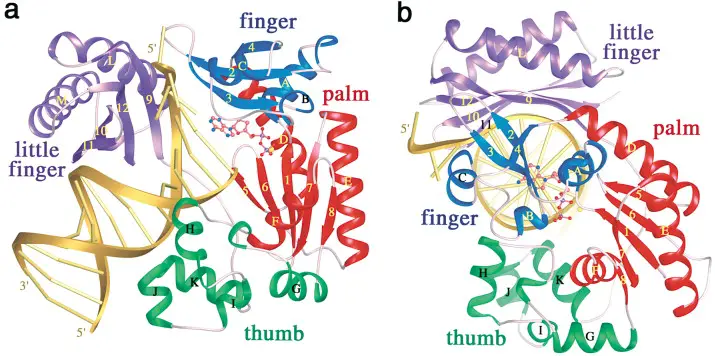
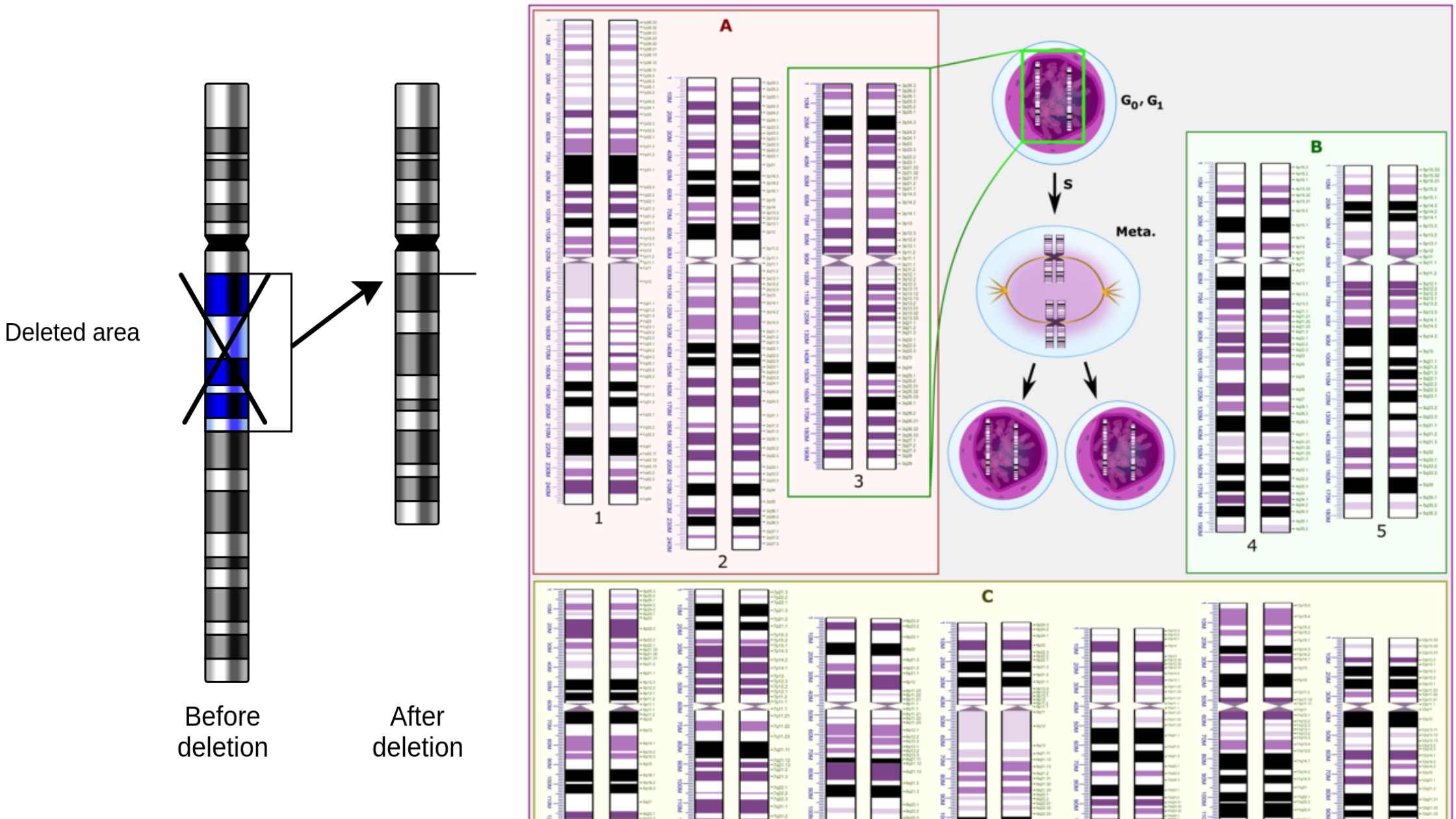
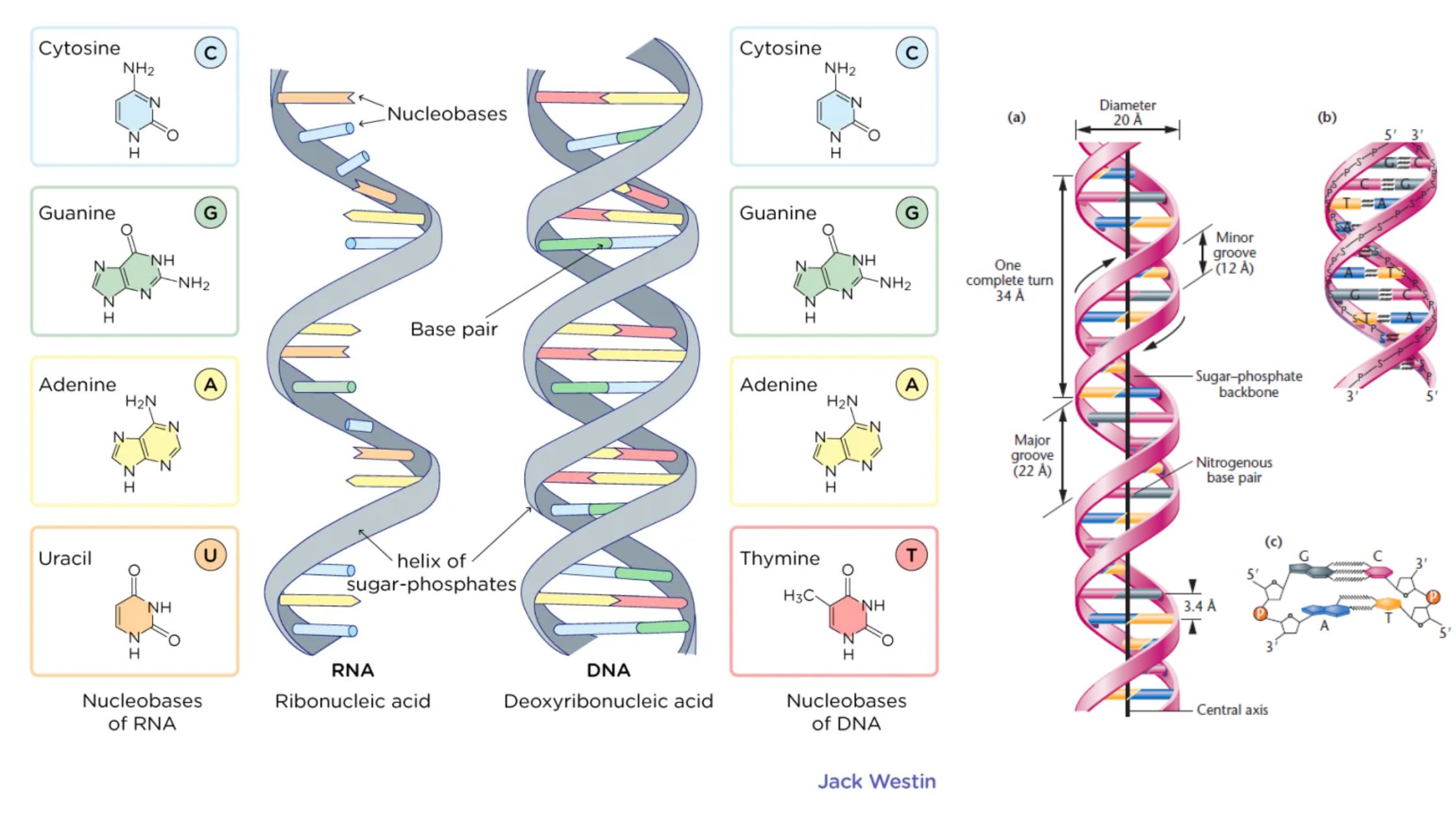
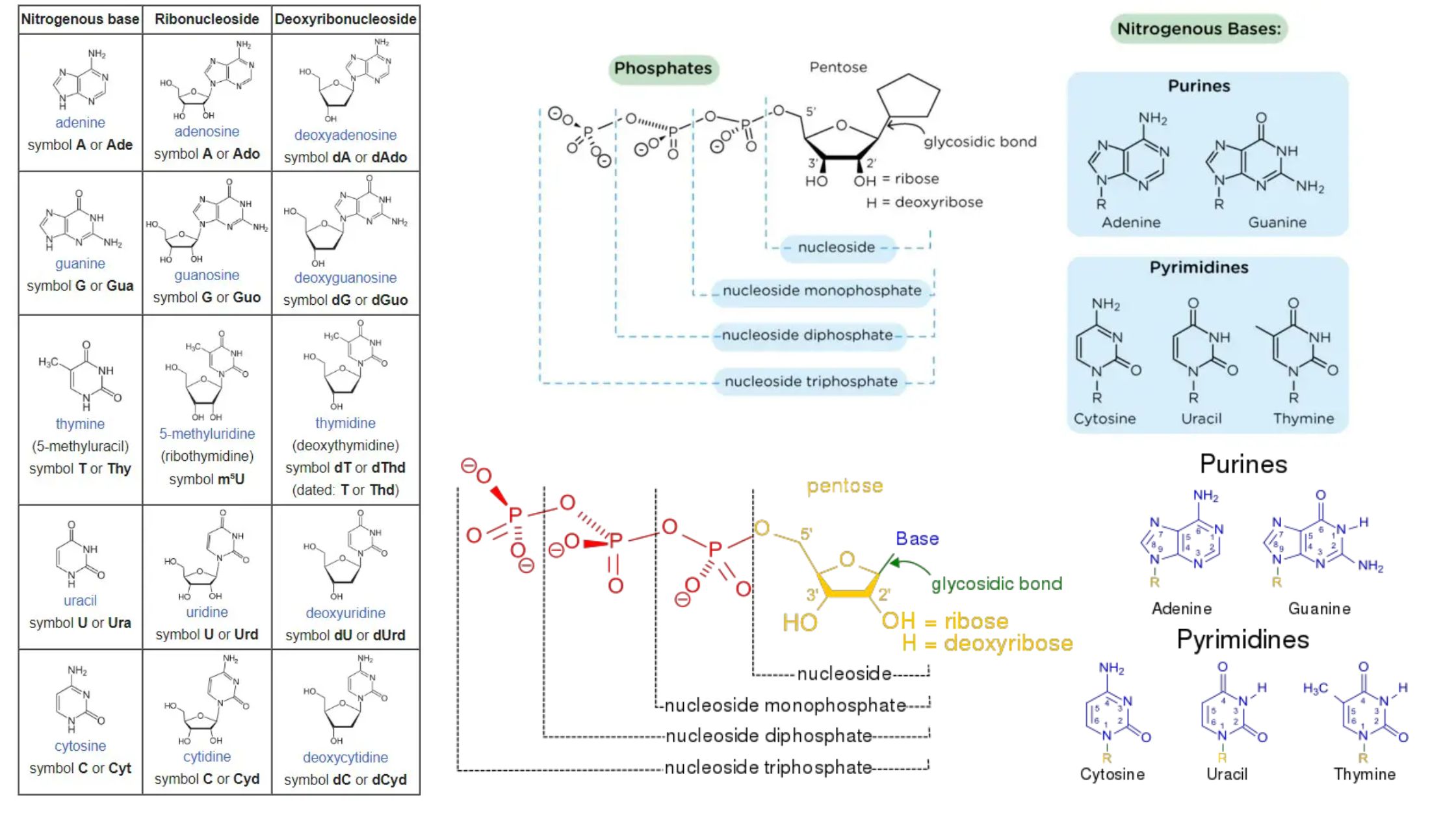
cDNA Synthesis – Principle, Protocol
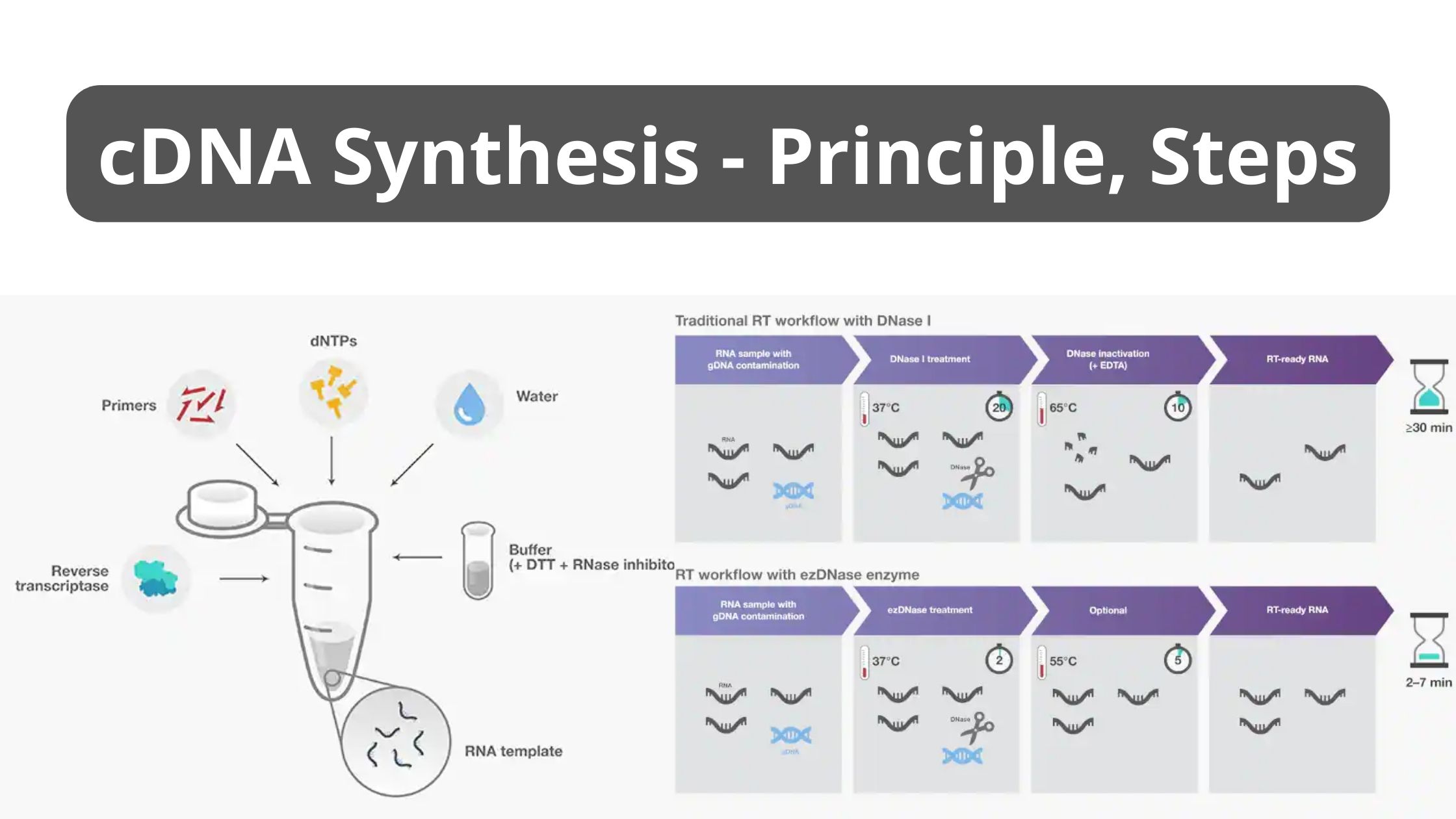
What is cDNA? cDNA synthesis principle cDNA synthesis steps There are different steps for synthesis of cdna such as; cDNA synthesis protocol 1. Prepare sample 2. Remove genomic DNA 3. Select reverse transcriptase Common reverse transcriptases and their attributes. AMV reverse transcriptase MMLV reverse transcriptase Engineered MMLV reverse transcriptase(e.g., Invitrogen SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase) RNase … Read more