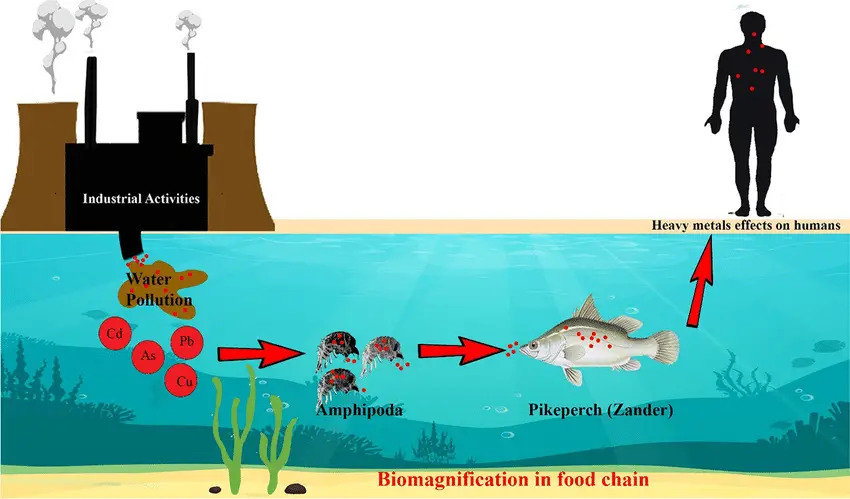
Waste Source, Definition, Types, Impacts
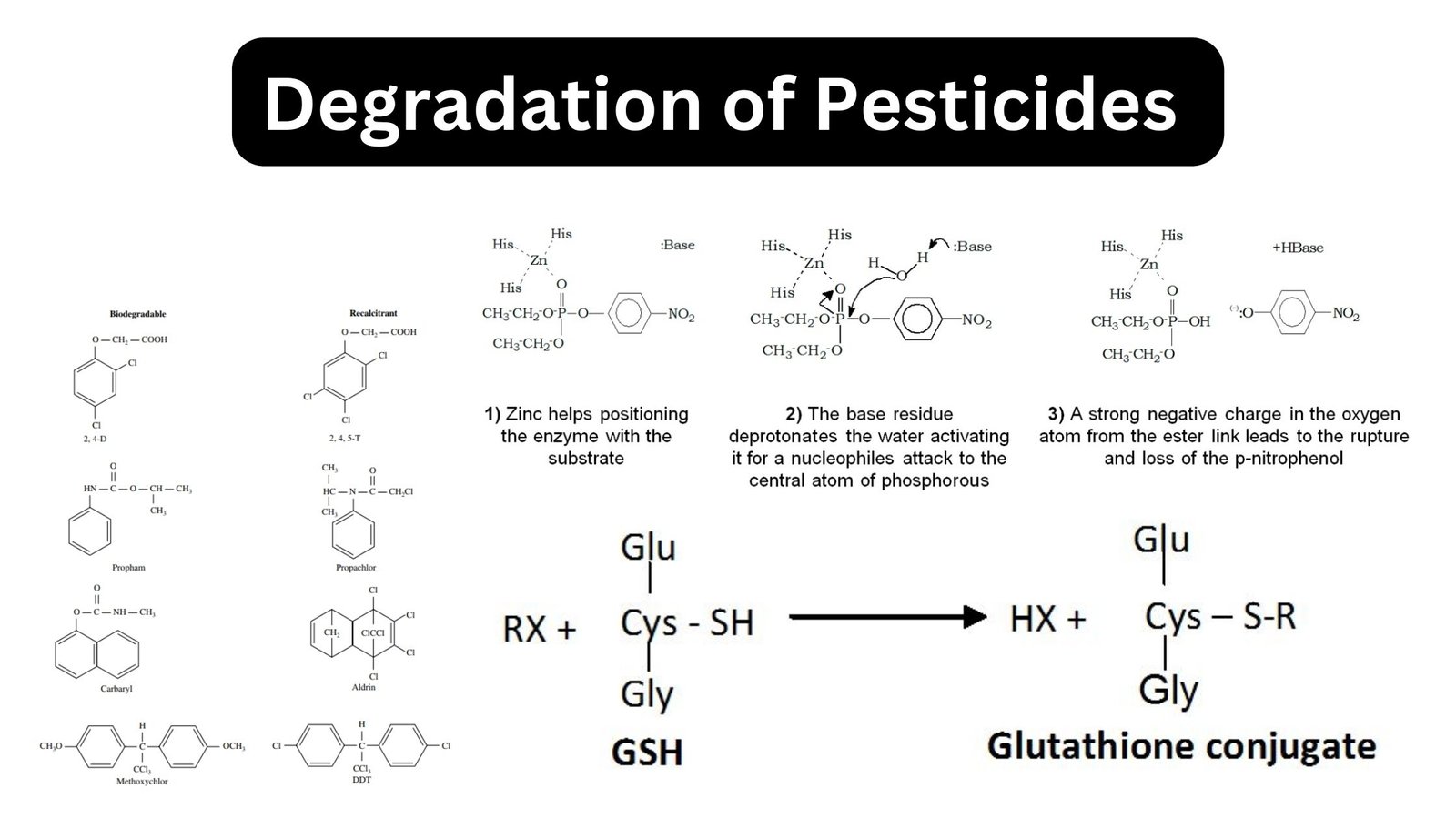
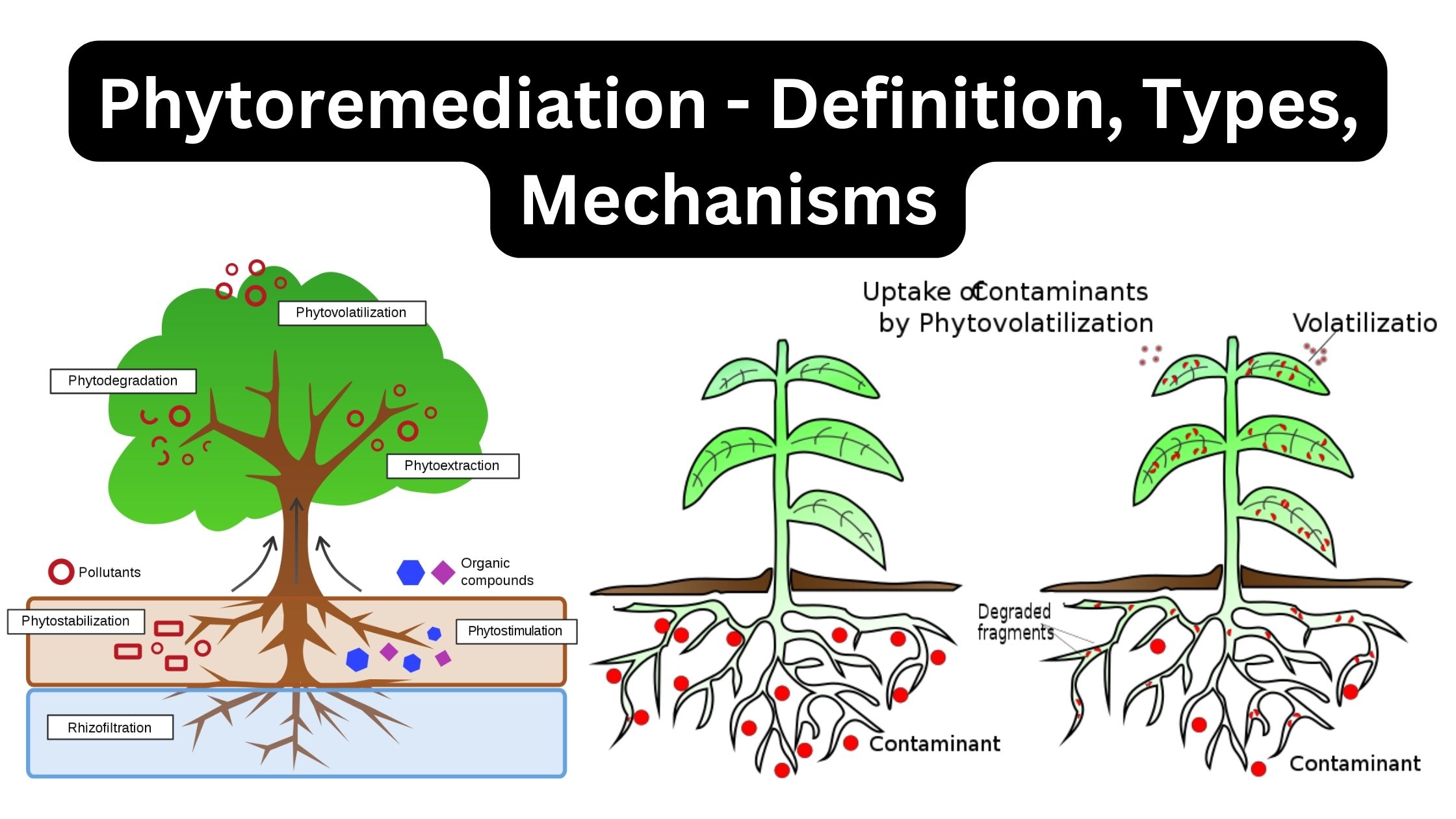
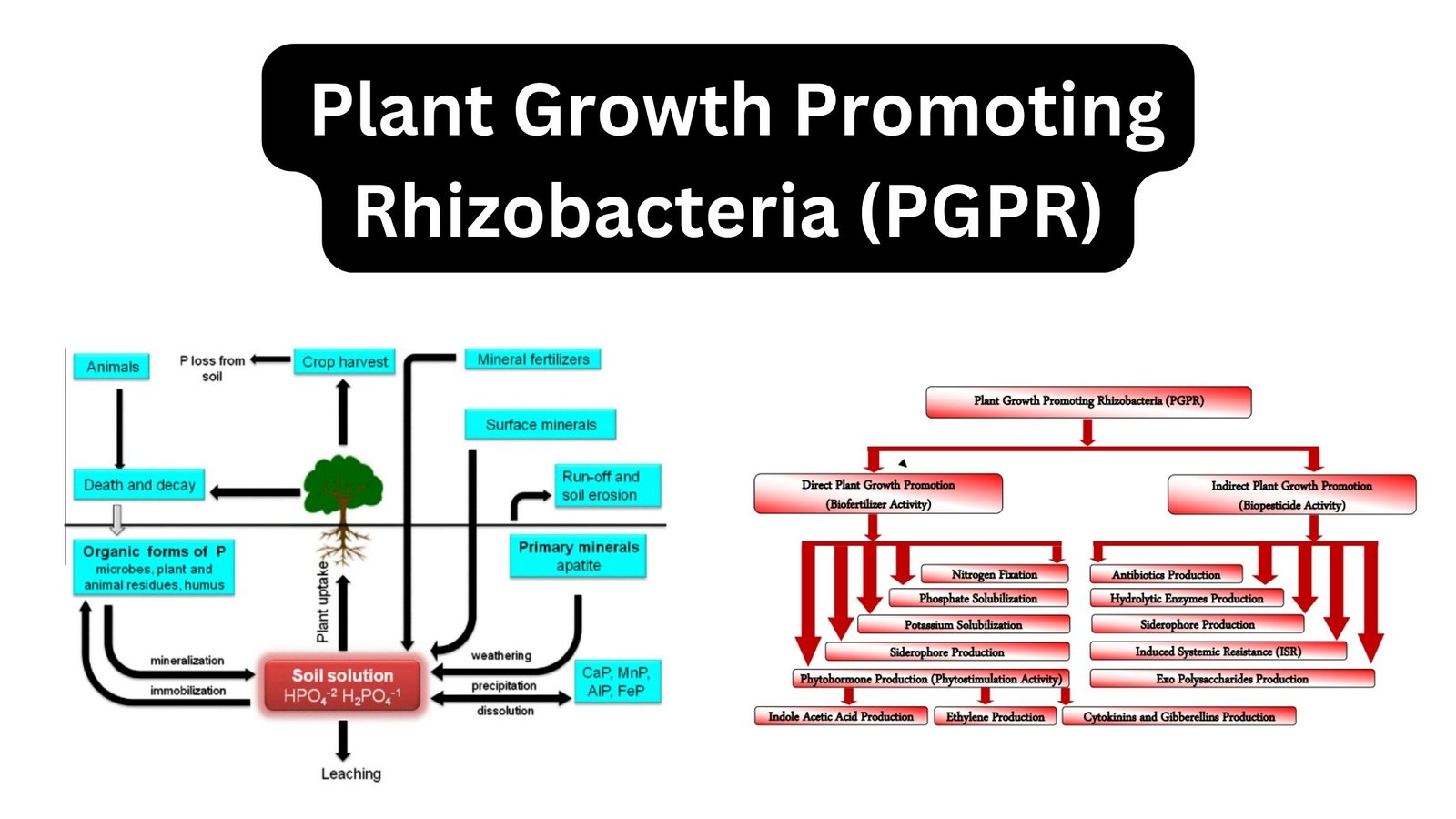
What is waste? Types of Waste Based on its physical properties On the basis of their physical features, trash can be classified as solid waste (such as garbage), liquid waste (such as wastewater), and gaseous waste. Based on pattern of use Based on the pattern of use, it can be classified into Based on source … Read more