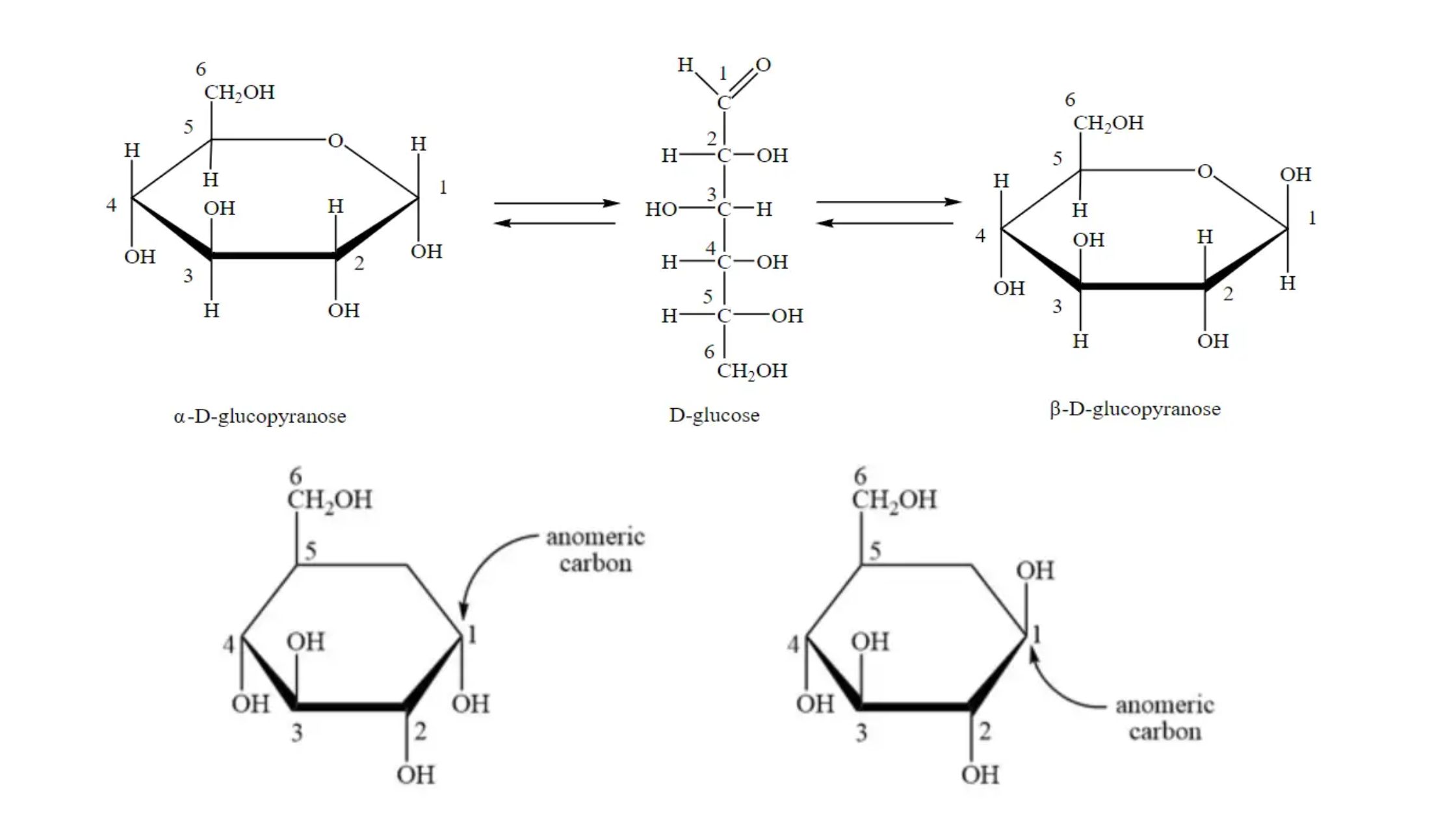
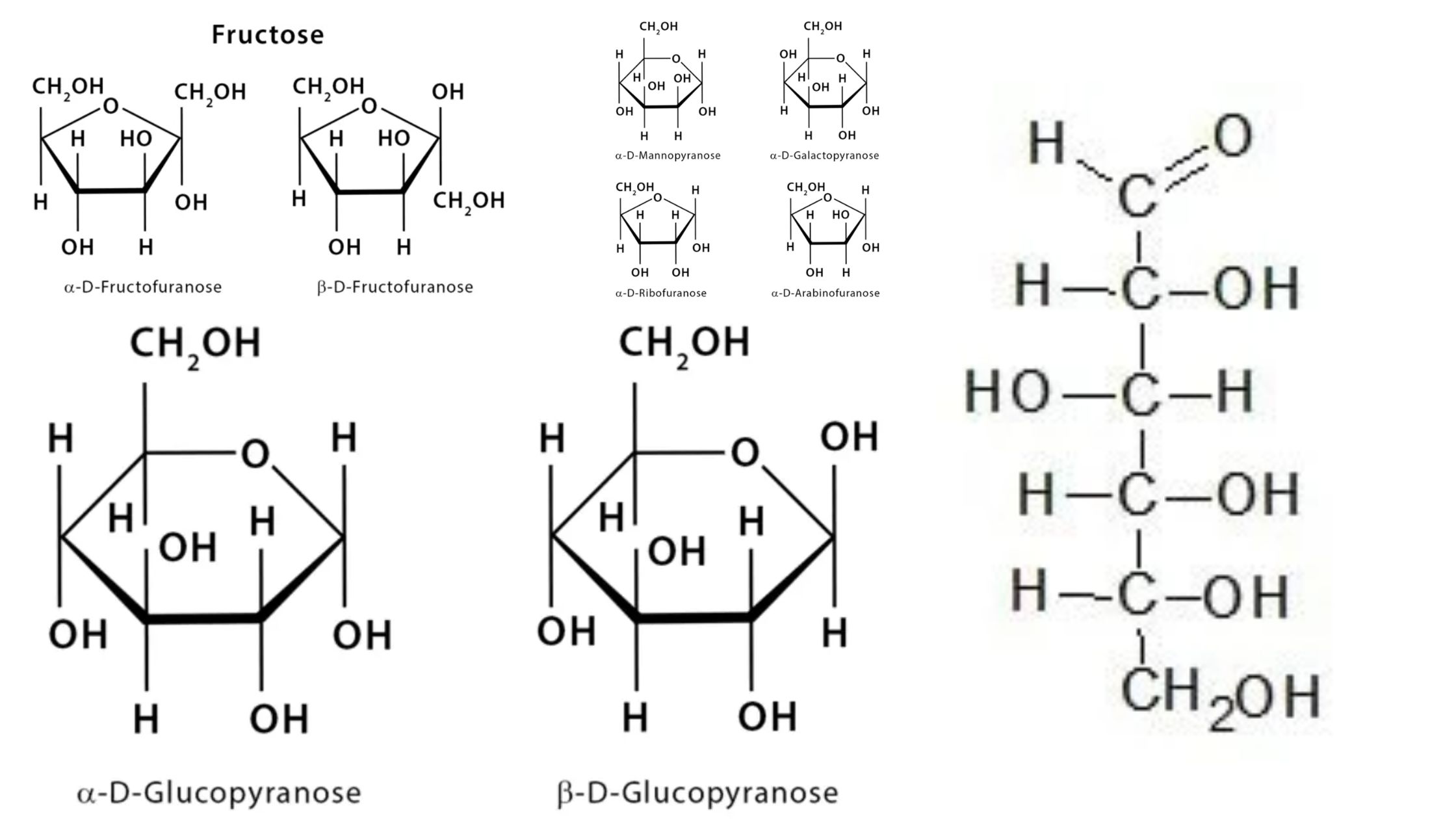
Anomer of Glucose
What is Anomer of glucose? Overview of Anomer Of Glucose Structure of Glucose Anomeric Carbon of Glucose Alpha-D-glucopyranose and beta-D-glucopyranose Significance The significance of the anomers of glucose lies in their impact on the chemical, physical, and biological properties of glucose. Here are some key points highlighting the significance of the anomers: In summary, the … Read more