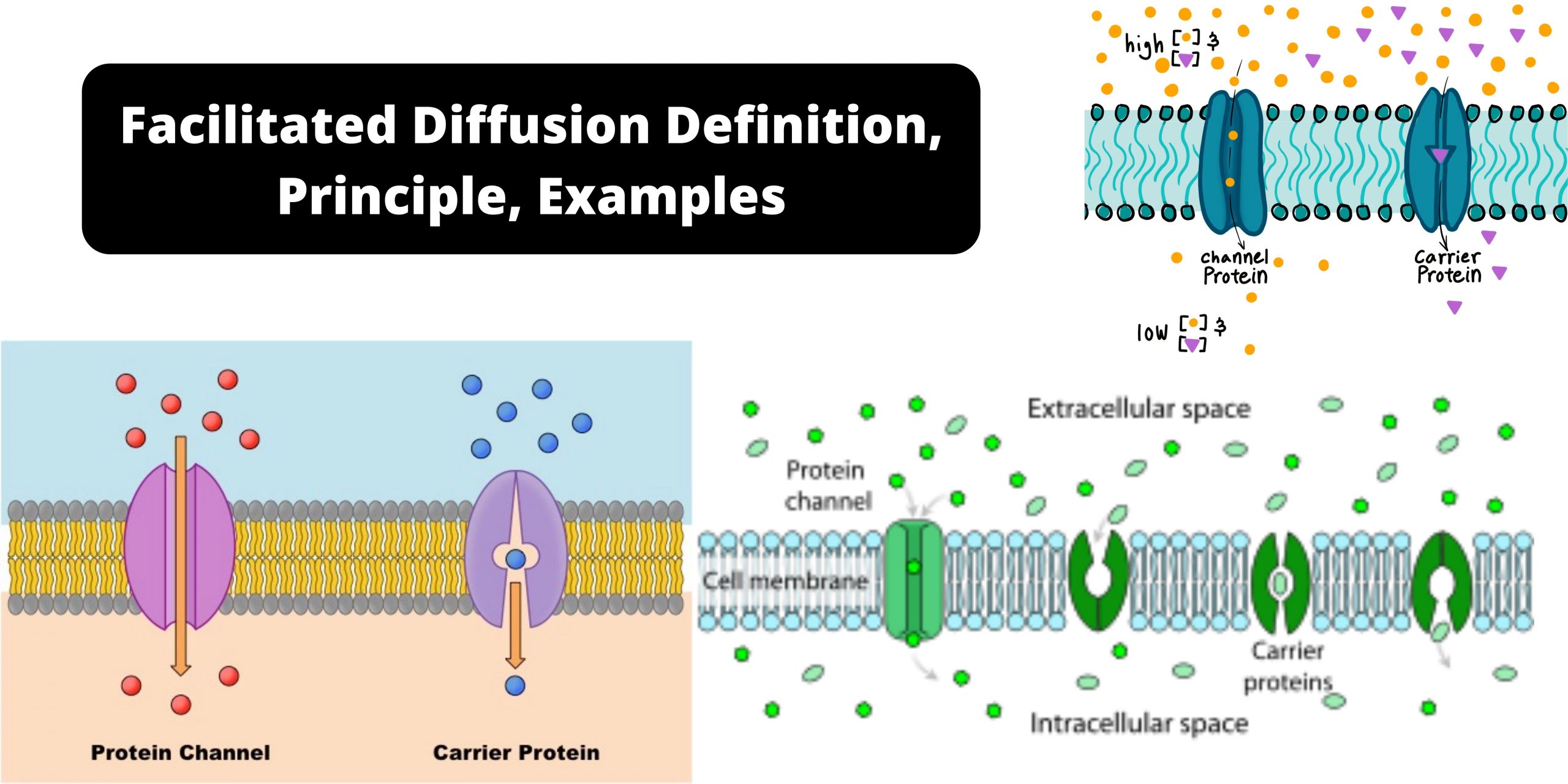
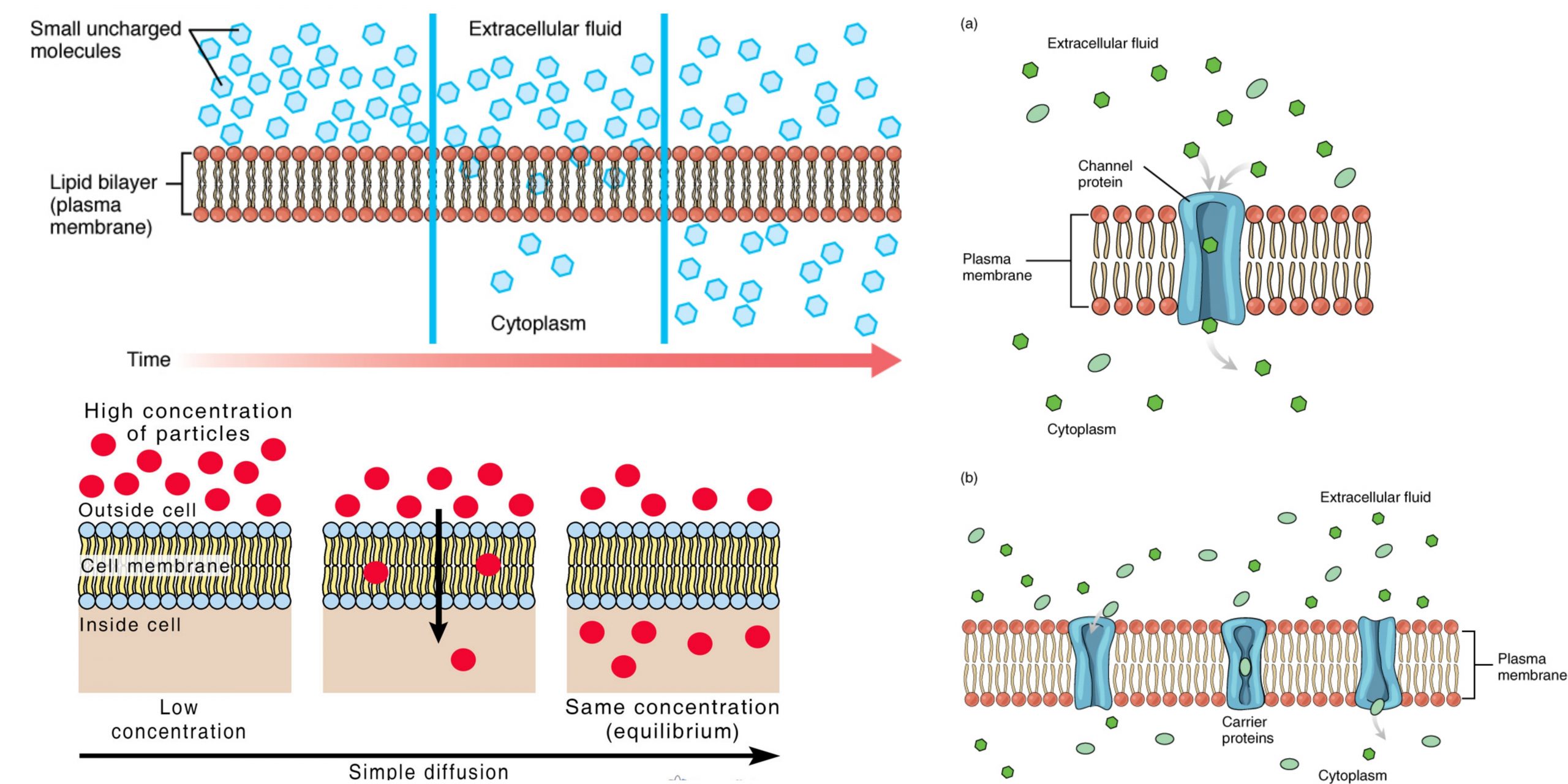
Binary fission – Definition, Types, Steps, Examples
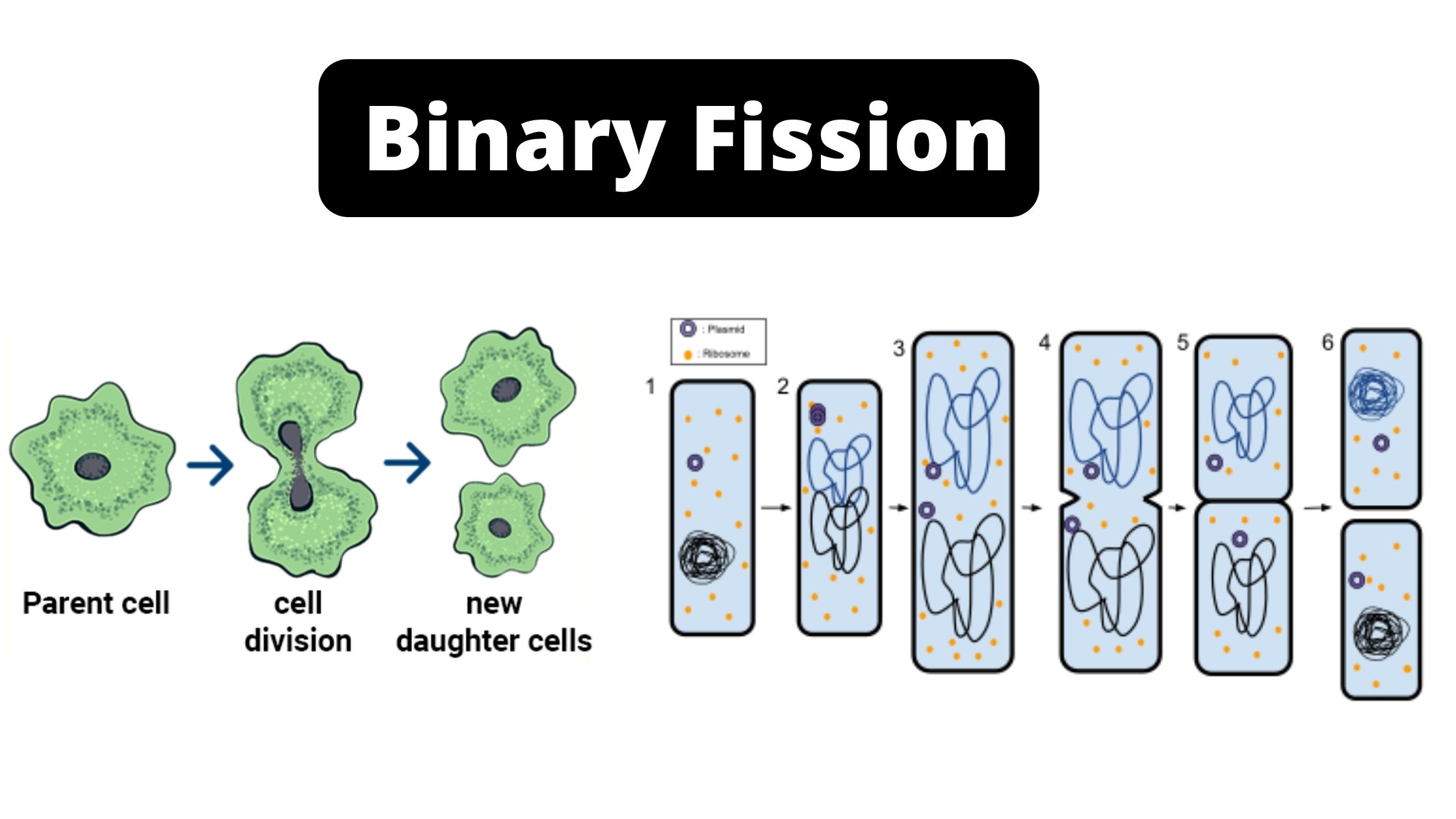
Definition of binary fission (What is binary fission?) Binary fission can be described as a kind of sexual reproduction in which one living cell, or organelle expands twice its size, and then splits into two identical cells, which means that each of the daughter cells can be expected to grow to what size as the … Read more