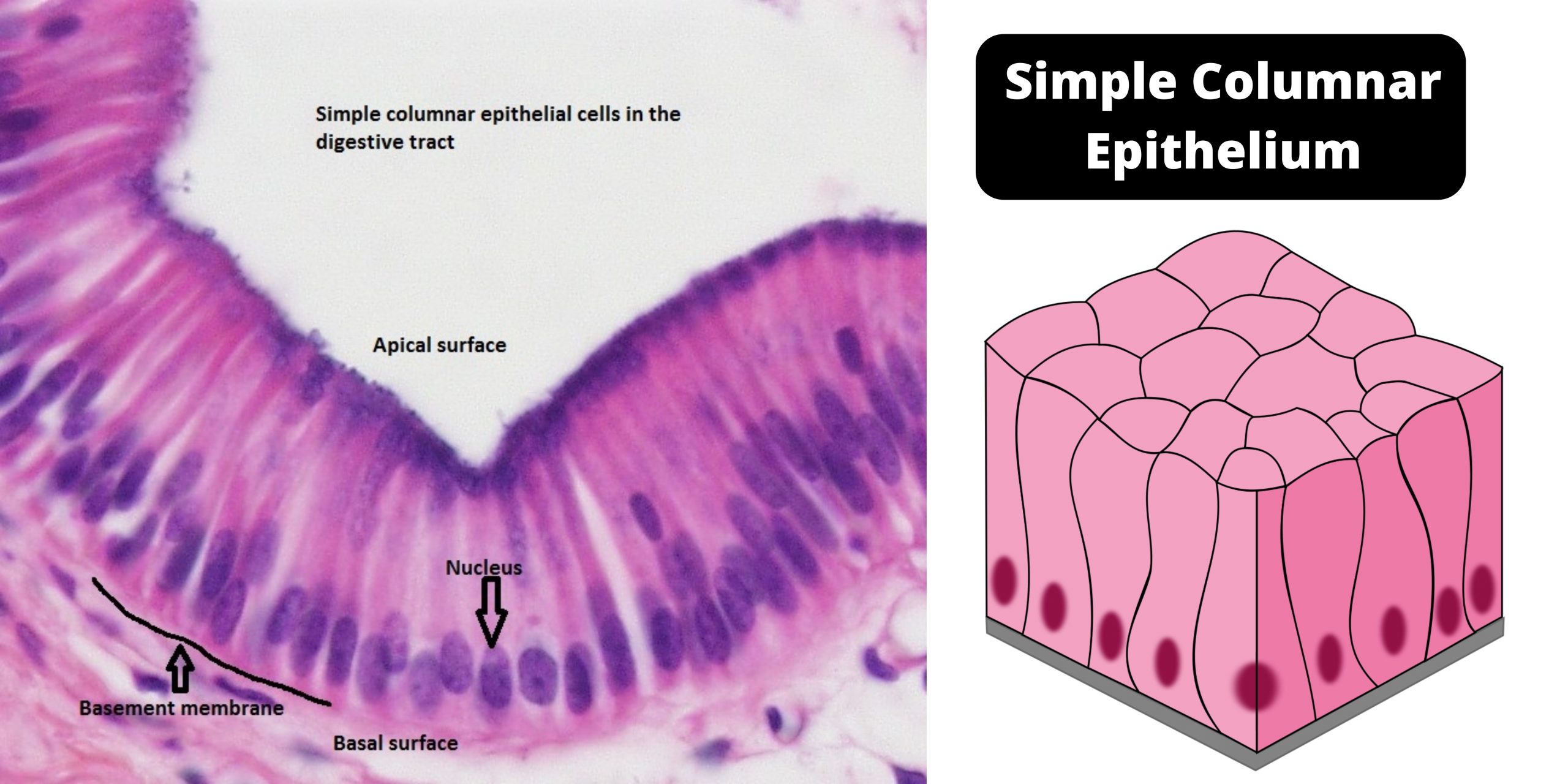
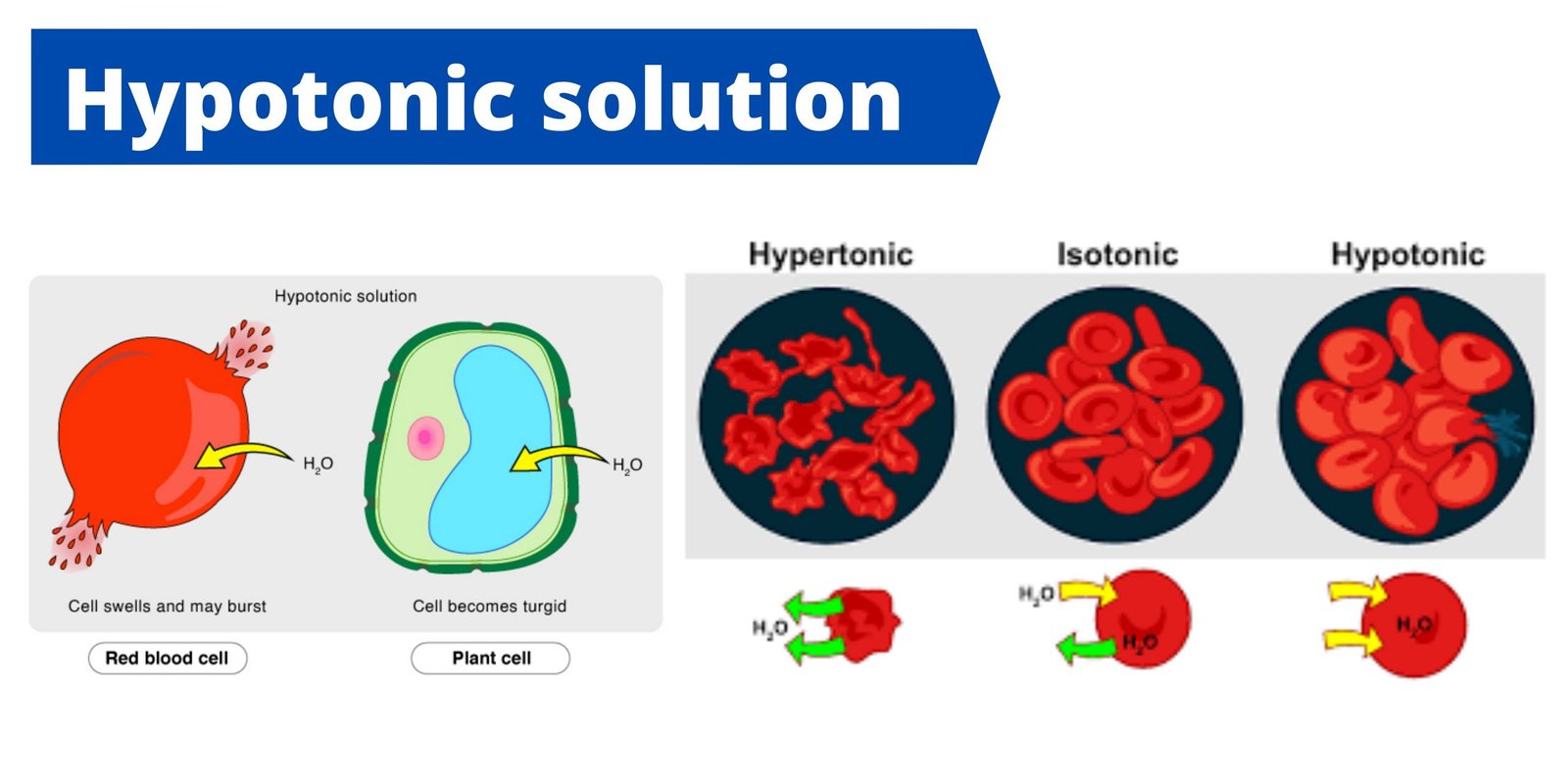
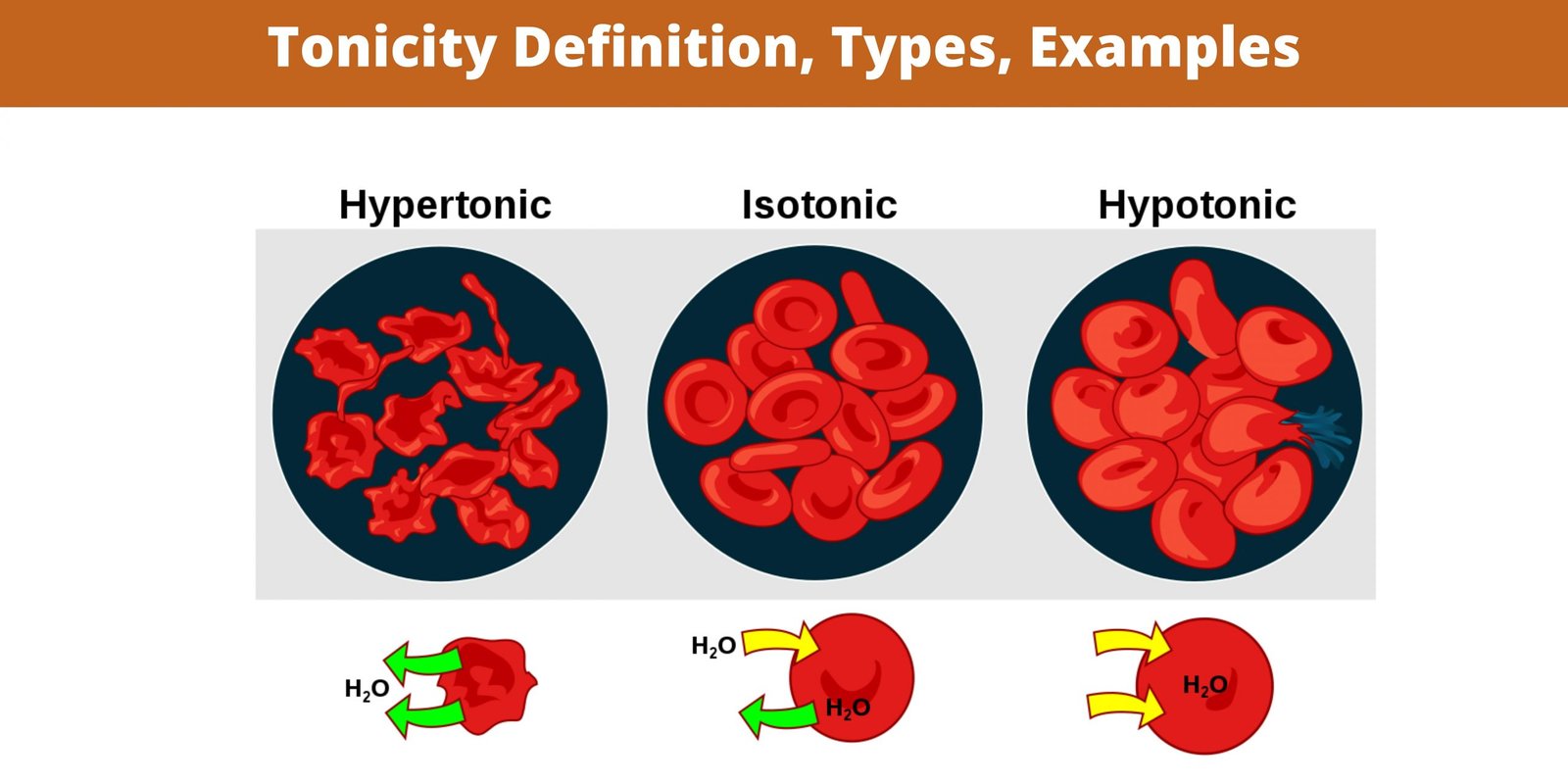
Simple columnar epithelium – definition, structure, functions, examples
Definition of Simple columnar epithelium The simple columnar epithelium, which is one type of epithelium, is made up of a single layer consisting of long, elongated cells. These cells are located in areas where absorption or secretion are the primary functions. The cells of the columnar epithelium can also be modified, just like cuboidal epithelium. … Read more