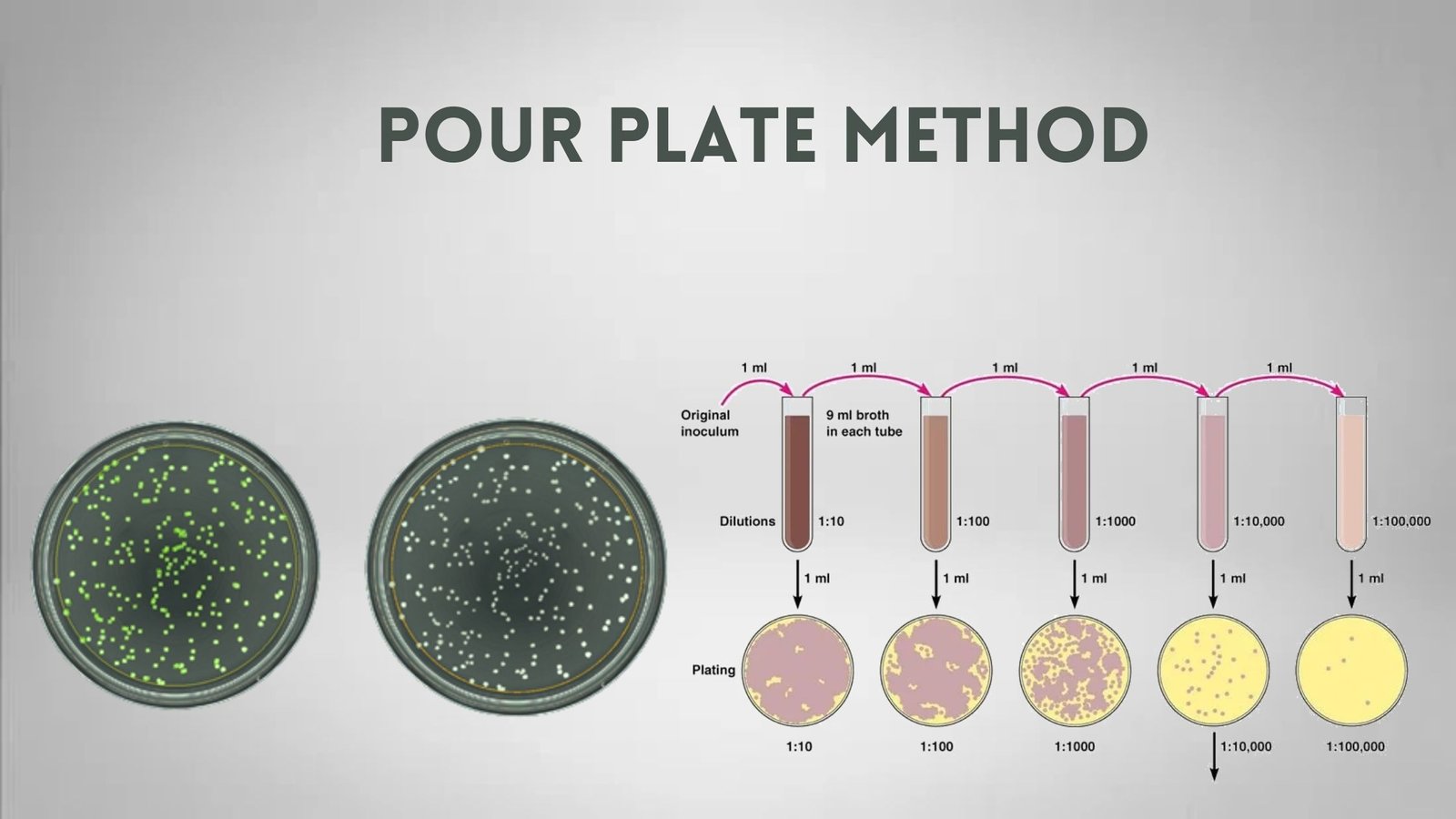
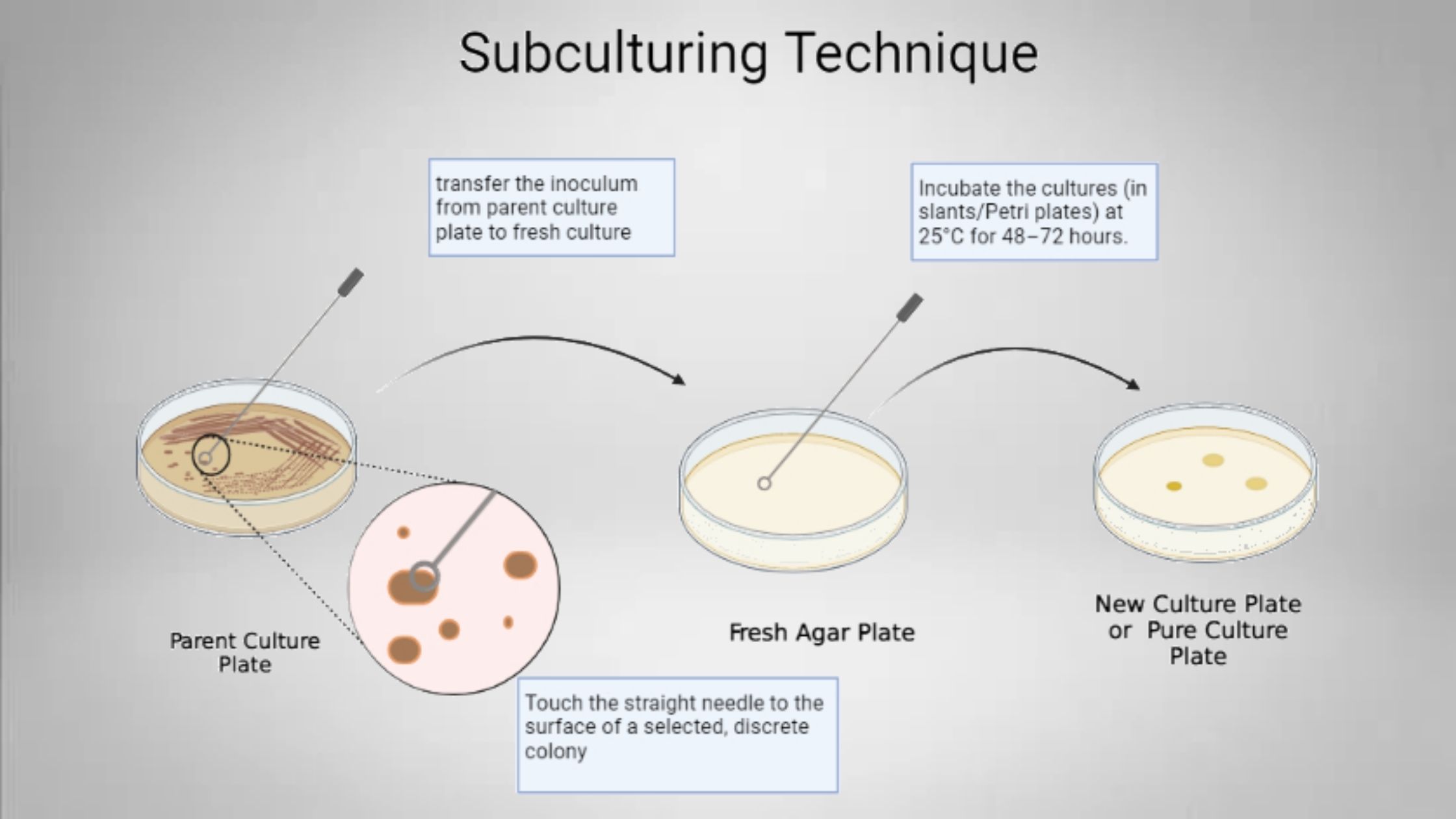
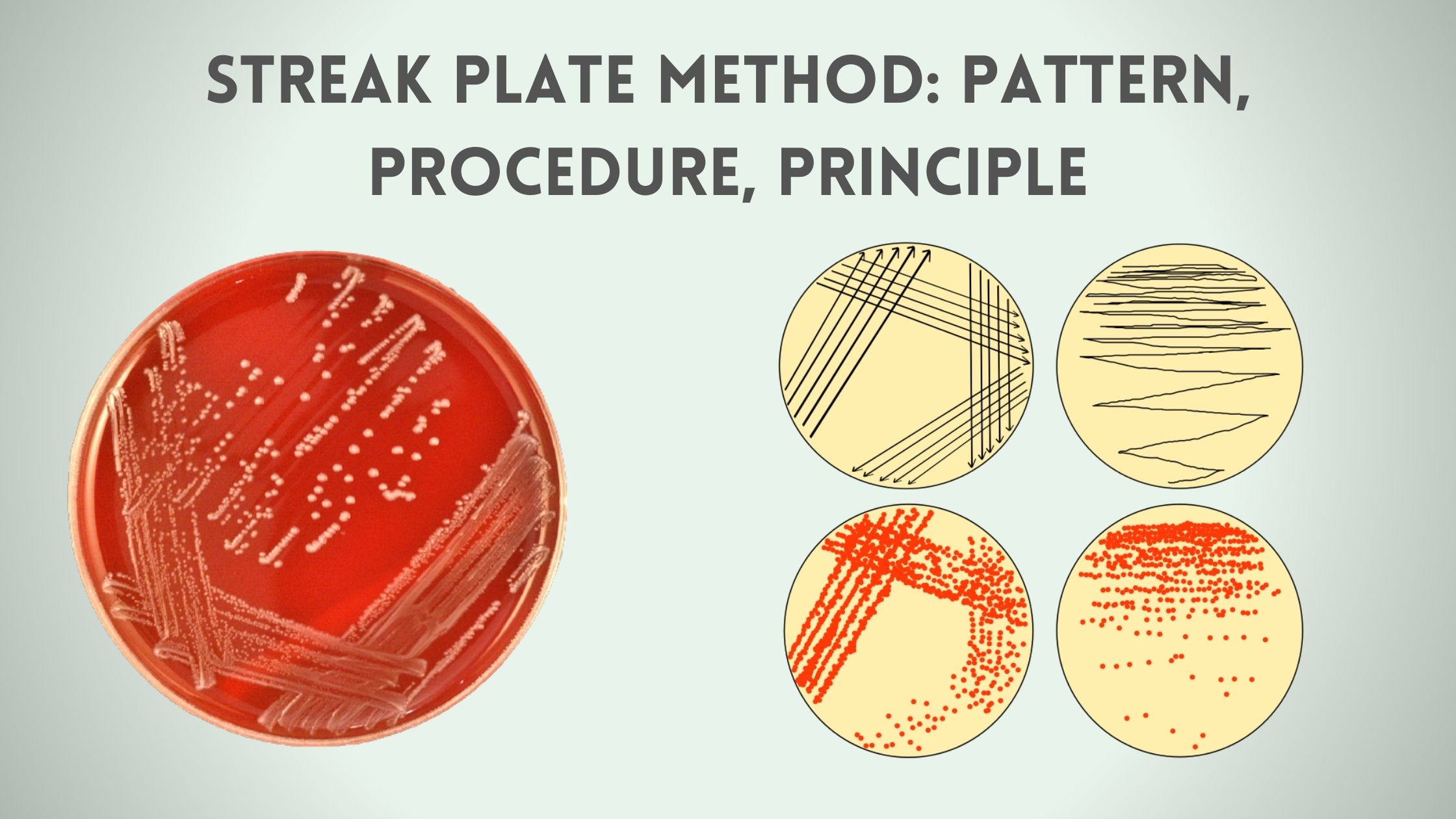
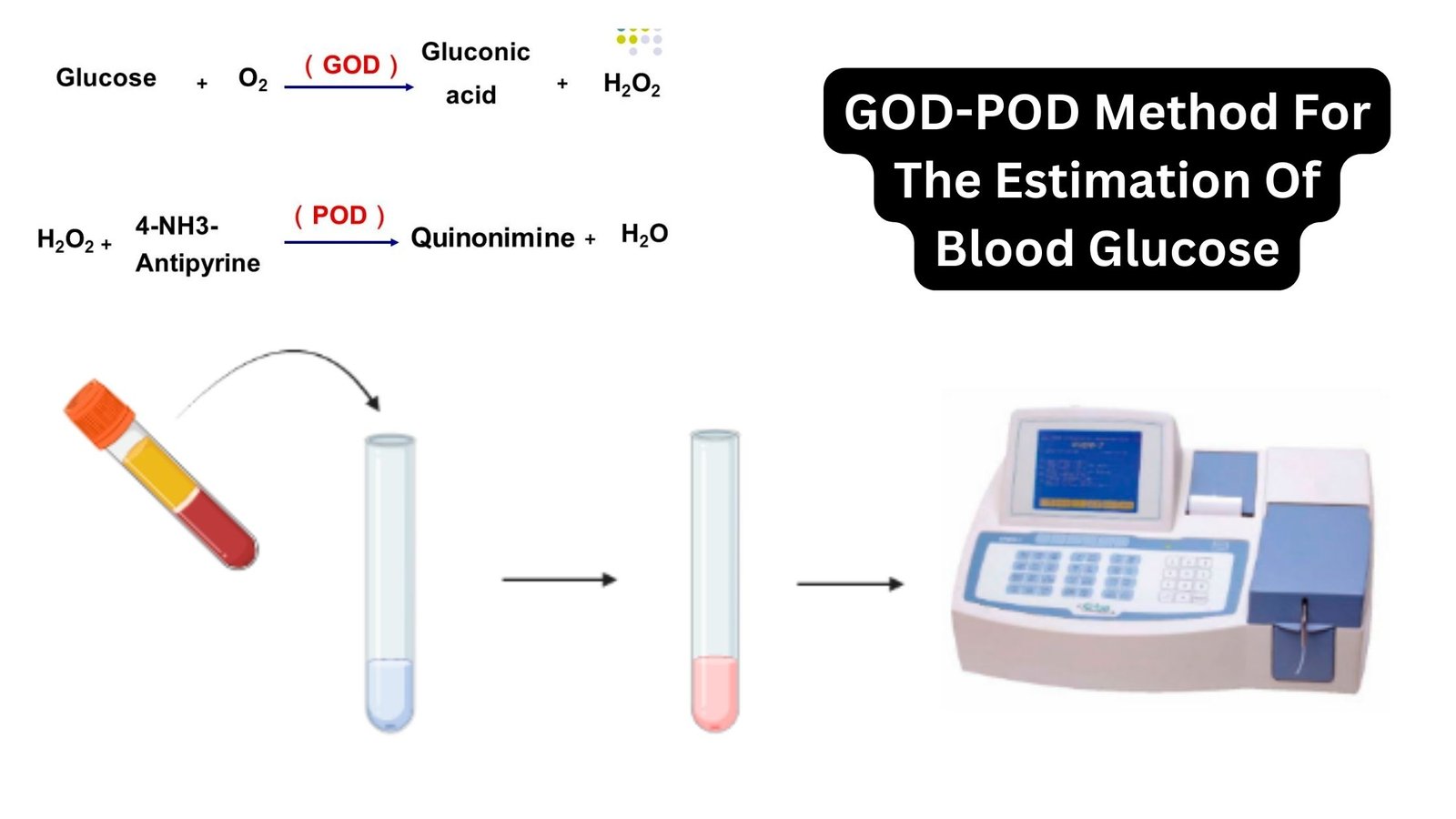
Rocket Immunoelectrophoresis – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Application
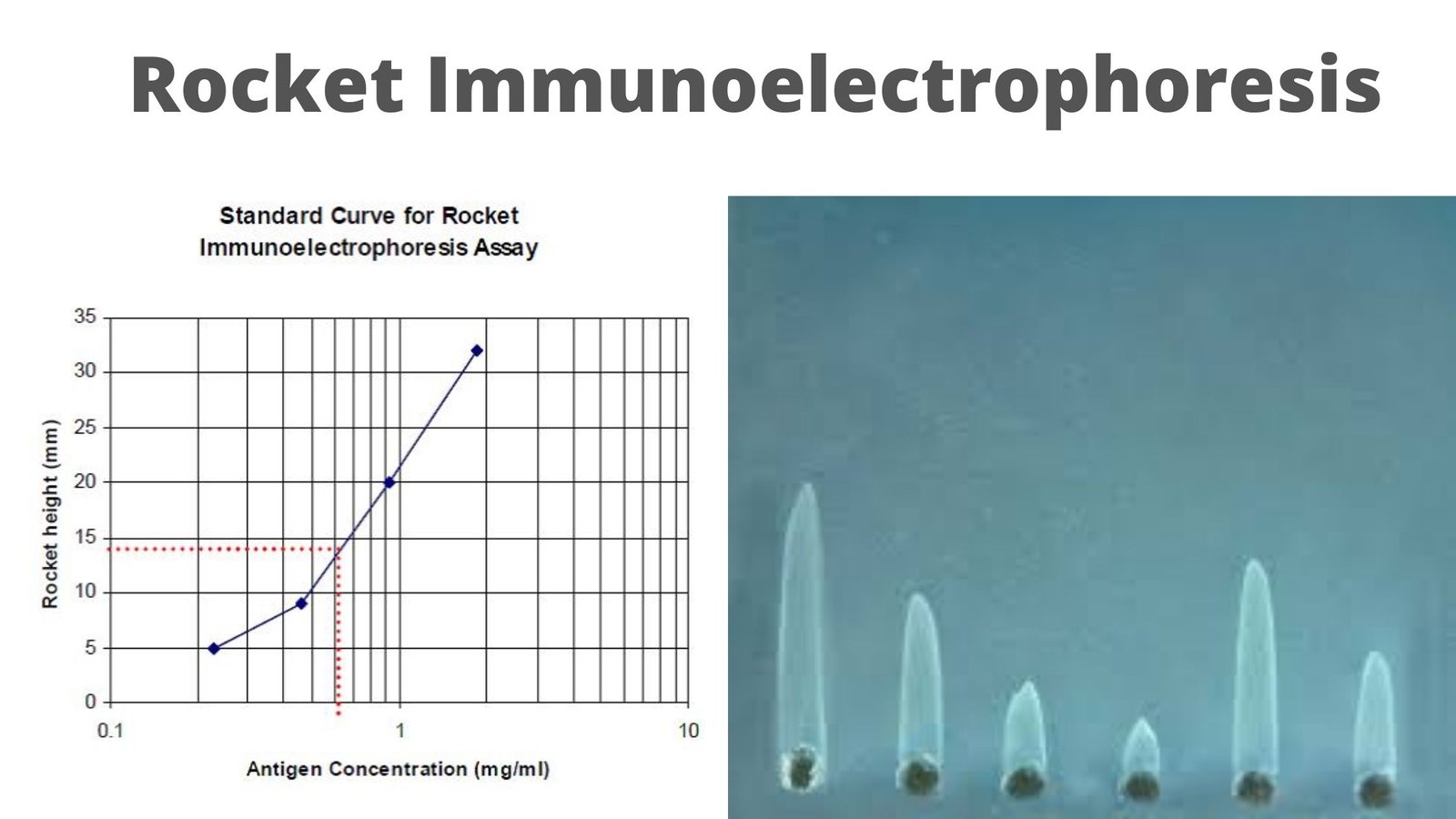
Rocket Immunoelectrophoresis (RIEP) also known as electro-immuno diffusion is a simple, quick and reproducible method for determining the concentration of antigen (Ag) in an unknown sample.