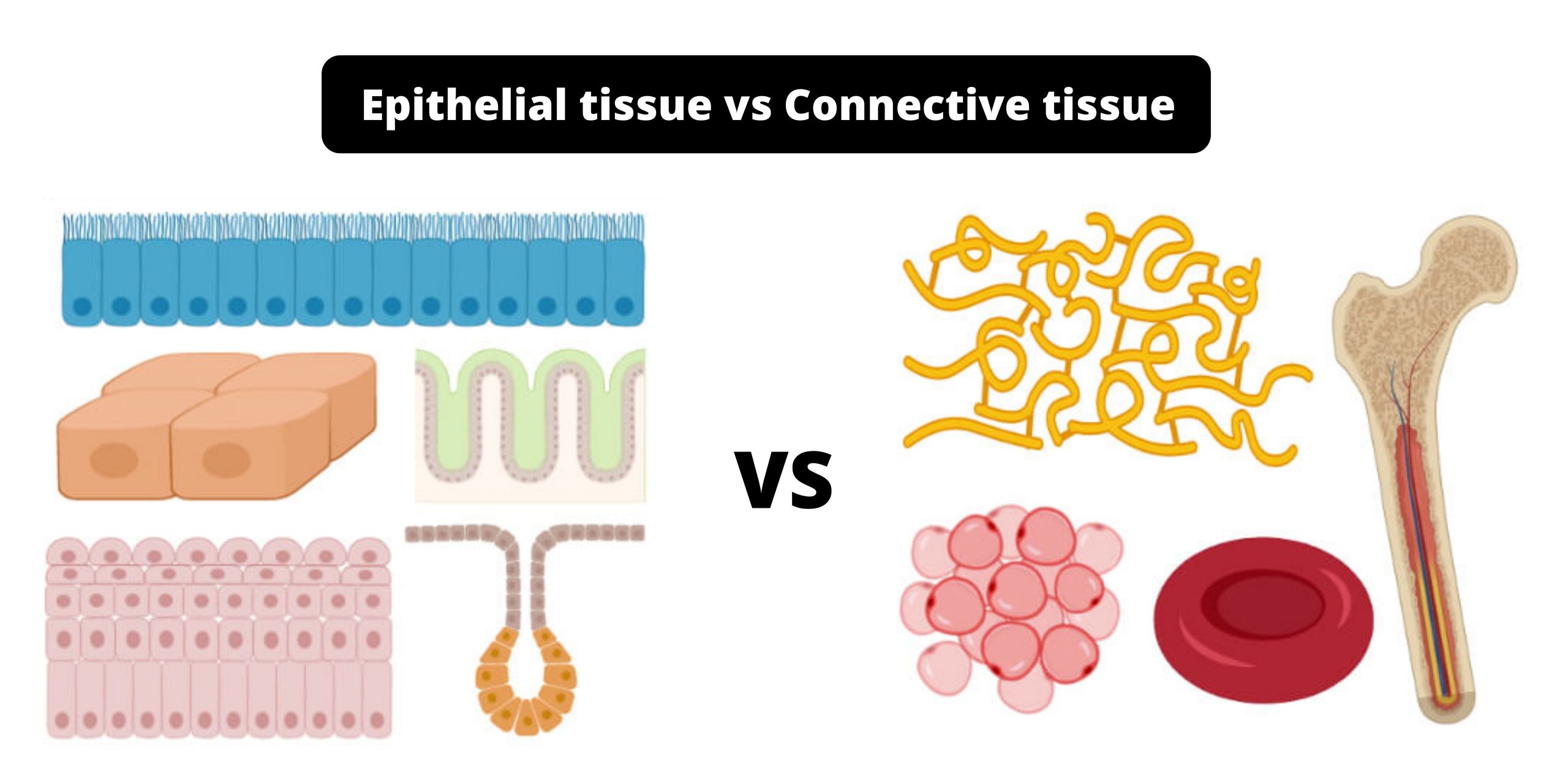
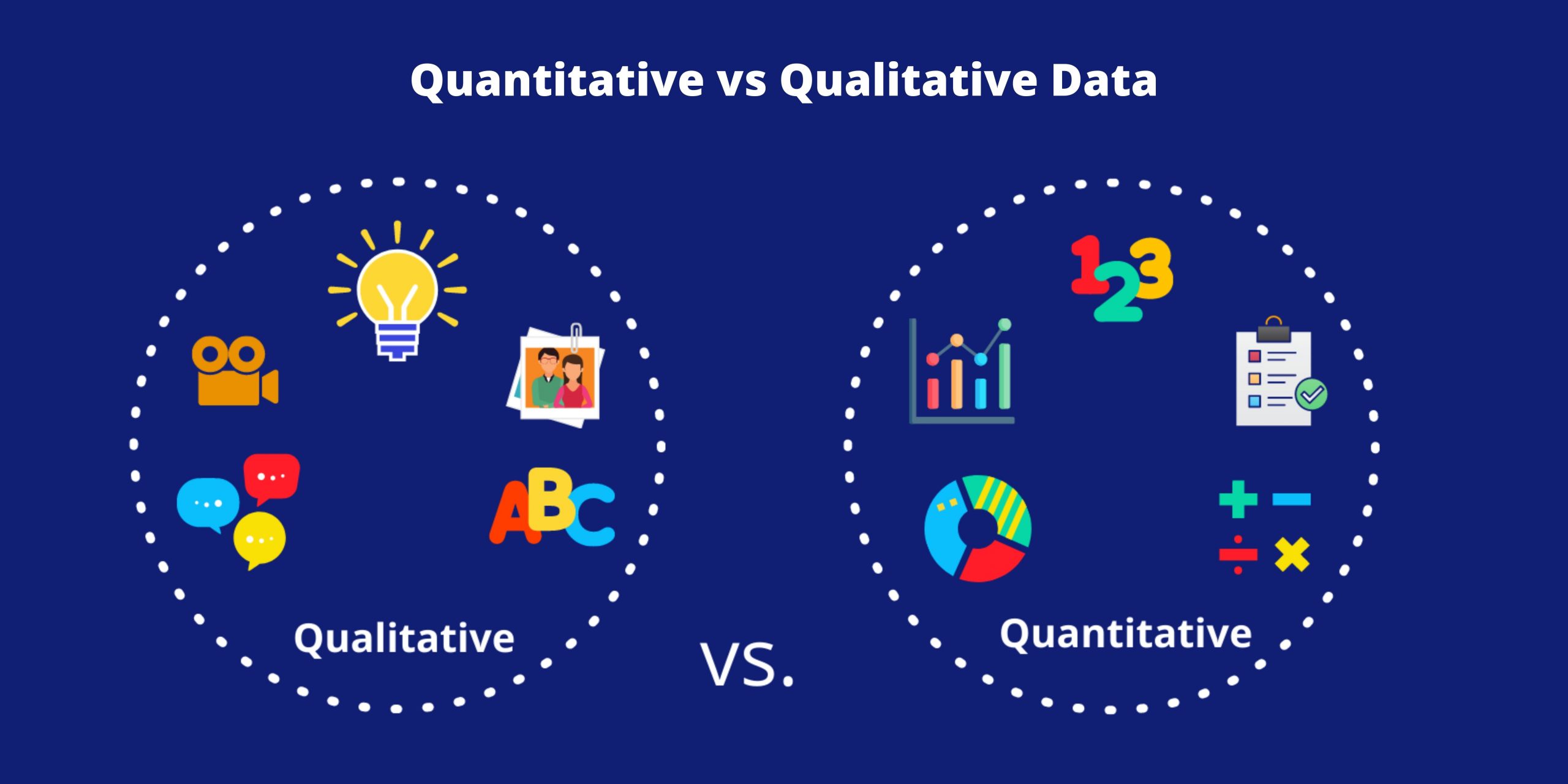
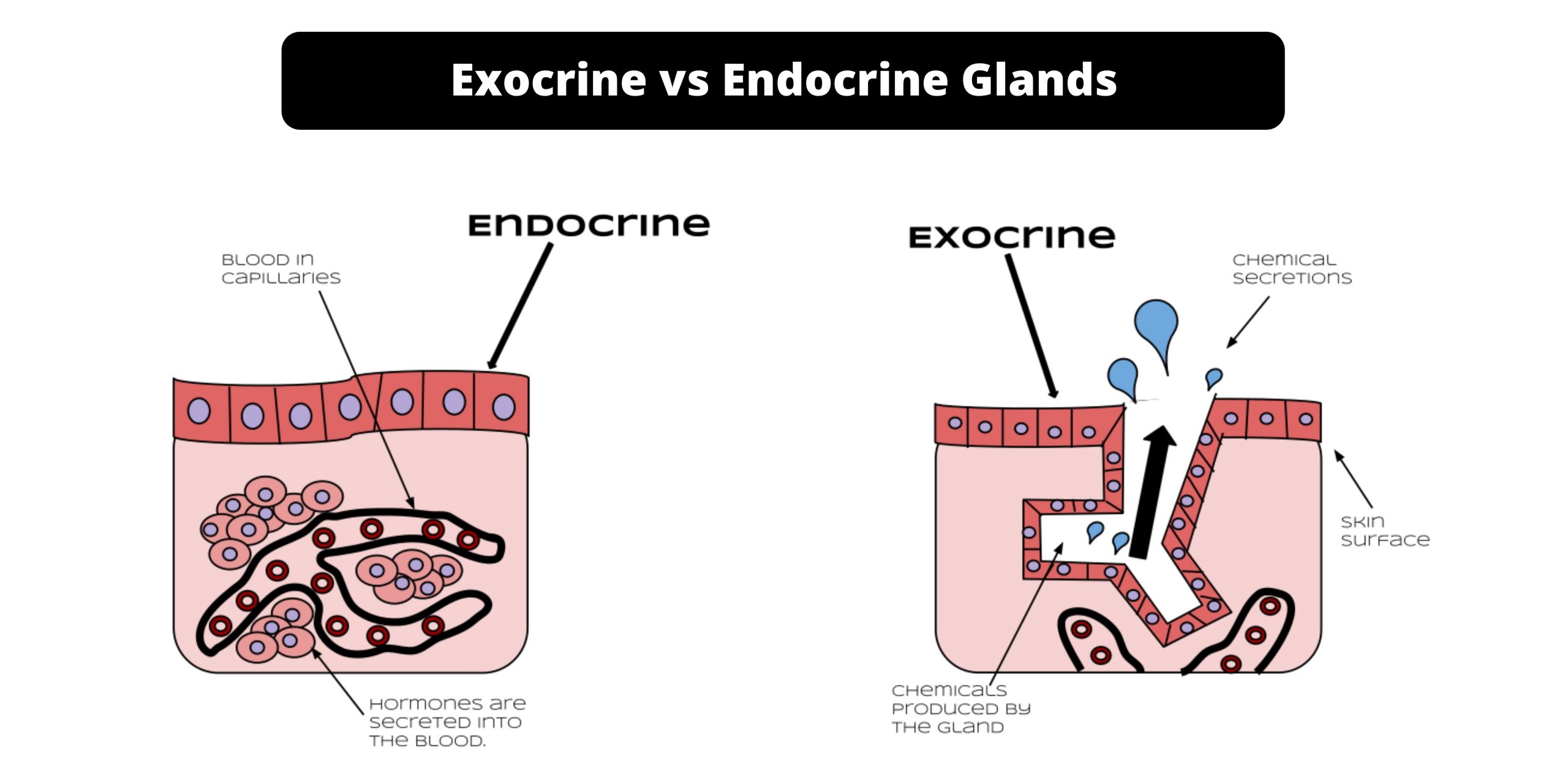
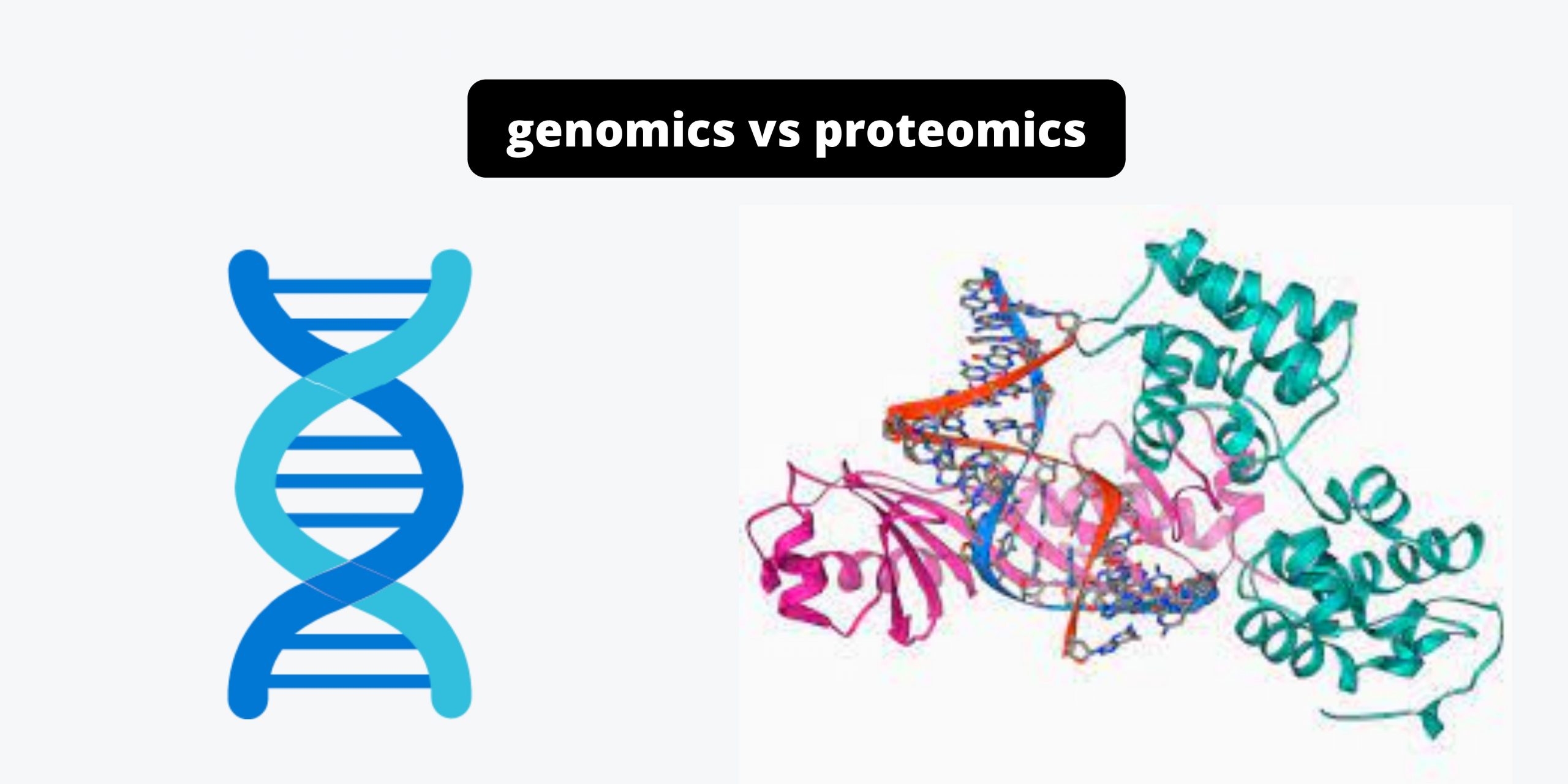
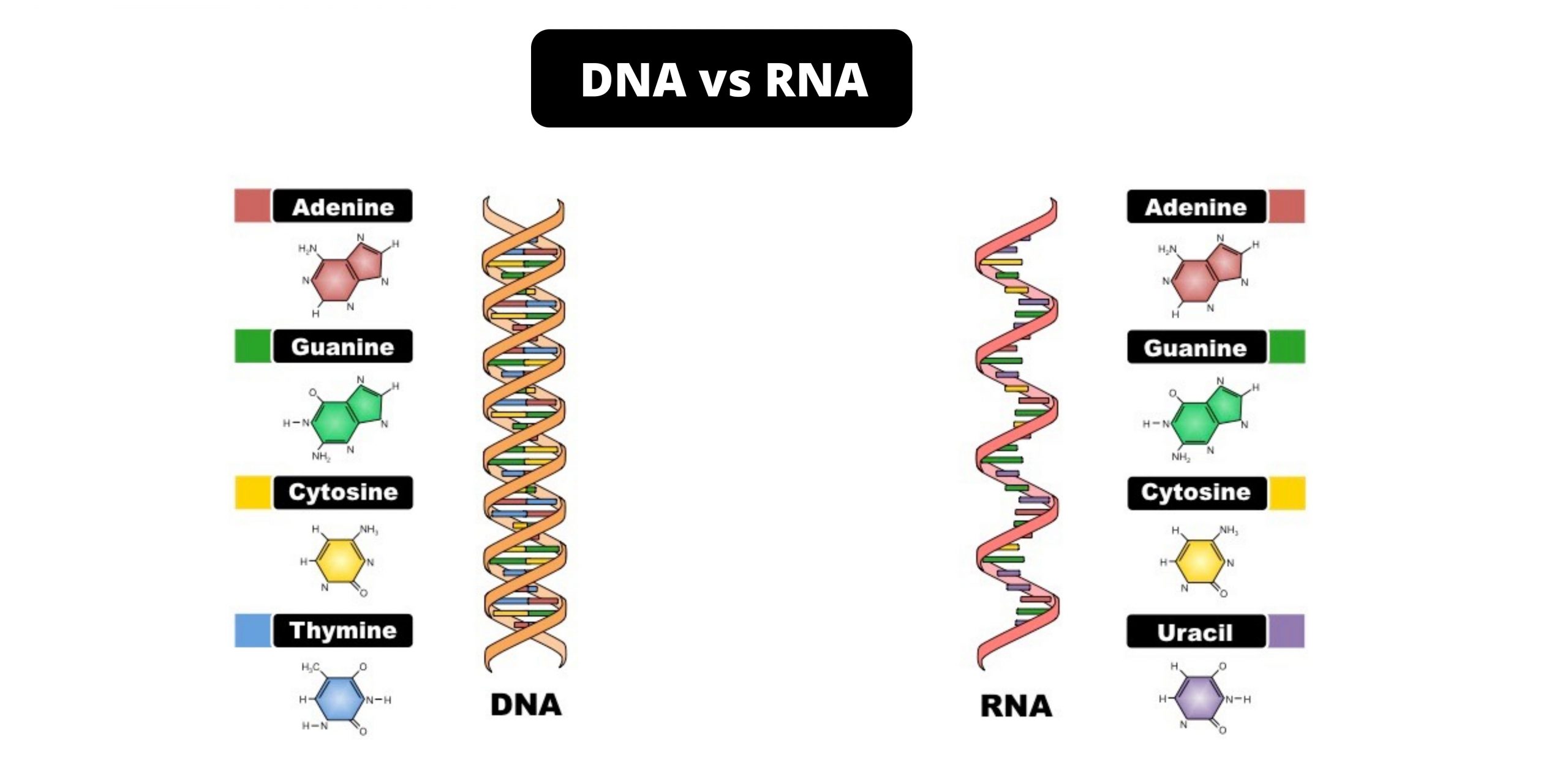
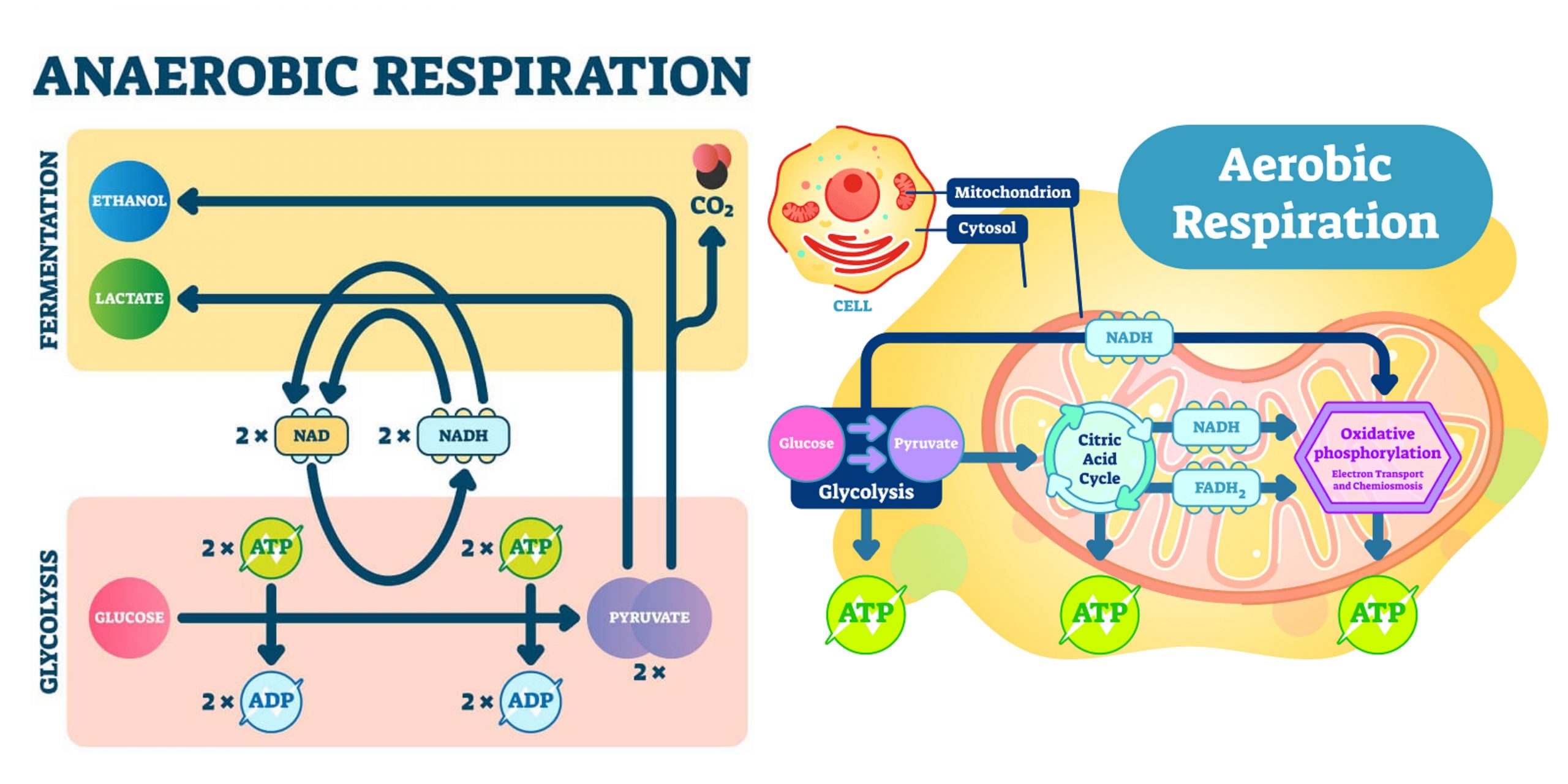
Difference between Primary and Secondary Succession
Primary succession refers to a type or ecological succession that occurs in an environment that has just been formed, but does not have any habitable soil. However, living organisms are then colonized for their first time.