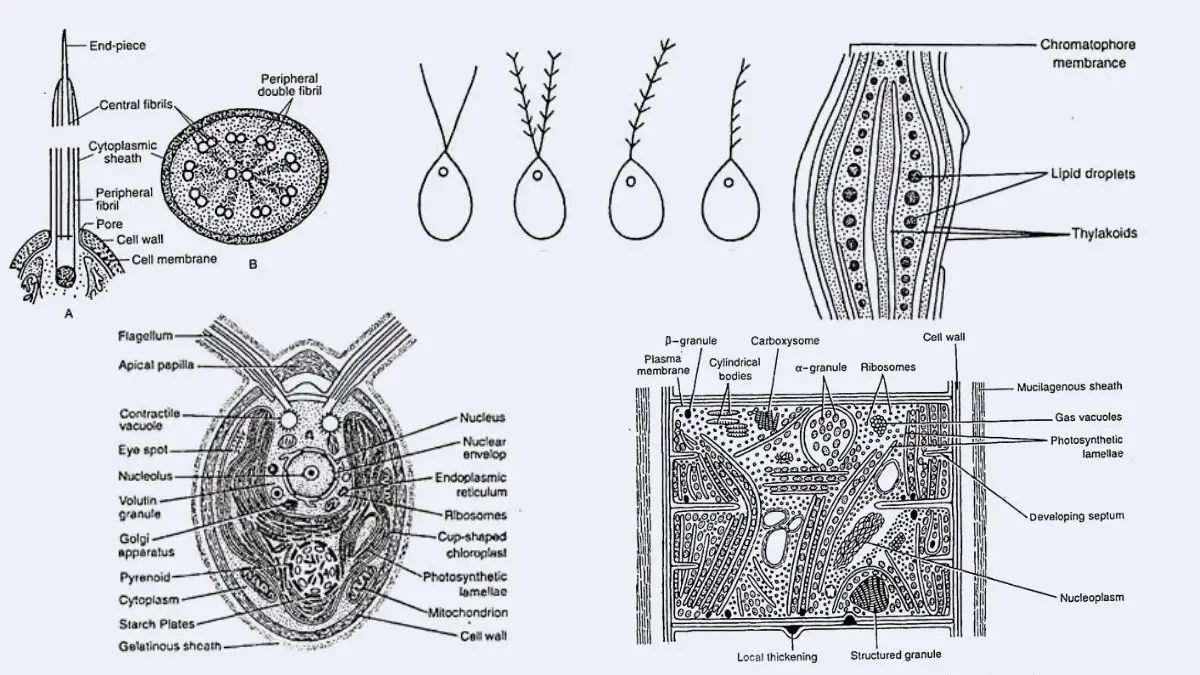
Desert Ecosystem – Definition, Types, Importance
A Desert Ecosystem is a system in which living things (plants, animals, microbes) interact with non-living parts (soil, air, water, temperature) in a region that is extremely dry. It is defined by very low rainfall (often less than about 250 mm per year), and scarcity of moisture is a crucial limiting factor. The system is … Read more