Lamina Propria – Definition, Structure, Functions
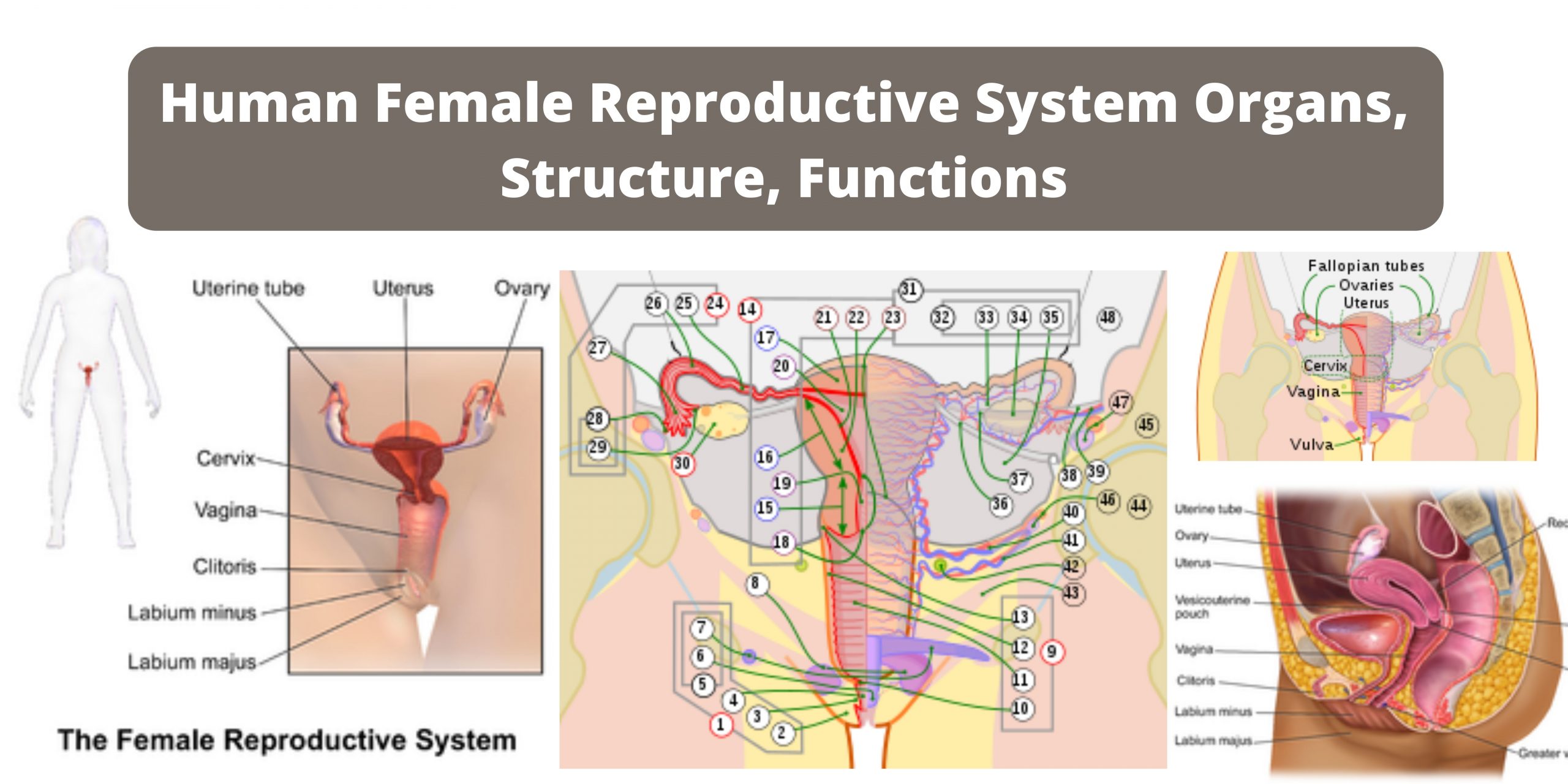
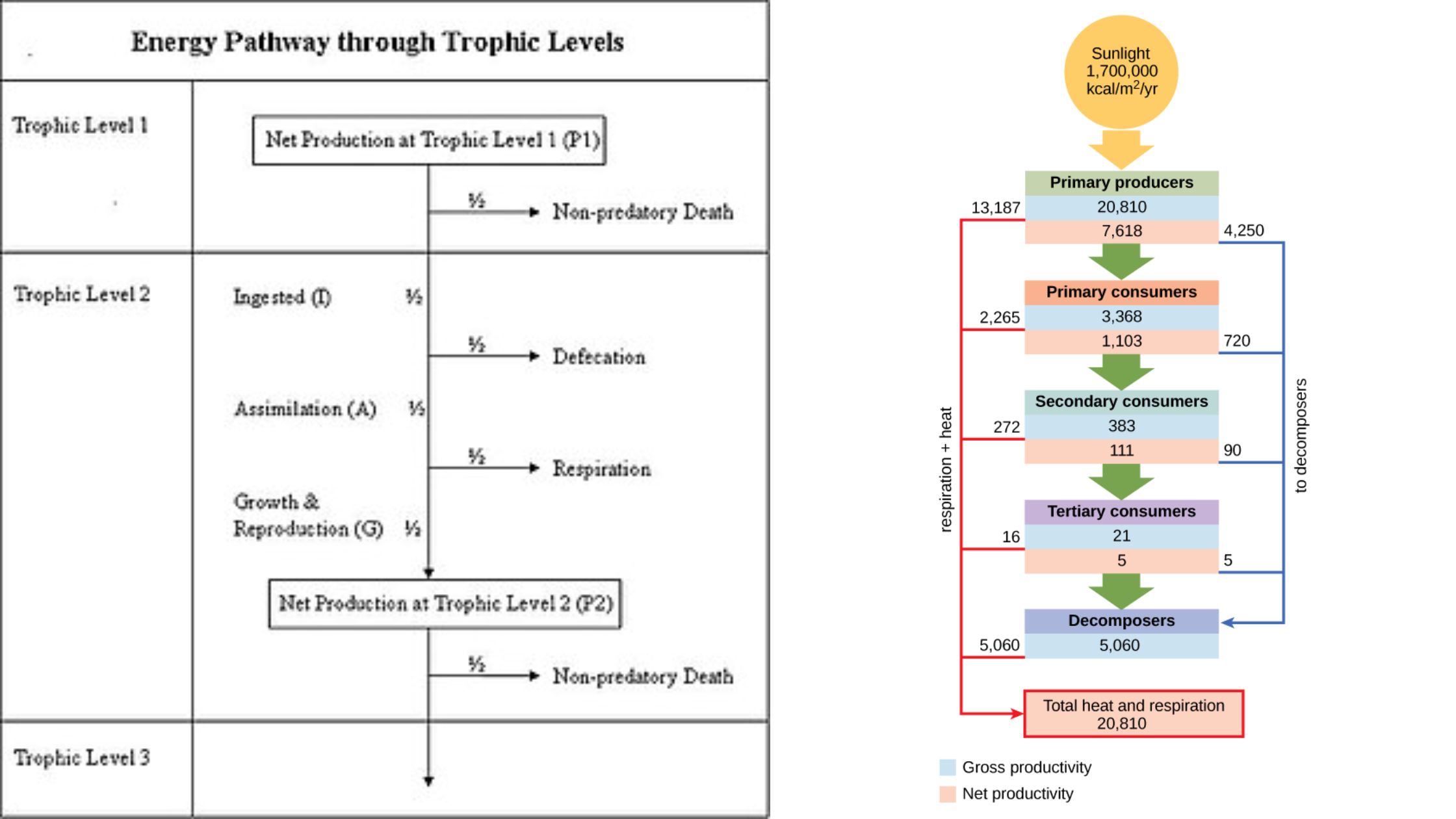
What is Lamina Propria? Definition of Lamina Propria The lamina propria is a layer of loose connective tissue found beneath the epithelium in mucous membranes, providing structural support, facilitating nutrient passage, and serving as a protective barrier against foreign substances and organisms. Lamina Propria Structure Lamina Propria Functions The lamina propria, an integral component of … Read more