Proteus – Overview
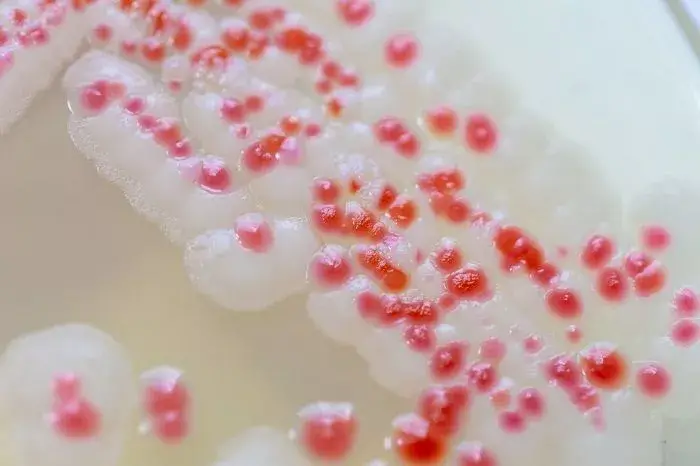
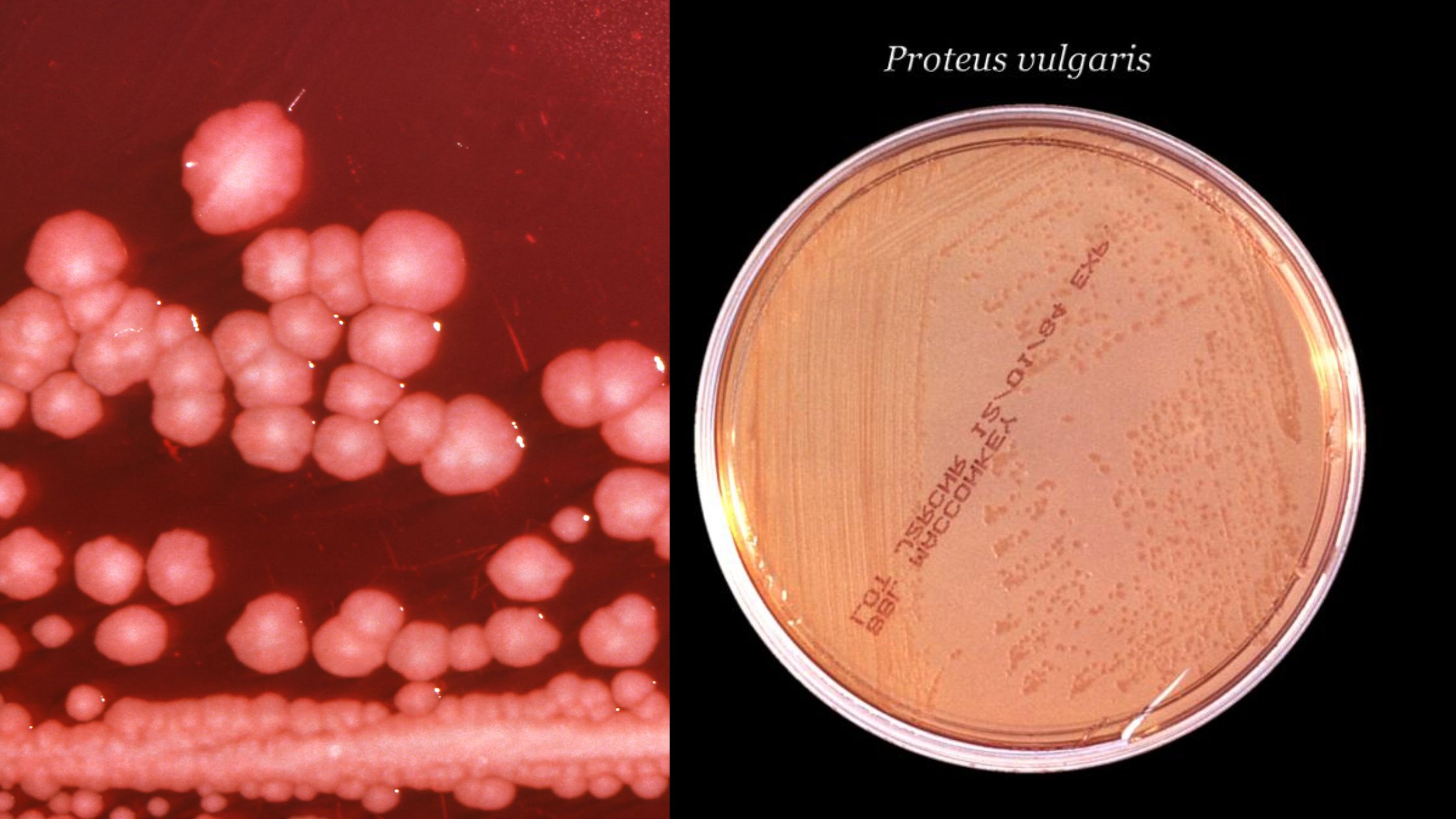
Morphology of Proteus Proteus demonstrates the following characteristics: Culture of Proteus Proteeae organisms are aerobic bacteria that thrive on common media like nutrient agar. On the medium, colonies of Proteus exude a putrefactive (or “fishy” or “seminal”) stench. Swarming Biochemical properties of Proteus Cell Wall Components and Antigenic Properties Antigens O and H are present … Read more