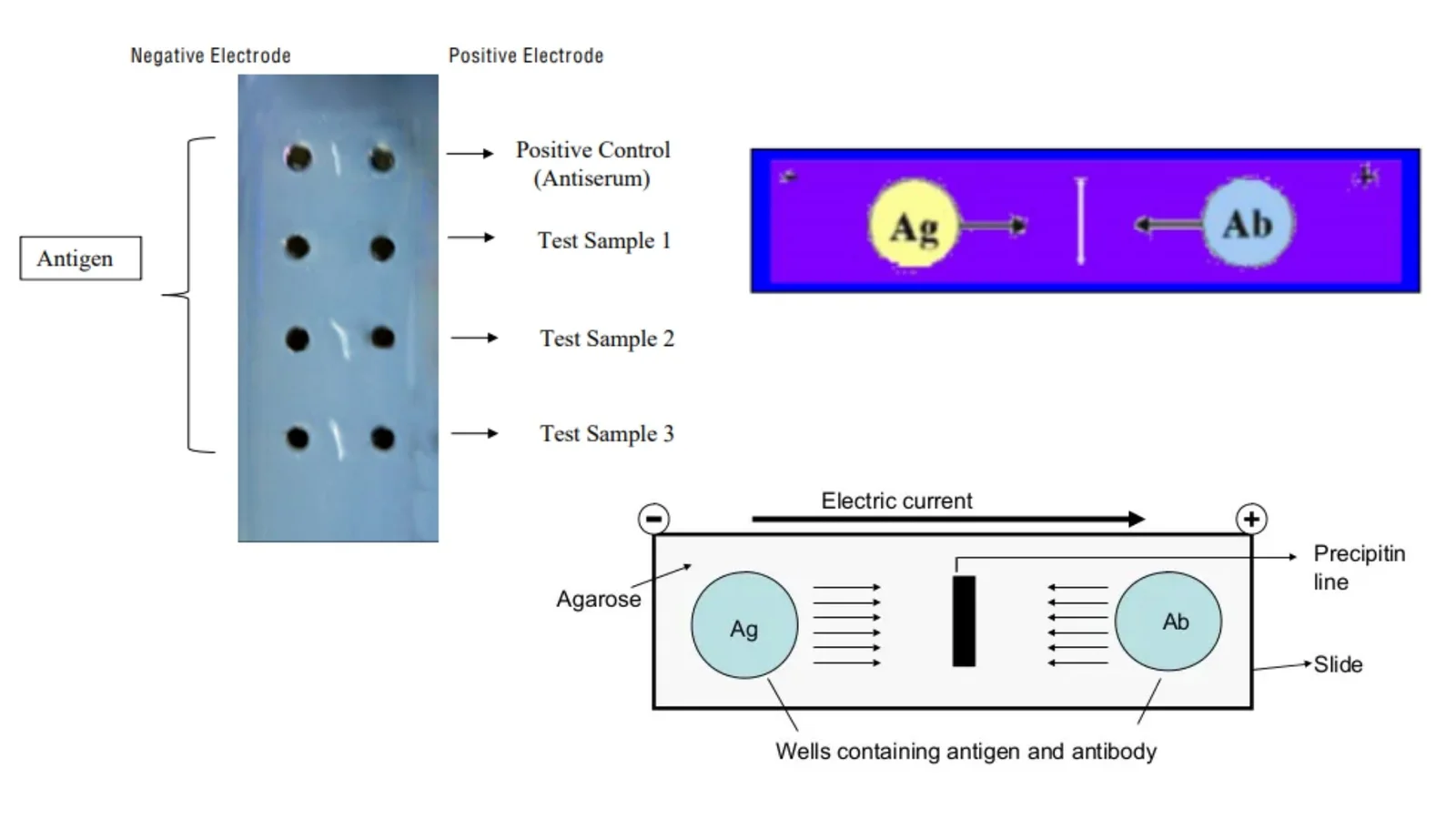
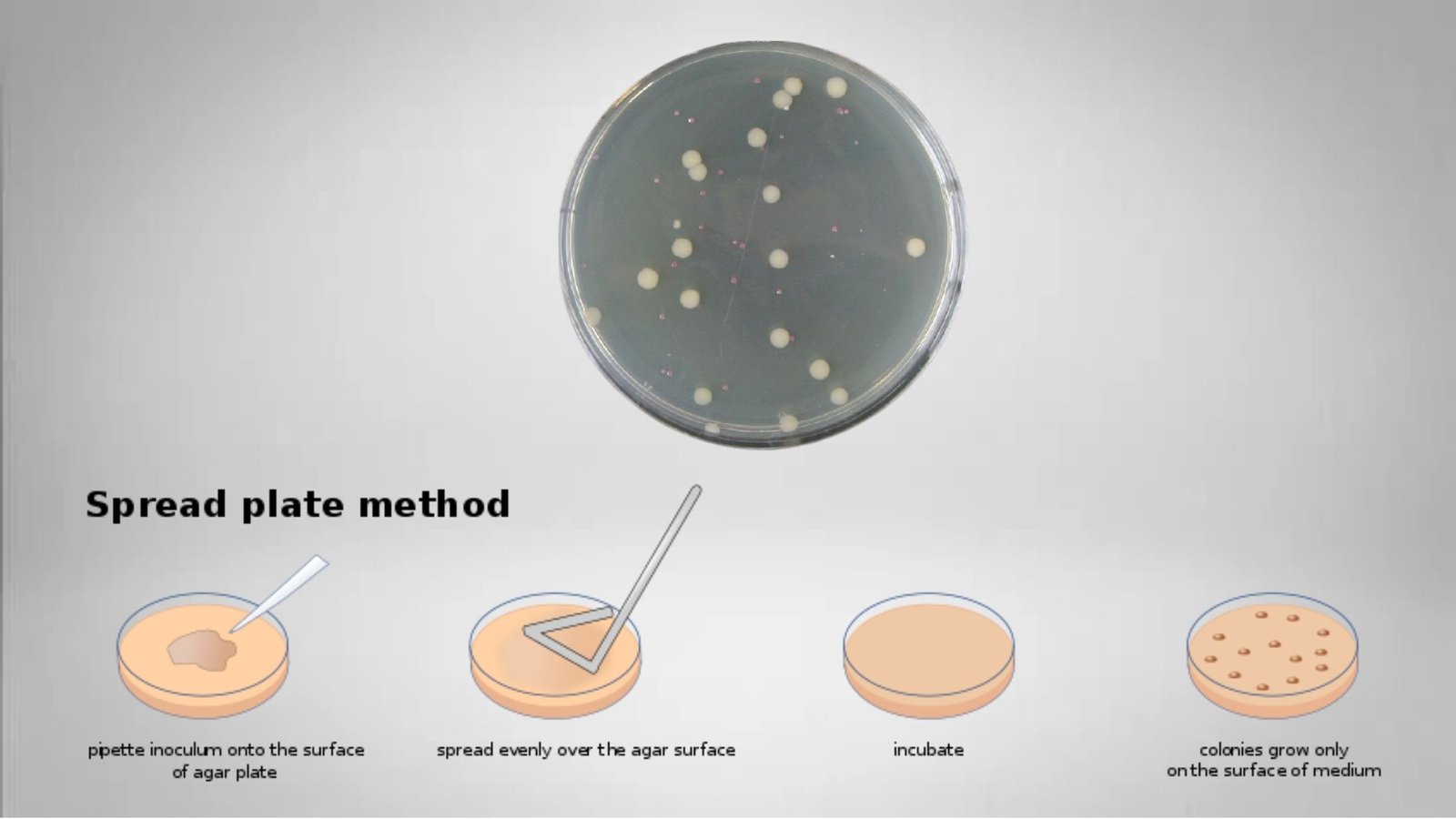
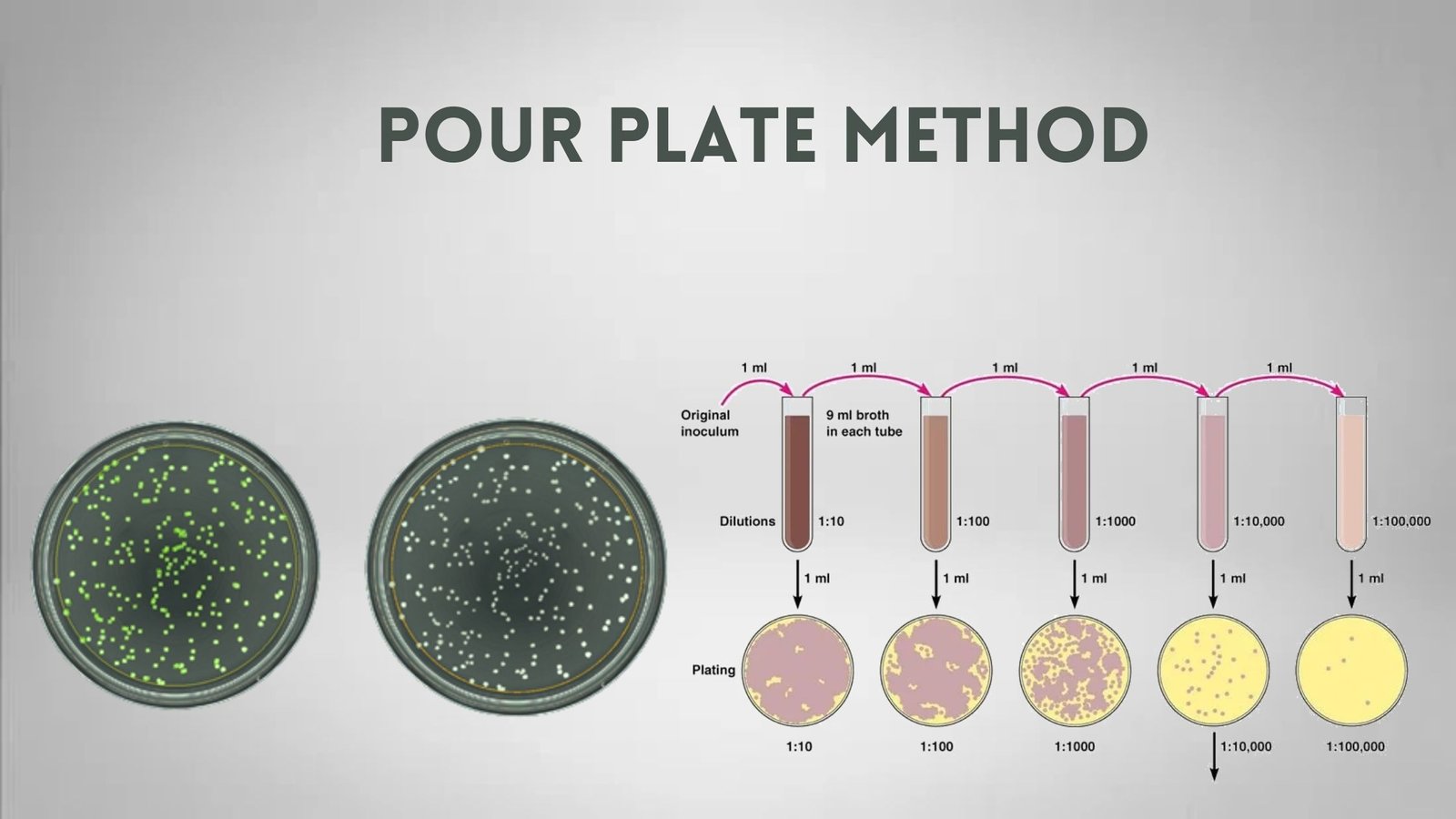
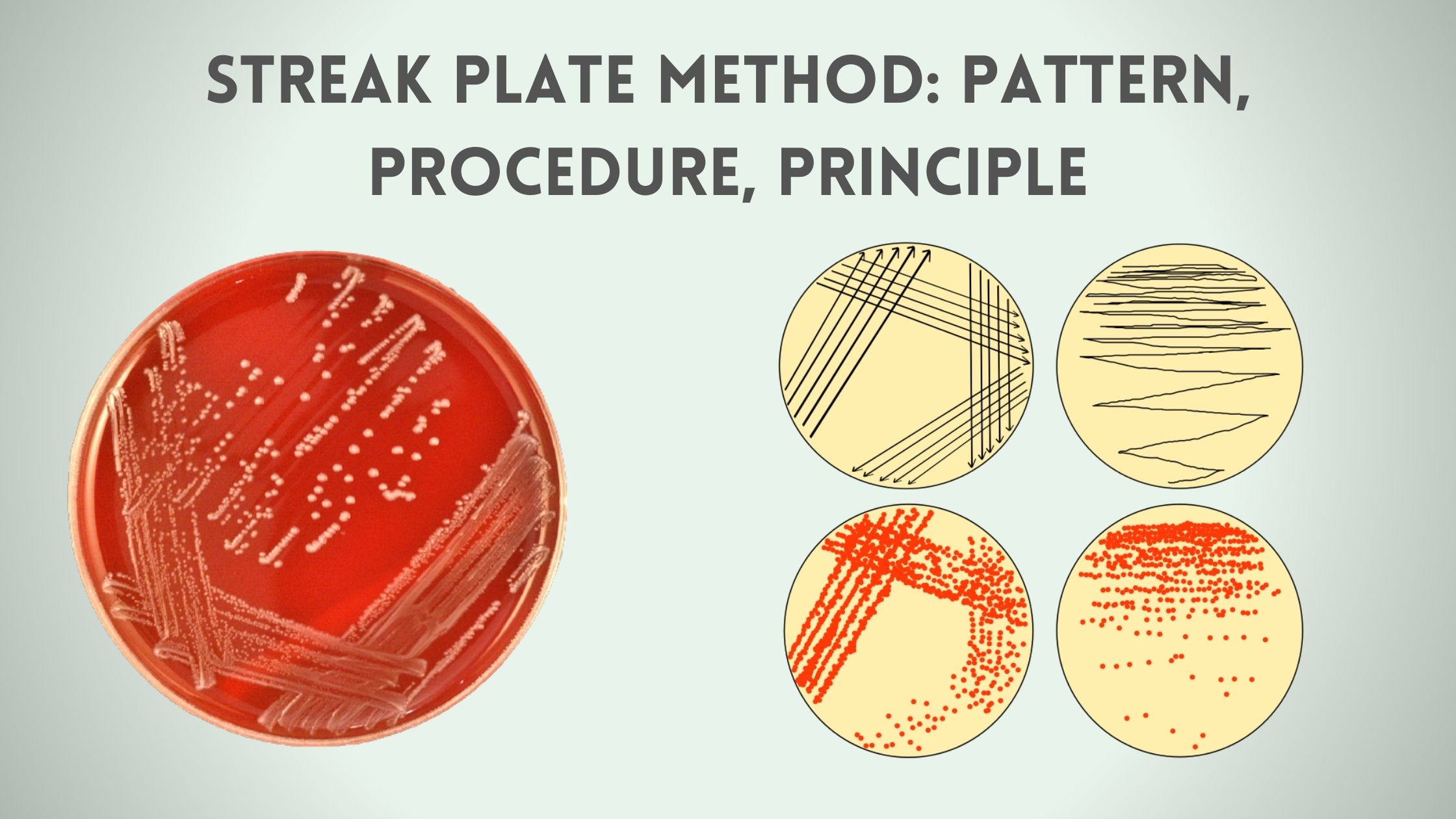
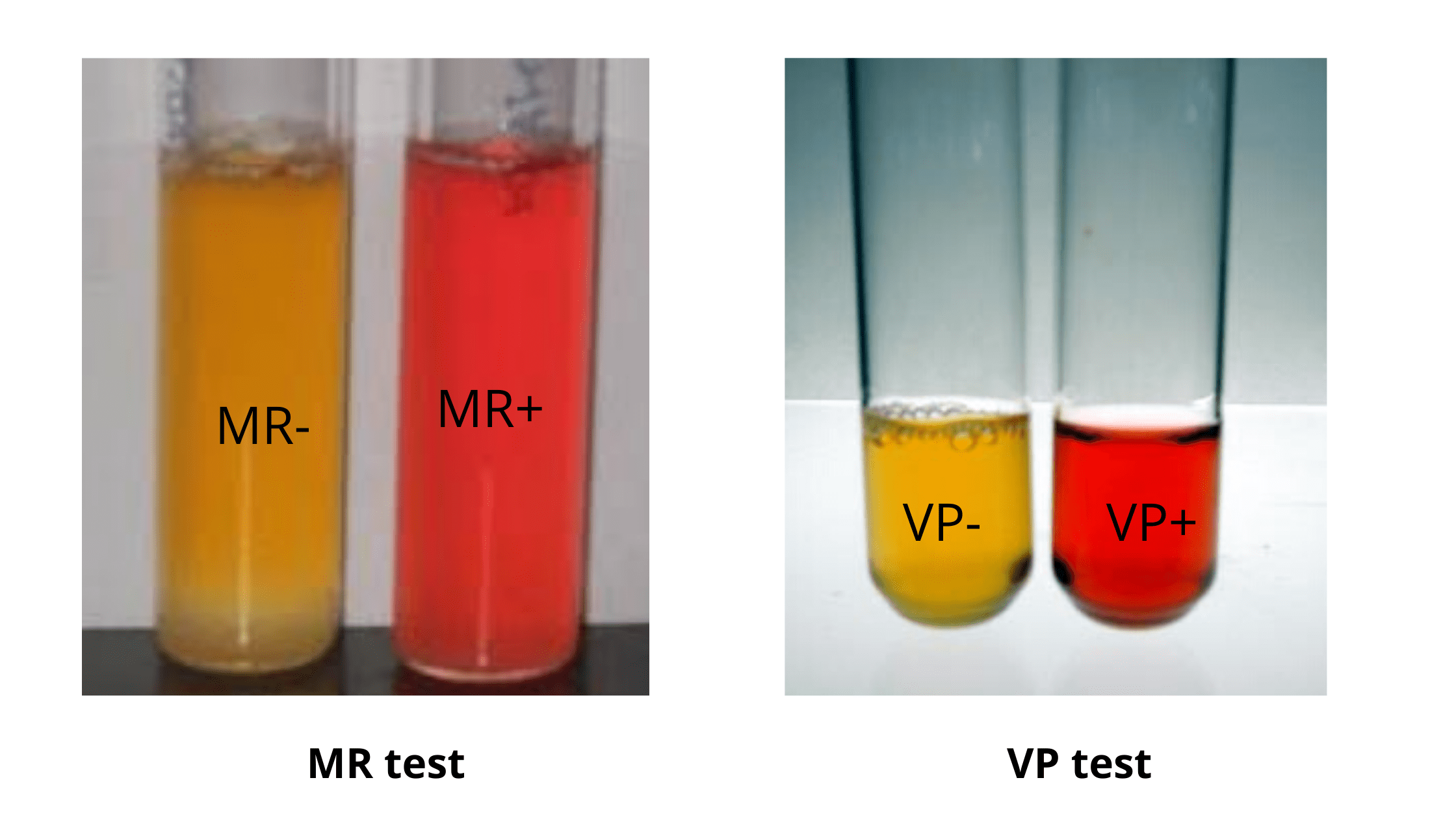
Counter Current Immunoelectrophoresis – Principle, Procedure, Result.
Counter current immunoelectrophoresis is a modification of immunoelectrophoresis in which antigen and antibody migrate towards opposite directions and form a visible white precipitate in the area between the wells.