Spread Plate Method in microbiology
The spread plate method is used to isolate individual colonies from a diluted sample of mix population. Different methods have been developed for the isolation of microorganisms from a mixture sample but among them Spread plate culture method is the most widely used technique in laboratory.
An ideal spread plate should contain visible and isolated colonies of bacteria that are evenly distributed in the plate and are countable.
Purpose of Spread Plate Method
The main purpose of the spread plate method is to isolate or count the individual bacteria present in a diluted sample containing a mixture of different species.
Spread Plate method principle
The spread plate technique is a method of isolation in which a diluted microbial sample containing more than one microorganism is deposited on a solidified agar plate and spread uniformly across the surface with an L-shaped glass rod while the media plate is spun on a turntable. With an accurately diluted sample, cells (CFUs) will be deposited far enough individual on the agar surface to grow into individual colonies.
The main principle behind this Spread Plate technique is that as the Petri dish rotated, at some stage, single cells will be deposited with the bent glass rod on to the agar surface, these cells will be separated from each other by a distance sufficient to allow the colonies that develop to be free from each other.
Requirement for Spread Plate Method
- 24 hour nutrient broth cultures
- Nutrient agar plates
- Lazy Susan turntable
- L-shaped bent glass rod
- 95 per cent alcohol
- Beaker (50 mL)
- Bunsen burner
- Wax marking pencil
Procedure for Spread Plate Method
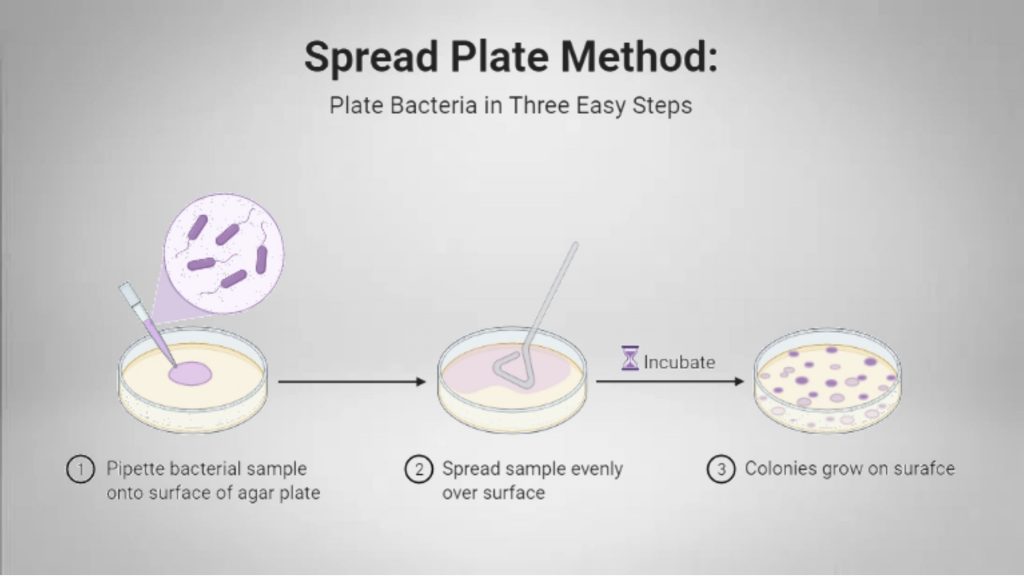
- Prepare different dilutions of the sample.
- Label the nutrient agar plate with Wax marking pencil. Mention the organism name, type of agar, date, and the plater’s name or initials.
- Lift the plate’s lid and use it as a shield to protect it from airborne contamination.
- Take a clean and sterile Pipette and Pipette out 0.1 ml sample from the appropriate desired dilution series onto the center of the surface of an agar plate.
- Replace the lid on plate.
- Properly dispose of the pipetting instrument used to inoculate the medium, because it is contaminated.
- Sterilize the L-shaped glass spreader by dipping this into 90% alcohol and then flame the glass spreader.
- Cool the rod for 10–15 seconds
- After farming the glass rod, lift the lid of the plate and use it as a shield from airborne contamination. Then touch the rod to the agar surface away from the inoculum to cool it.
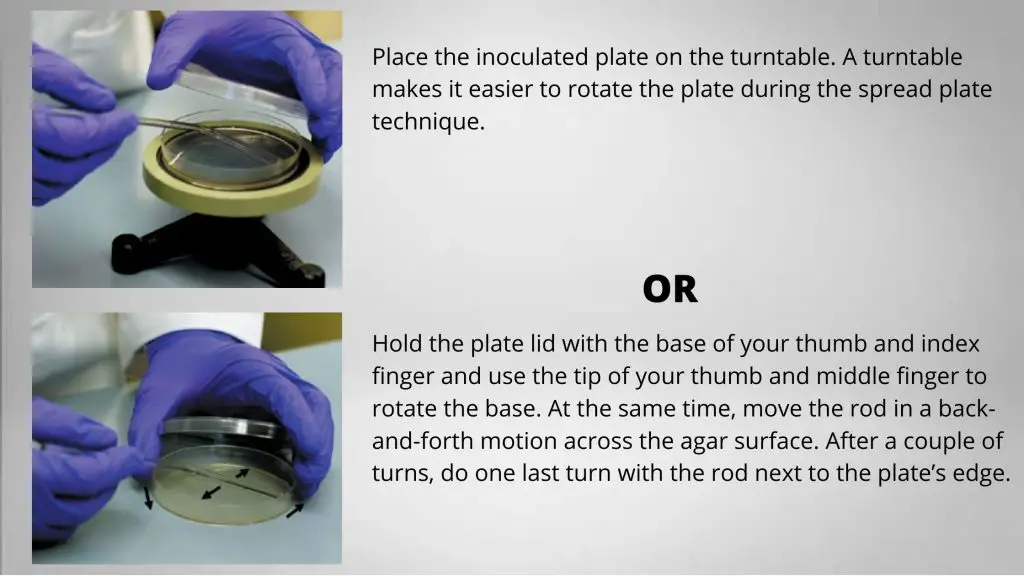
- During spreading hold the plate lid with the base of your thumb and index finger and use the tip of your thumb and middle finger to rotate the base. At the same time, move the rod in a back-and-forth motion across the agar surface. After a couple of turns, do one last turn with the rod next to the plate’s edge. Alternatively, place the plate on a rotating platform and spread the inoculum.
Or
Place the inoculated plate on the turntable. A turntable makes it easier to rotate the plate during the spread plate technique.
- Remove the rod from the plate and replace the lid.
- Return the rod to the alcohol in preparation for the next inoculation. There is no need to flame it again.
- Incubate the plate in an inverted position at the appropriate temperature for the assigned time.
Note: If you plated a volume of inoculum greater than 0.5 mL, wait a few minutes and allow it to soak in before inverting the plate.
Observation and Result
After incubation observes the colonies on the agar plate. Some of the colonies will be free from each other. Select any colony from the plate and record the elevation, pigmentation, and size.
Importance of Spread Plate
- In microbiology, the Spread Plate Technique with serial dilutions is a vital research tool.
- This technique is used to study the cultural characteristics of the specimen.
- It is used to separate the bacteria in discrete colonies from the sample carrying more than 1 bacterium.
- Used to study the Sensitivity and/or Resistance properties of a bacteria against a particular Drug/Antibiotics.
- Used to get sufficient growth of the bacterium for different tests.
- Used to determine the viable numbers of the bacteria in the specimen.
- Spread Plate mythos used for transportation or short-term storage of the specimen.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spread Plate Technique
Advantages
- In spread plate method, the isolation of the organism is easy because no subsurface colonies appear in this method.
- Heat-sensitive bacteria are not affected.
Disadvantages
- The optimum method for aerobes while microaerophilic tends to grow slower.
- The dilutions should be Accurate.
- The volume of inoculum greater than 0.1 mL on the nutrient agar not soak well and may result in colonies to coalesce as they form.
- Enumeration difficulty can be formed if the colonies are Crowded.
References
- https://aslopubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.4319/lo.1960.5.1.0078
- Hartman D. (2011). Perfecting your spread plate technique. Journal of microbiology & biology education, 12(2), 204-5. doi:10.1128/jmbe.v12i2.324
- https://paramedicsworld.com/microbiology-culture-techniques/spread-plate-culture-method-isolation-bacteria-microorganism-pure-culture/medical-paramedical-studynotes#.XGFykFwzbIU
- https://microbeonline.com/spread-plate-technique-principle-procedure-results/
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/spread-plate-technique-principle-procedure-and-uses/
- https://www.micro.iastate.edu/video/microbiology-004-spread-plate-method
- http://www.expertsmind.com/questions/explain-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-spread-plate-method-30175983.aspx
Wonderful
Thank You