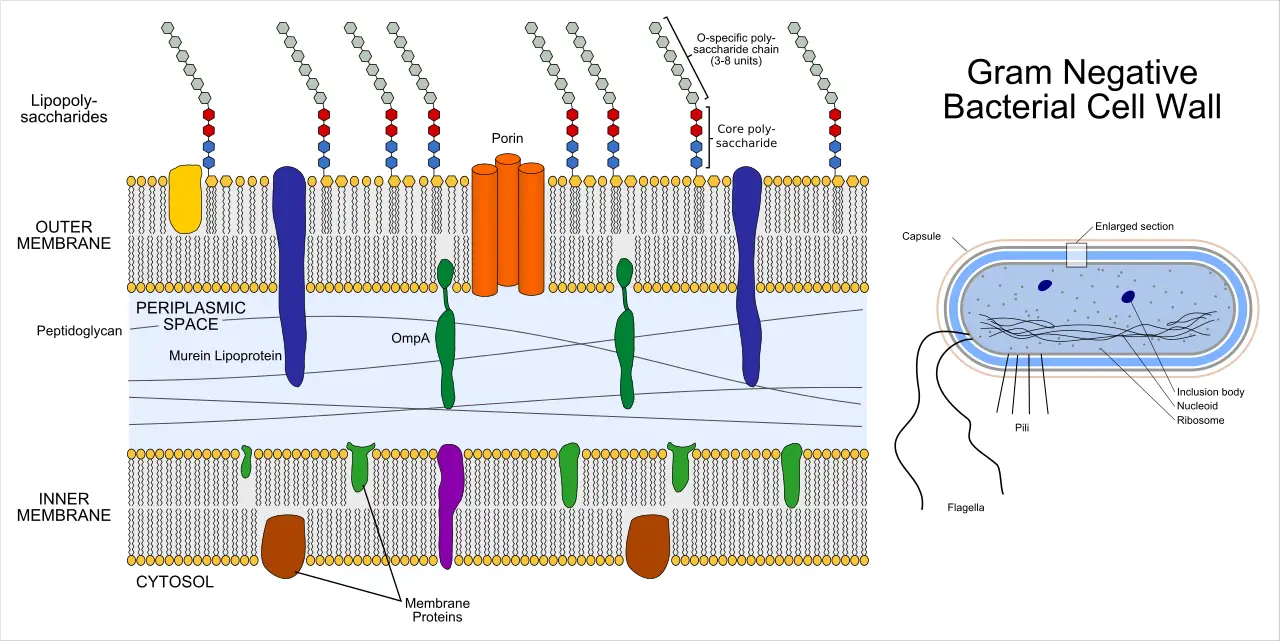
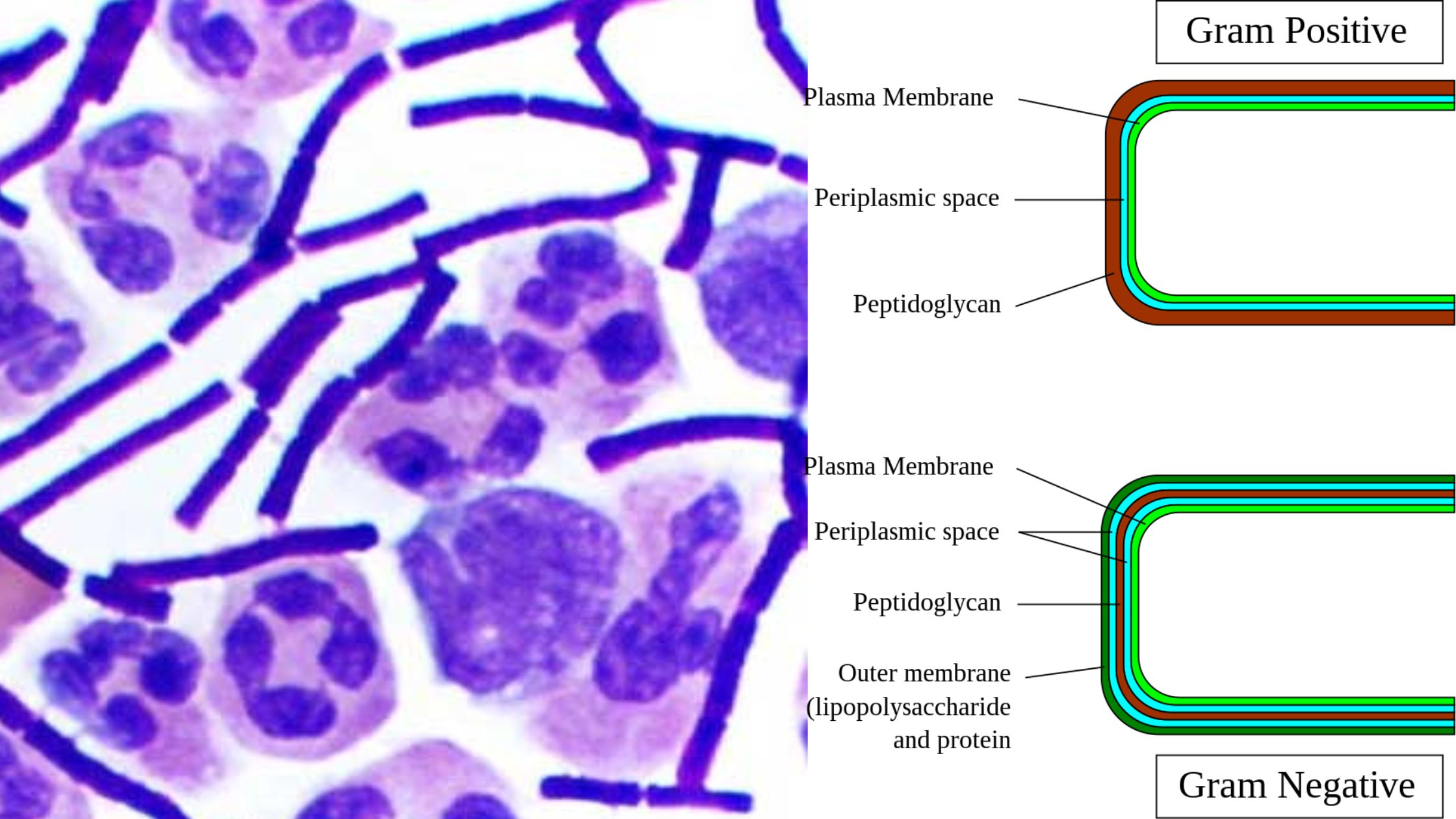
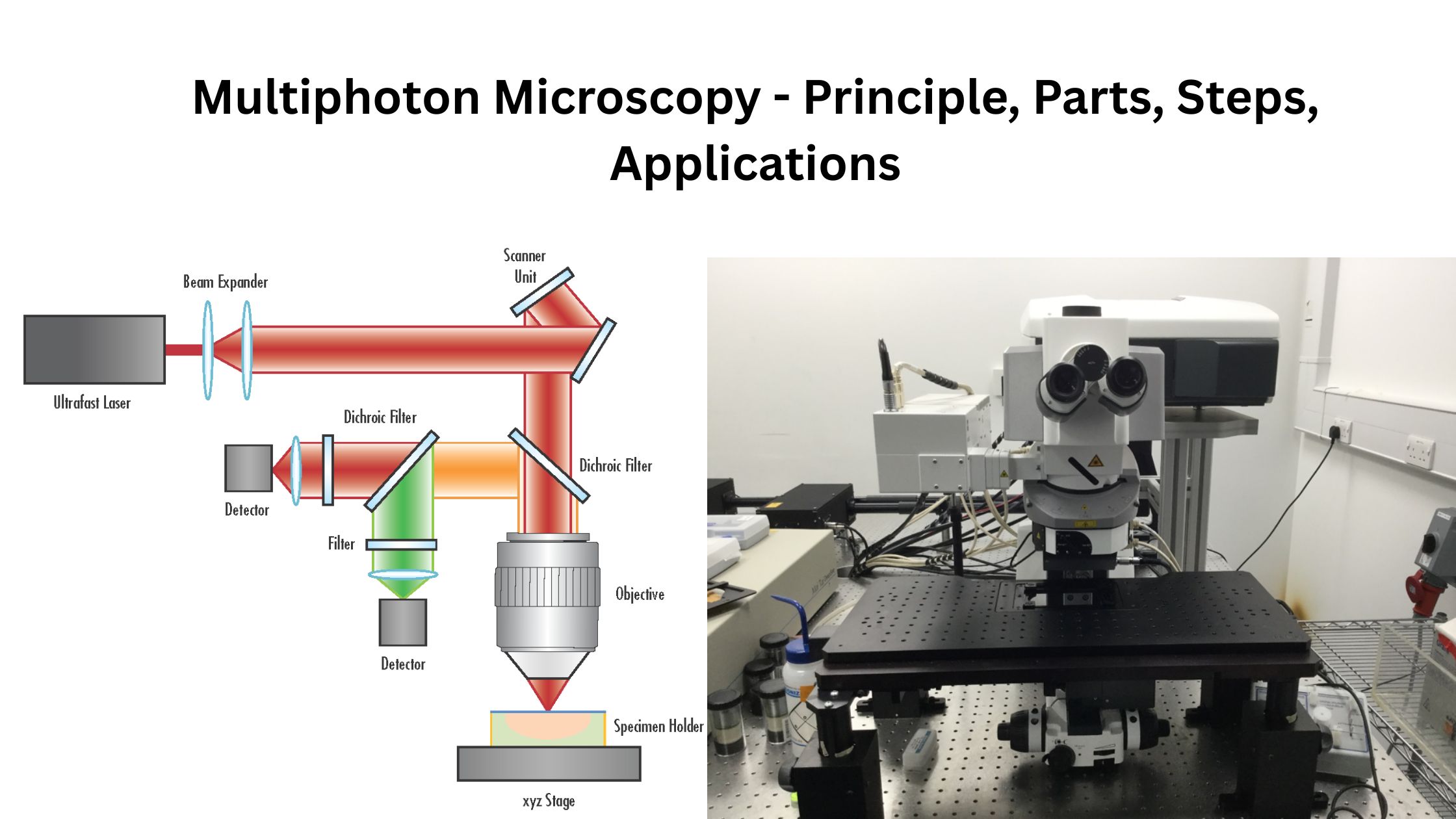
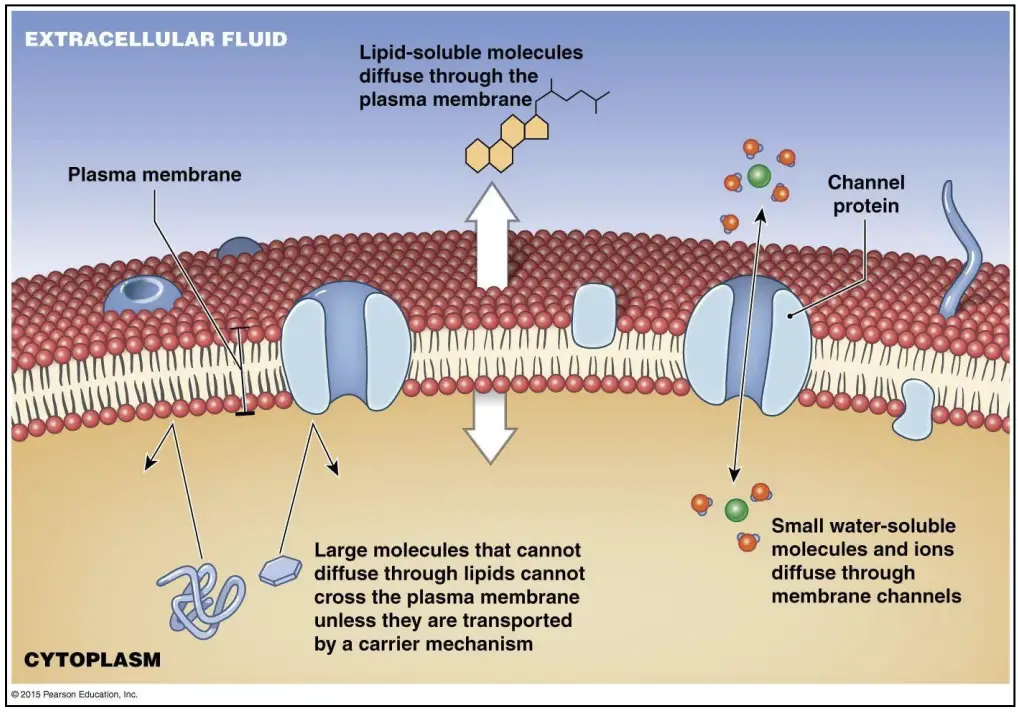
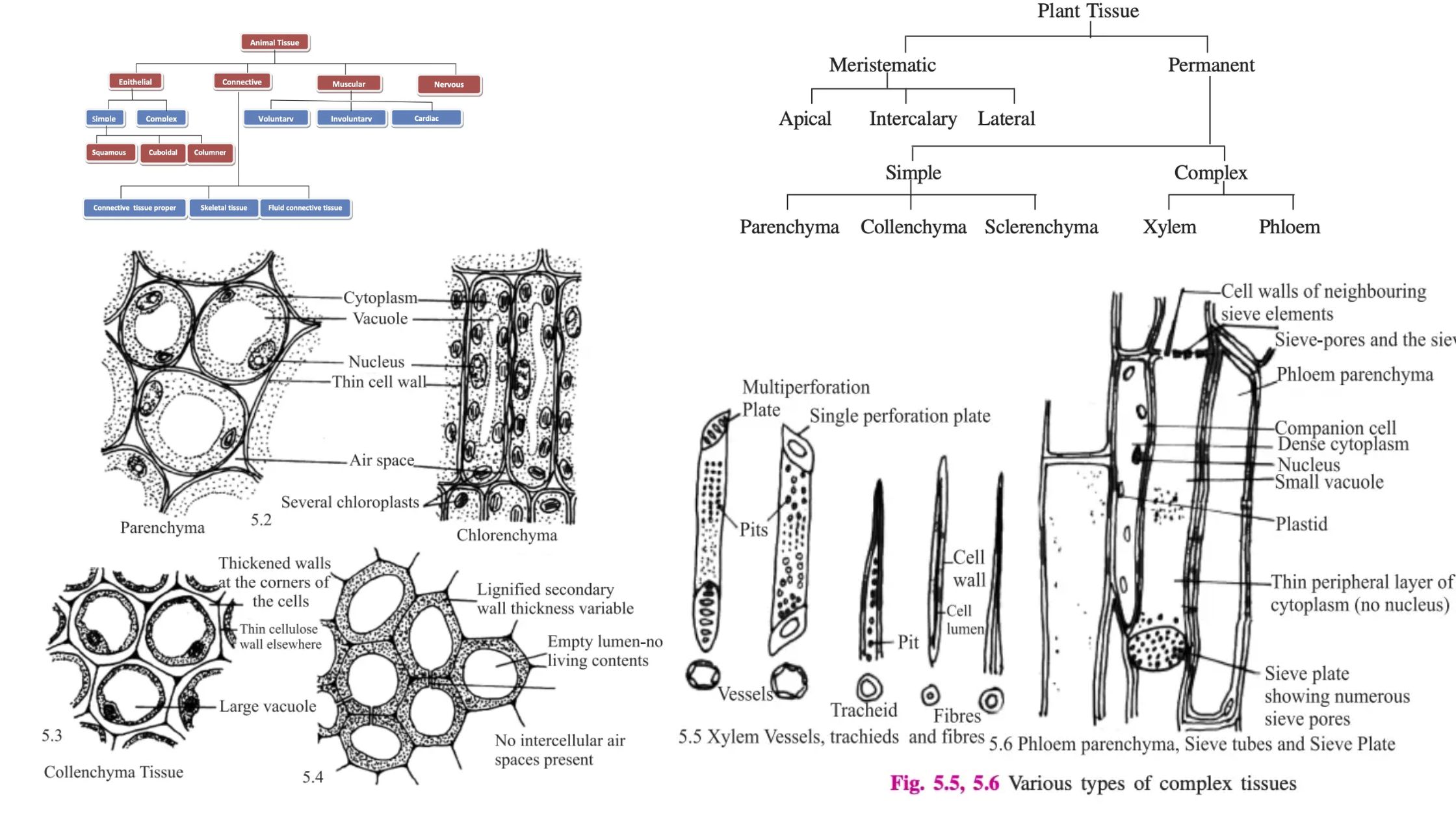
Gram-Negative Bacteria – Structure, Characteristics, Examples
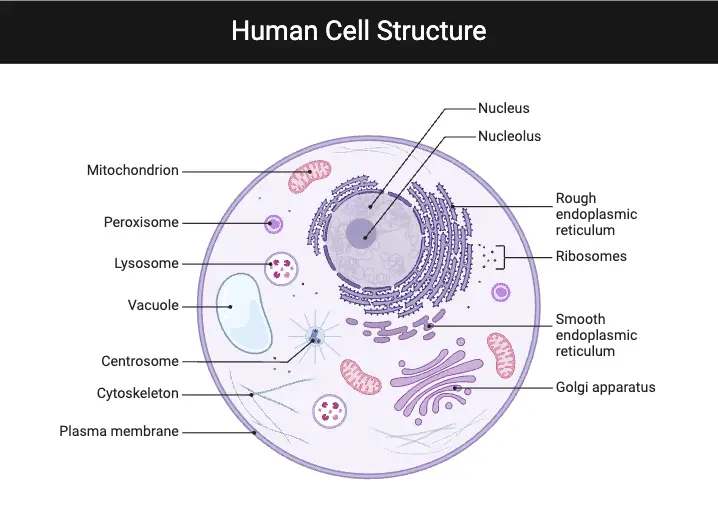
Gram-negative bacteria are a diverse group of microorganisms known for their unique cell structure, which plays a key role in how they interact with the environment and cause infections. Unlike Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer sandwiched between two membranes. The outer membrane contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which can trigger strong immune responses … Read more