A hematocrit centrifuge is a laboratory instrument which is used to determine the hematocrit value of blood. It is the percentage volume of red blood cells present in the total volume of whole blood and this value is also referred to as packed cell volume (PCV). It is commonly used in hematology laboratories for routine blood examination and diagnosis of different blood related disorders.
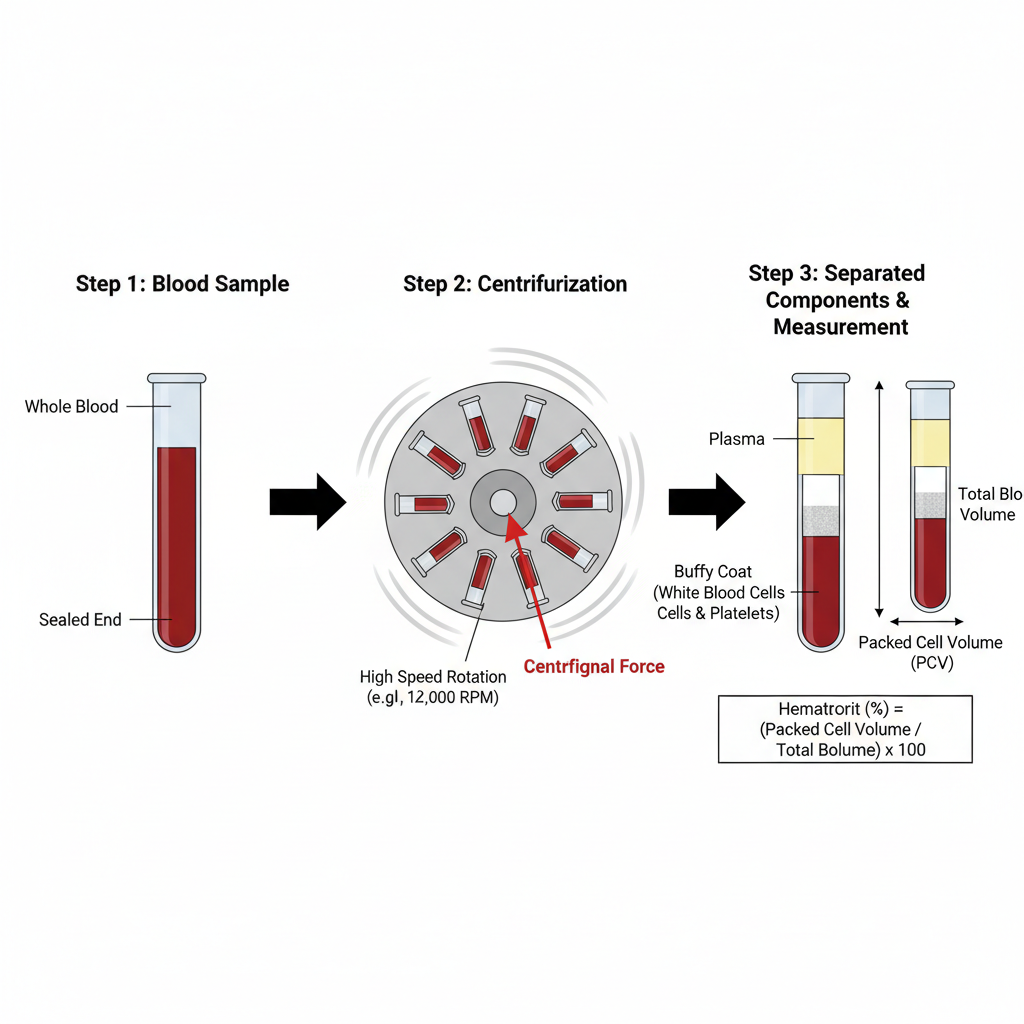
It works on the principle of centrifugal force. When blood sample is rotated at very high speed the heavier components settle down faster. The red blood cells being heavier are packed at the bottom of the tube while the lighter plasma remains at the top. A thin layer of white blood cells and platelets is formed in between which is referred to as buffy coat.
In this method a small amount of blood is taken in a narrow glass capillary tube and one end of the tube is sealed. The tube is then placed in the rotor of the hematocrit centrifuge and rotated at high speed generally around 11,000–12,000 revolutions per minute for few minutes. After centrifugation the blood gets separated into plasma buffy coat and packed red blood cells.
After the process is completed the hematocrit value is measured by comparing the height of packed red blood cells with the total height of blood column using a hematocrit reader. This test is useful in the diagnosis of conditions like anemia polycythemia and dehydration. Even though automated methods are available the hematocrit centrifuge is still considered as a standard and reliable method in many laboratories.
Working Principle of Hematocrit centrifuge
The working principle of hematocrit centrifuge is based on the application of centrifugal force for separation of blood components. It works on the fact that different components of blood have different densities. When a blood sample is subjected to high speed rotation the components separate according to their weight and density.
In this process a blood sample is taken in a capillary tube and one end of the tube is sealed. The tube is then placed in the hematocrit centrifuge and rotated at very high speed usually between 11,000 to 12,000 revolutions per minute. Due to rapid rotation a centrifugal force much greater than gravitational force is produced which accelerates the sedimentation of blood cells.
As a result of this force the heavier and denser red blood cells move towards the bottom of the capillary tube. The lighter plasma remains at the upper portion of the tube. In between these two layers a thin greyish white layer is formed which is referred to as buffy coat and it contains white blood cells and platelets.
After complete centrifugation the blood is clearly separated into three layers. The packed red blood cells form the lower layer and their height is measured against the total height of the blood column. This value is expressed as hematocrit or packed cell volume (PCV). This principle is commonly used for estimation of red blood cell volume in blood samples.
Parts of Hematocrit Centrifuge and their Functions
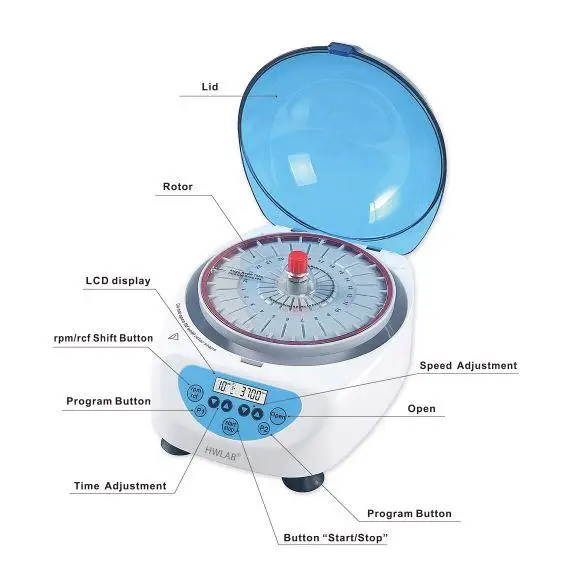
The different parts of hematocrit centrifuge and their functions are listed below–
- Rotor – It is the central rotating part of the centrifuge. The rotor holds the capillary tubes in radial grooves and rotates at very high speed to produce centrifugal force for separation of blood components based on density.
- Rotor Lid (Cover) – It is placed over the rotor to secure the capillary tubes during centrifugation. It prevents displacement and breakage of tubes during high speed rotation. In some centrifuges it also helps in reading the hematocrit value.
- Rubber Gasket – It is present around the inner side of the rotor. It provides cushioning support to the capillary tubes and prevents their breakage. It also helps in holding the sealed end of the capillary tube firmly.
- Motor – The motor provides power to rotate the rotor. It generates the required centrifugal force which is necessary for sedimentation of red blood cells.
- Safety Lid and Locking System – It is the outer protective lid of the centrifuge. It prevents operation when the lid is open and protects the user from accidents. It also cuts off power if the lid is opened during spinning.
- Timer – It is used to set the duration of centrifugation. Proper timing is required for complete packing of red blood cells and accurate hematocrit value.
- Braking System – It helps in stopping the rotor quickly after completion of centrifugation. It reduces waiting time and wear of the motor.
- Reader Scale (Microhematocrit Reader) – It is used to measure the packed cell volume after centrifugation. It compares the height of packed red blood cells with the total height of blood column and gives the result in percentage.
- Thermal Cutout Switch – It is a safety device which protects the centrifuge from overheating. It cuts off the power supply when excessive temperature is reached.
- Imbalance Detector – It detects uneven loading of capillary tubes in the rotor. It prevents damage to the centrifuge by stopping operation when imbalance occurs.
Operating Procedure of Hematocrit Centrifuge
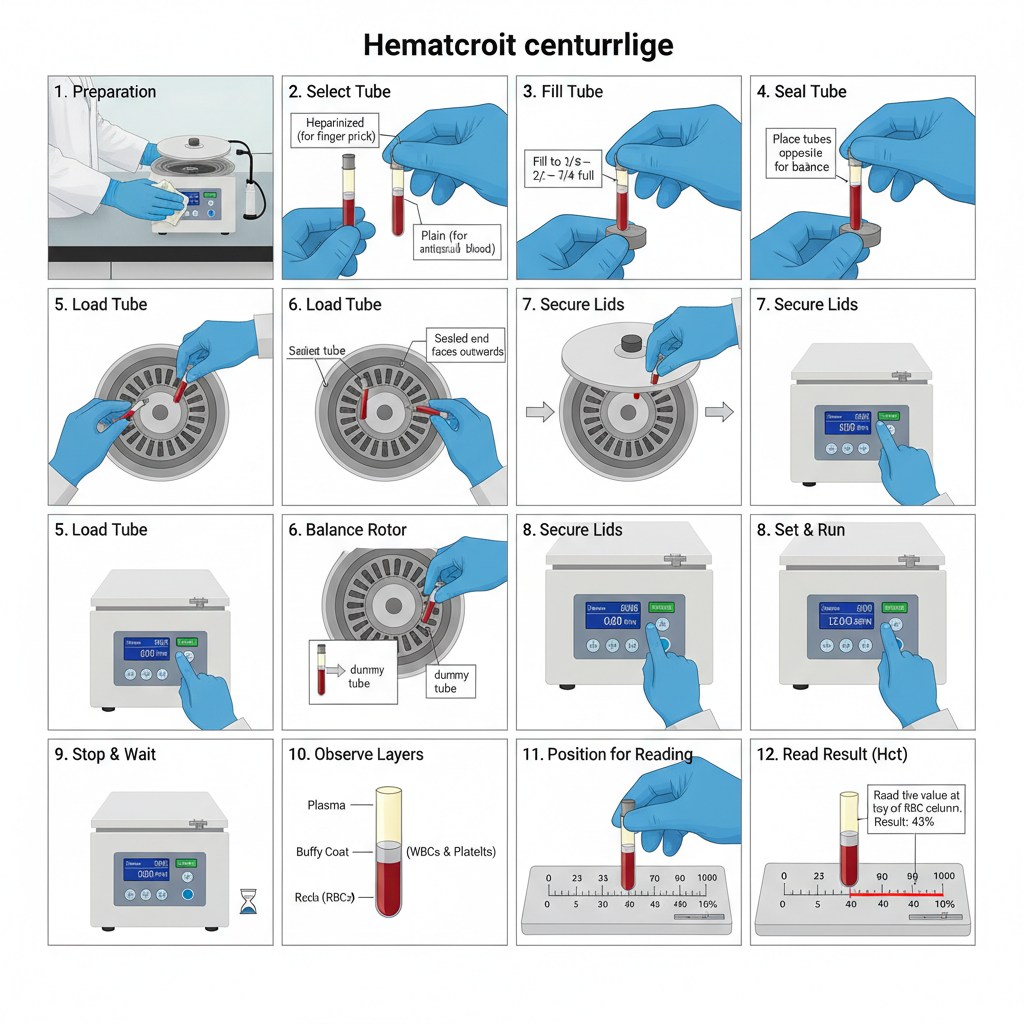
The operating procedure of hematocrit centrifuge is carried out in a stepwise manner which is given below–
- Preparation and safety– The centrifuge is placed on a flat and stable surface. The rotor and chamber are checked to ensure that they are clean and free from damage. Gloves and laboratory coat is worn while handling blood samples.
- Selection of capillary tube– Heparinized capillary tubes are used for direct finger prick blood samples. Plain capillary tubes are used when blood is already mixed with anticoagulant like EDTA.
- Filling of capillary tube– Blood is allowed to enter the capillary tube by capillary action. The tube is filled up to about two third to three fourth of its length.
- Sealing of capillary tube– One end of the capillary tube is sealed with sealing clay by inserting the dry end vertically into the clay tray. The tube is withdrawn with slight twisting to ensure proper sealing.
- Loading of tubes in rotor– The centrifuge lid is opened and the rotor lid is unscrewed. The capillary tubes are placed in the rotor grooves with the sealed end facing outward towards the rubber gasket.
- Balancing of rotor– The tubes are placed opposite to each other to maintain balance. If odd number of samples are present a dummy tube filled with water is placed opposite to balance the load.
- Securing the rotor and lid – The rotor lid is tightened properly to prevent breakage of tubes. The main centrifuge lid is then closed and locked.
- Setting time and operation– The timer is set generally for 4 to 5 minutes. The centrifuge operates at a fixed high speed usually between 11,000 to 12,000 RPM. The power switch is turned on and the centrifuge is allowed to run without interruption.
- Stopping the centrifuge– After completion of time the centrifuge is allowed to stop completely. The lid is not opened while the rotor is in motion.
- Removal of tubes– The lid is opened and the capillary tubes are removed carefully to avoid mixing of separated layers.
- Observation of layers– After centrifugation three layers are observed. The lower layer is packed red blood cells. The middle thin layer is buffy coat containing white blood cells and platelets. The upper layer is plasma.
- Reading of hematocrit value– The capillary tube is placed on the microhematocrit reader. The bottom of red cell column is aligned with zero mark and the top of plasma column with hundred mark. The value is read at the top of red blood cell column excluding buffy coat.
How to load hematocrit blood test into centrifuge
The steps for loading hematocrit blood test into centrifuge are given below–
- Preparation of centrifuge – The main lid of the centrifuge is unlocked and opened. The rotor lid is also opened or unscrewed to expose the grooves present in the rotor.
- Orientation of capillary tubes – The blood filled capillary tubes are placed in the rotor grooves. The sealed end of the tube (clay sealed end) must always face outward towards the rim of the rotor and not towards the center.
- Positioning against rubber gasket – The capillary tubes are placed in such a way that the sealed end touches the rubber gasket present inside the rotor. This helps in preventing tube breakage and also keeps the sealing plug intact during centrifugation.
- Balancing of rotor load – The tubes are loaded opposite to each other to maintain balance. If odd number of tubes are used a dummy capillary tube filled with water is placed exactly opposite to the unpaired tube.
- Securing the rotor lid – After placing all the tubes properly the rotor lid is closed and tightened firmly. Improper tightening may lead to breakage of capillary tubes during spinning.
- Closing of main lid – The outer centrifuge lid is closed completely and locked before starting the centrifuge. This step is essential for safe operation of the hematocrit centrifuge.
Uses of hematocrit centrifuge
- It is used for measuring packed cell volume (PCV) of blood which indicates the percentage of red blood cells in total blood volume.
- It is used in diagnosis of anemia by detecting decrease in red blood cells in blood sample.
- It is used to detect polycythemia where abnormal increase in red blood cells is observed.
- It is helpful in identifying dehydration as increased hematocrit value indicates plasma loss.
- It is used as an early indicator in Dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) due to plasma leakage.
- It is used in diagnosis of conditions like congenital heart failure chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and kidney disorders.
- It is used for separation of blood components into plasma buffy coat and red blood cells by centrifugal force.
- It is used as a reference or gold standard method to verify automated hematology analyzer results.
- It is used for visual examination of plasma for hemolysis lipemia and icterus and buffy coat for abnormal cells.
- It is used for monitoring patient response during treatment and to assess oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
- It is useful in screening of erythropoietin (EPO) abuse in athletes.
- It is used in pediatric and resource limited settings as it requires very small amount of blood sample.
- It is used for calculation of red blood cell indices like MCV and MCHC using hematocrit value.
- It is used in veterinary laboratories for hematological examination of animal blood samples.
Advantages of hematocrit centrifuge
- It requires very small volume of blood sample which is suitable for pediatric neonatal and hypovolemic patients.
- It gives rapid results as centrifugation and reading can be completed in short time.
- It is considered as gold standard method for validation of doubtful automated hematology results.
- It is simple to operate and does not require highly skilled personnel for routine use.
- The equipment is low cost and maintenance requirement is minimal as compared to automated analyzers.
- It allows direct visual examination of plasma for detection of hemolysis icterus and lipemia.
- It does not require dilution of blood sample which reduces chances of dilution related errors.
- It is reliable in screening of anemia especially in resource limited and rural laboratory settings.
- It is portable and suitable for use in small laboratories field studies and primary health centers.
Limitations of hematocrit centrifuge
- It shows trapped plasma error as small amount of plasma remains between packed red blood cells leading to slightly high PCV value.
- This error is increased in abnormal red blood cell conditions like sickle cell anemia iron deficiency and spherocytosis.
- Improper sealing of capillary tube may cause leakage during centrifugation resulting in falsely low hematocrit value.
- Incomplete packing of red blood cells occurs if centrifugation speed or time is insufficient which gives falsely high results.
- The reading is done manually so results may vary depending on observer skill and judgement.
- Excess anticoagulant like EDTA may cause shrinkage of red blood cells leading to low hematocrit reading.
- Presence of micro clots in sample interferes with proper packing and gives incorrect results.
- Hemolysed samples give false readings due to destruction of red blood cells.
- Buffy coat may be mistakenly included in red cell column causing false increase in PCV.
- There is risk of tube breakage and biohazard exposure due to use of glass capillary tubes.
- It is labor intensive and time consuming when compared to automated hematology analyzers.
FAQ
Q1. What is a hematocrit centrifuge?
A hematocrit centrifuge is a laboratory instrument used to determine the hematocrit value of blood. It is mainly designed to separate blood components by rapid spinning of capillary tubes. It is commonly used in clinical and diagnostic laboratories.
Q2. How does a hematocrit centrifuge work?
It works on the principle of centrifugal force. When blood filled capillary tubes are rotated at high speed the heavier red blood cells move to the bottom while lighter components remain above. This separation allows measurement of packed cell volume.
Q3. What is hematocrit?
Hematocrit is the percentage volume of red blood cells present in whole blood. It indicates the proportion of red cells in relation to total blood volume. It is usually expressed as percentage.
Q4. What does a hematocrit centrifuge measure?
It measures the packed cell volume (PCV) of blood. This represents the volume occupied by red blood cells after centrifugation. The value reflects oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
Q5. What are the applications of a hematocrit centrifuge?
It is used for estimation of PCV diagnosis of anemia polycythemia dehydration and dengue. It is also used for separation of blood components and validation of automated analyzer results.
Q6. What factors should you consider when buying a hematocrit centrifuge?
Speed range capacity safety features size noise level and ease of maintenance should be considered. Availability of spare parts and warranty is also important. The centrifuge should meet laboratory workload requirement.
Q7. Where are hematocrit centrifuges used?
They are used in hospitals diagnostic laboratories blood banks research laboratories and veterinary labs. They are also used in rural and primary health centers. Field laboratories commonly use them due to simplicity.
Q8. What are the different types of hematocrit centrifuge options?
Manual and digital hematocrit centrifuges are commonly available. Some are fixed speed while others are variable speed models. Microhematocrit centrifuges are most commonly used.
Q9. How do you determine the hematocrit value using a centrifuge?
Blood is filled in a capillary tube and sealed at one end. After centrifugation the length of packed red cell column is compared with total blood column using a hematocrit reader. The value is expressed as percentage.
Q10. What components of blood are separated by a hematocrit centrifuge?
Red blood cells plasma and buffy coat are separated. Plasma forms the top layer buffy coat remains in middle and red blood cells settle at bottom. These layers are clearly visible after spinning.
Q11. What medical conditions can a hematocrit centrifuge help diagnose?
It helps in diagnosis of anemia polycythemia dehydration dengue hemorrhagic fever and some heart and kidney disorders. It also supports monitoring of treatment response. Changes in PCV indicate disease condition.
Q12. What are the typical speed (RPM) and RCF for a hematocrit centrifuge?
The typical speed ranges between 10,000 to 15,000 RPM. The relative centrifugal force is usually around 10,000 to 15,000 g. Exact values depend on model and manufacturer.
Q13. How do you prepare a blood sample for a hematocrit centrifuge?
Blood is collected using anticoagulant usually EDTA. Capillary tubes are filled up to required level and sealed properly. The sample should be free from clots and hemolysis.
Q14. Can hematocrit centrifuges process multiple samples at once?
Yes multiple capillary tubes can be processed simultaneously. The rotor is designed to hold several tubes at a time. This increases efficiency and saves time.
Q15. How do you clean and maintain a hematocrit centrifuge?
The rotor and chamber should be cleaned regularly with mild disinfectant. Spills should be removed immediately after use. Regular inspection balancing and servicing helps maintain accuracy and safety.
- AELAB. (2025, June 9). 10-step guide to centrifuge calibration for accurate lab results. https://aelabgroup.com/10-step-guide-to-centrifuge-calibration-for-accurate-lab-results/
- Ajwad, A. A. (n.d.). Determination of packed cell volume (PCV) or hematocrit (Hct) value [Lecture notes]. University of Diyala. https://medicine.uodiyala.edu.iq/uploads/AMA%20Files/Lectures/2/Physiology/Dr.%20Asmaa%20Abbass/Course%201/PCV.pdf
- Drucker Diagnostics. (2025). Centrifuge calibration check: Step-by-step guide. https://druckerdiagnostics.com/resources/calibration-check/
- eClinpath. (2025). Hematocrit/packed cell volume. https://eclinpath.com/hematology/tests/hematocrit/
- Fisher Scientific. (n.d.). Centrifugation theory. https://www.fishersci.se/se/en/scientific-products/centrifuge-guide/centrifugation-theory.html
- GF Health Products. (2008). Hematocrit centrifuge model 410E user manual. https://www.rehabmart.com/pdfs/hematocrit_user_manual.pdf
- Gulati, G., Uppal, G., & Gong, J. (2022). Unreliable automated complete blood count results: Causes, recognition, and resolution. Annals of Laboratory Medicine, 42(5), 515–530. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9057813/
- Hettich Instruments. (n.d.). Hematocrit determination. https://www.hettweb.com/applications/hematocrit/
- Hunsaker, W. G. (1969). Effect of centrifugal force on packed cell volume and trapped plasma in avian blood. Poultry Science, 48(2), 705–711. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0480705
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023, September 19). Hematocrit test. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/hematocrit/about/pac-20384728
- Mondal, H., & Zubair, M. (2024, October 6). Hematocrit. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542276/
- Nall, R. (2018, September 29). Hematocrit test. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/hematocrit
- National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). Hematocrit test. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/hematocrit-test/
- New Life Scientific. (2023, July 3). Centrifuge care and maintenance. https://newlifescientific.com/blogs/new-life-scientific-blog/centrifuge-care-and-maintenance
- Pearson, T. C., & Guthrie, D. L. (1982). Trapped plasma in the microhematocrit. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 78(5), 770–772. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7137120/
- Scientific Instrument Center. (2019, May 14). Centrifuges – care and maintenance. https://sicweb.com/blog/40-centrifuges-care-and-maintenance
- Suparyati, & Putri, D. M. (2025). Comparison of hematocrit values using the microhematocrit method and the automatic hematology analyzer. Journal of Indogenius, 4(3), 760–767. https://doi.org/10.56359/igj.v4i3.655
- Wennecke, G. (2004, September). Hematocrit – a review of different analytical methods. Acute Care Testing. https://acutecaretesting.org/en/articles/hematocrit–a-review-of-different-analytical-methods