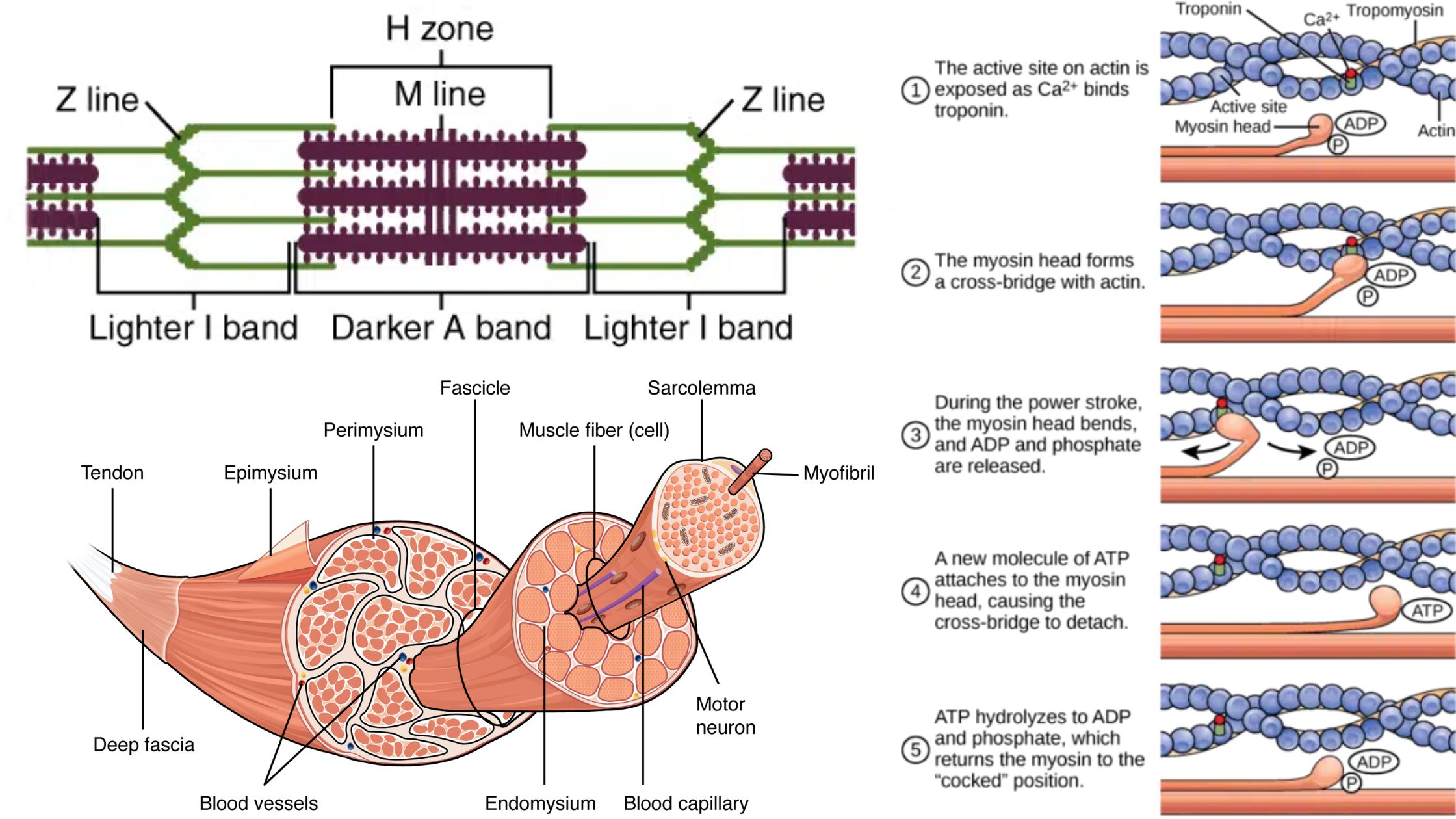
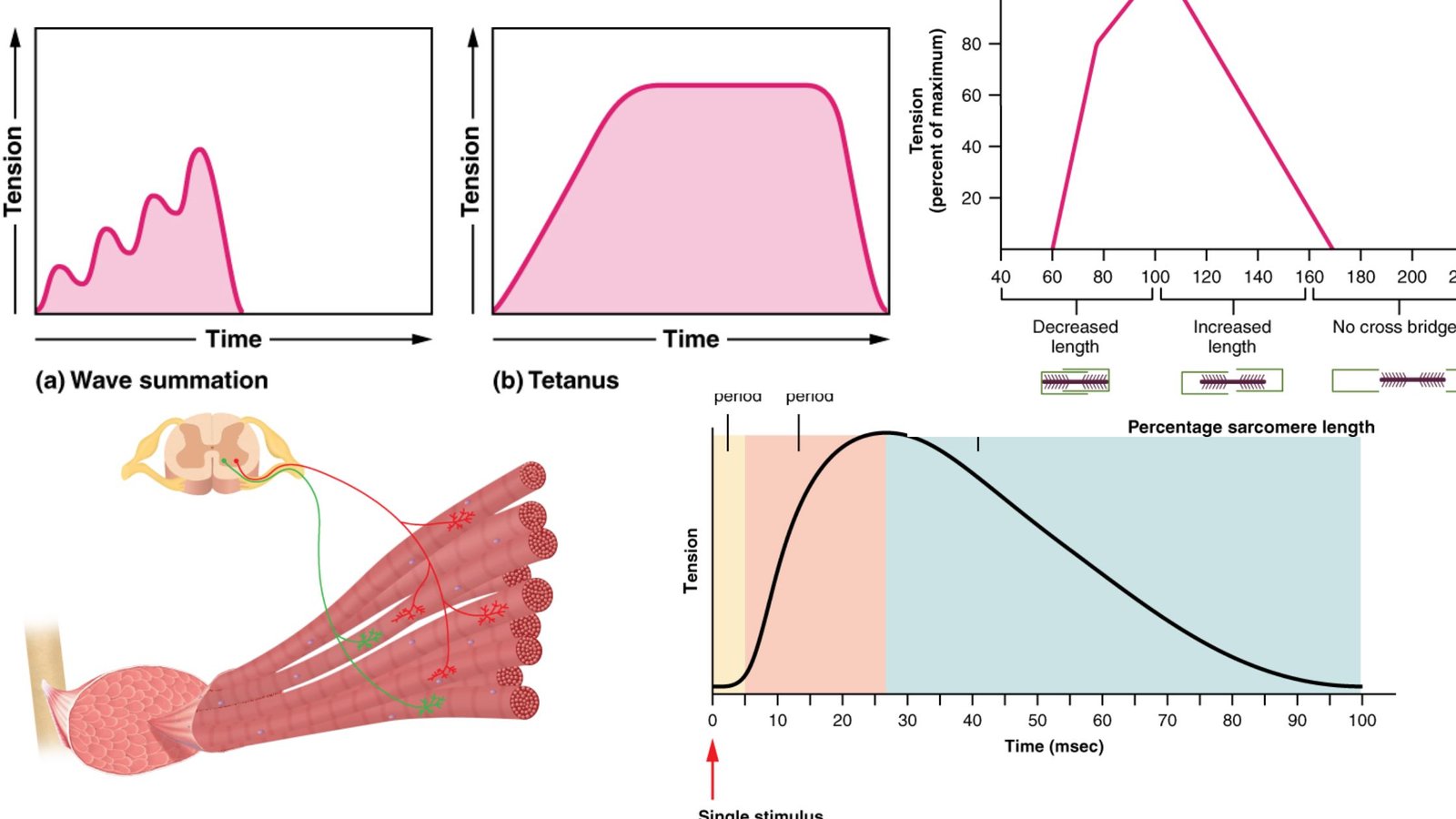
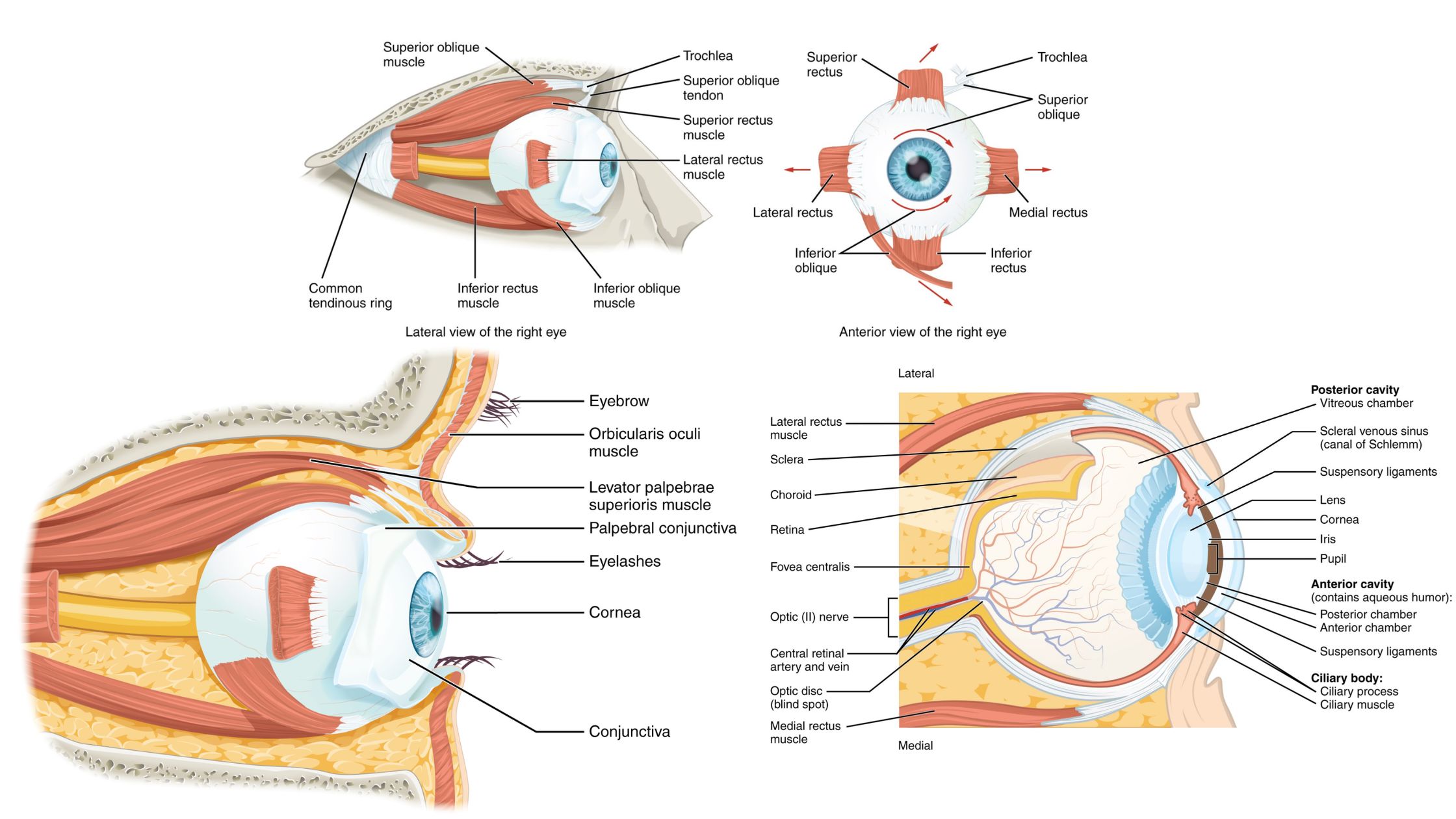
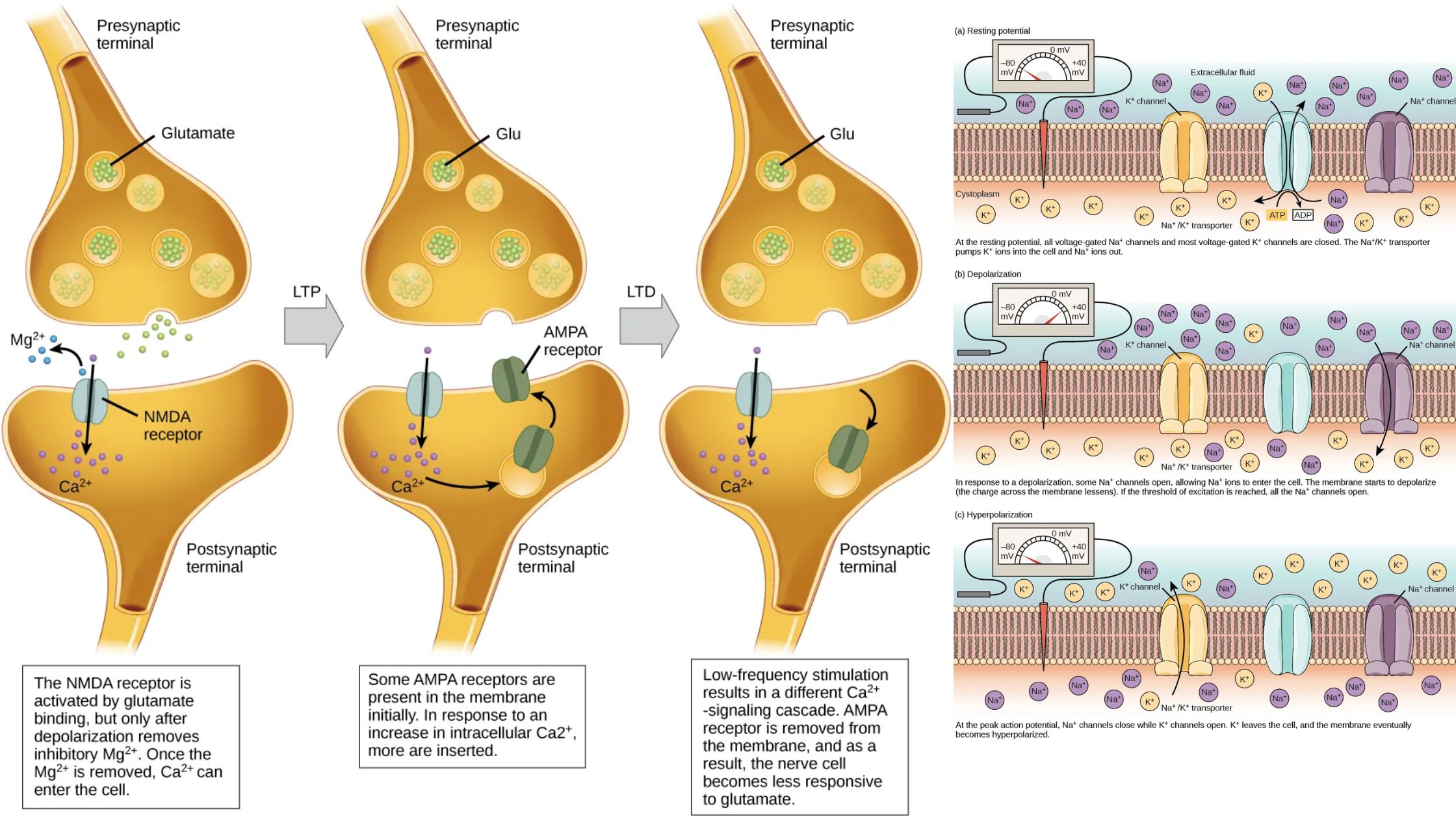
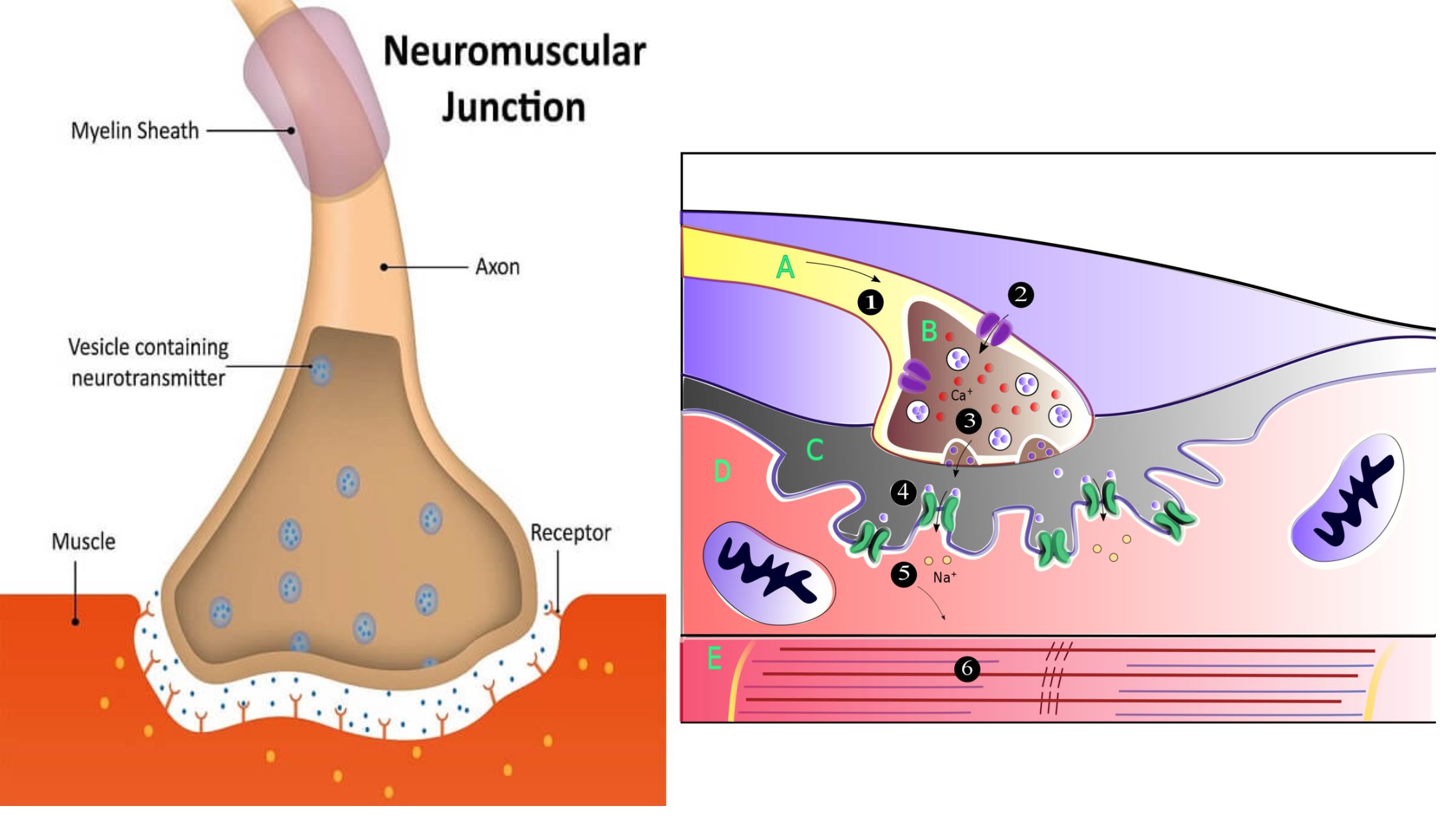
Nervous System – Definition, Parts, Functions
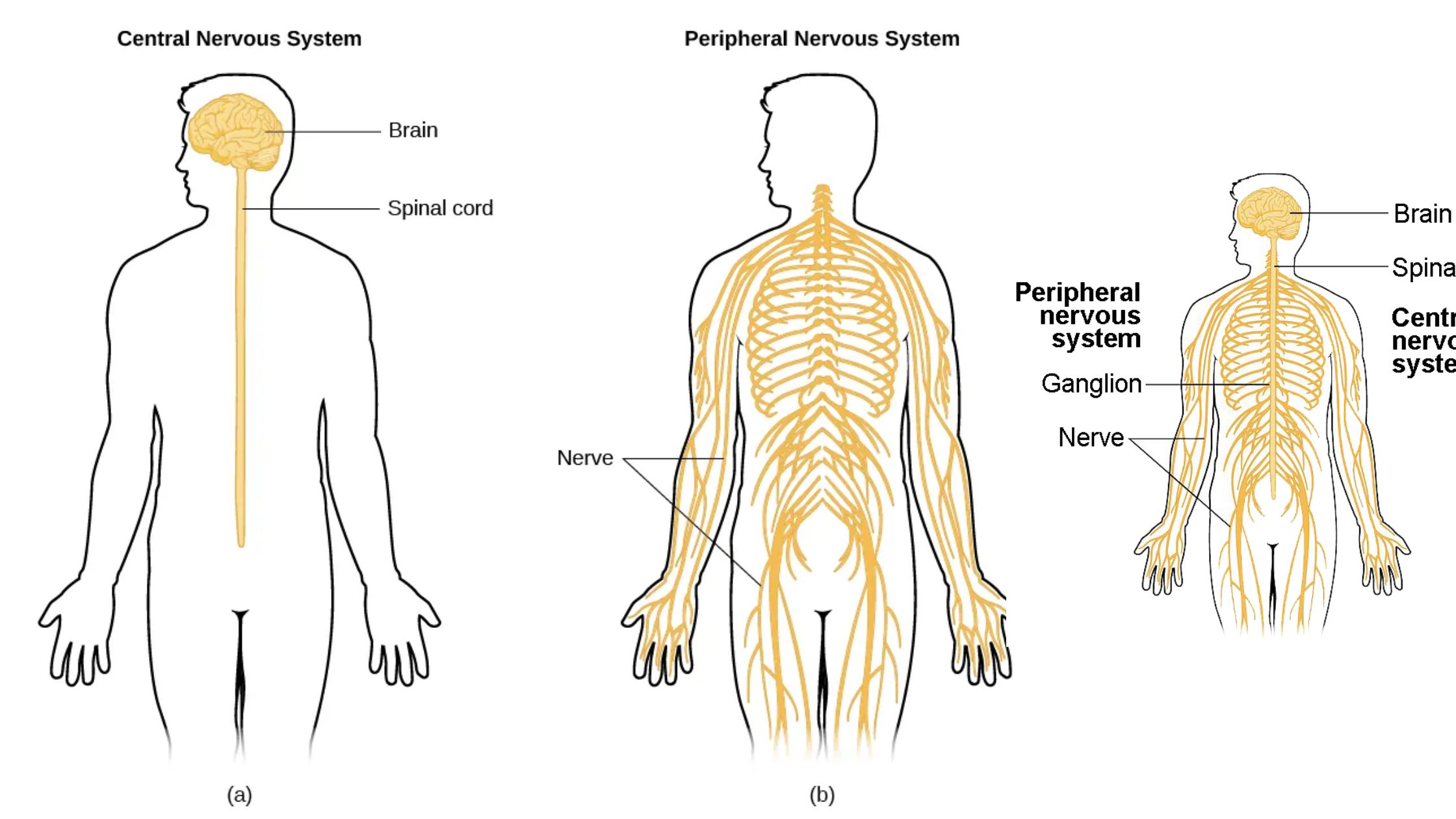
What is Nervous System? Definition of Nervous System The nervous system is a complex network of cells and tissues that coordinates and regulates the activities of an organism by transmitting electrical signals between different parts of the body. Cells of the Nervous System Neurones Glial Cells Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymal cells Nervous System Structure and … Read more