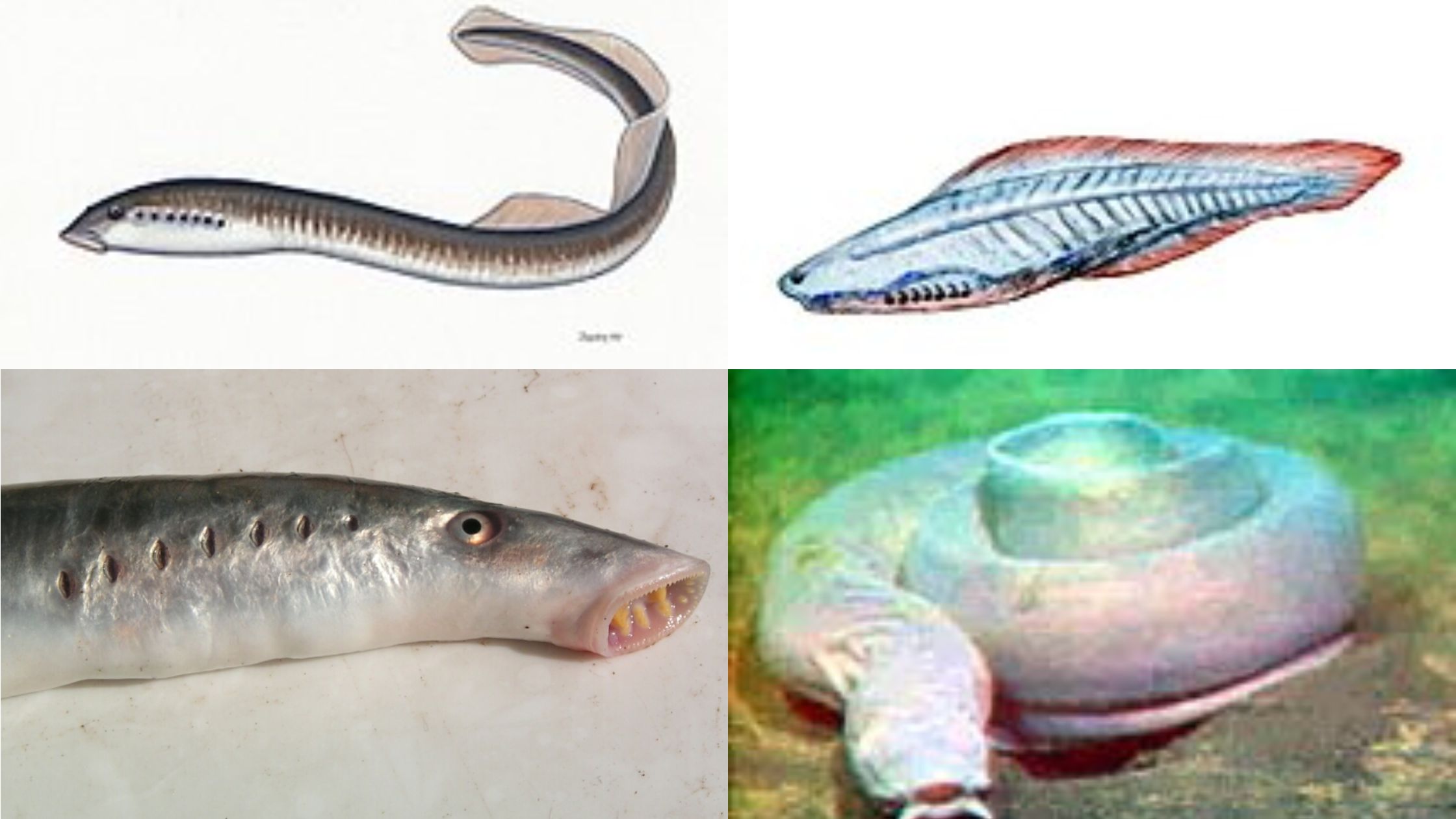
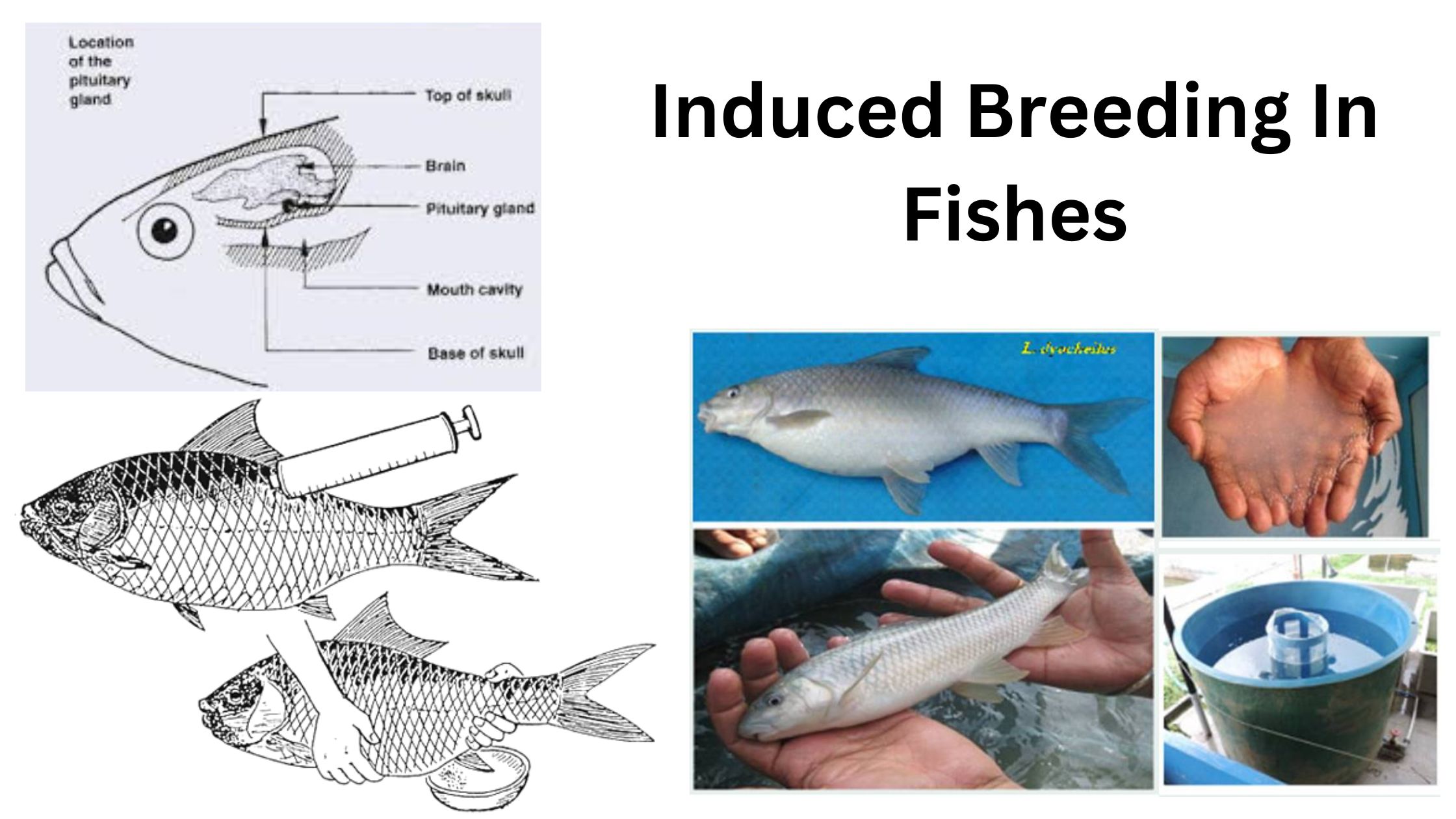
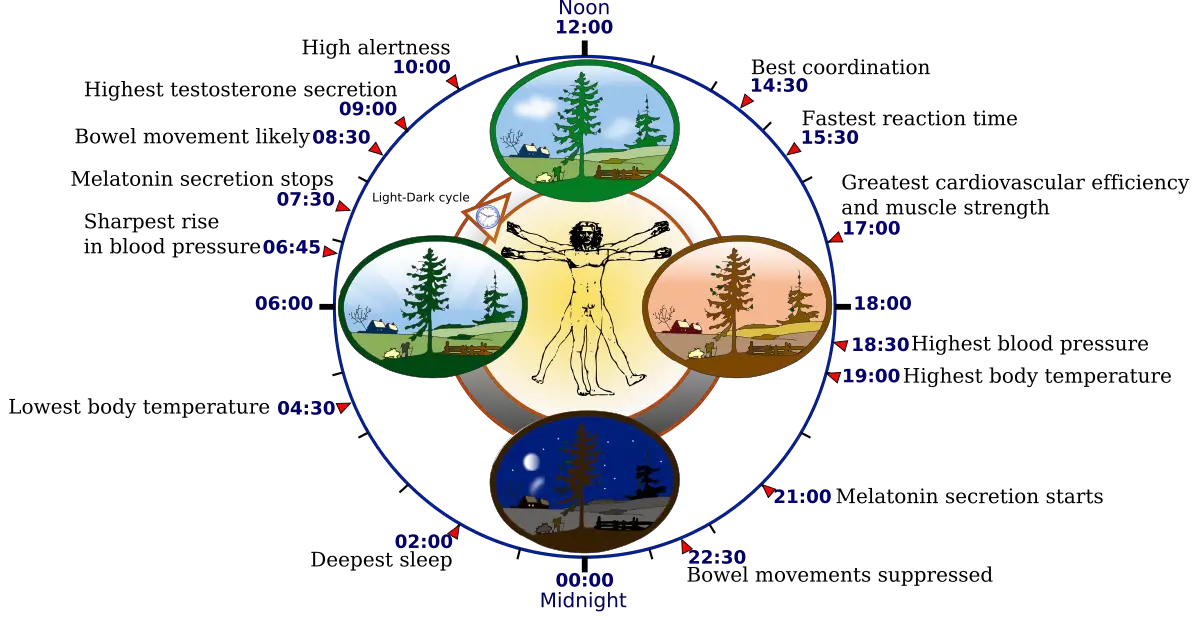
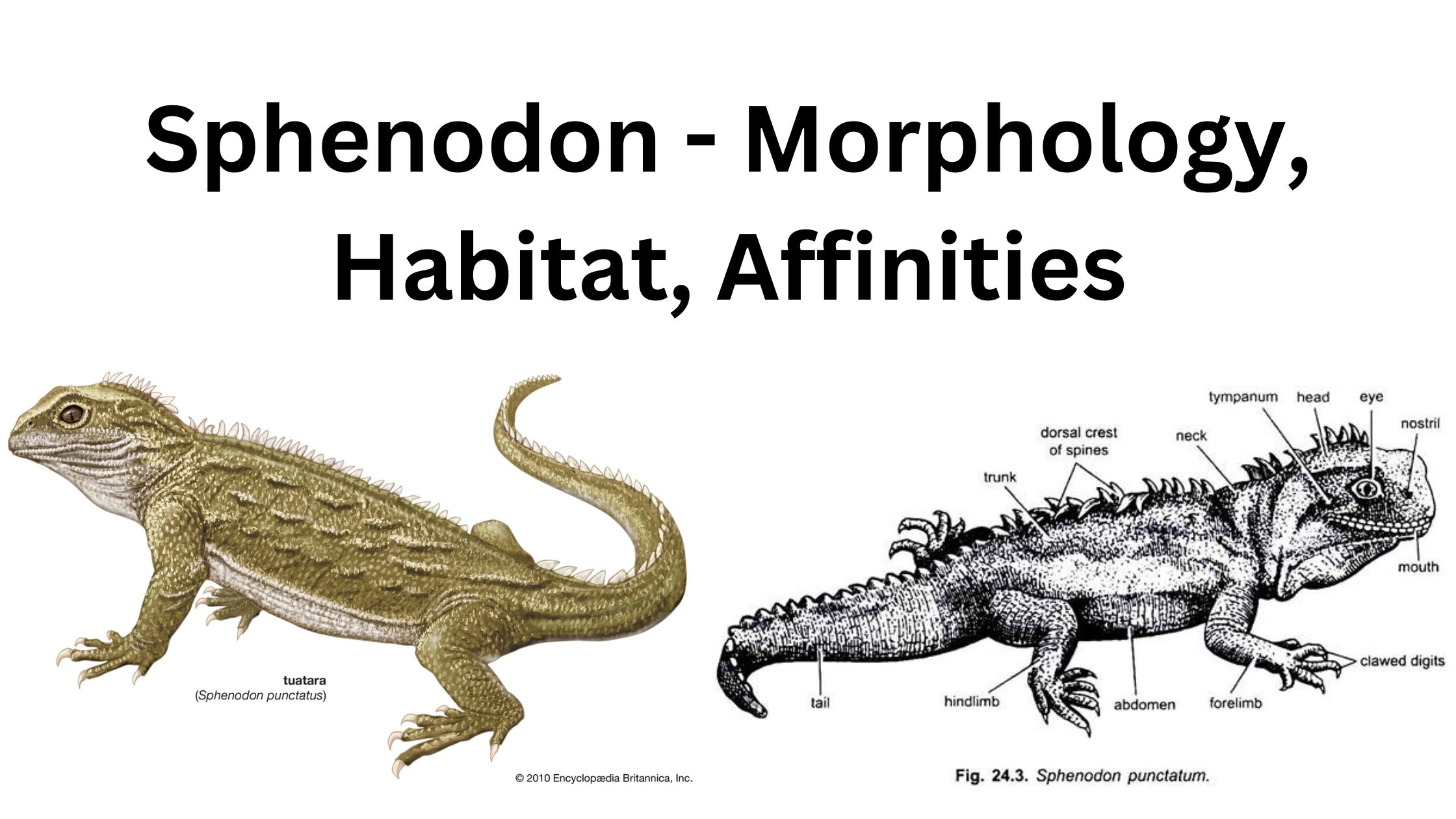
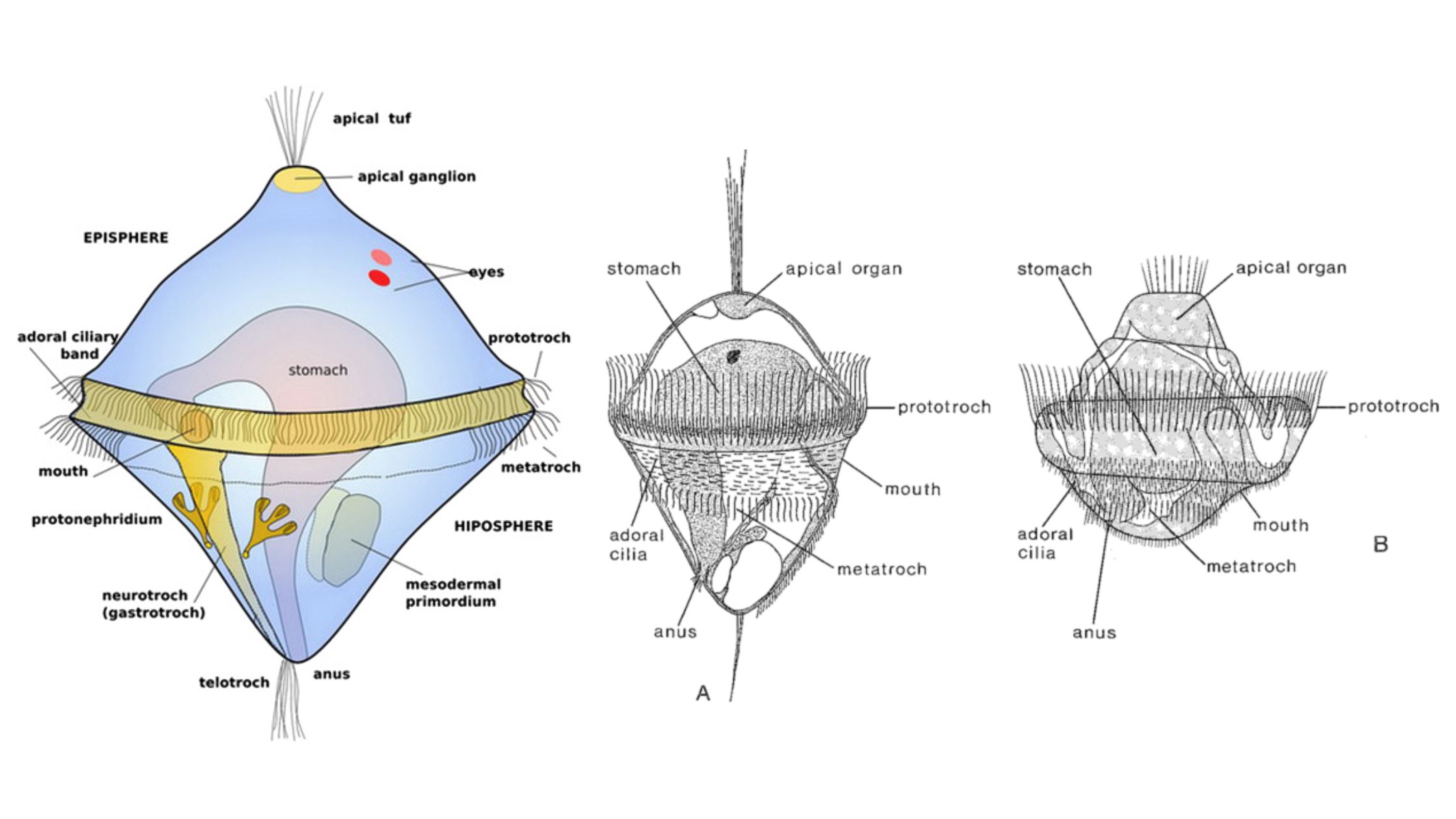
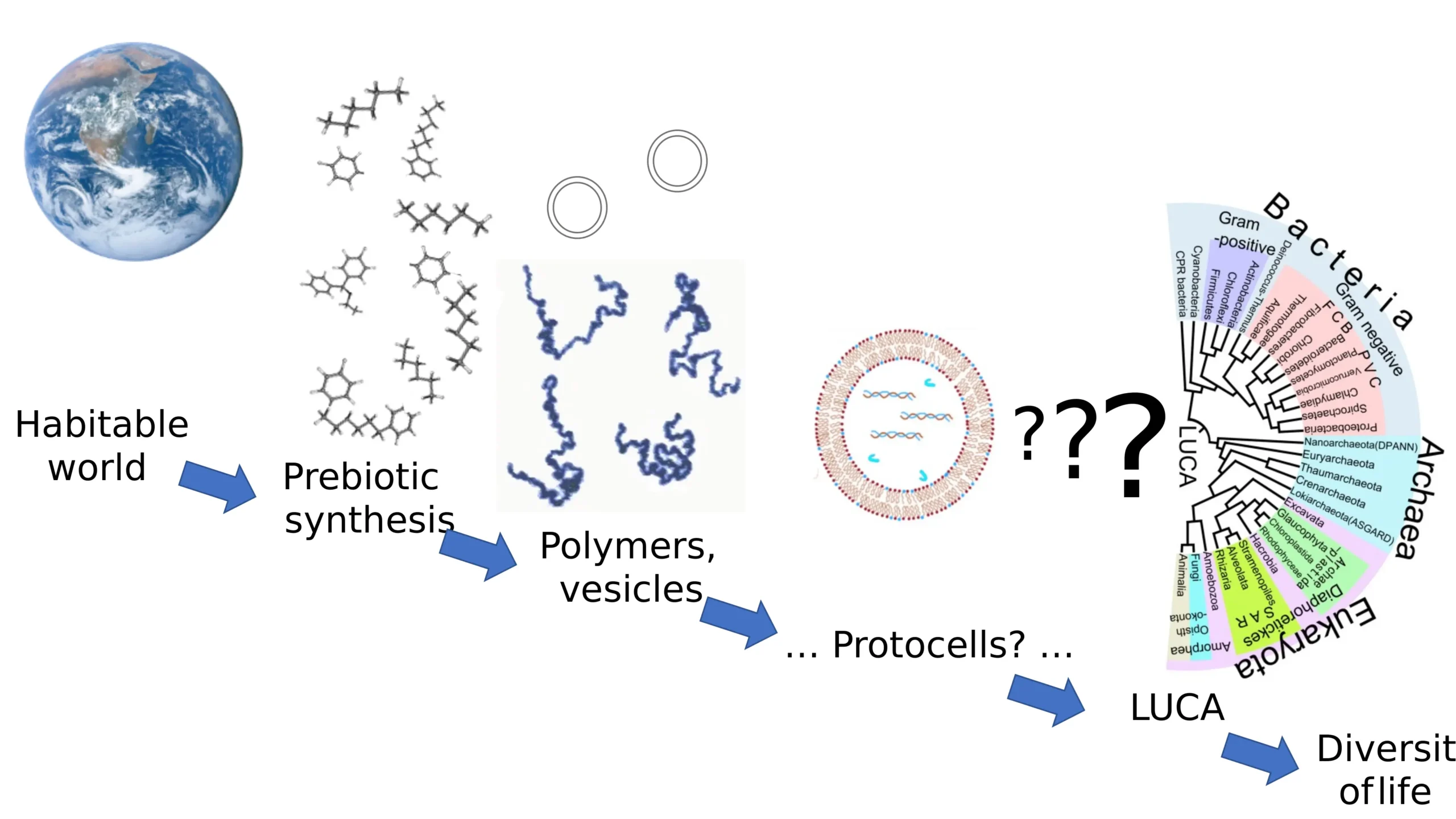
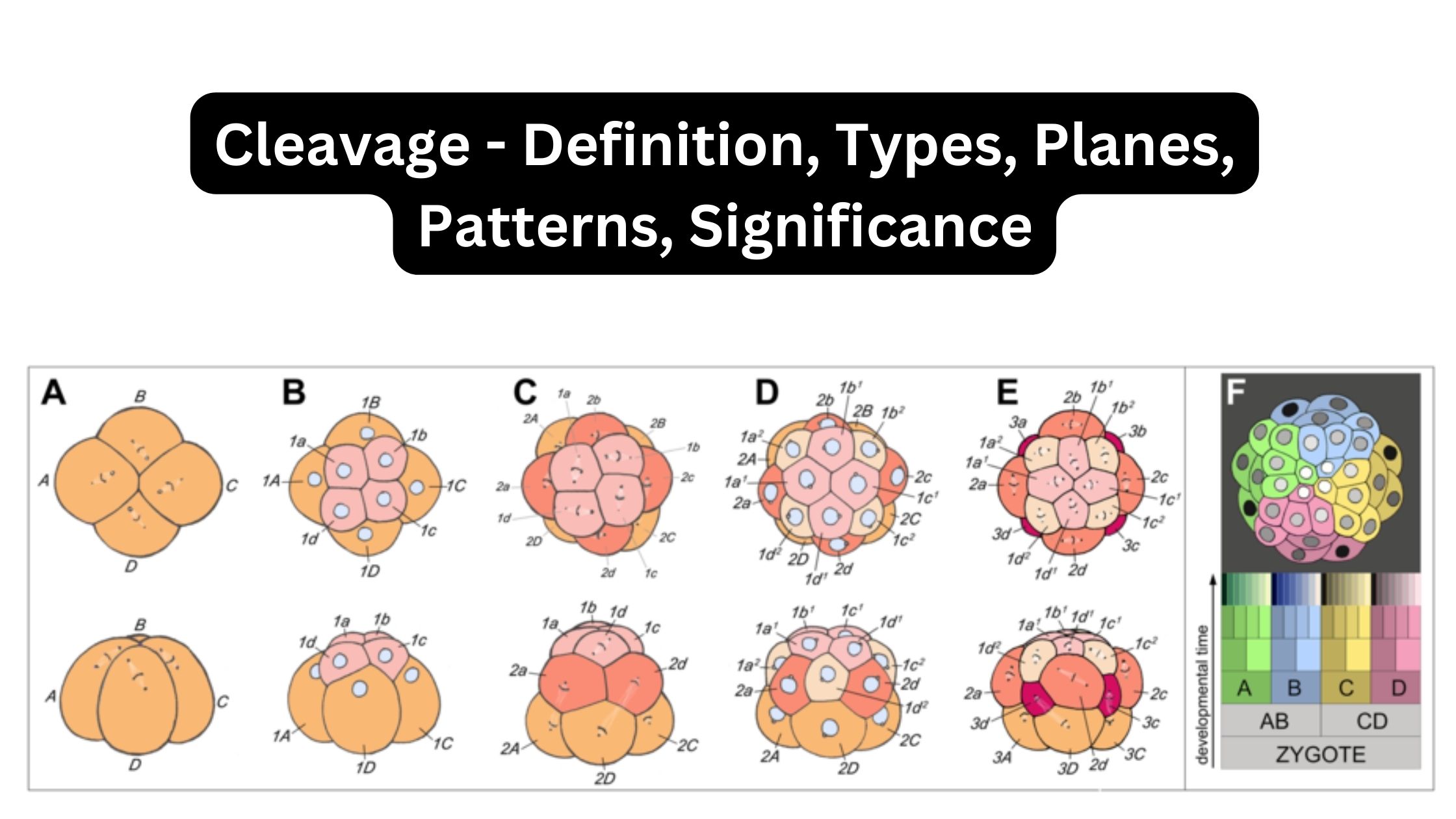
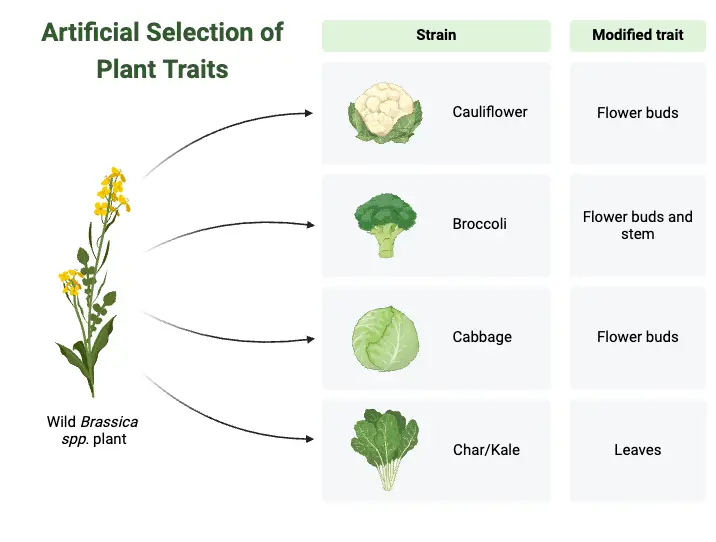
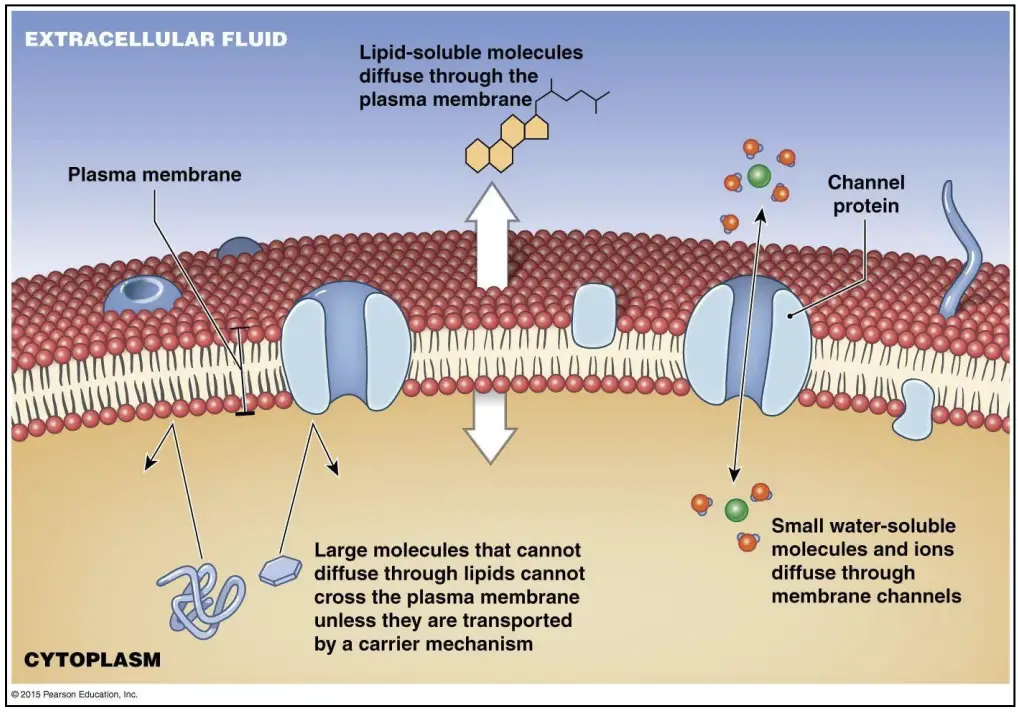
Agnatha – Characteristics, Classification, Morphology, Reproduction
Agnatha is the superclass of vertebrates in which true jaws are absent. It is the group that represent the most primitive and earliest craniates, and in this group the mouth parts are simple without any jaw elements. It is the condition where the animals show a very old vertebrate body plan which is already present … Read more