Speciation – Definition, Causes, Types, Process
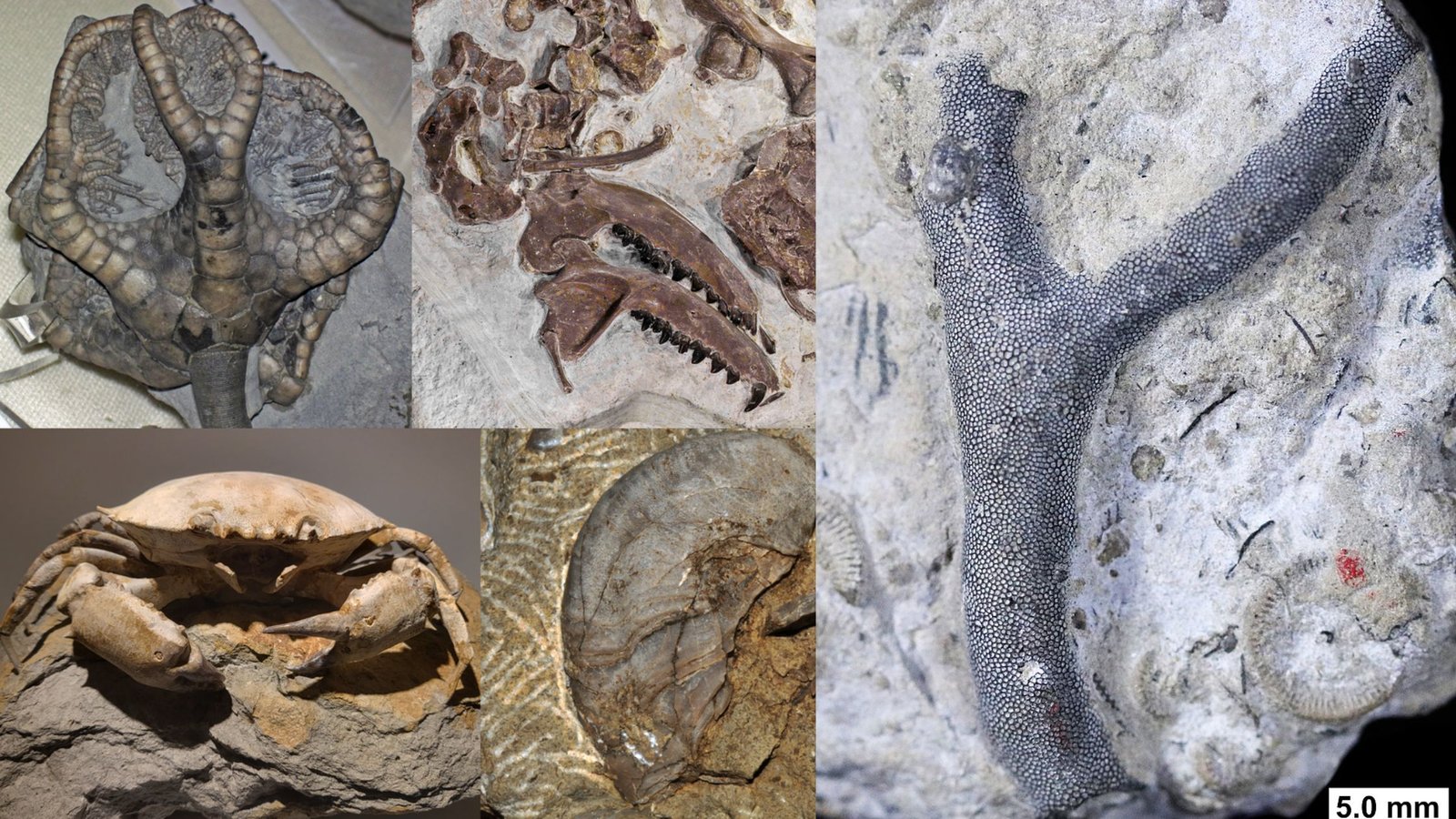
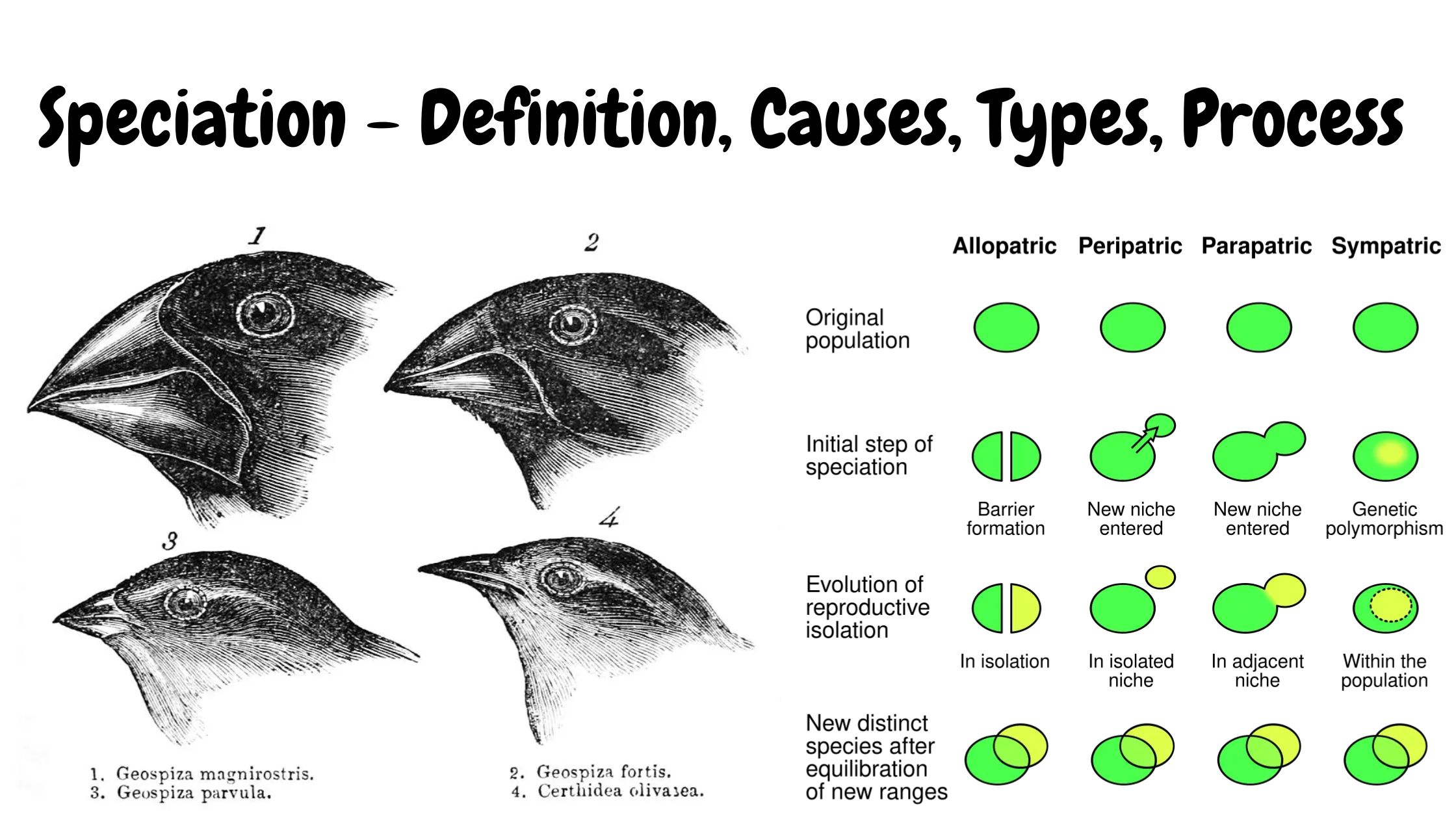
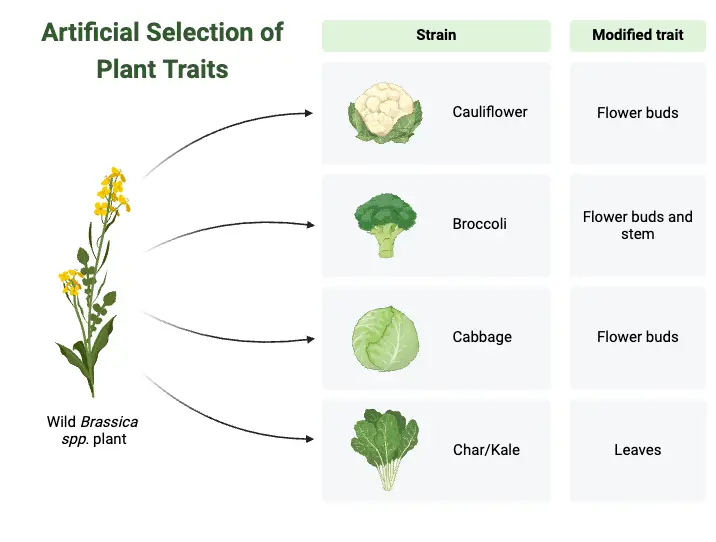
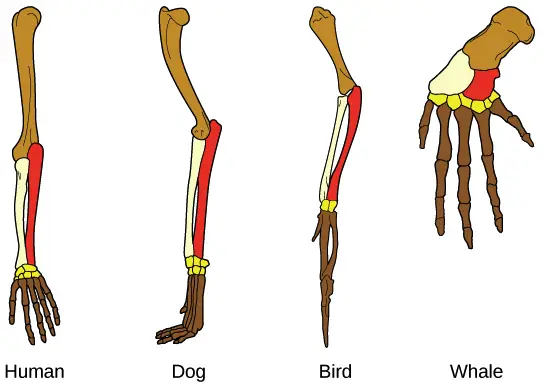
What is Speciation? Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new species are formed from a pre-existing species. It is the process where a single ancestral population is gradually divided into two or more distinct species. This process occurs when population of a species becomes isolated from each other and the gene flow between them … Read more