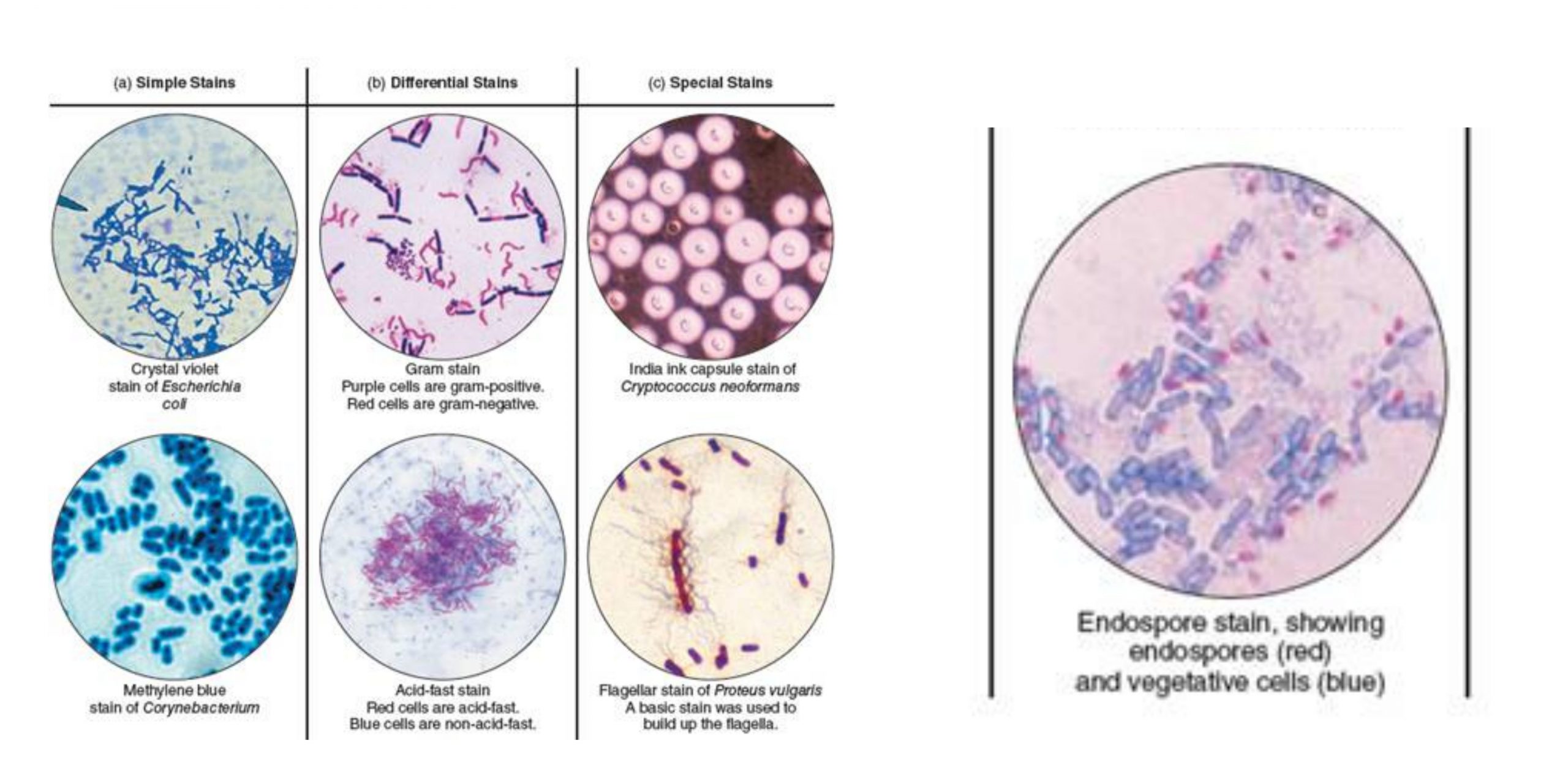
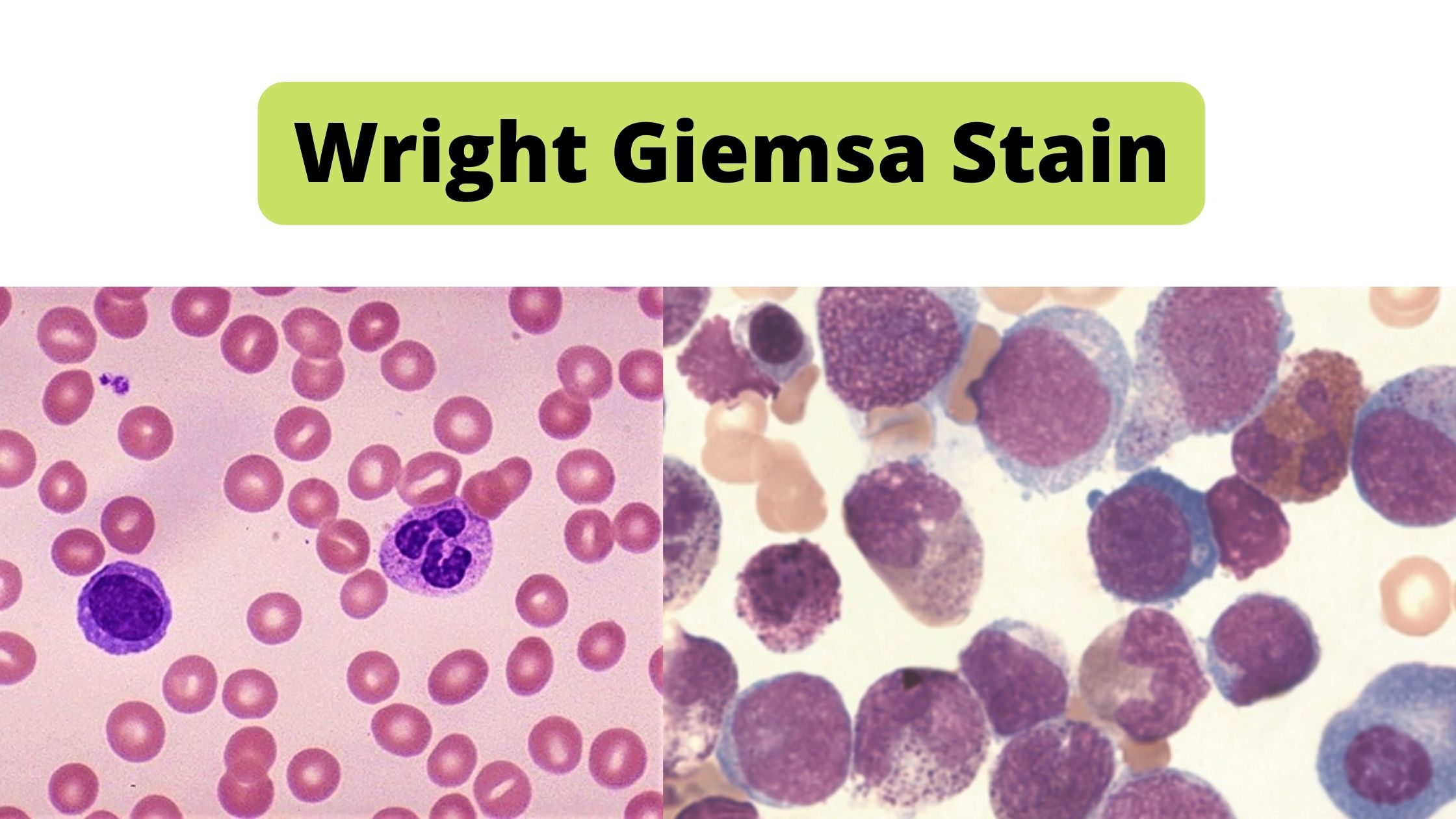
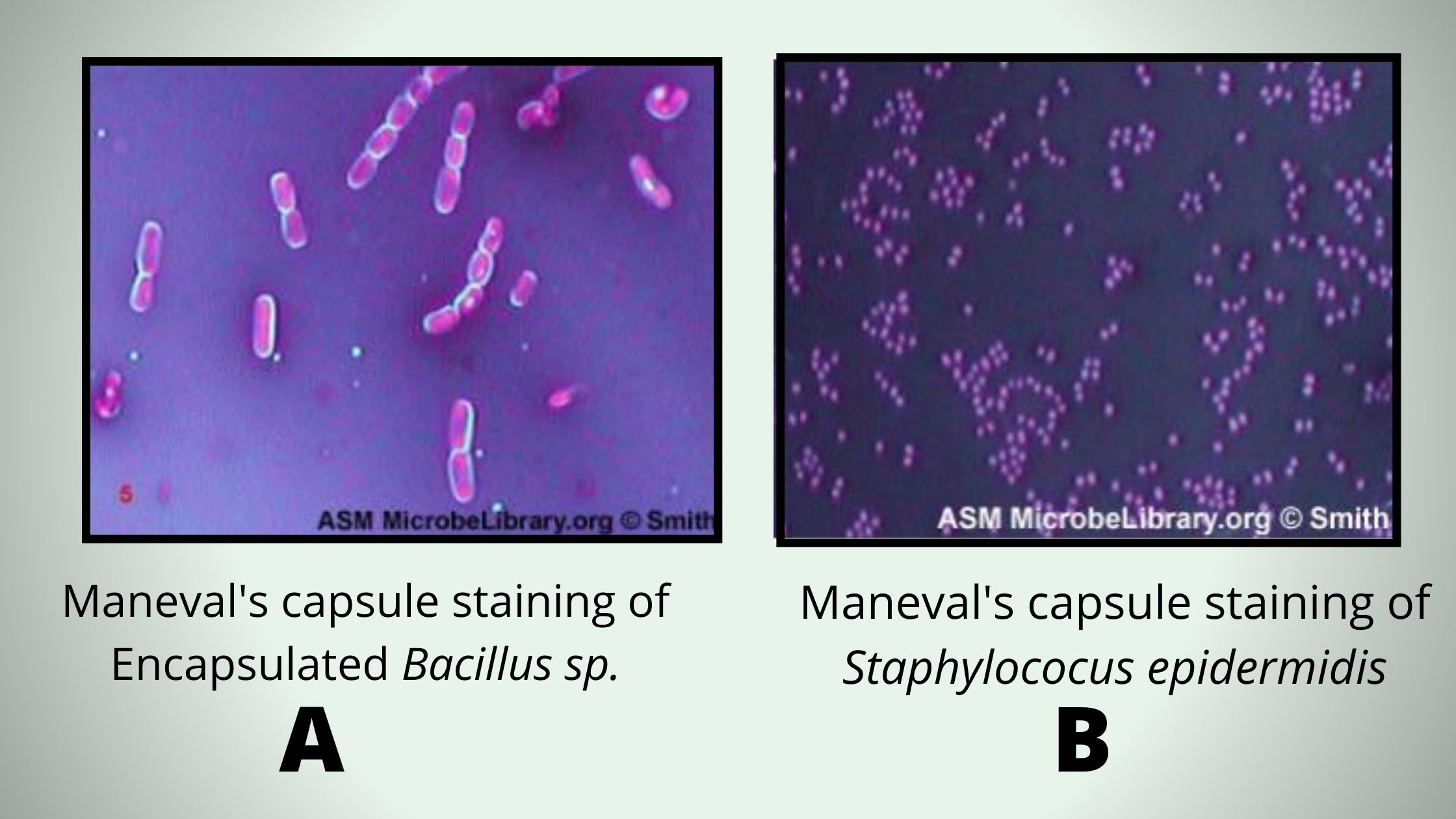
Types of Stains used in Microbiology
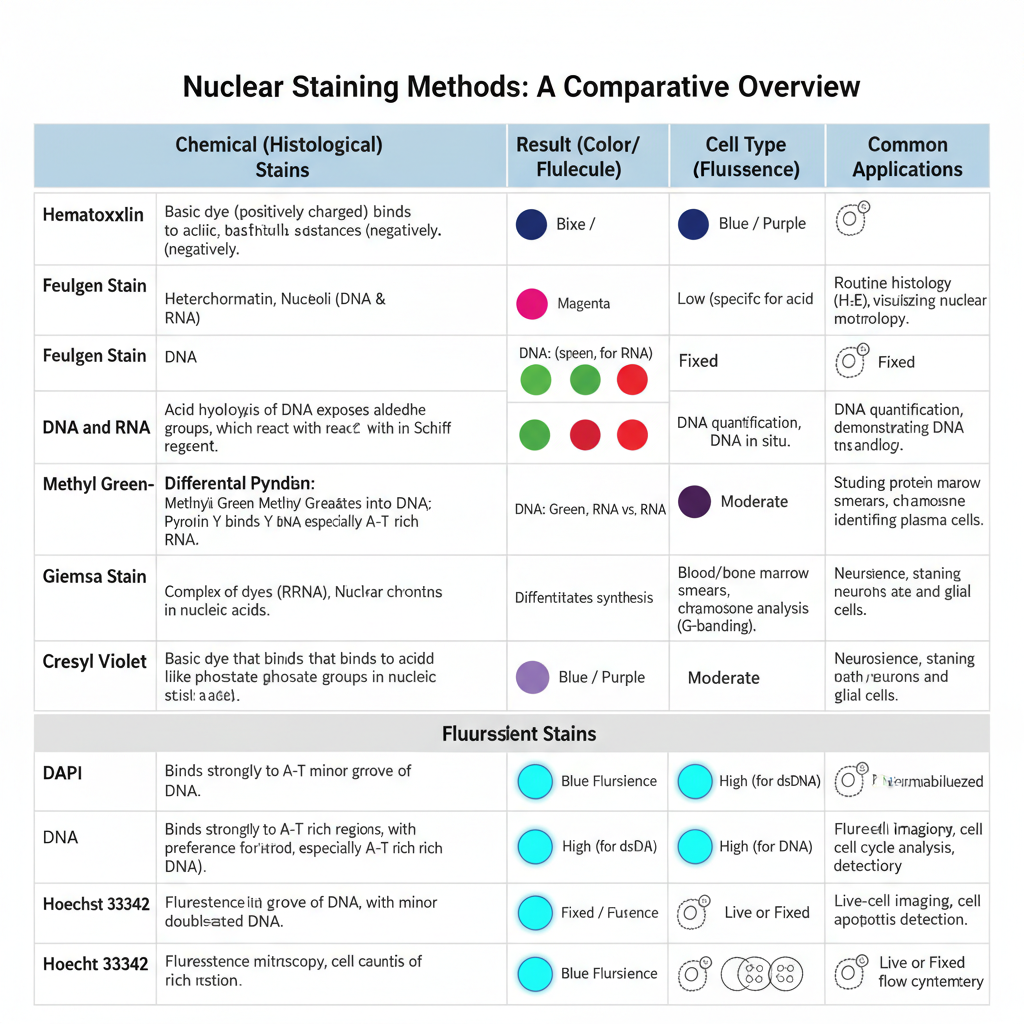
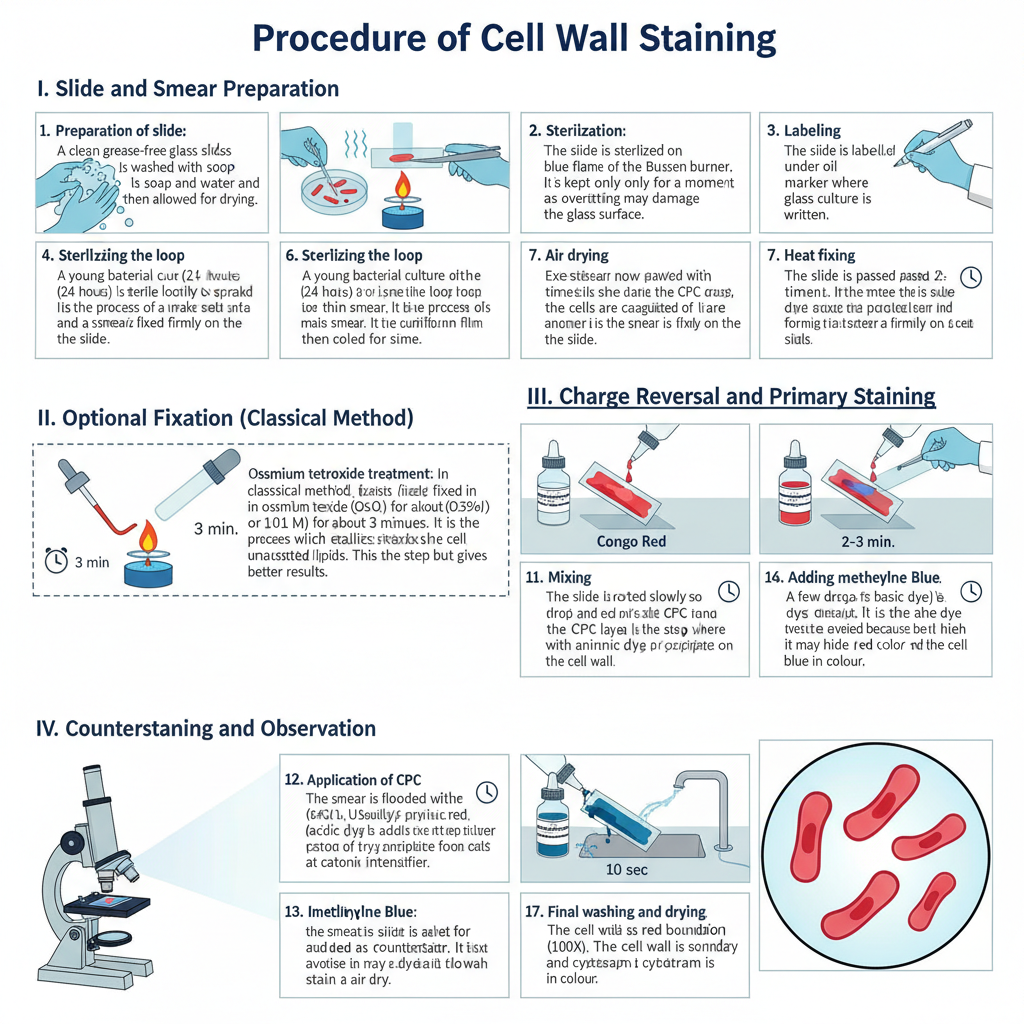
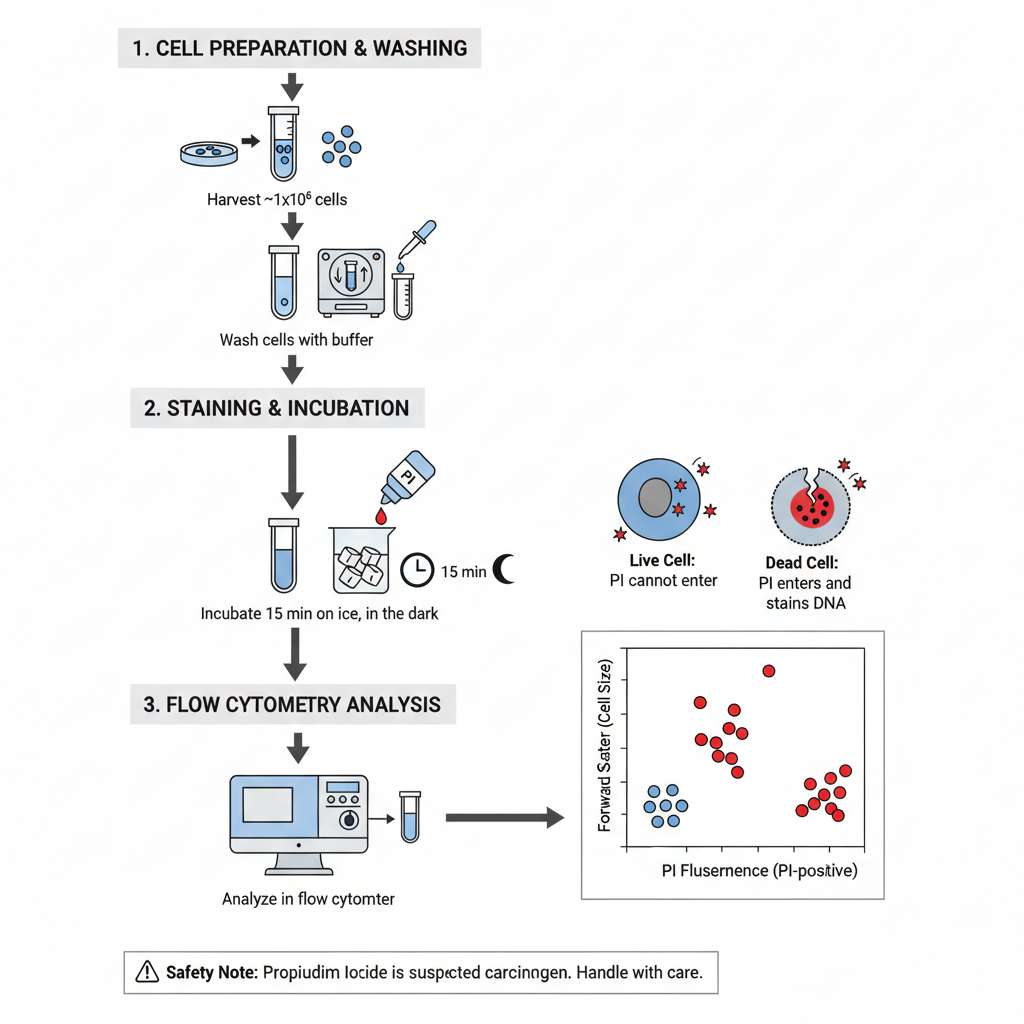
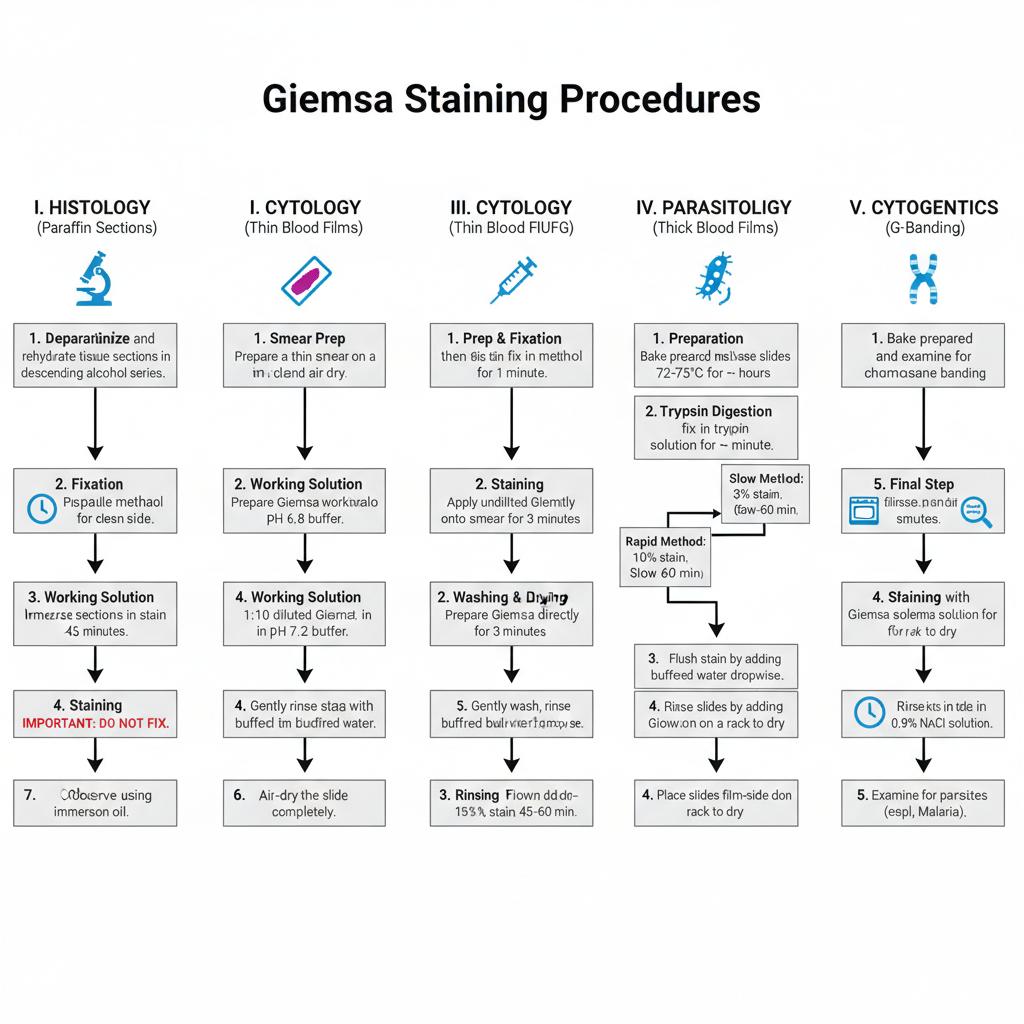
Different stains react or concentrate on different areas of a tissue or cell These properties can be utilized to highlight certain areas or regions. A few of the most well-known biological staining methods can be found below. If not otherwise indicated All of these dyes can be used on tissues and cells that are fixed as well as essential dyes (suitable for use in live organisms) are indicated.