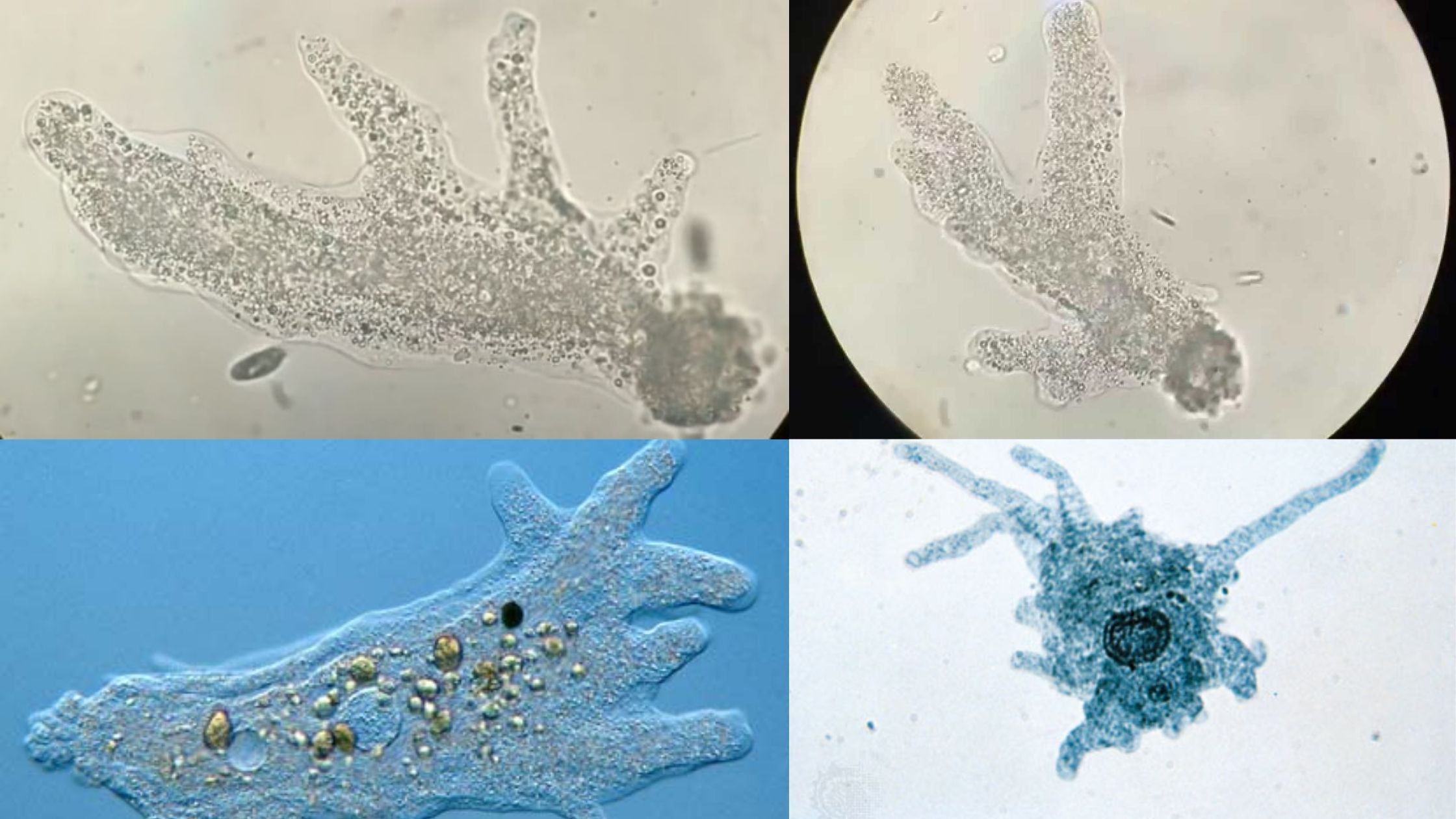
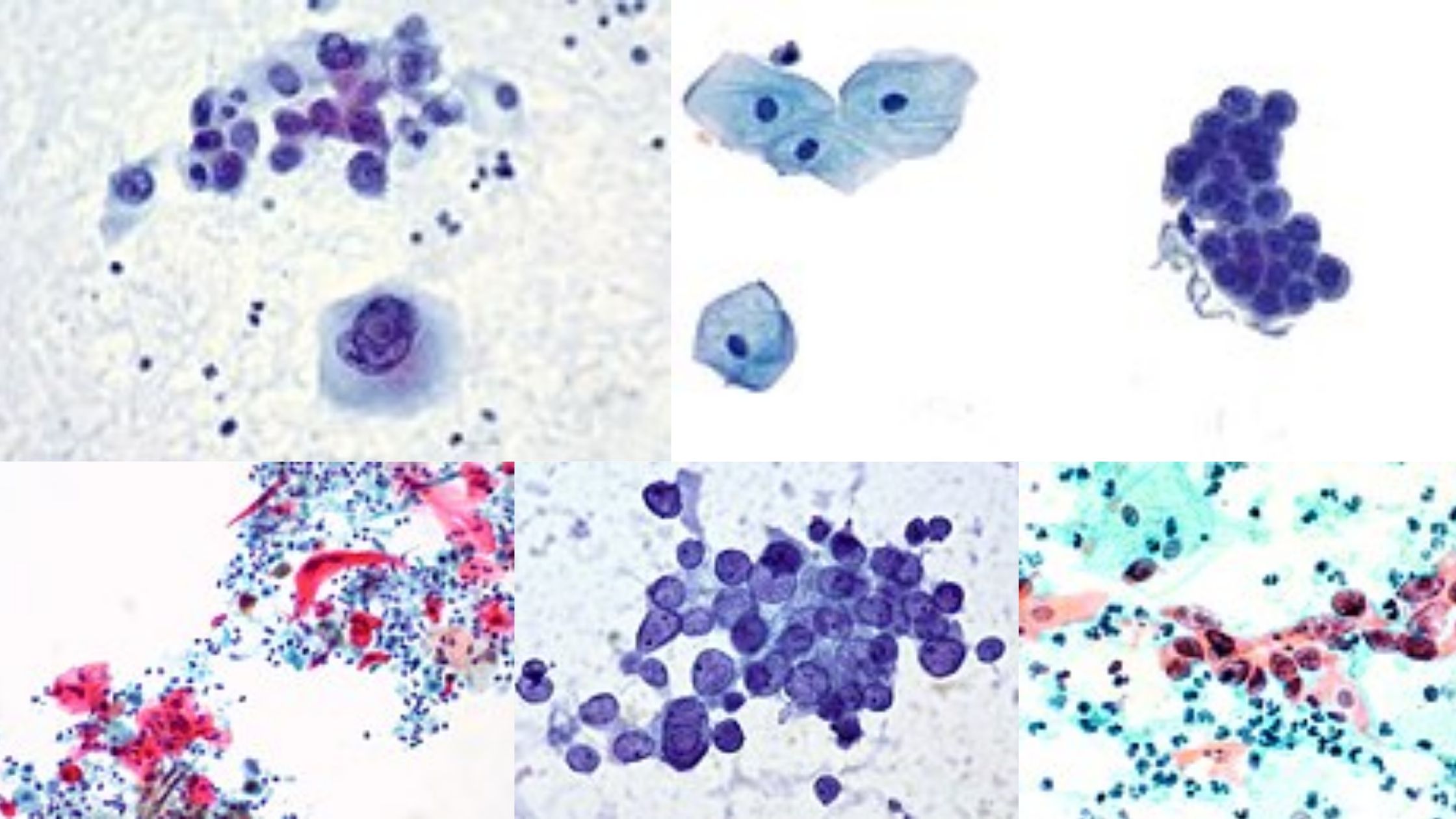
Amoeba Staining – Principle, Methods, Procedure, Result, Uses
Amoeba staining is the process used in laboratories for observing the structural details of free-living and intestinal amoebae. It is needed because most amoebae are transparent in fresh samples, and their internal parts cannot be seen clearly without color contrast. It is the process that helps in identifying pathogenic forms like Entamoeba histolytica from non-pathogenic … Read more