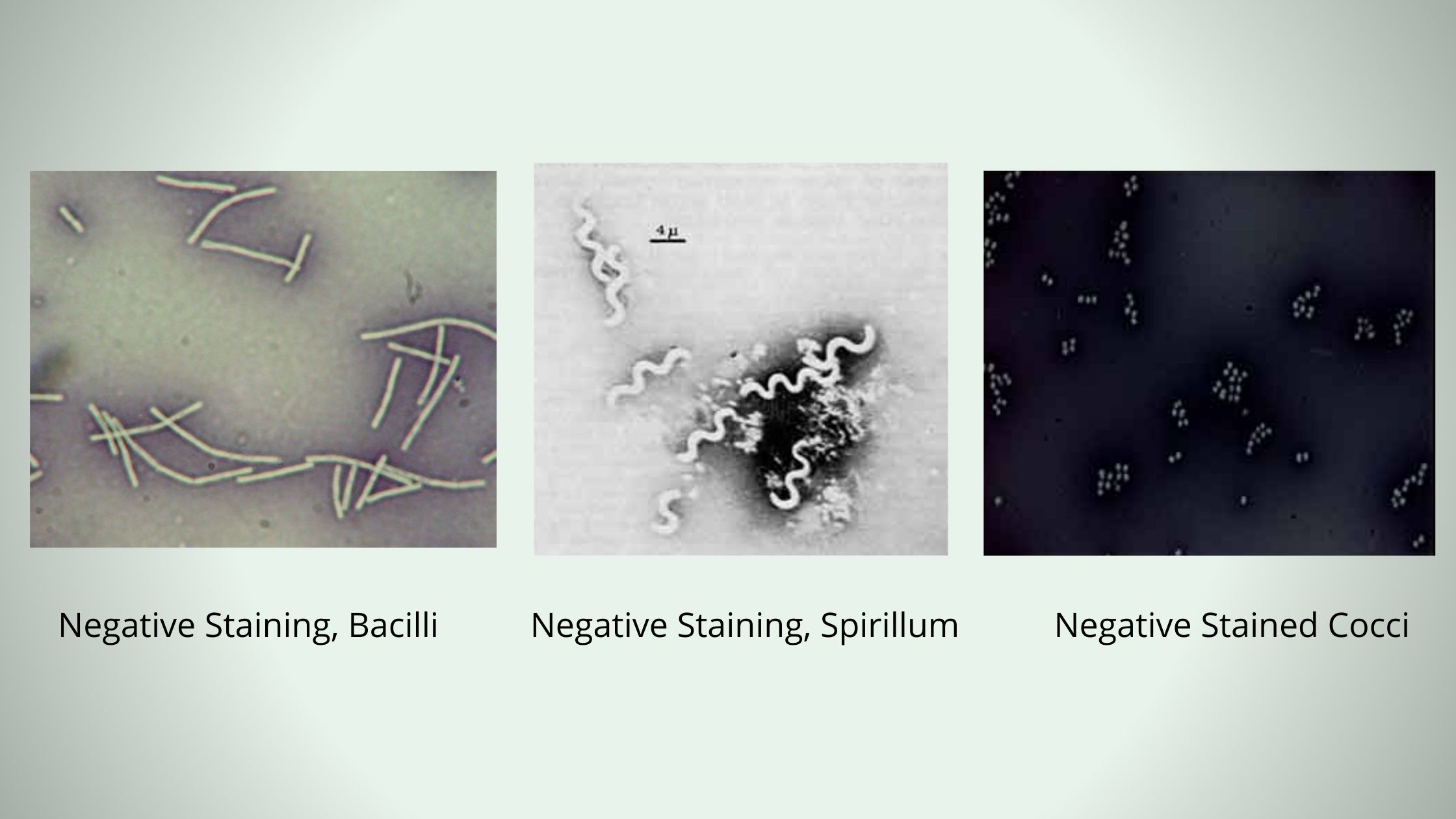
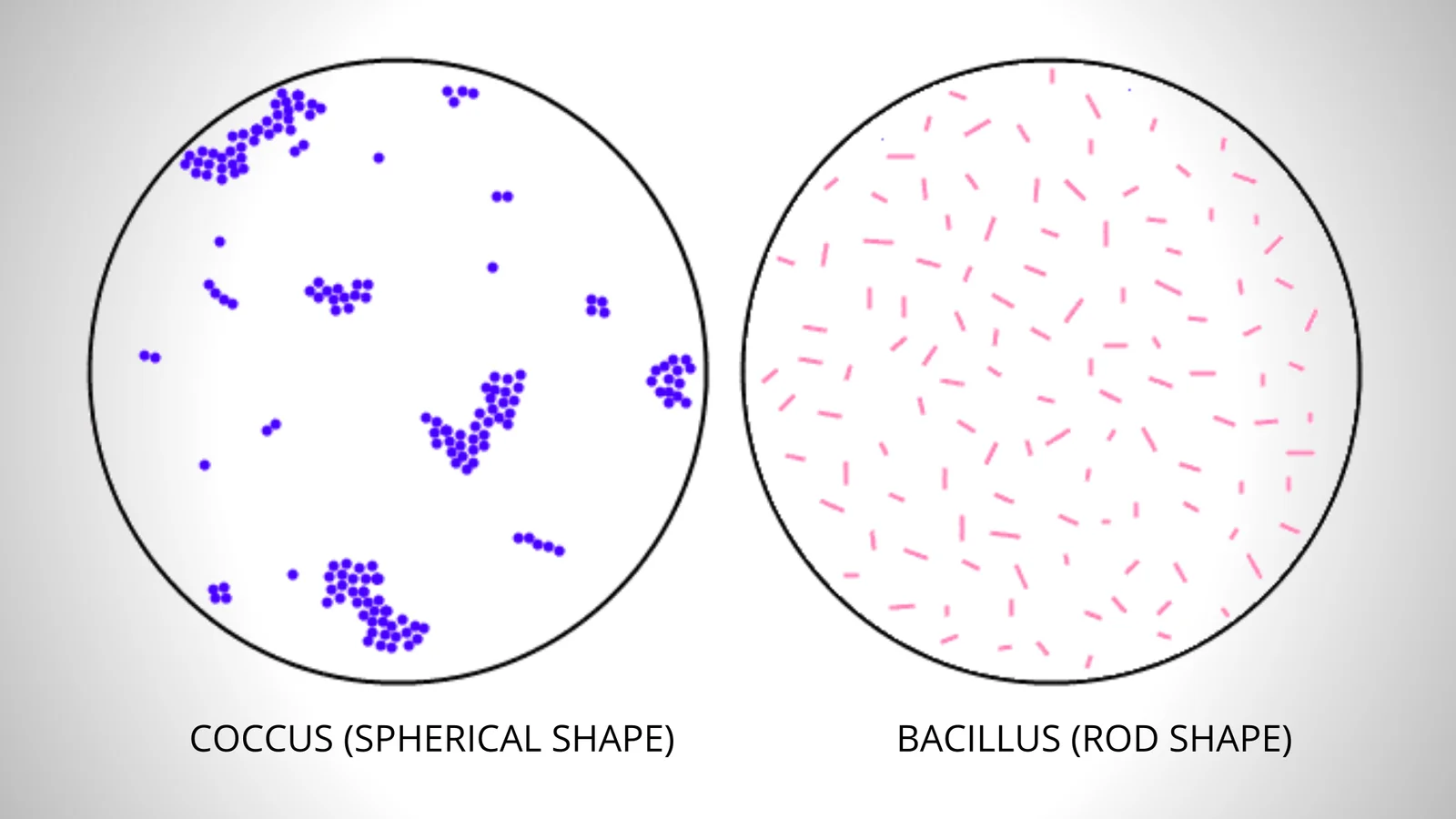
Negative Staining – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
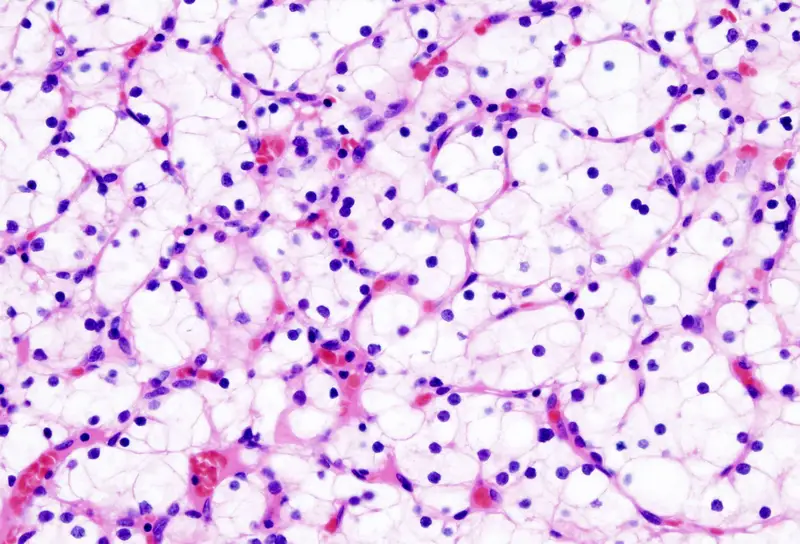
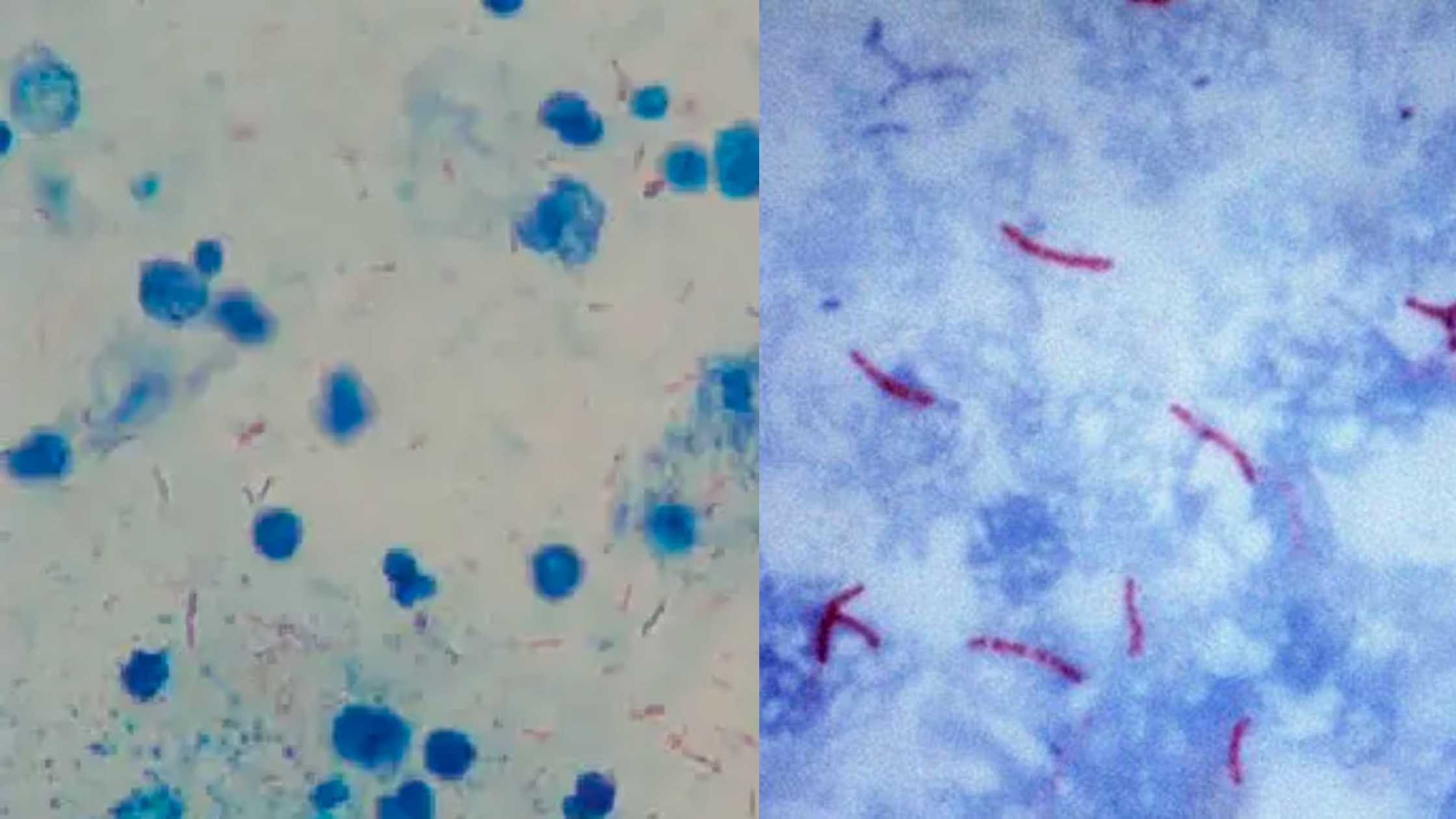
In negative staining method, an acidic dye is used known as India Ink or Nigrosin. When the bacterial cells are exposed to this stain, due to the presence of acidic nature it readily gives up a hydrogen ion (proton) and the chromophore. As a result, the dye becomes negatively charged, now the bacterial cell surface deflects the stain.