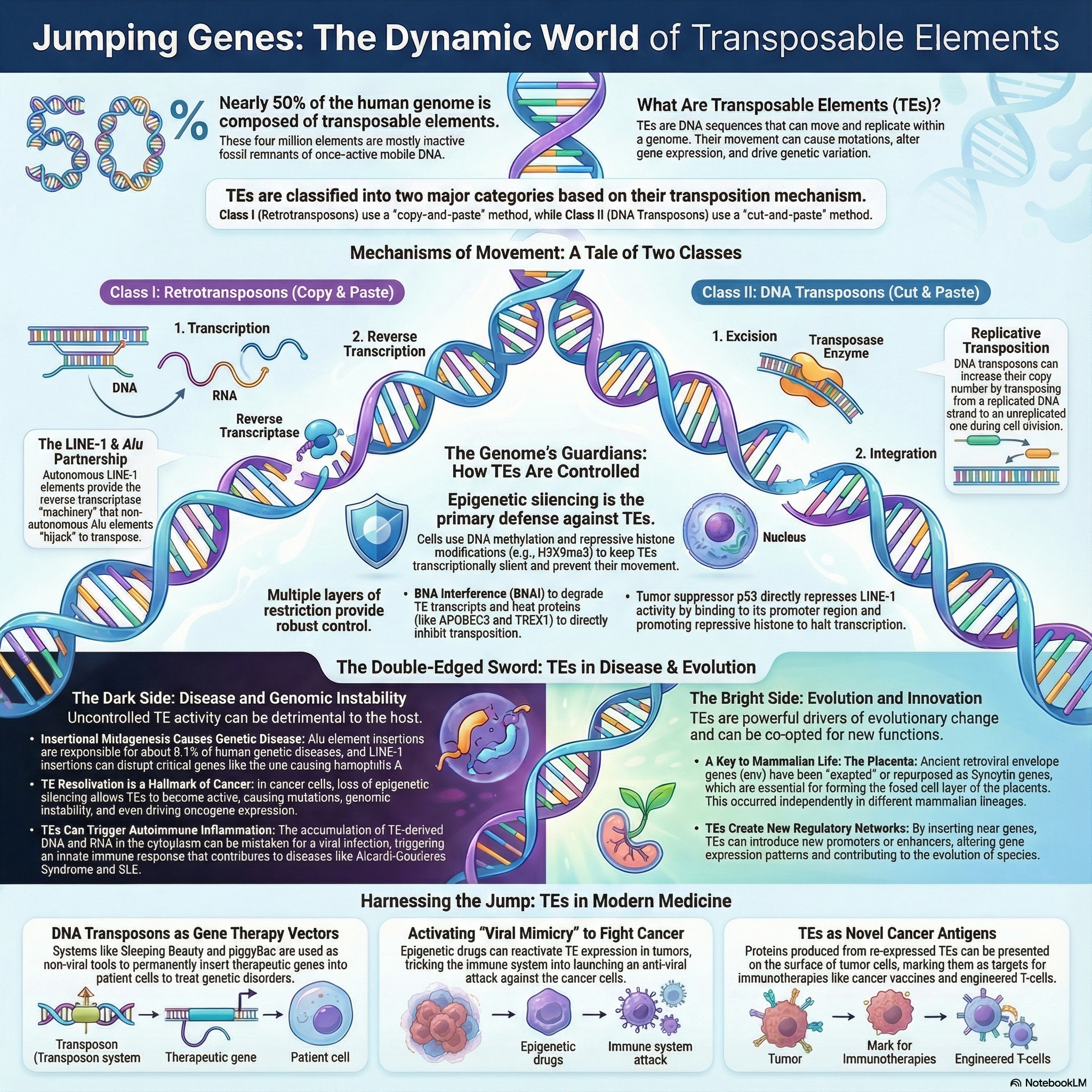
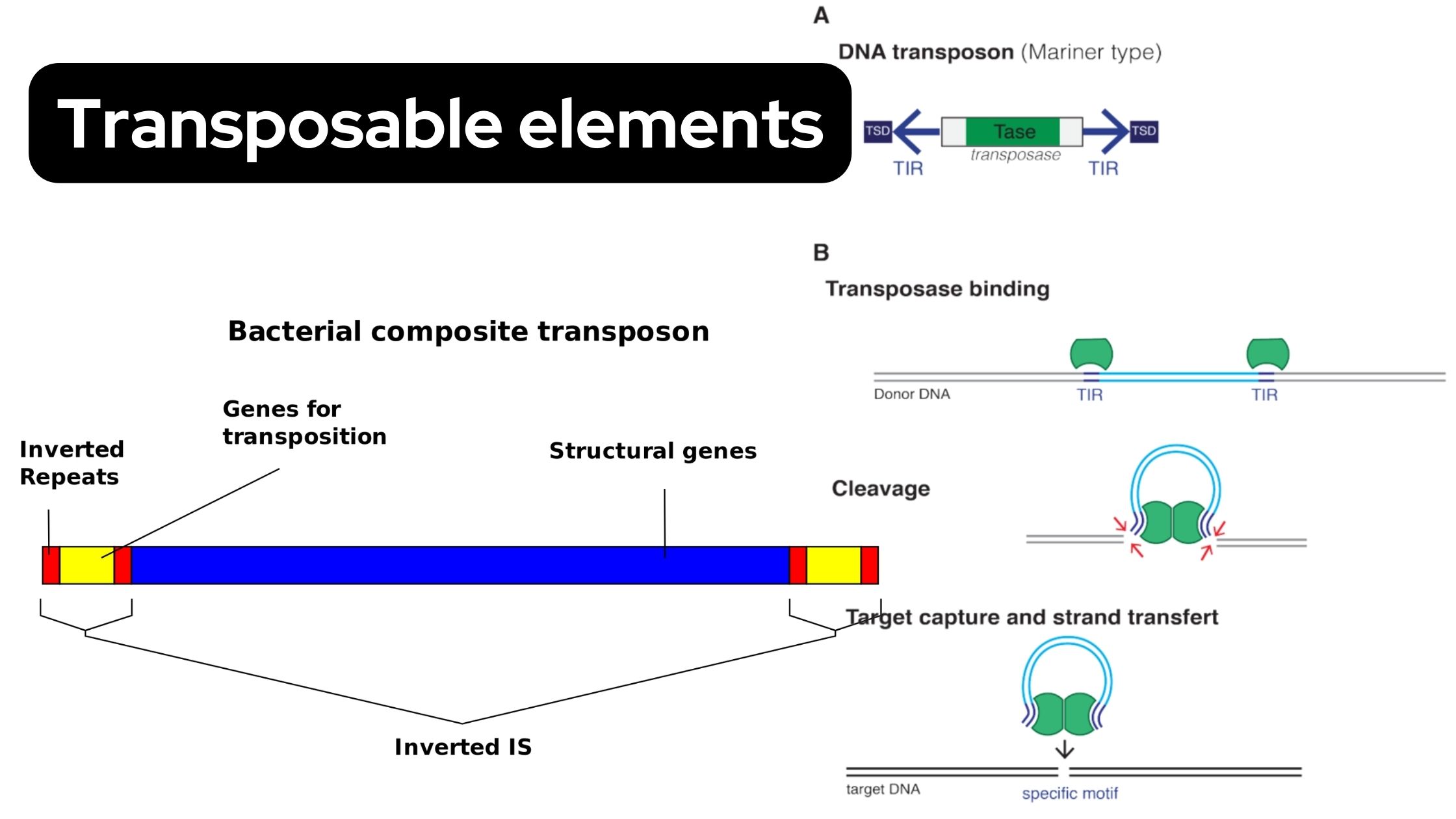
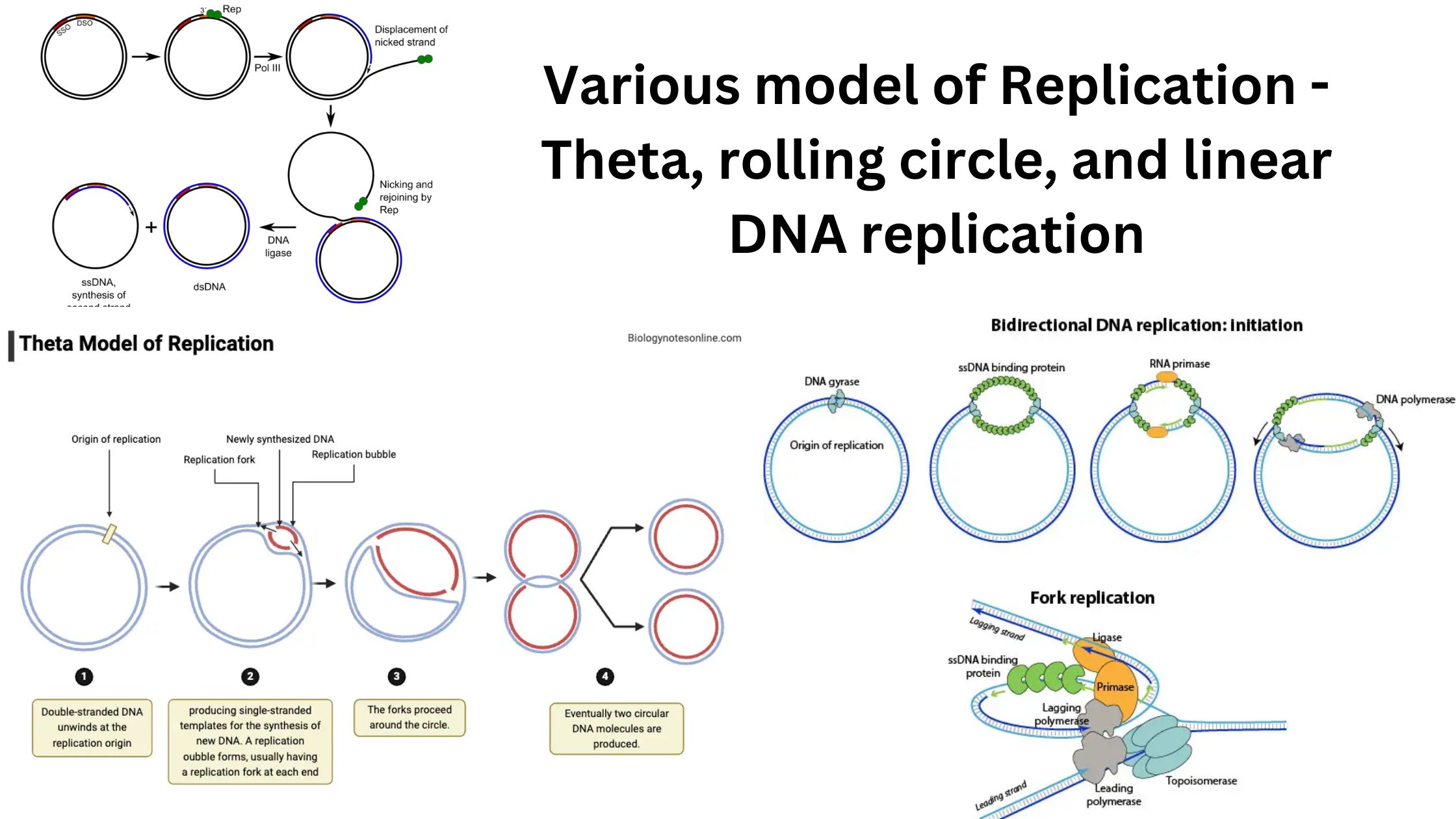
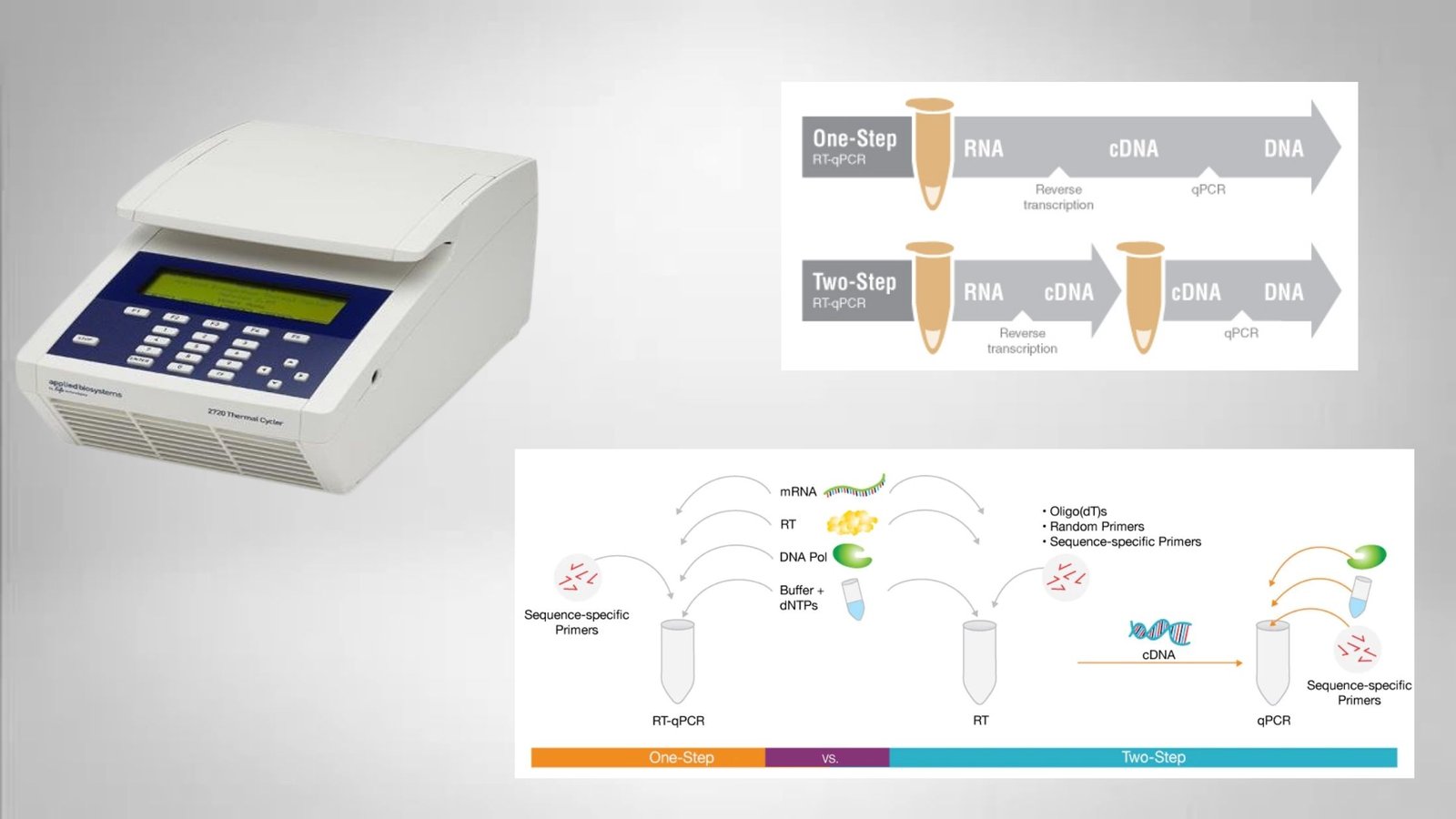
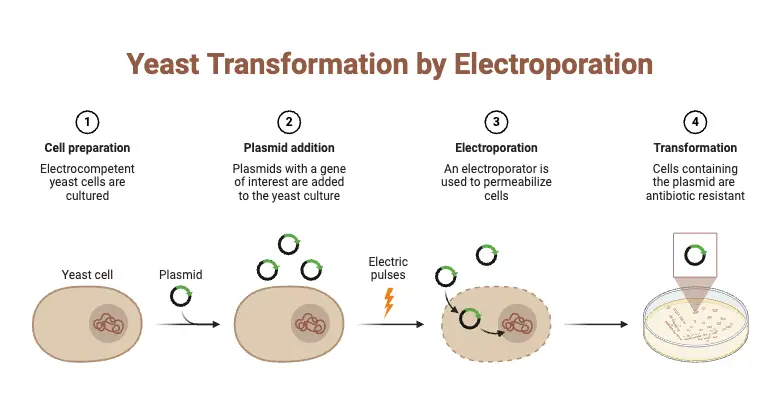
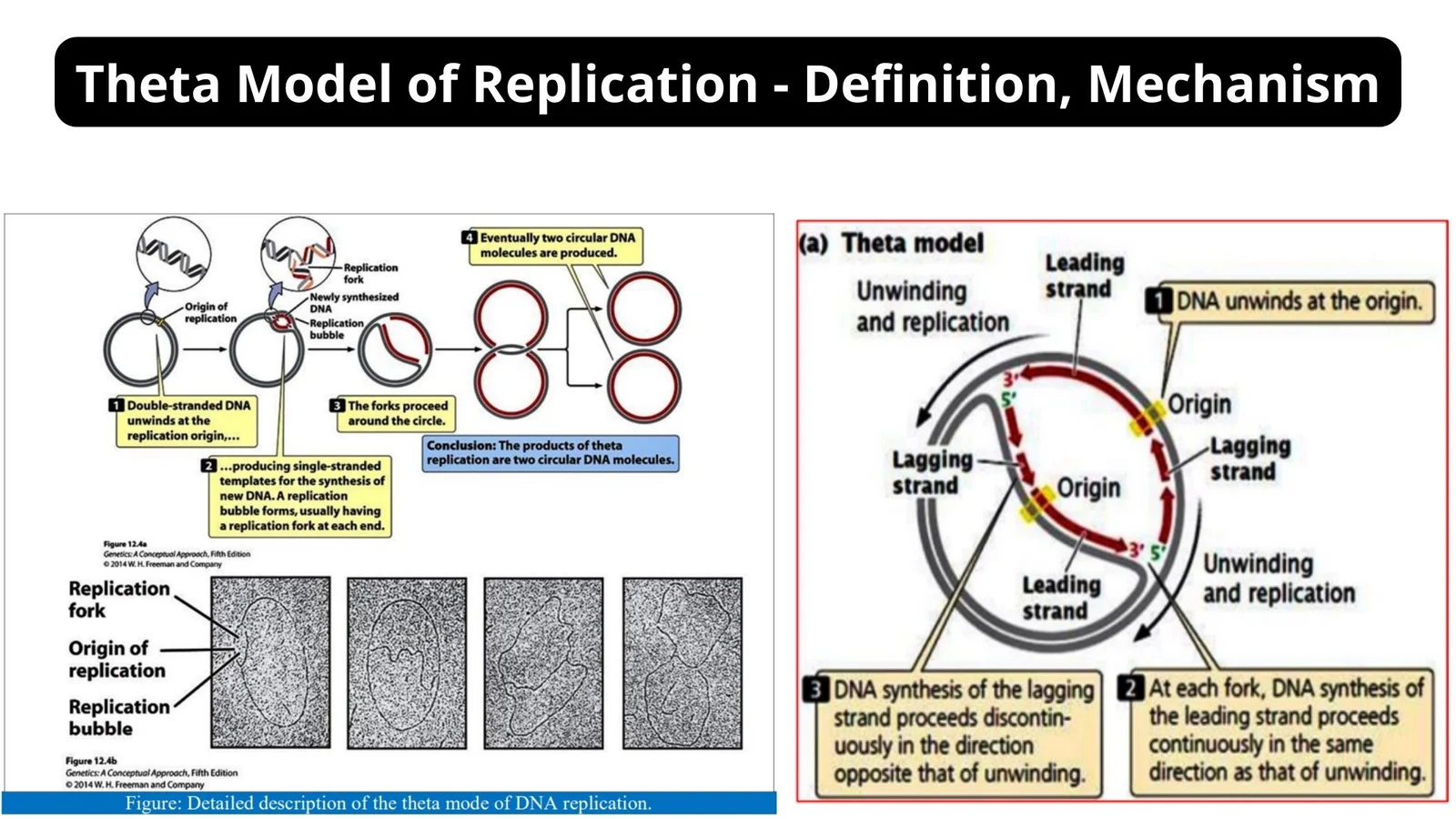
Replicative Transposition of DNA Transposons and Retrotransposons
What is replicative transposition? Replicative transposition is a type of transposition in which the transposable element is duplicated during its movement from one site to another. It is the process where the original transposable element remains at the donor site and a new copy is inserted into the target DNA. This is referred to as … Read more