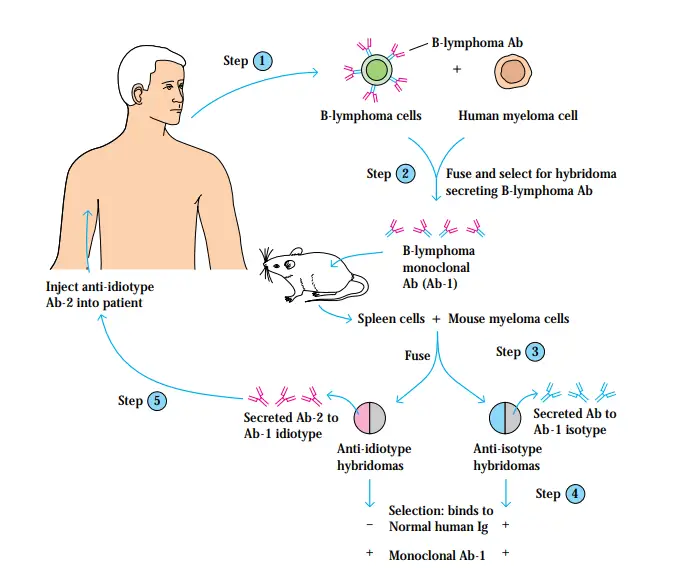
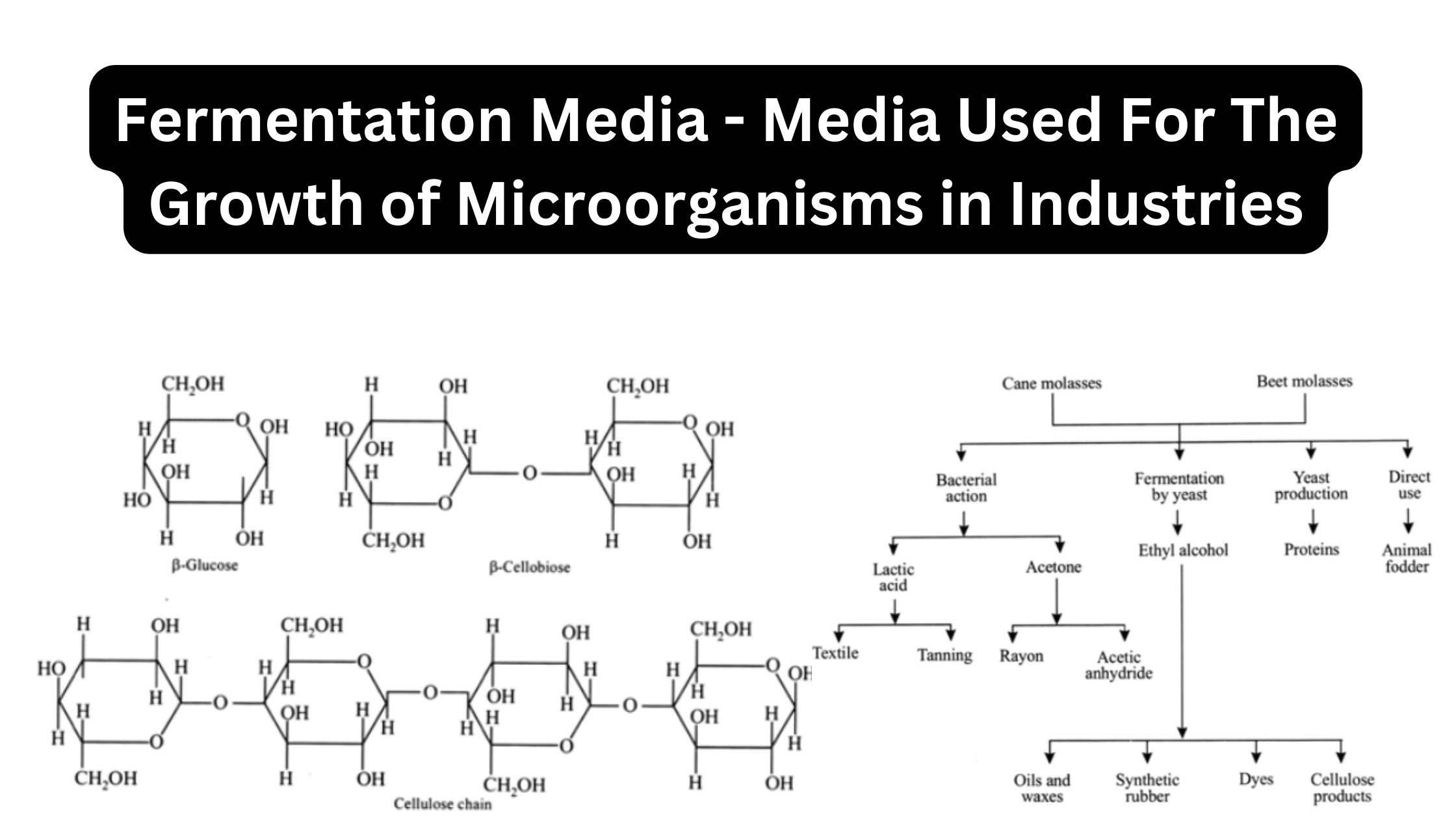
Neutrophil – Definition, Structure, Functions
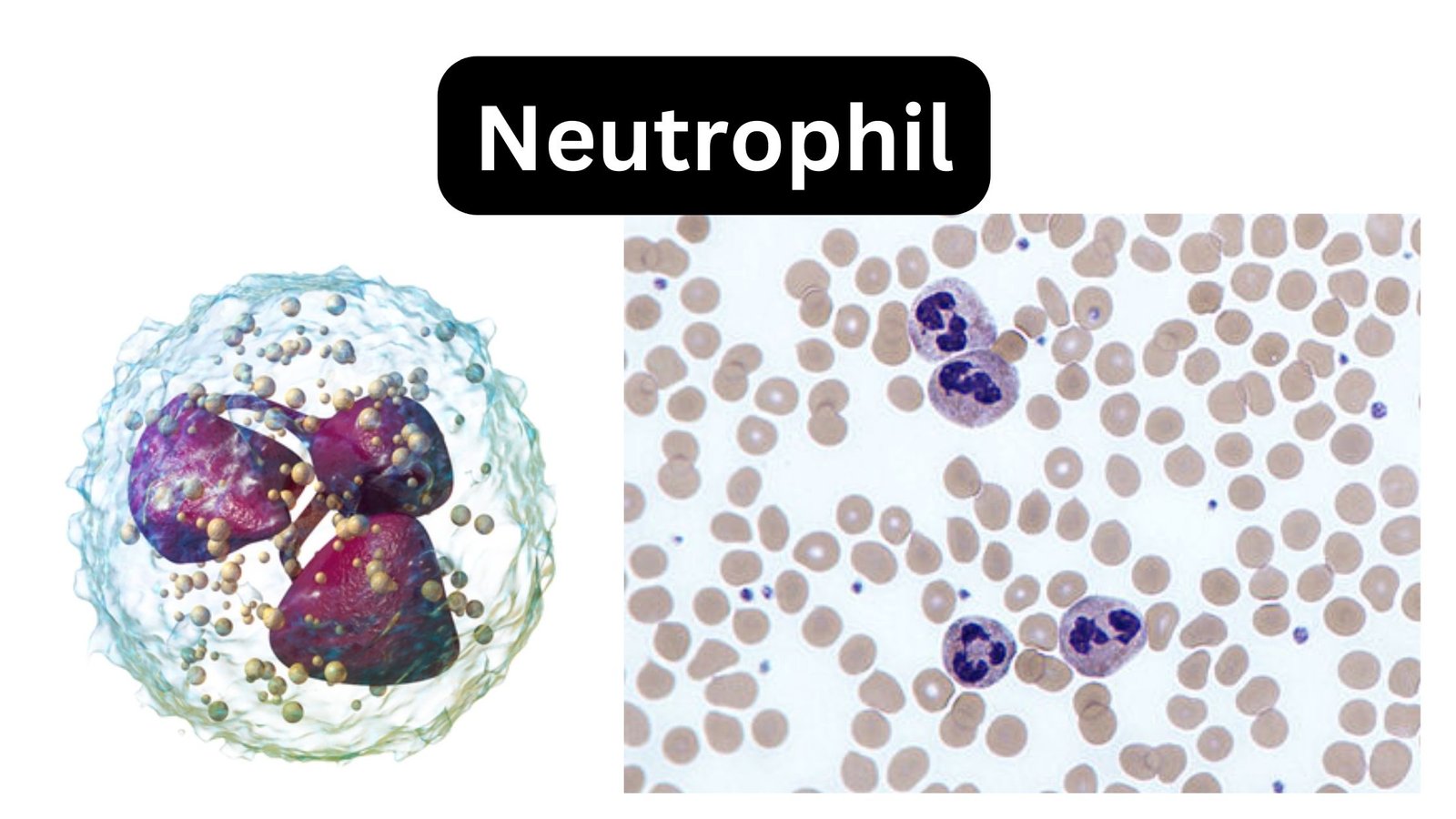
What are Neutrophils? Neutrophils Definition Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system’s defense against infections. They are highly mobile and act as phagocytes, engulfing and destroying bacteria and other harmful substances. Neutrophils are characterized by their multi-lobed nuclei and stainable cytoplasmic granules. They are part … Read more