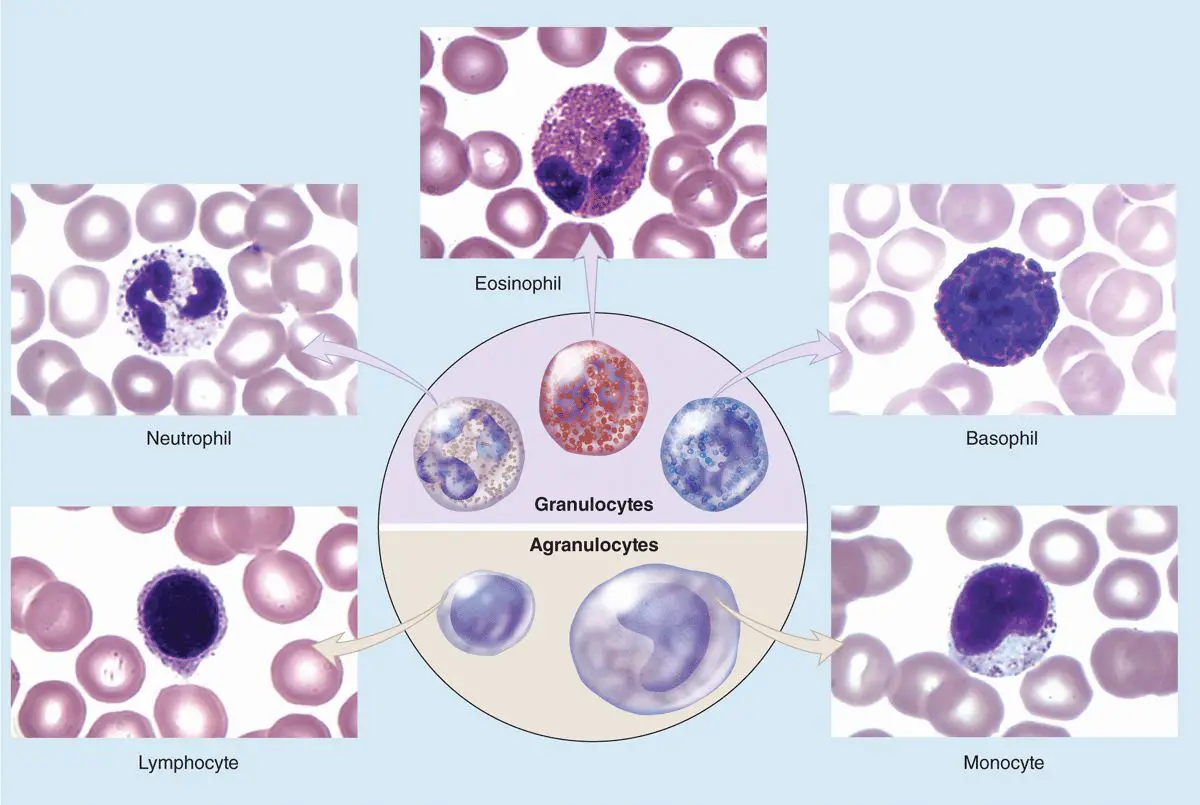
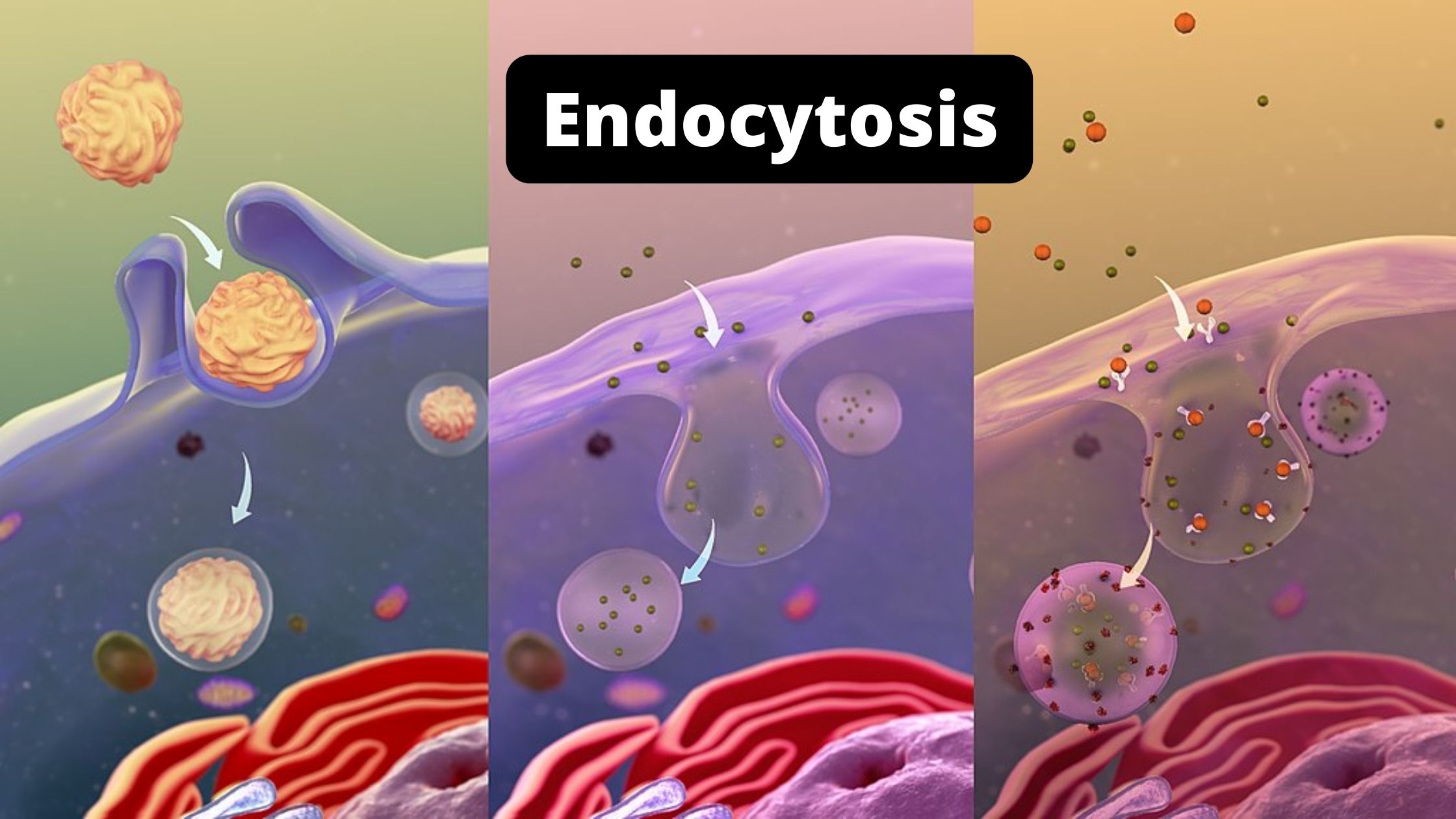
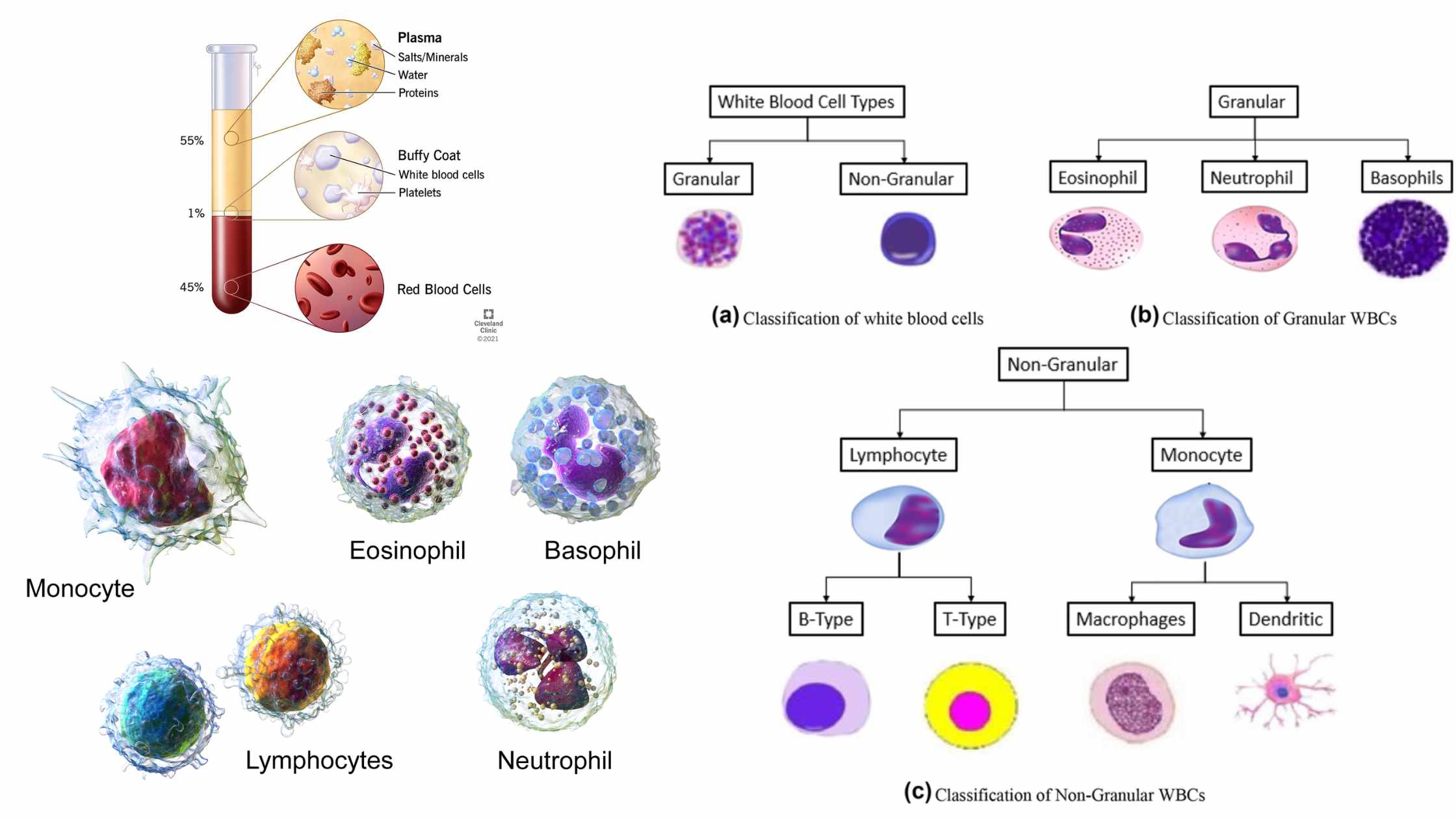
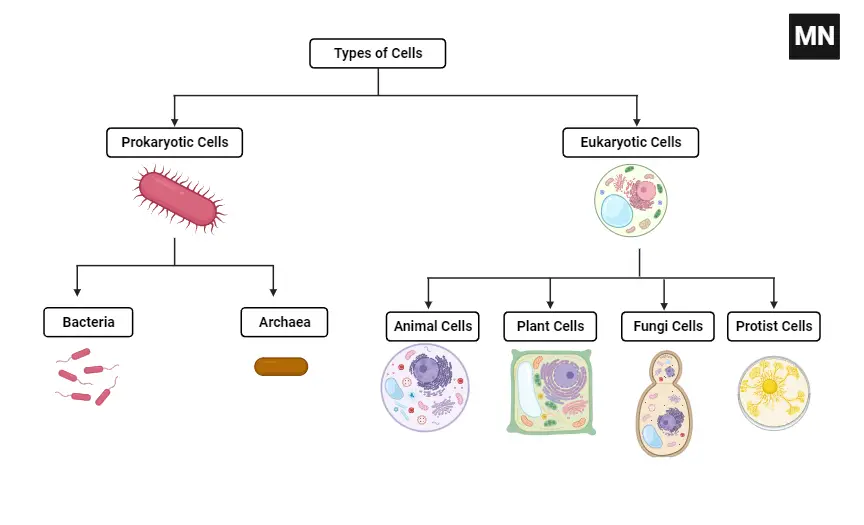
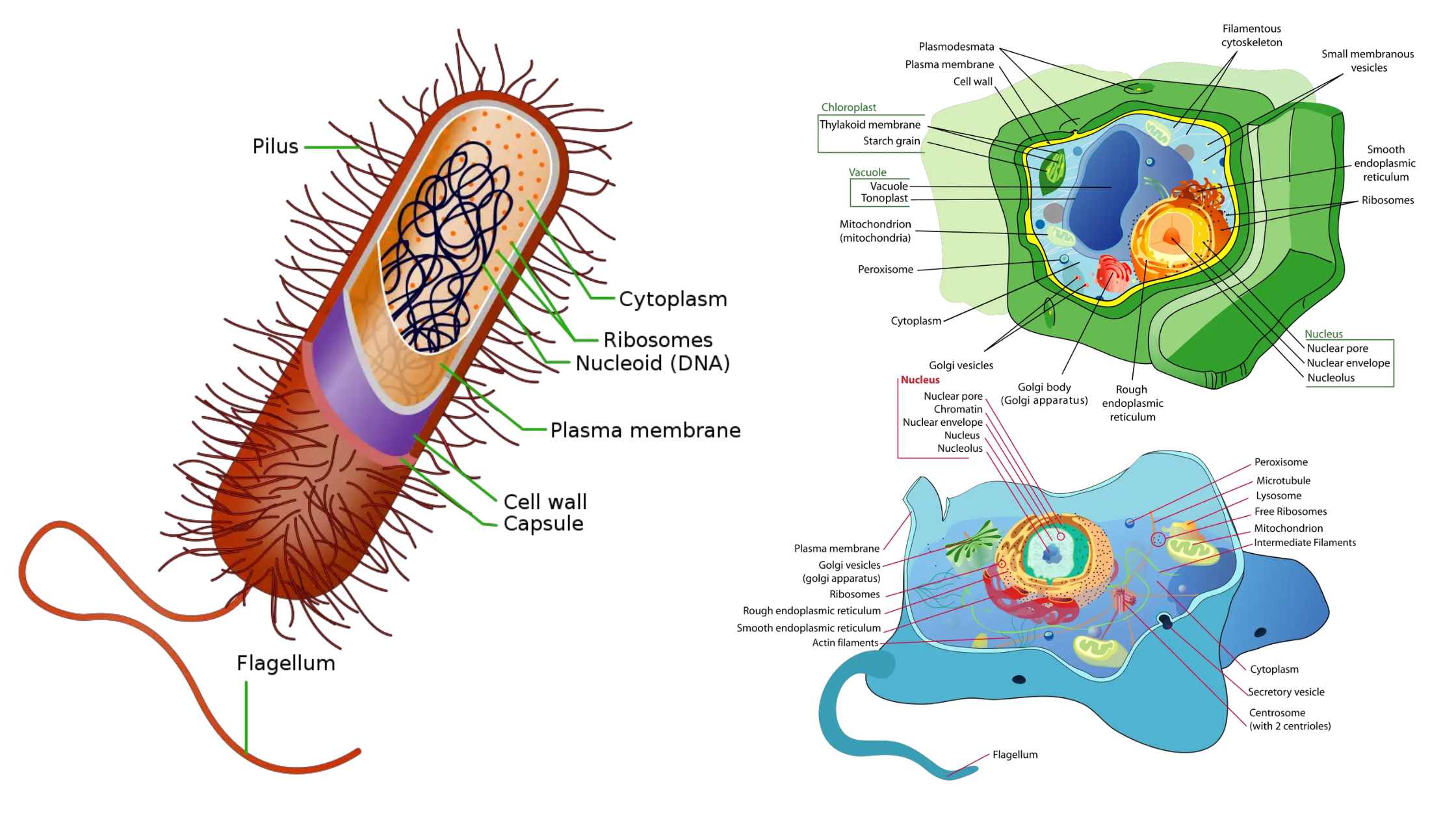
Golgi Body (Golgi Complex) – Structure, Functions
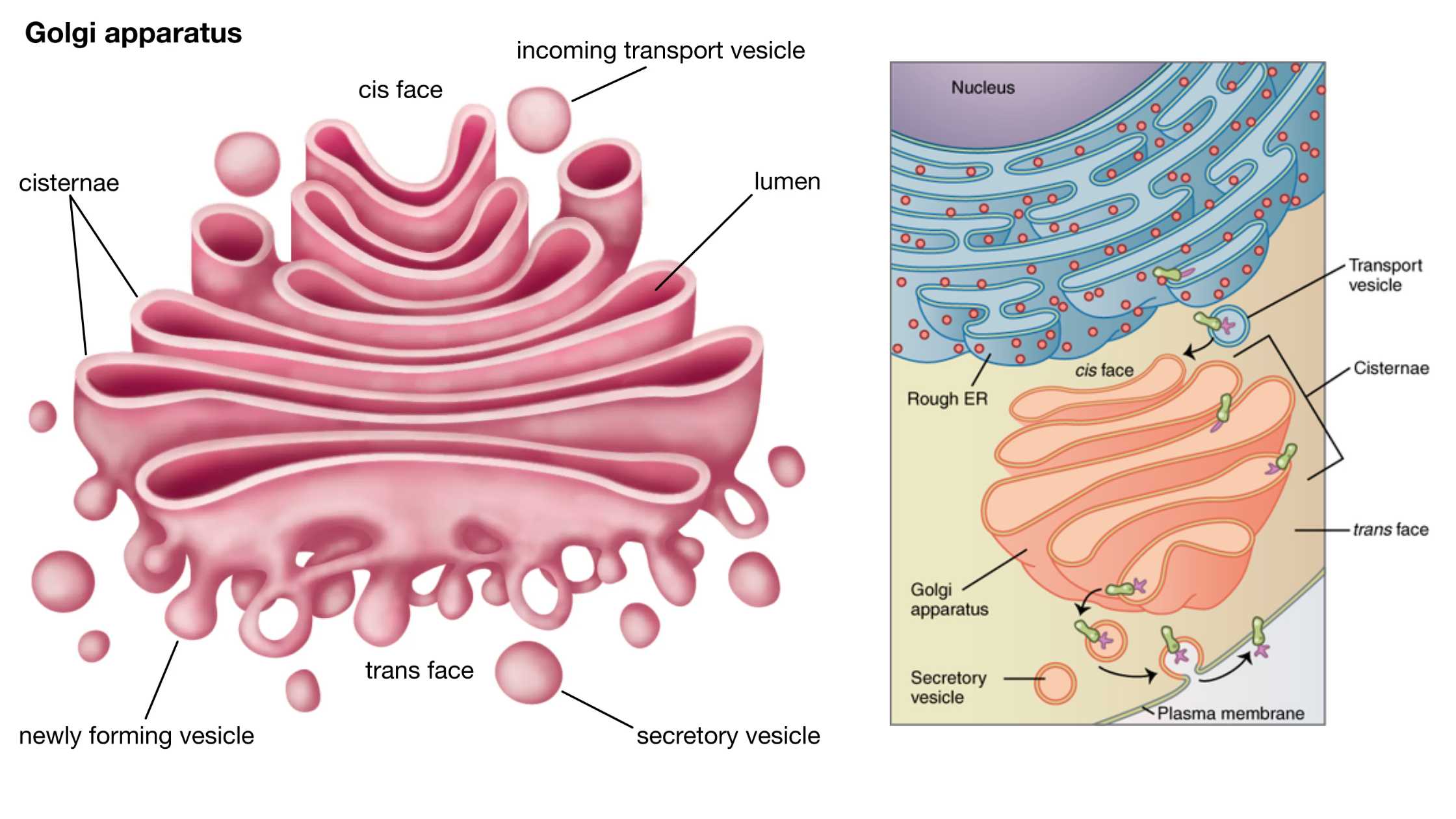
What is Golgi Body (Golgi Complex)? Definition of Golgi Body (Golgi Complex) The Golgi body, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi apparatus, is a membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It functions primarily in the processing, packaging, and distribution of proteins and lipids, which are transported in vesicles to various destinations within … Read more