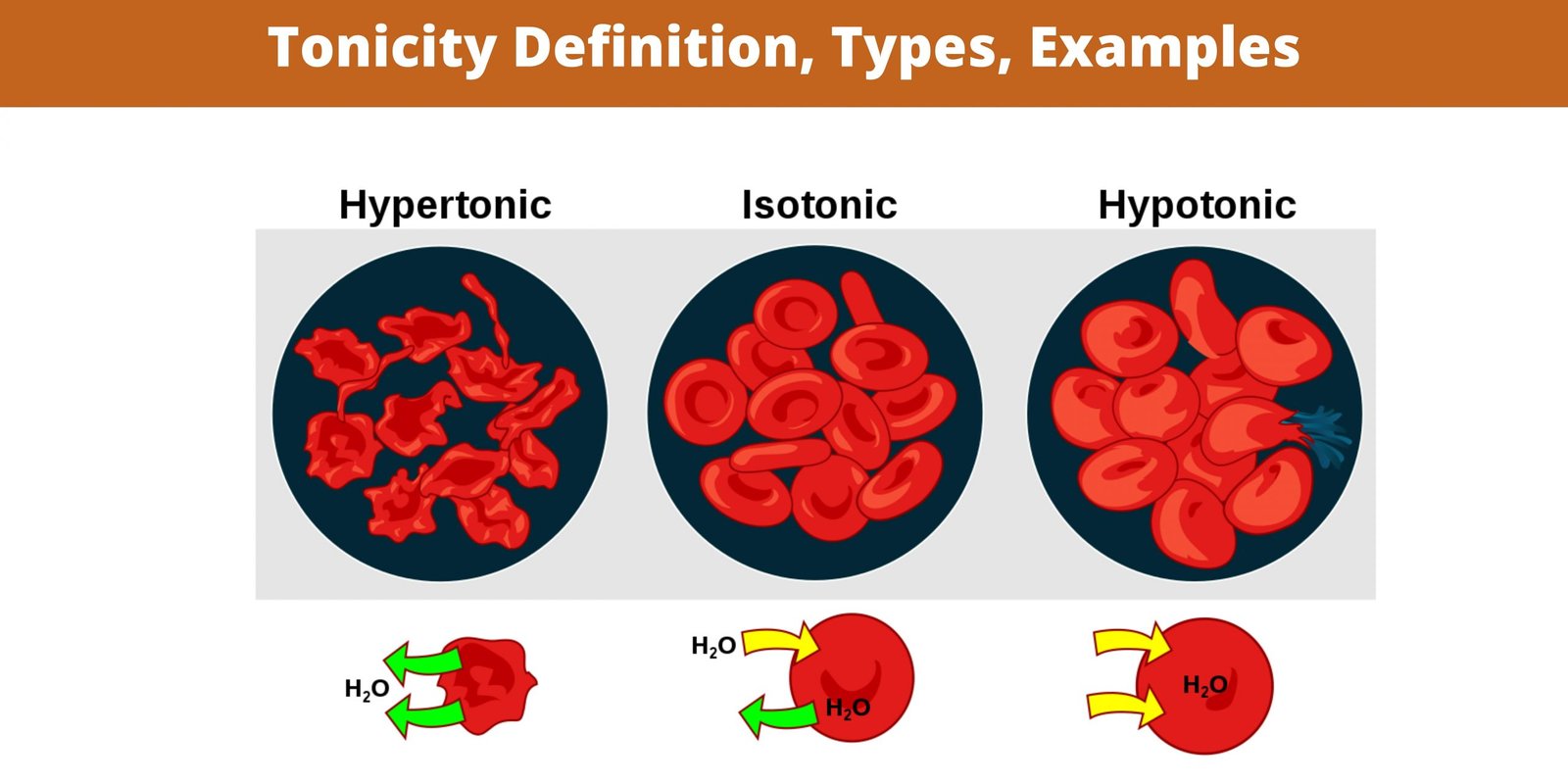
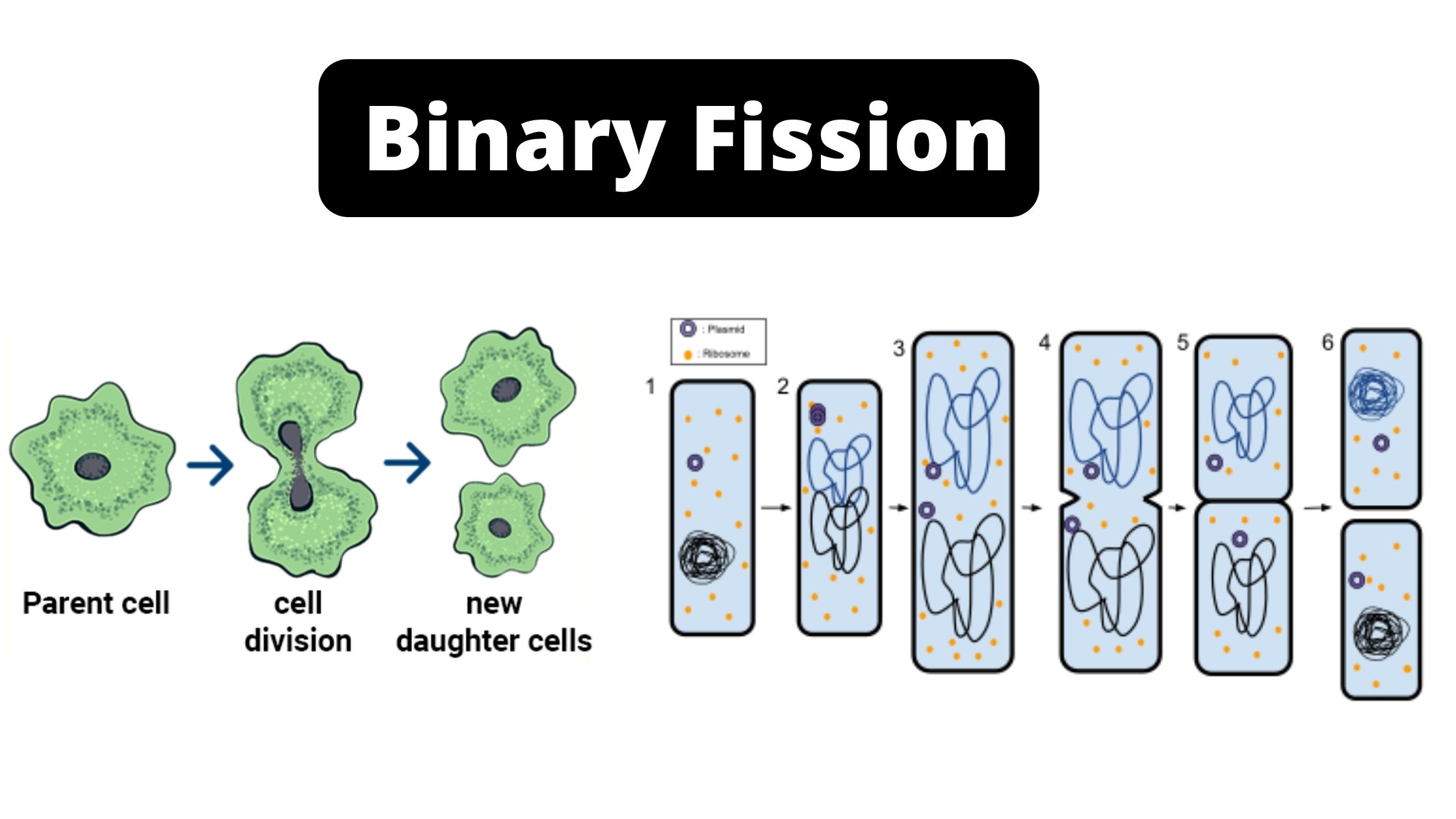
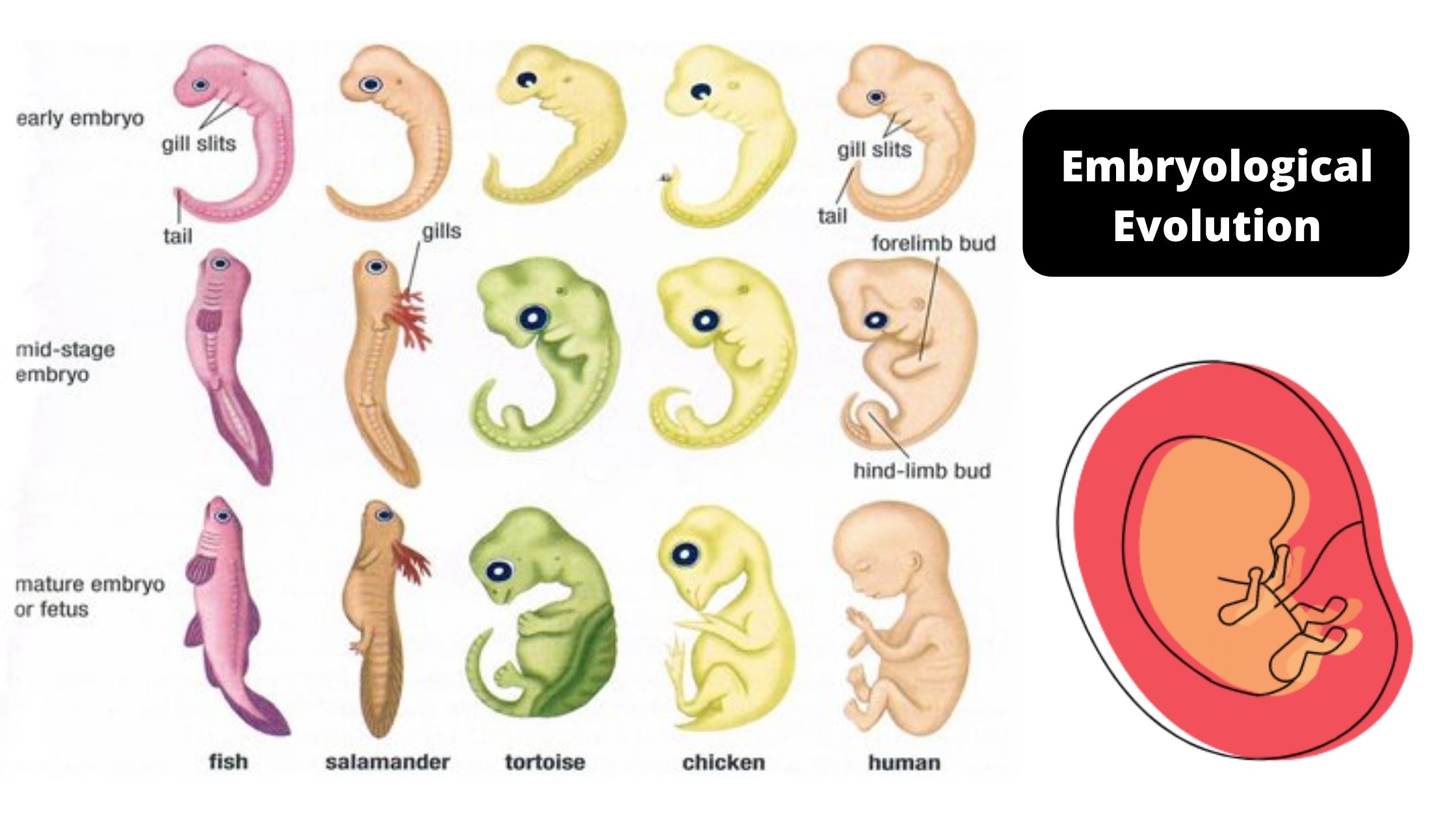
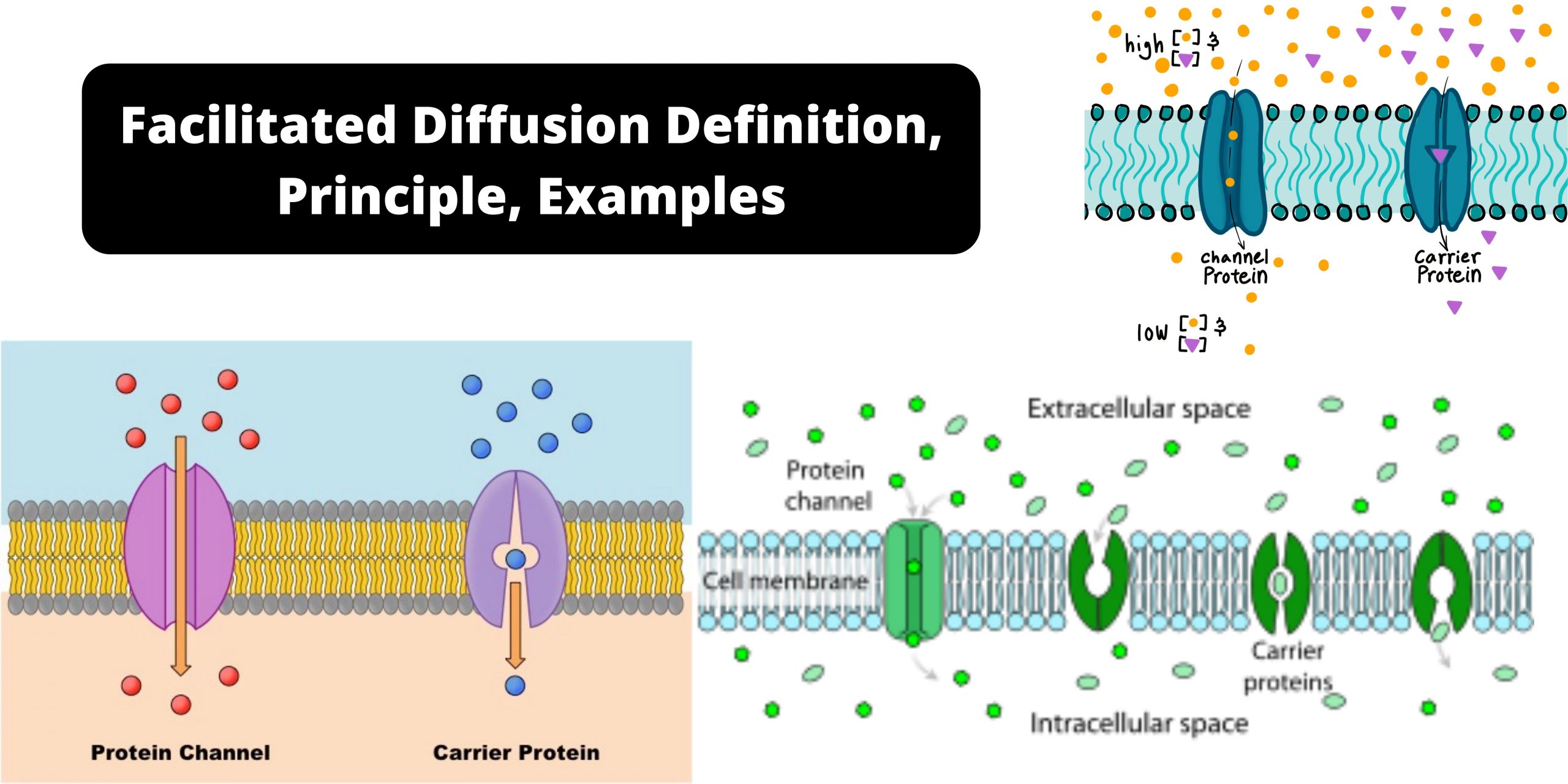
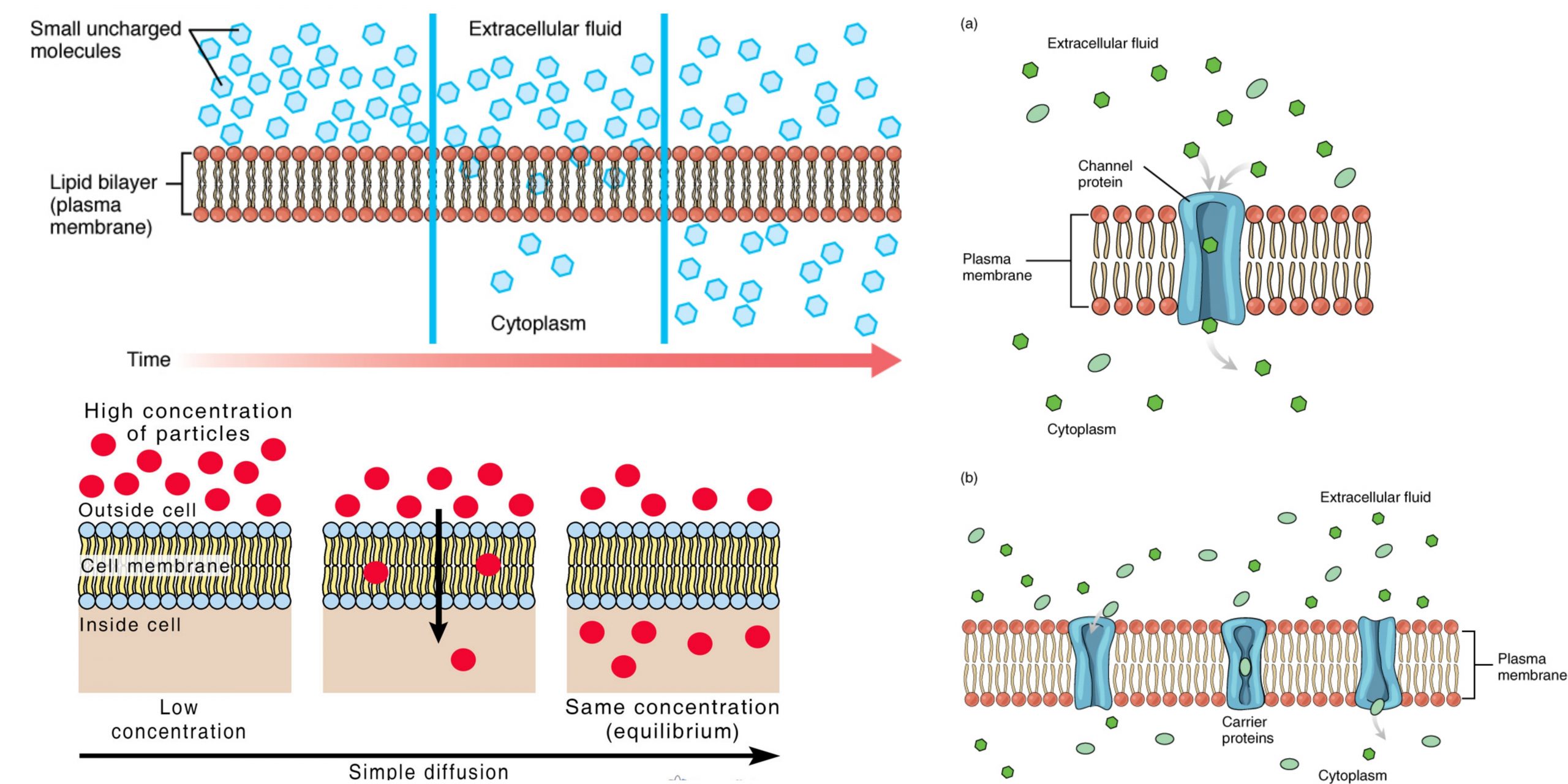
Tonicity – Definition, Types, Examples
To function properly, cells must be kept turgid. To function properly, a well-watered plant will grow and produce fruits and flowers. A plant that is not watered for several days will wilt and eventually die. This happens because water leaves the cell and causes the cell to lose its turgidity. Based on the concentration of … Read more