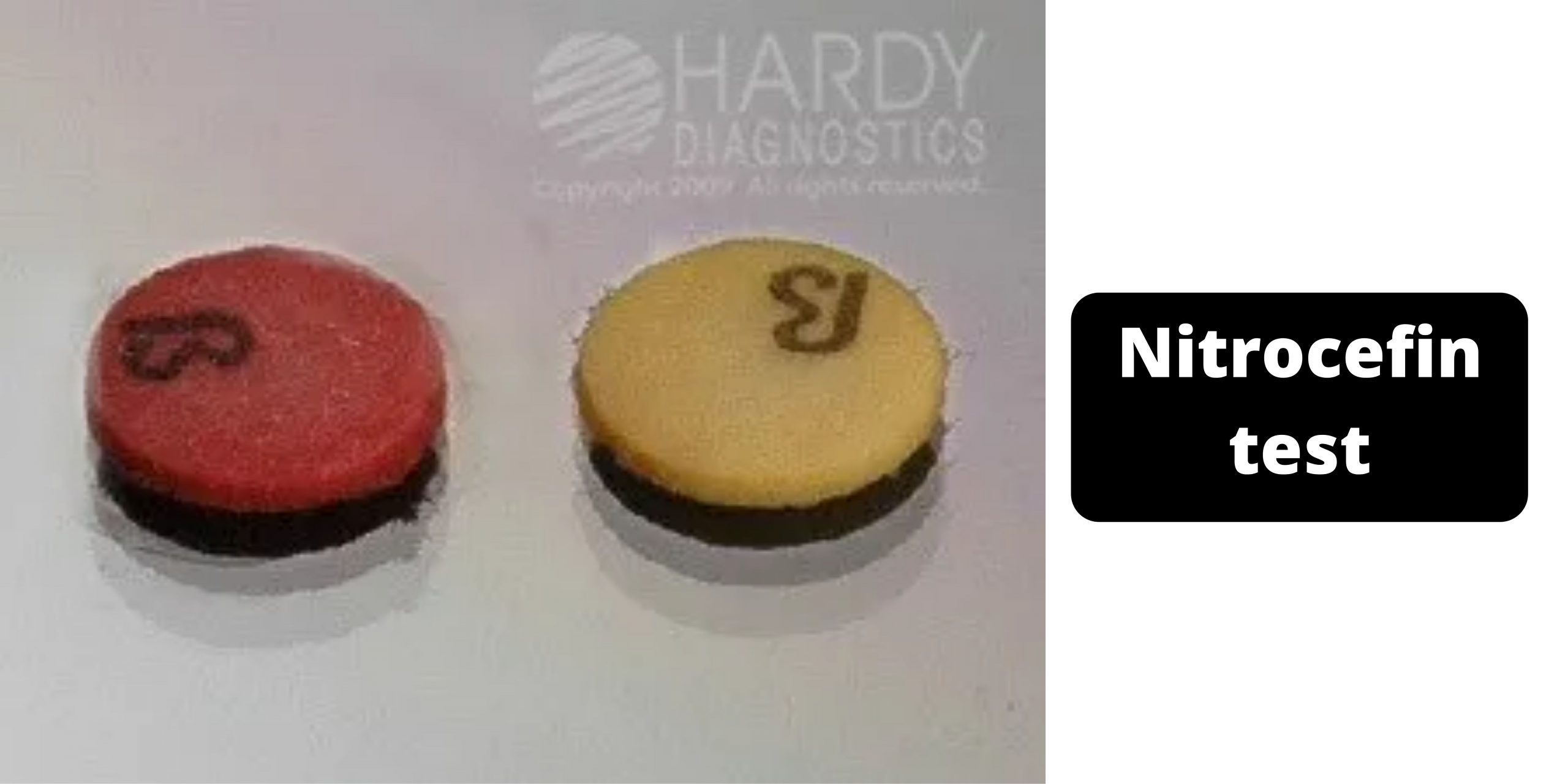
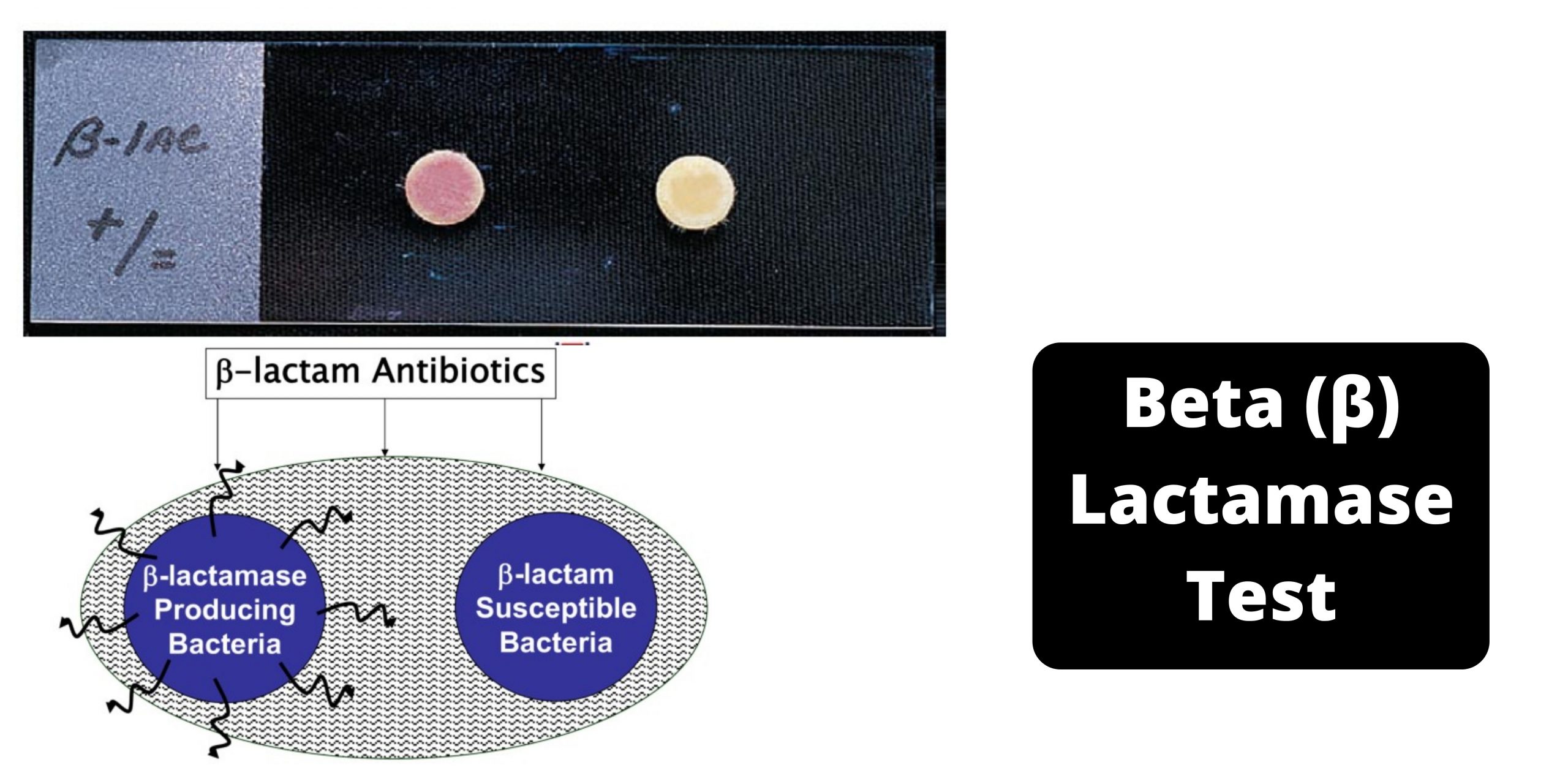
Beta (β) Lactamase Test – Principle, Procedure, Results
Many bacteria produce a group of enzymes known as beta-lactamases that are mediated through genes in plasmids or the chromosomes. Beta-lactamase can be a constant process or it may be triggered through contact with antimicrobials. Beta-lactamases hydrolyze (and consequently inhibit) the beta-lactam ring of many Cephalosporins as well as penicillins. Beta-Lactamase Test is a rapid test to determine the presence of beta-lactamase , an enzyme that is produced by the strains from Staphylococcus aureus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Branhamella catarrhalis as well as Haemophilus influenzae.