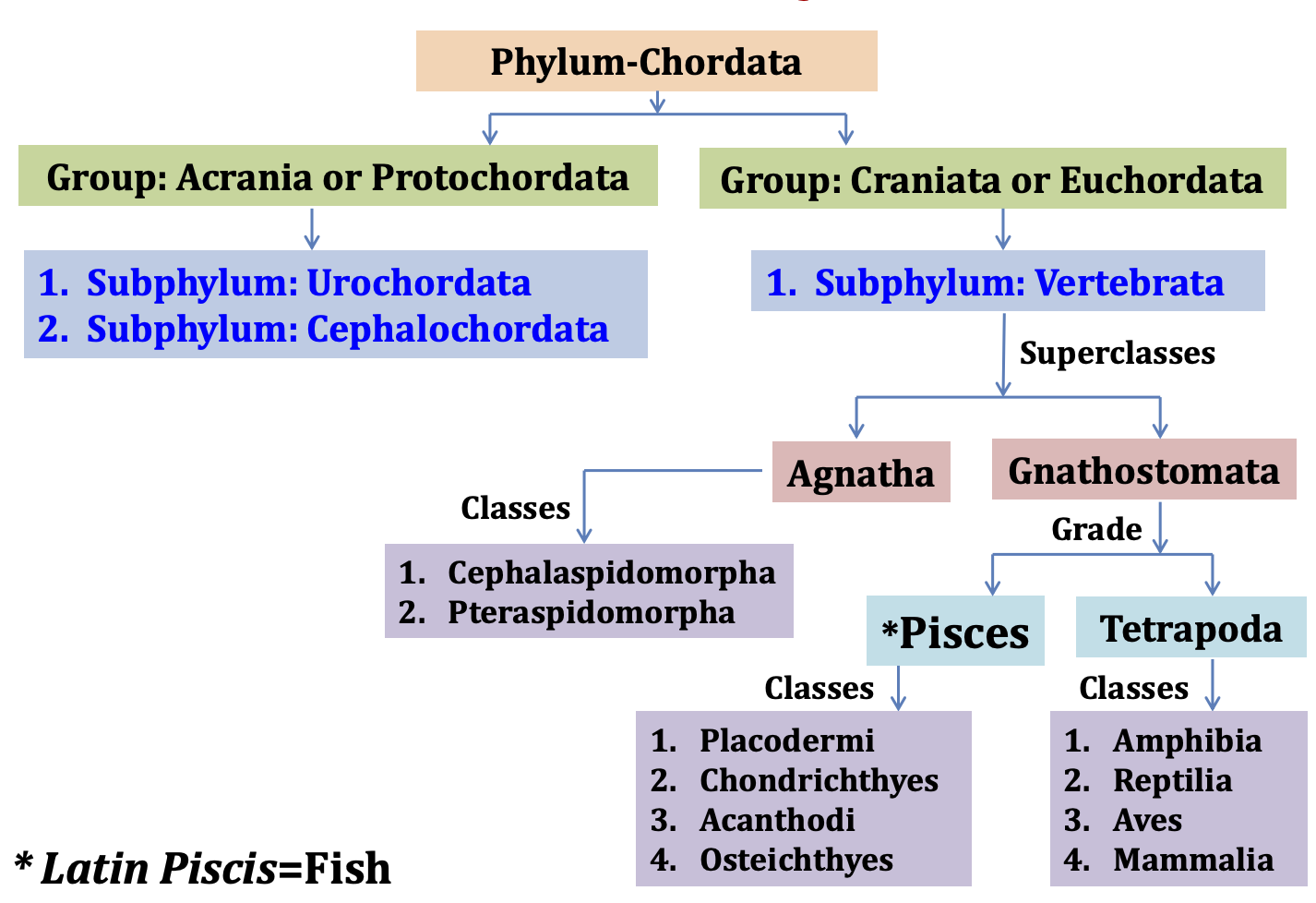
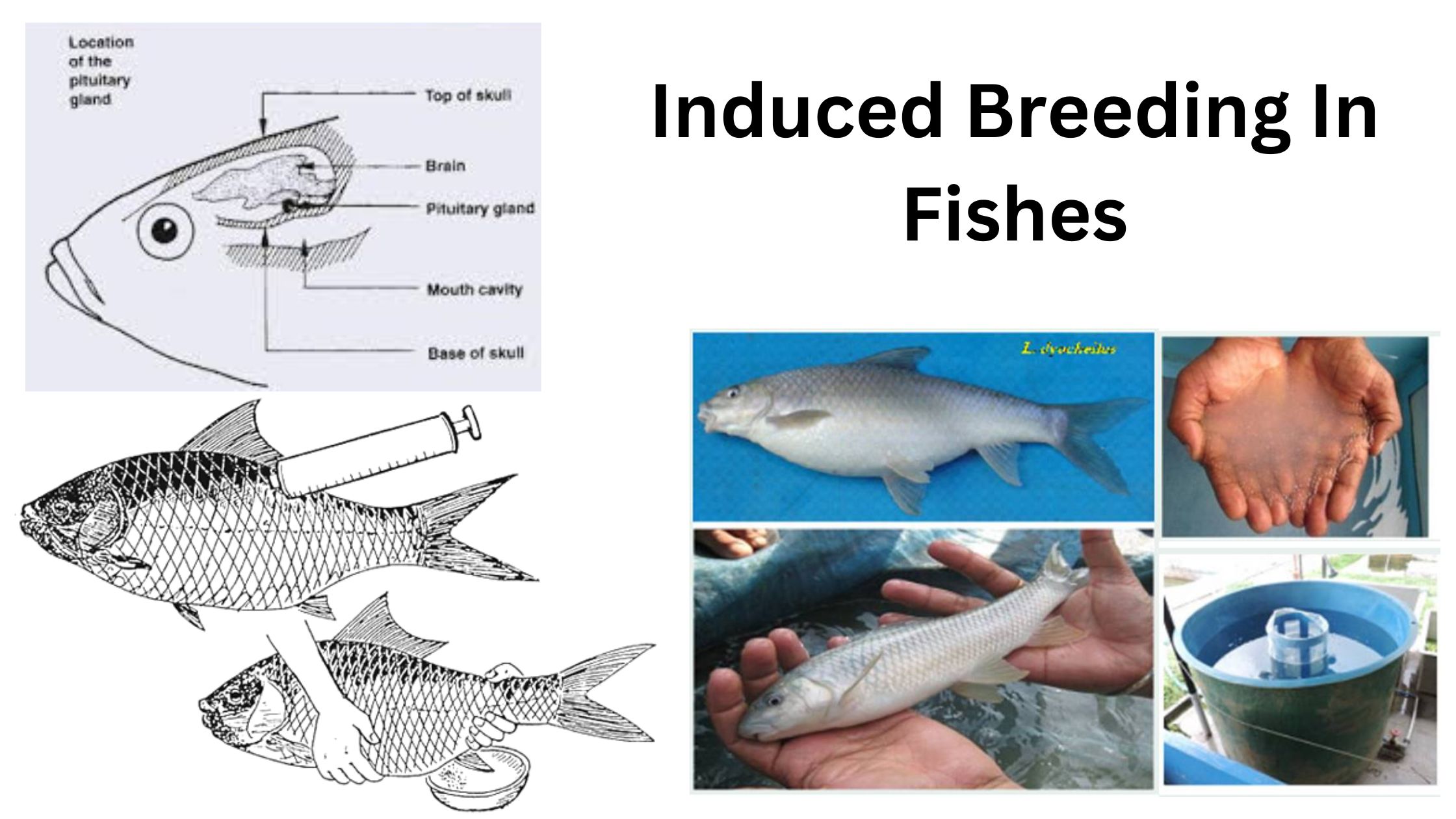
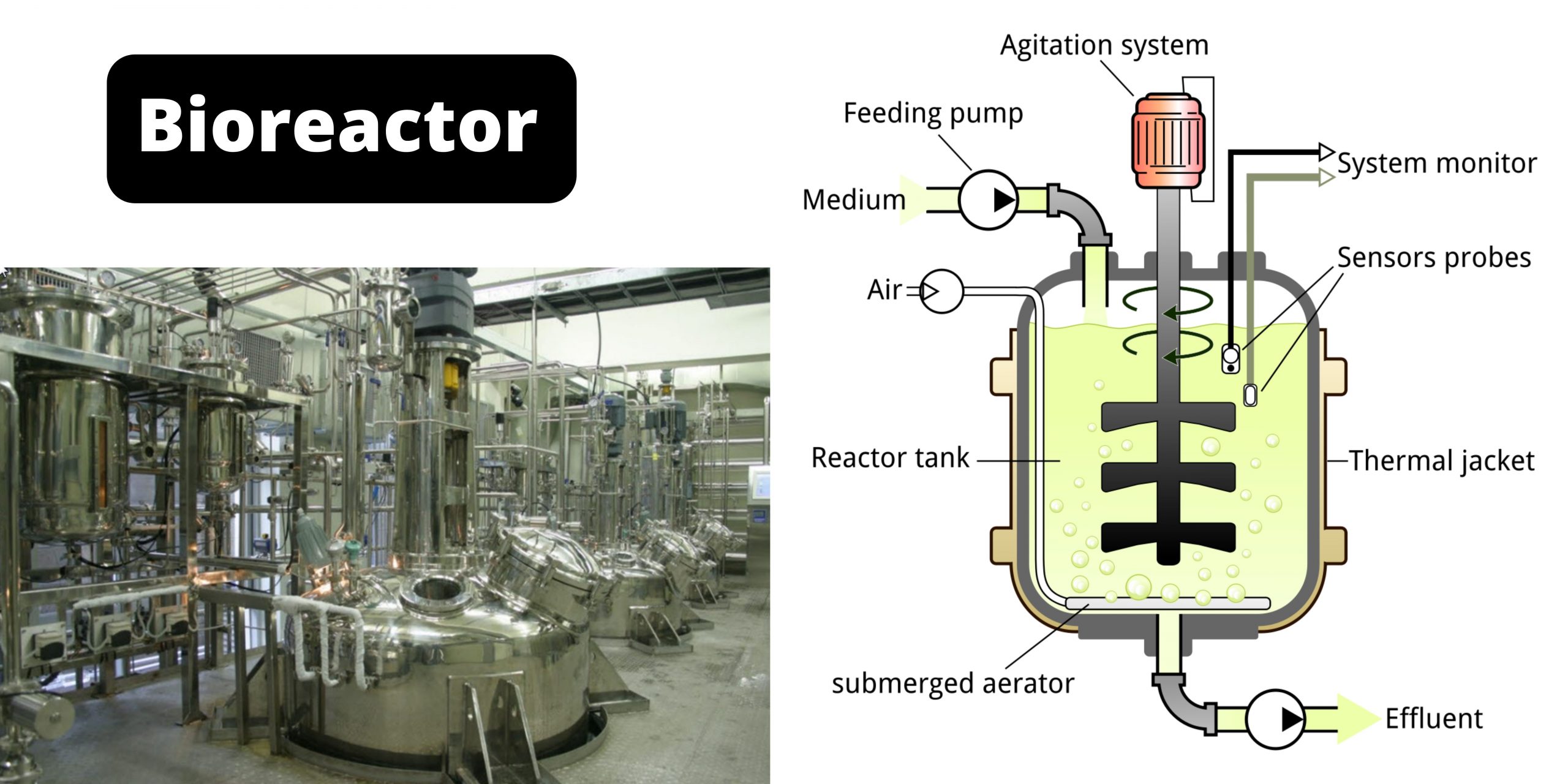
Classification of Fish (pisces) – Systematic Classification and Based on feeding habit, habitat and manner of reproduction
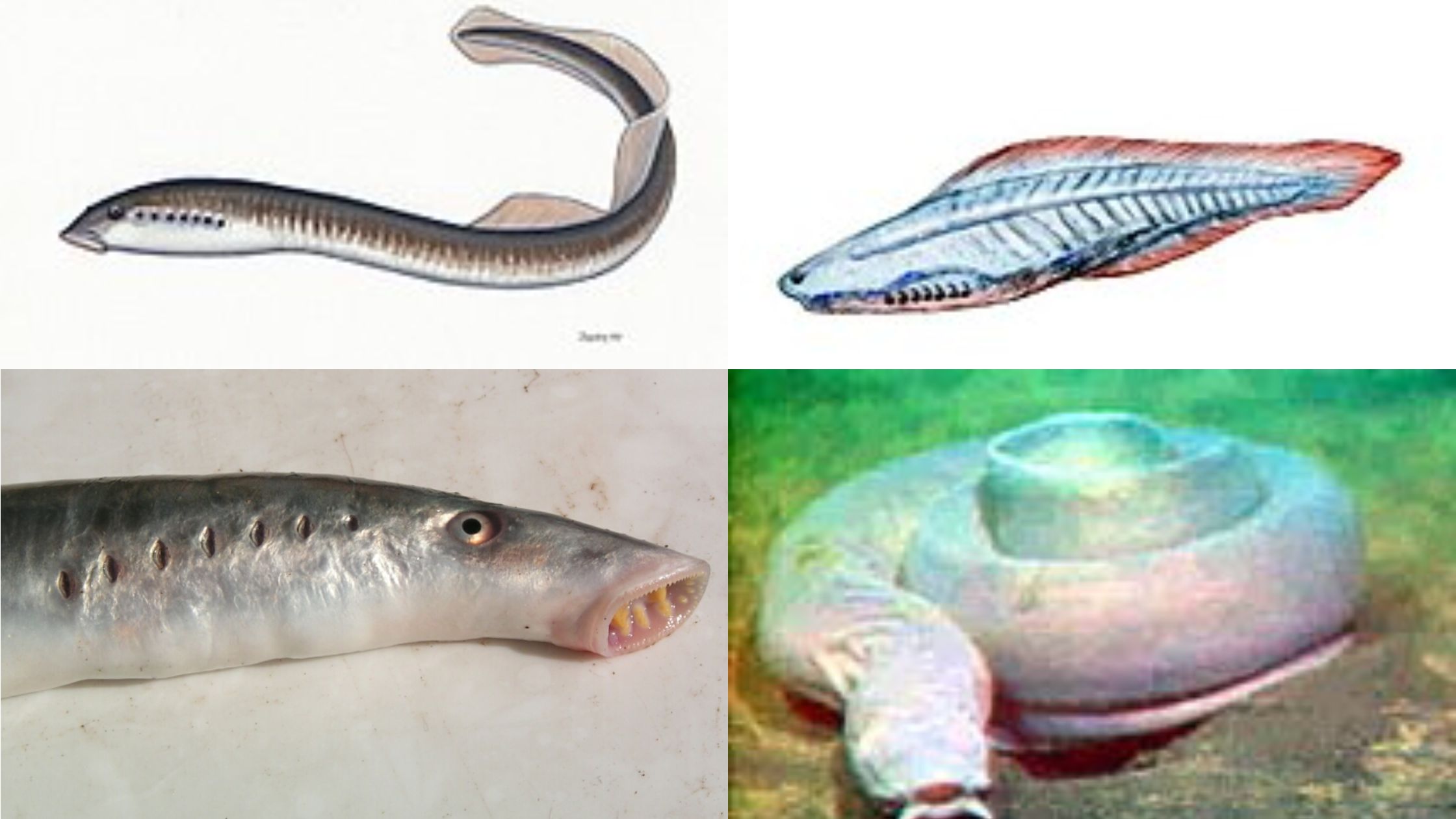
A fish is an aquatic vertebrate which is mostly characterized by the presence of gills throughout life, a streamlined body, and paired as well as unpaired fins which helps in swimming. It is the group that comprises jawless forms like hagfish and lampreys, cartilaginous fishes like sharks and rays, and the bony fishes which is … Read more