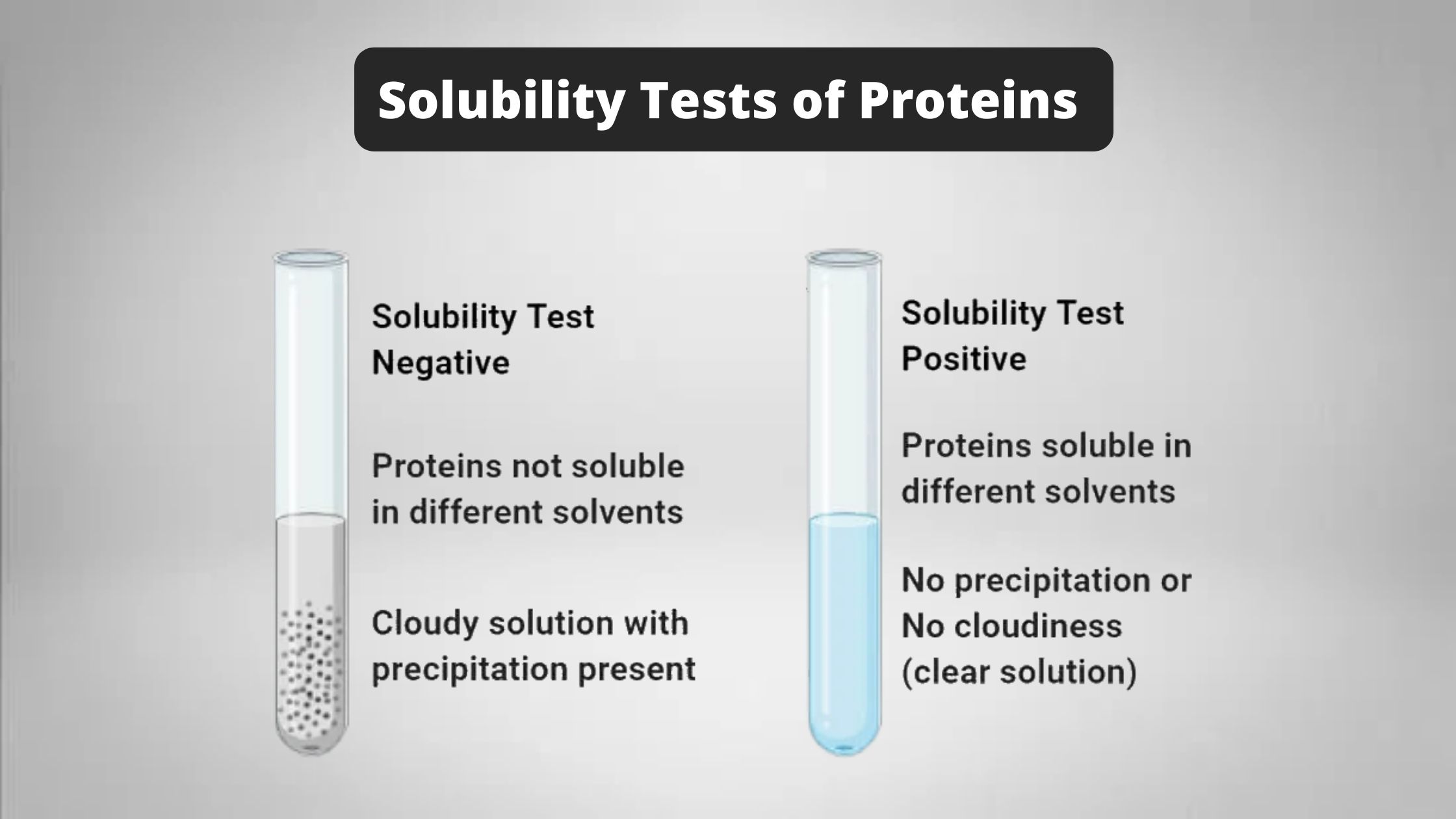
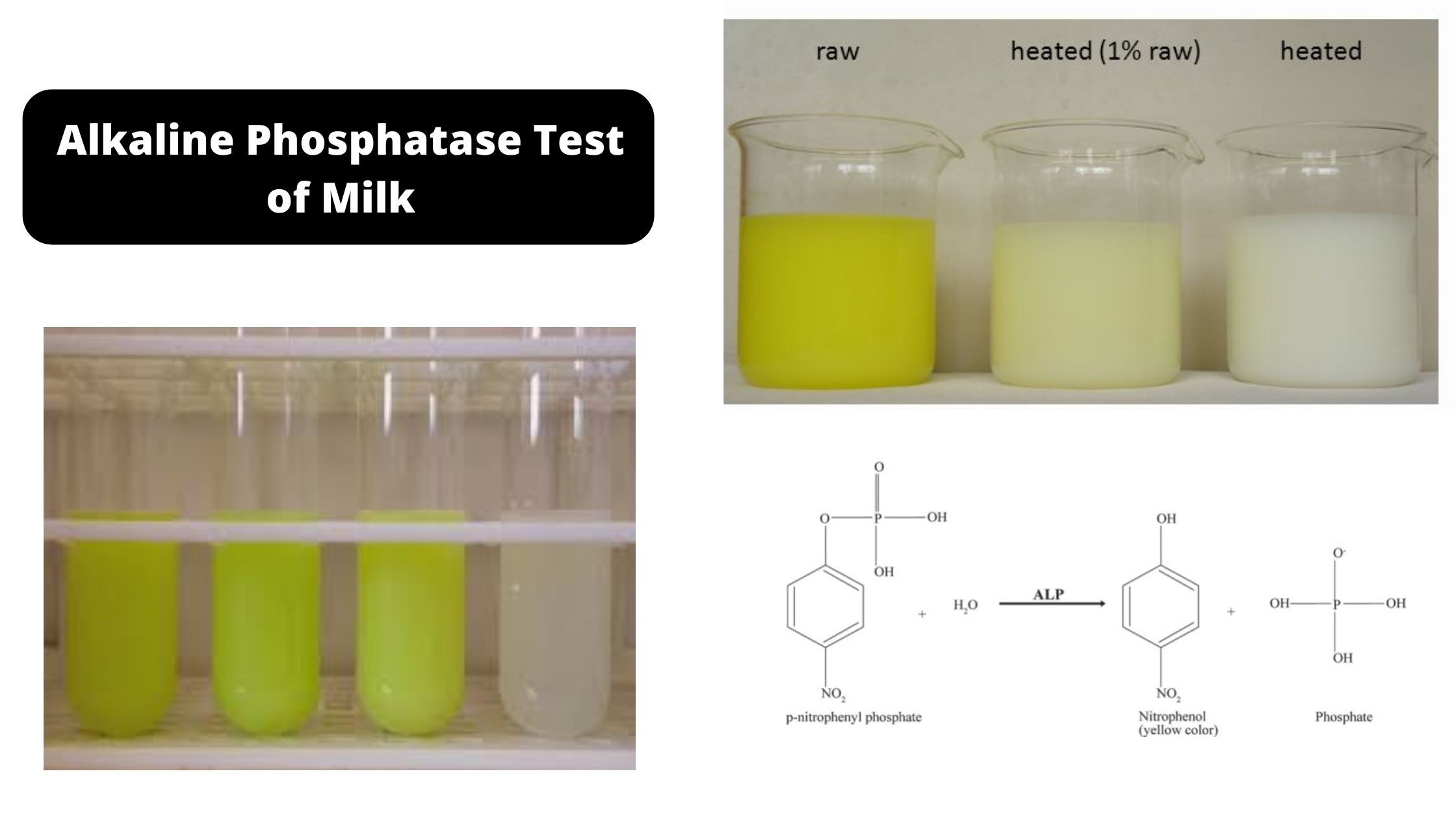
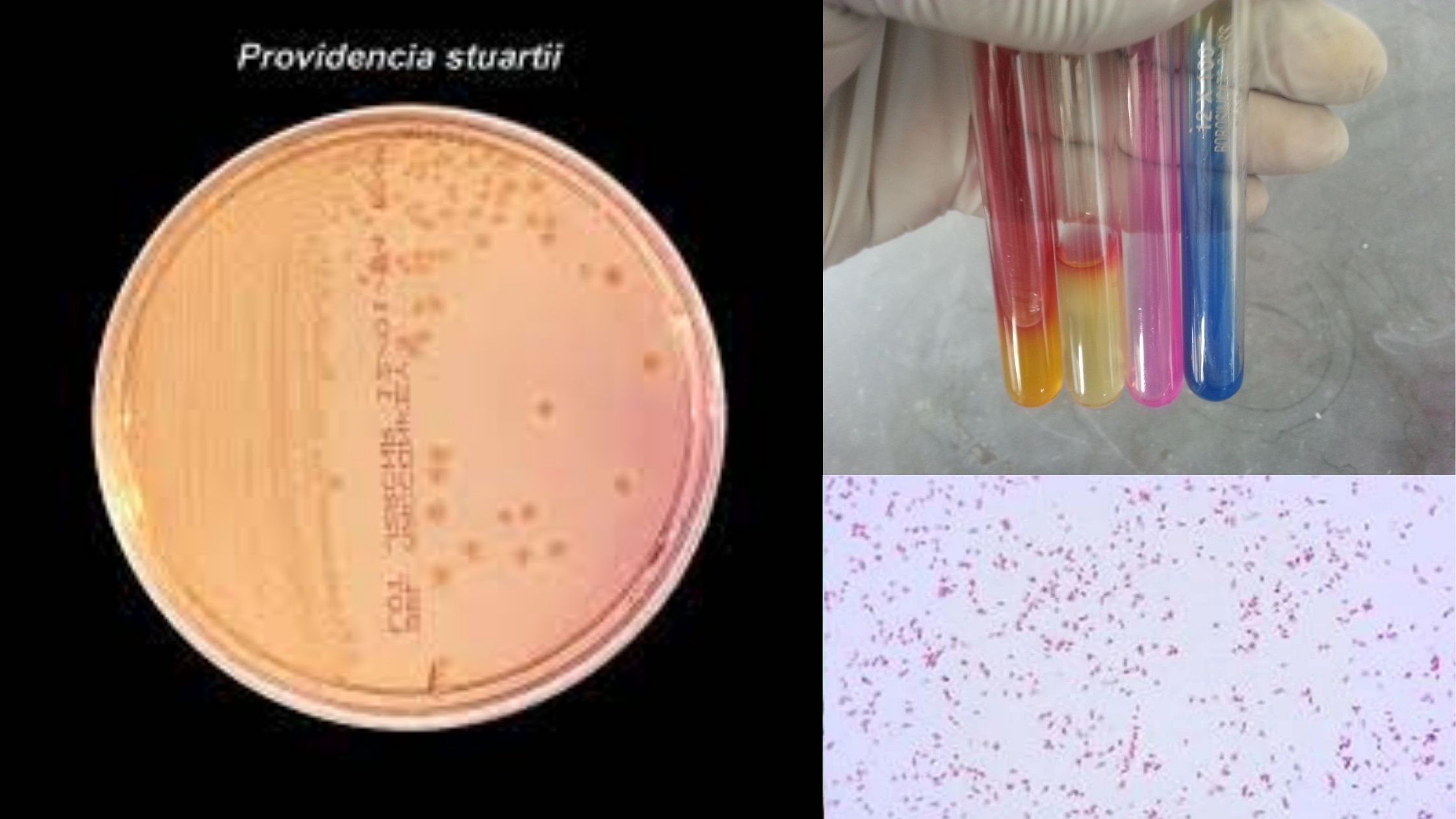
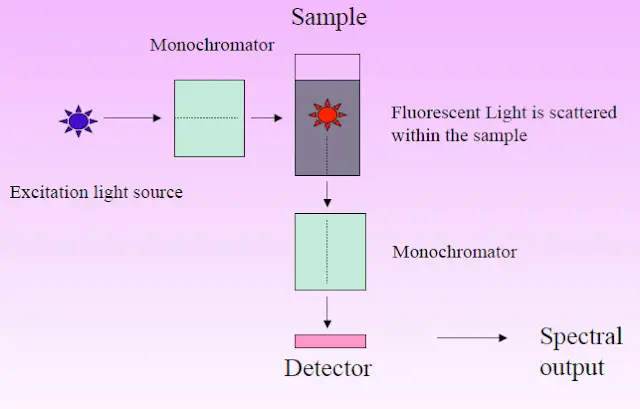
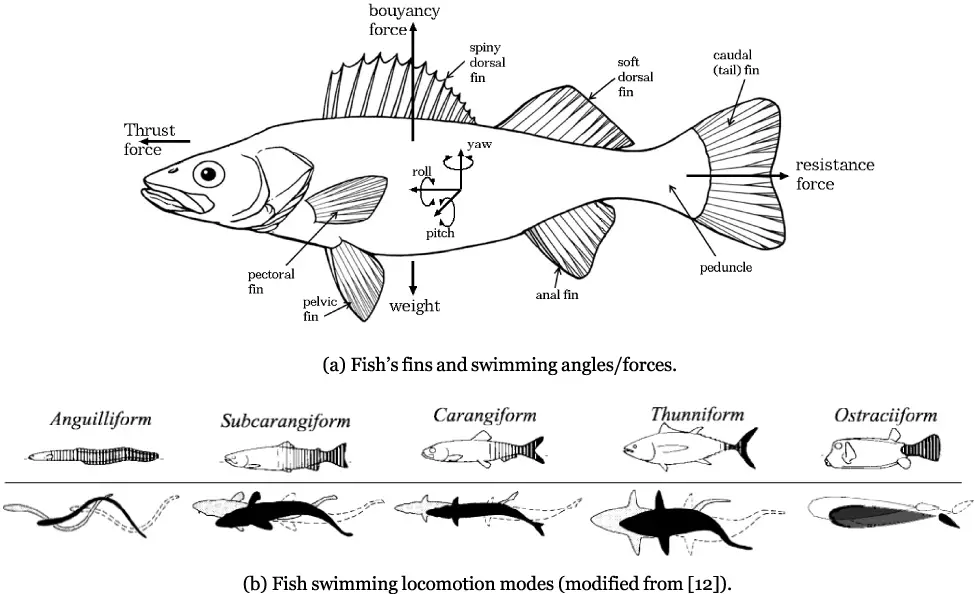
Rapid Furfural Test for Glucose and Fructose – Principle, Procedure, Result
Rapid Furfural Test is a qualitative chemical test used to differentiate ketohexoses from aldohexoses based on the rate of dehydration reaction. It is mainly used for the identification of fructose and other ketose sugars in the presence of aldose sugars like glucose. It is based on the principle that ketohexoses are dehydrated rapidly when heated … Read more