Prophase I – Definition, Stages, Importance
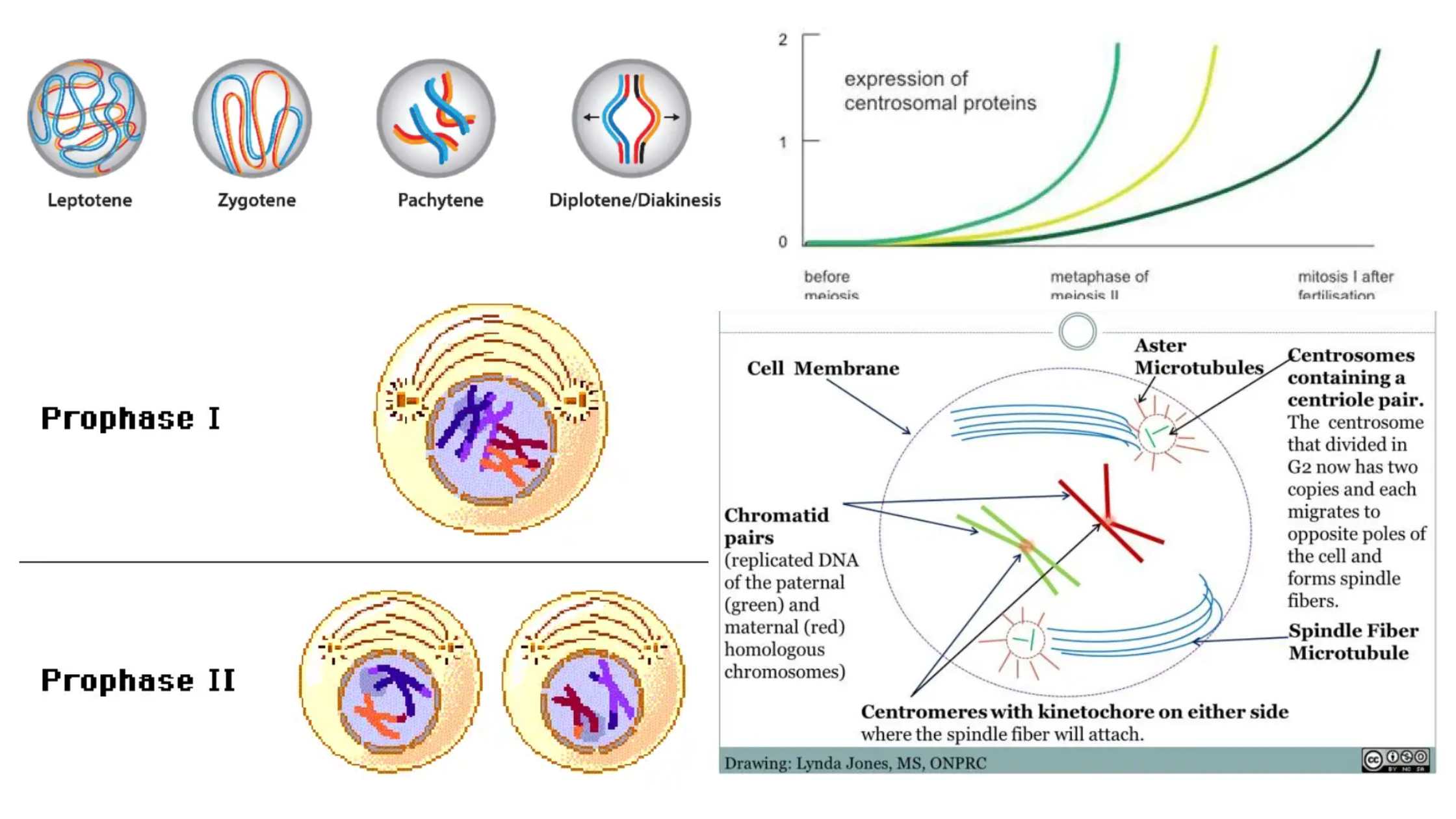
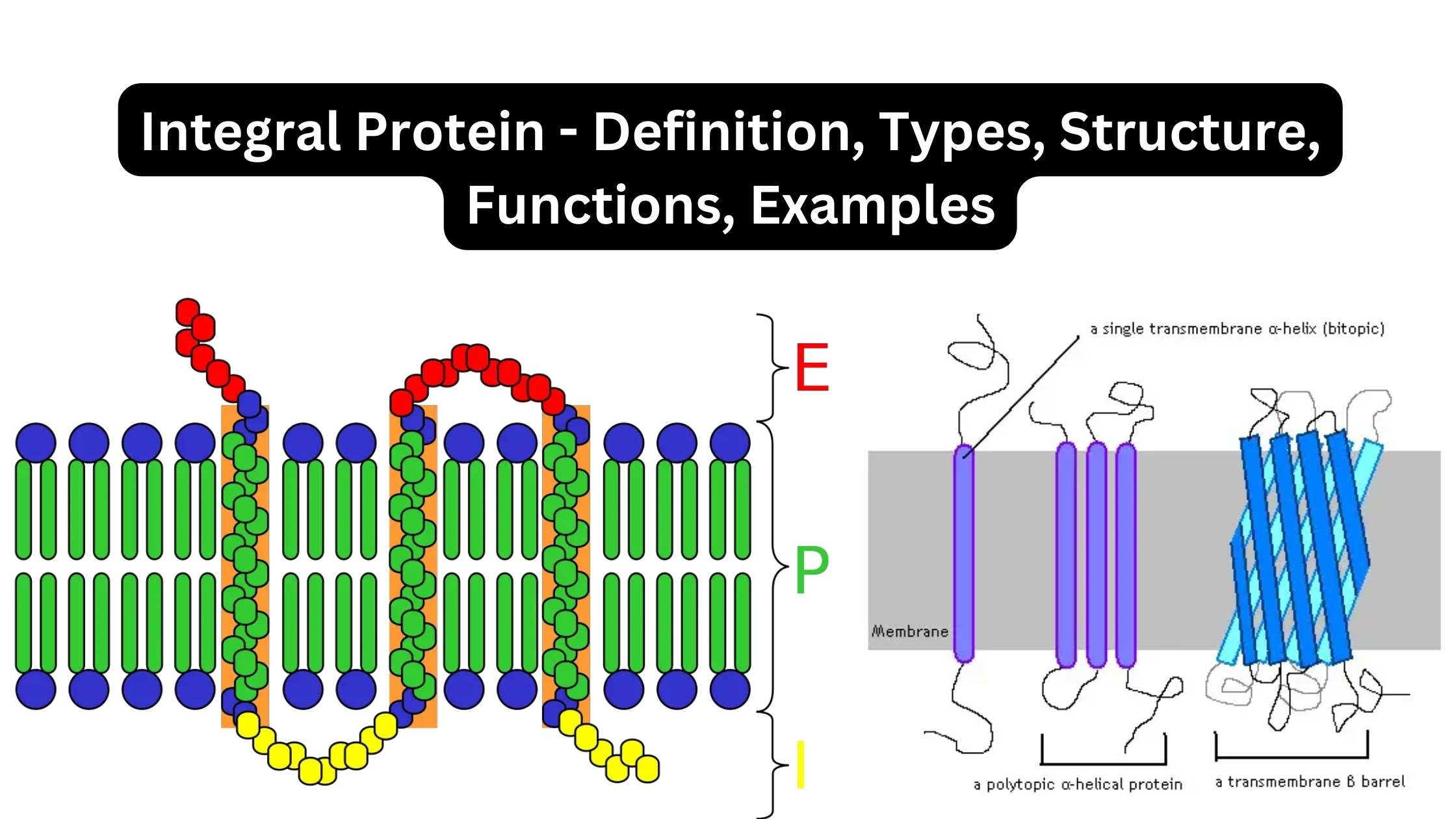
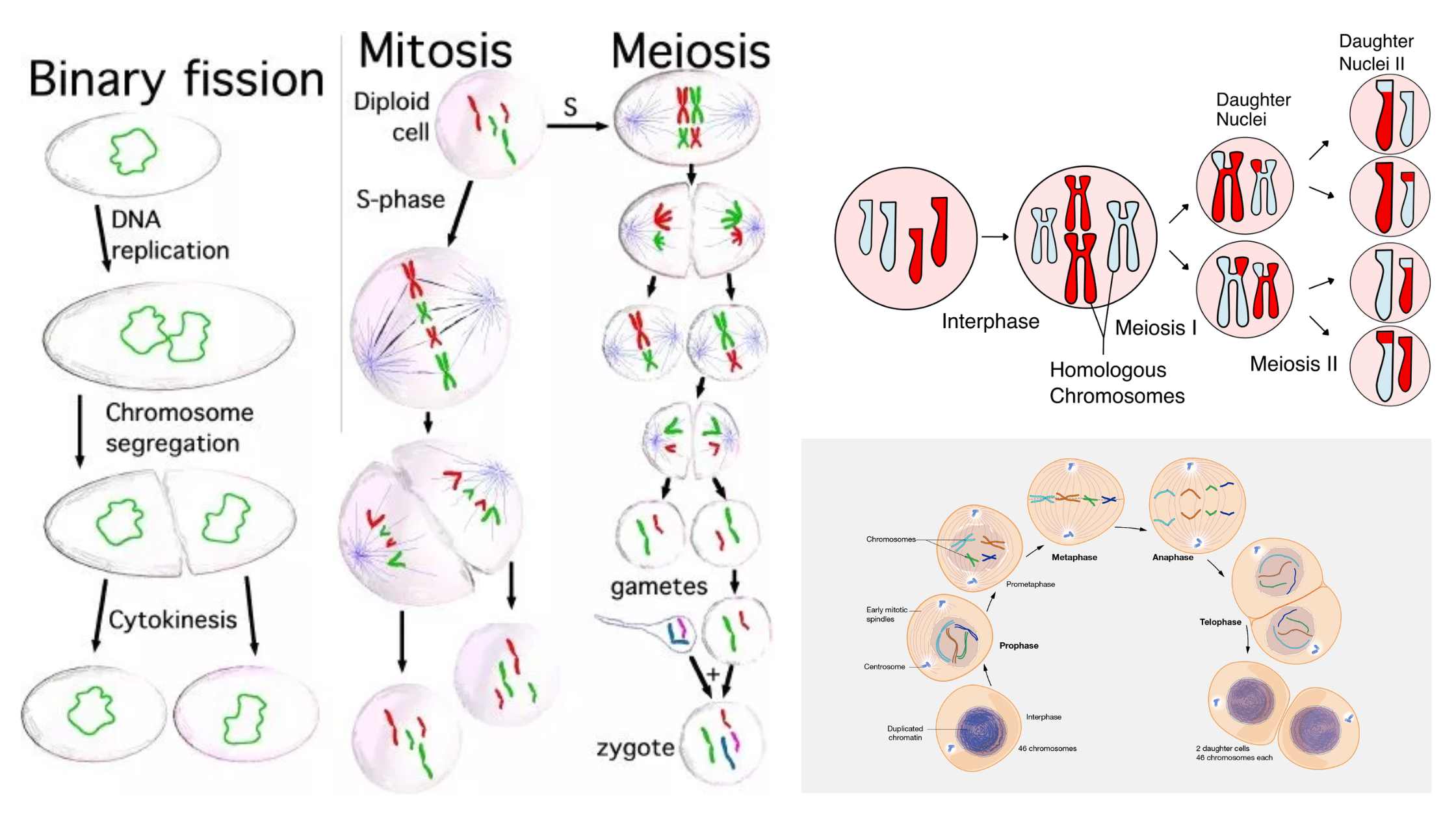
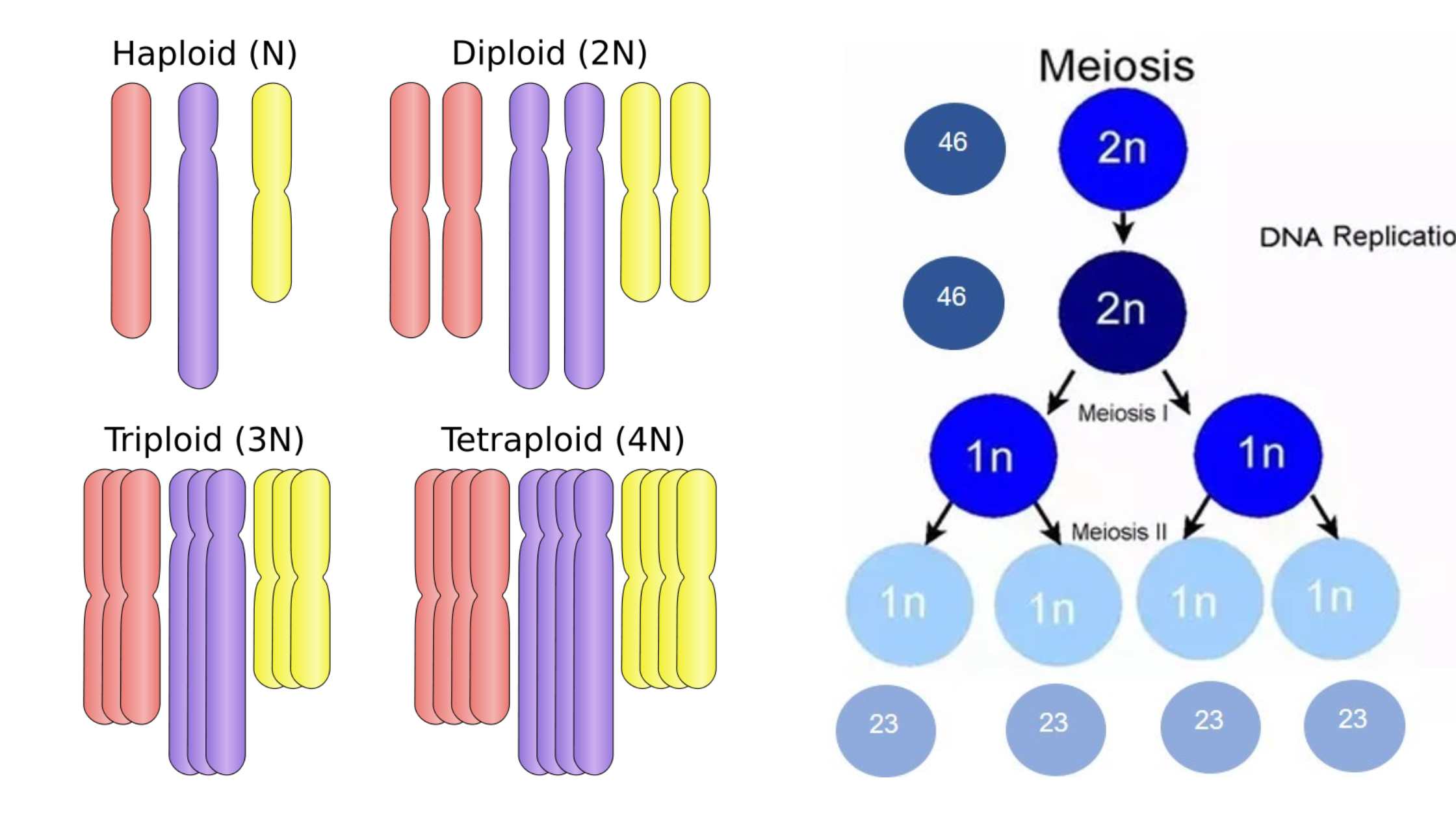
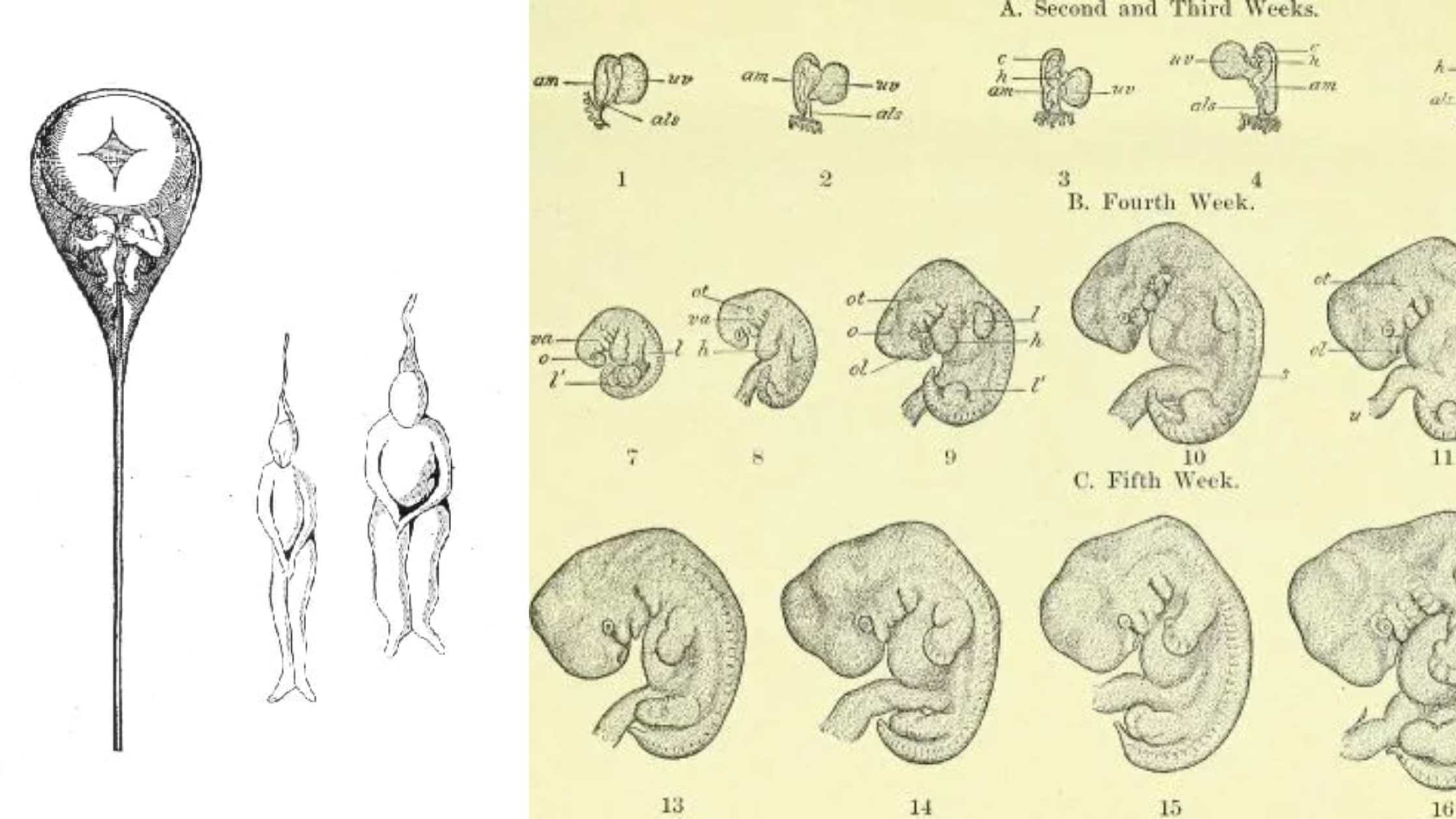
What is Prophase I? Definition of Prophase I Prophase I is the initial stage of meiosis I, characterized by the exchange of genetic material between paired homologous chromosomes through homologous recombination, leading to increased genetic variation. This phase encompasses five sub-stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis. Prophase I Glossary of Terms By understanding these … Read more