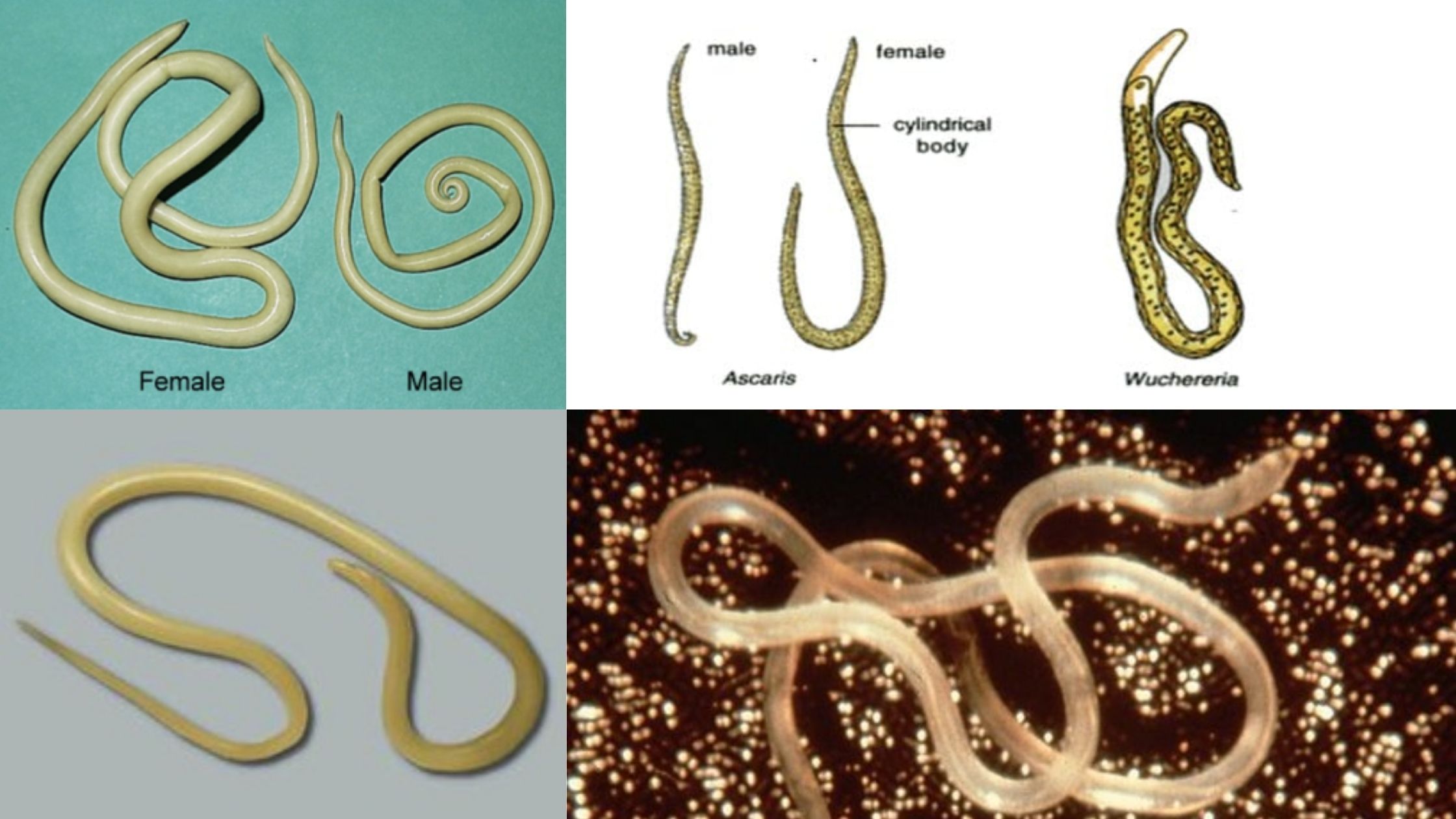
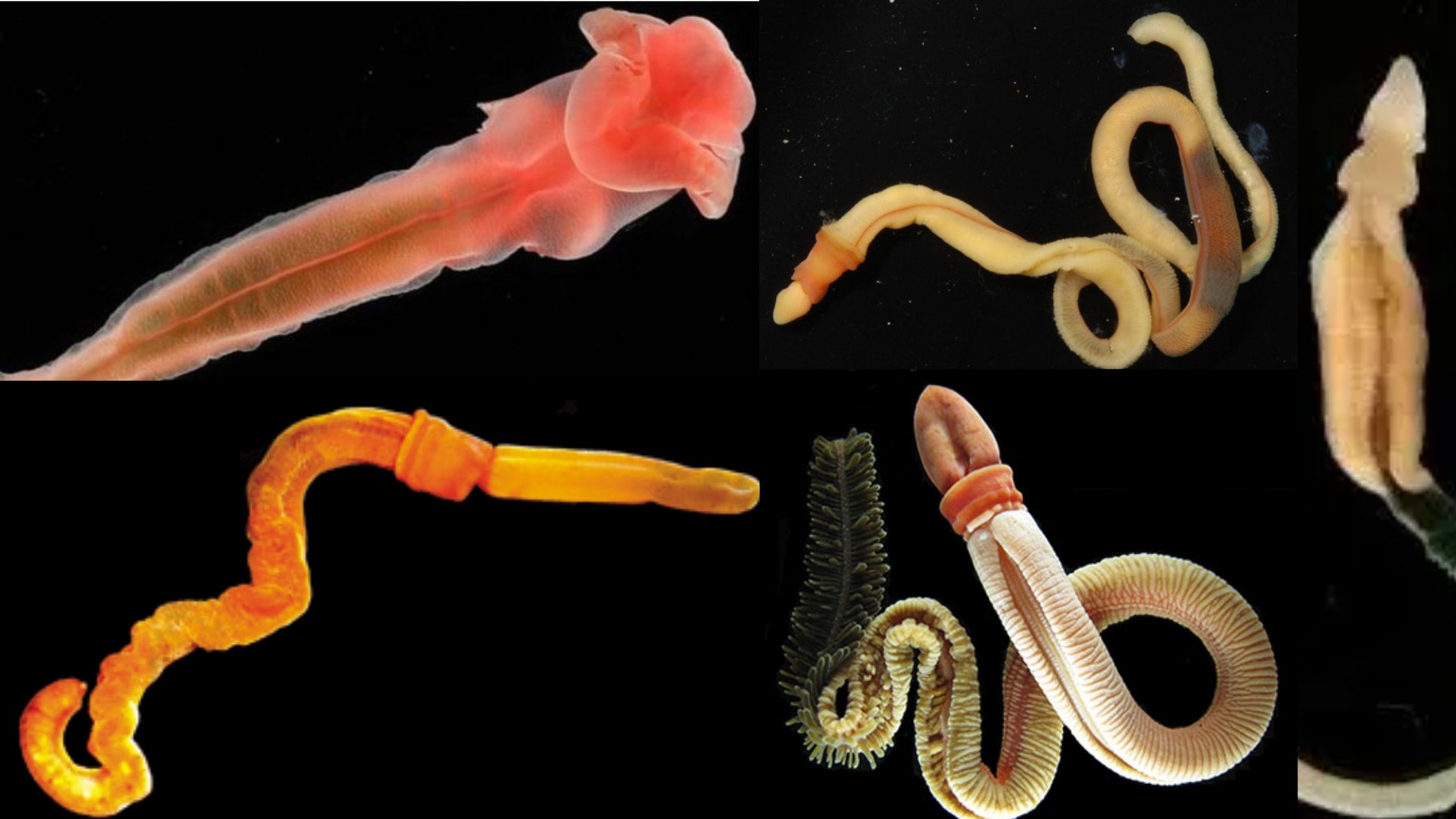
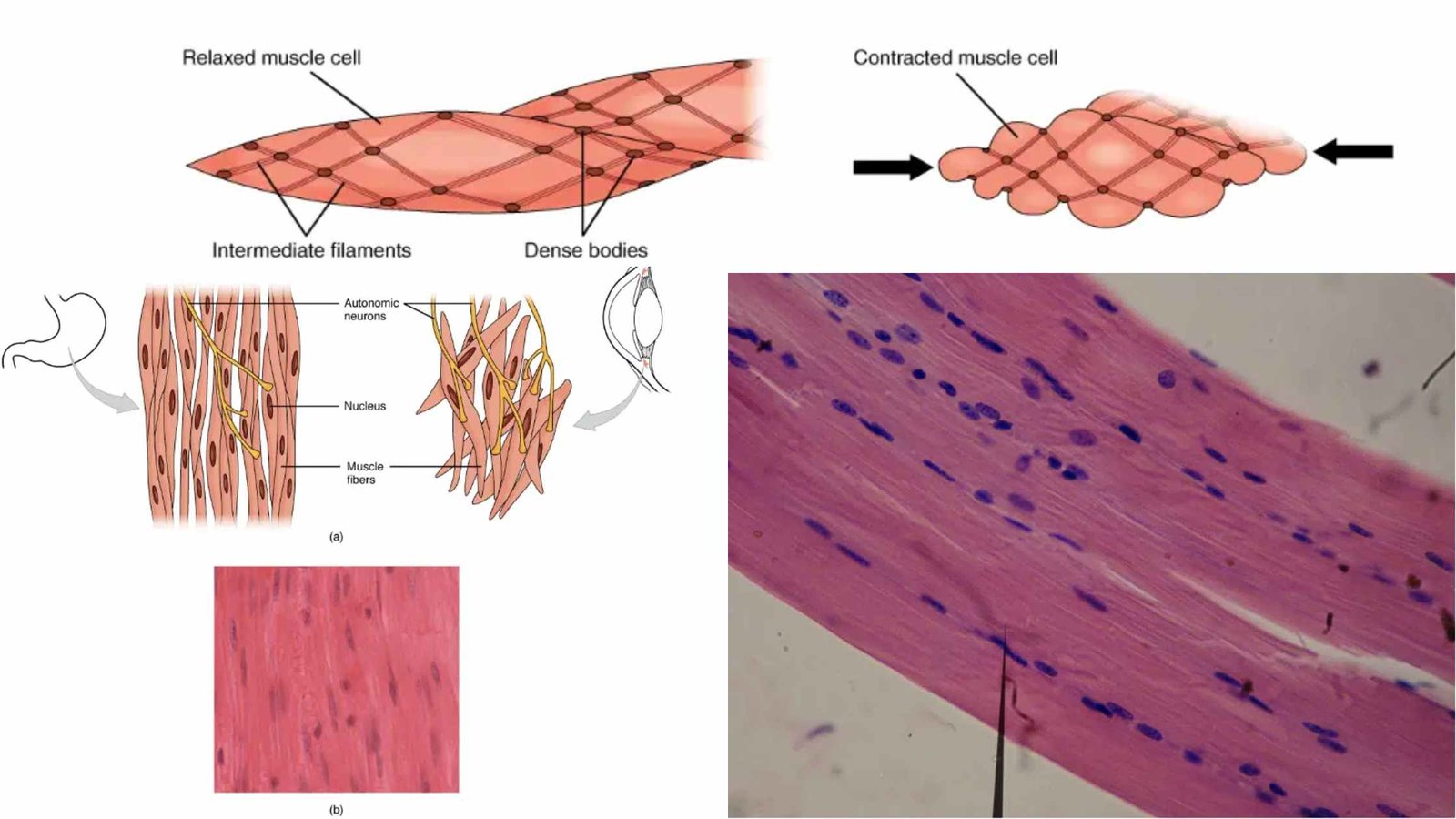
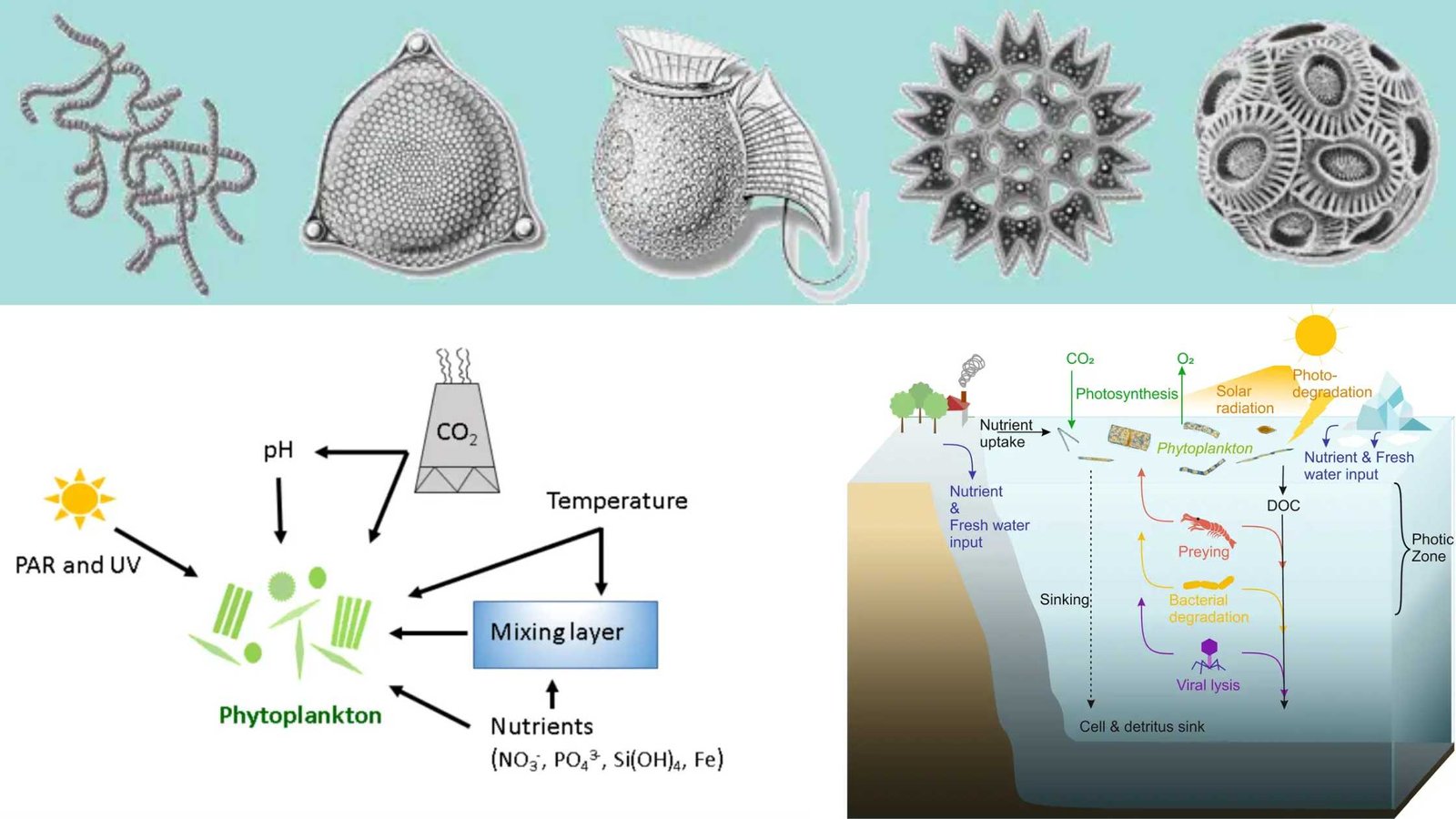
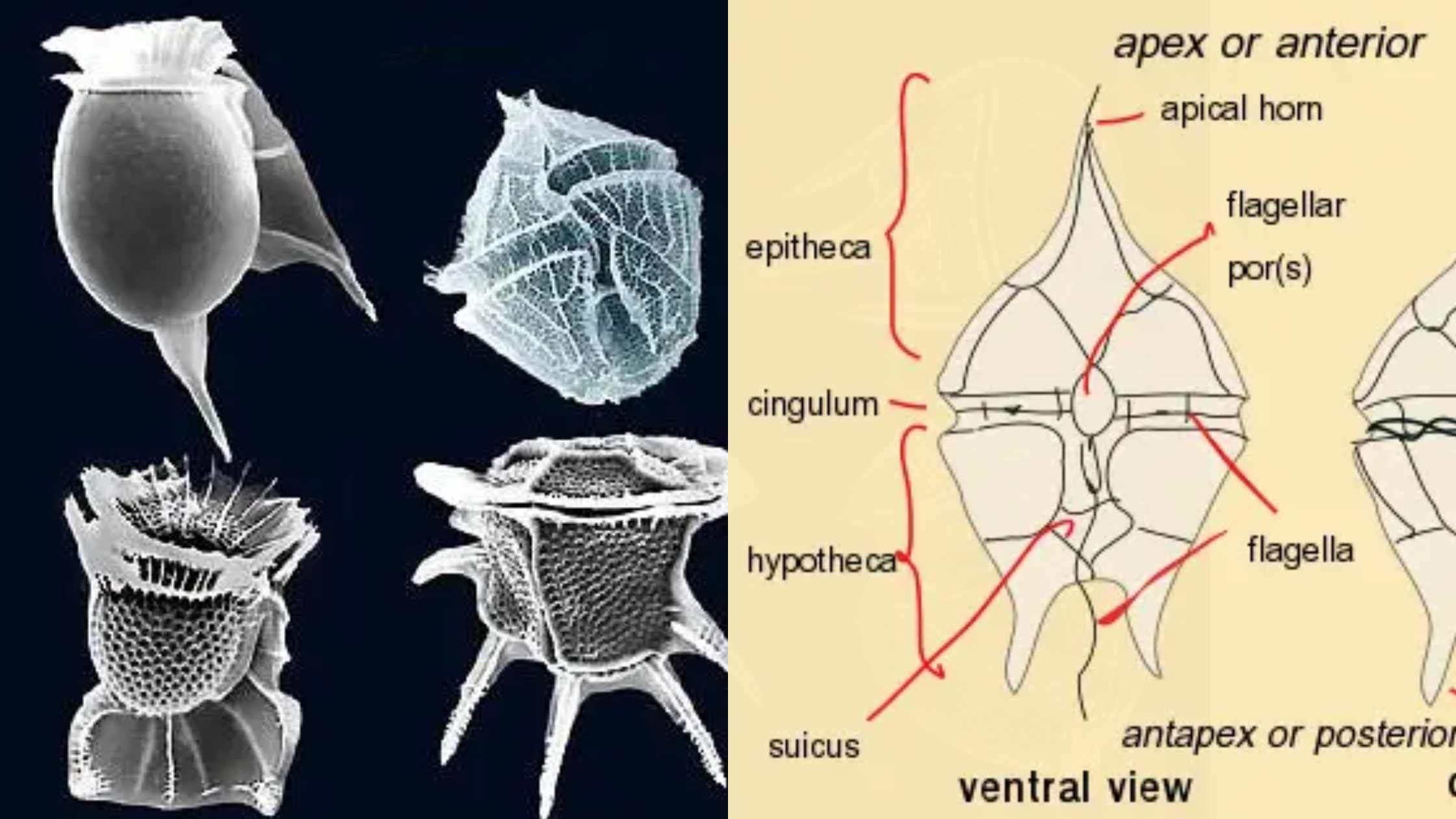
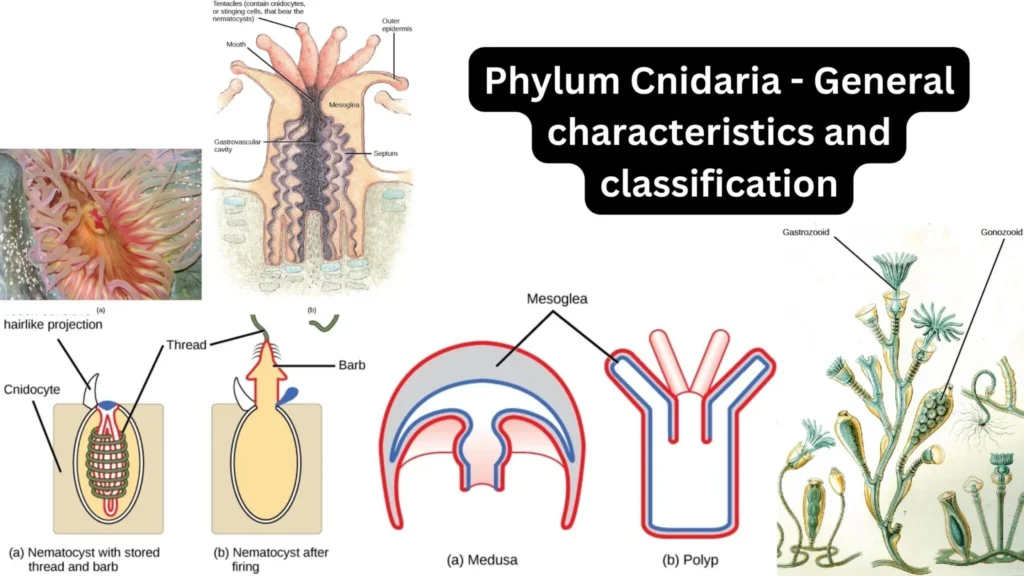
Kingdom Animalia – Different Phylum, Classification, Characteristics
Overview of Kingdom Animalia The Kingdom Animalia is a large group of multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic in their nature. They get their food from outside sources. While they cannot create their own food and this is among the most characteristic traits of plant cells, animal cells do not have a cell wall like … Read more