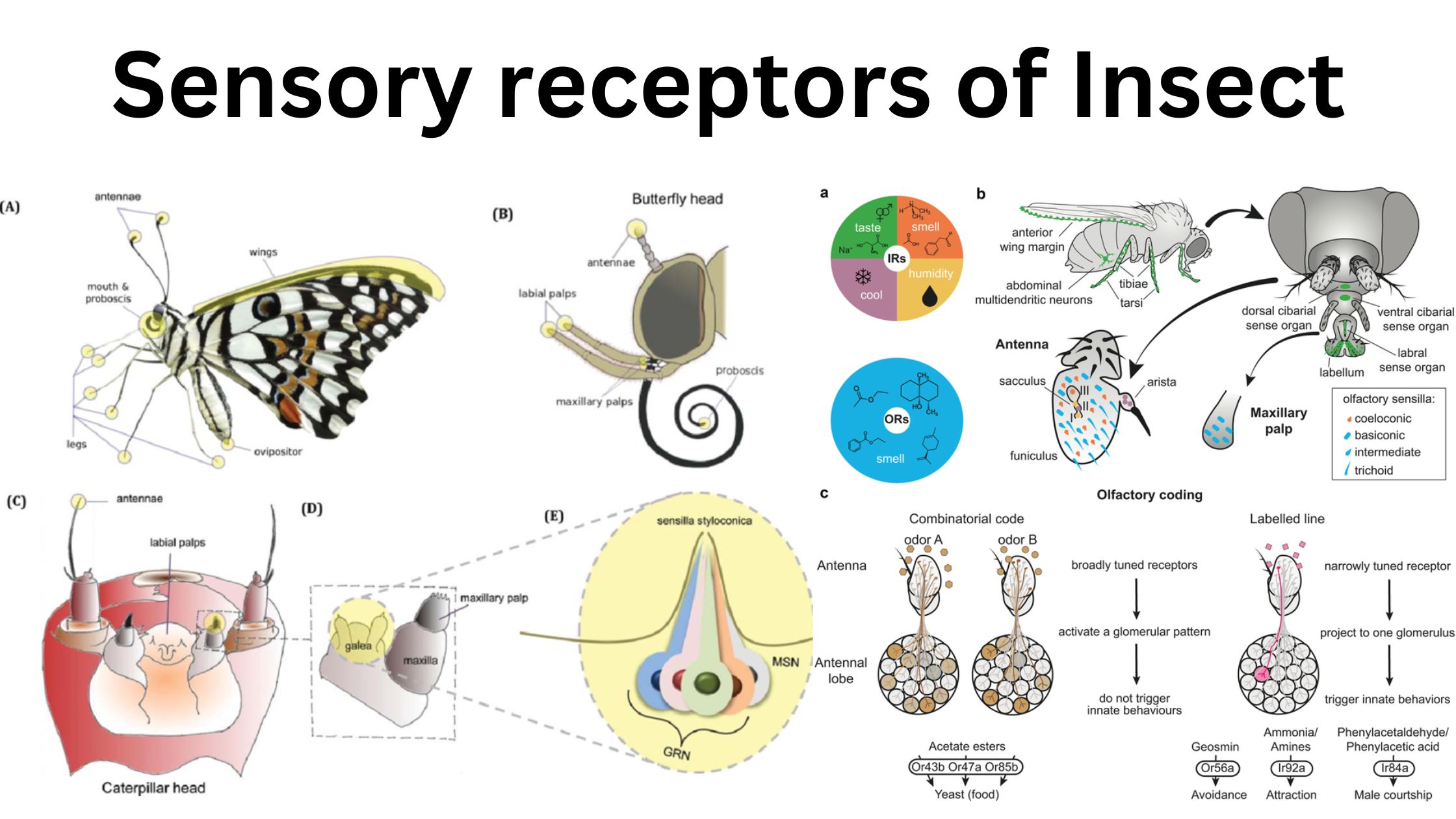
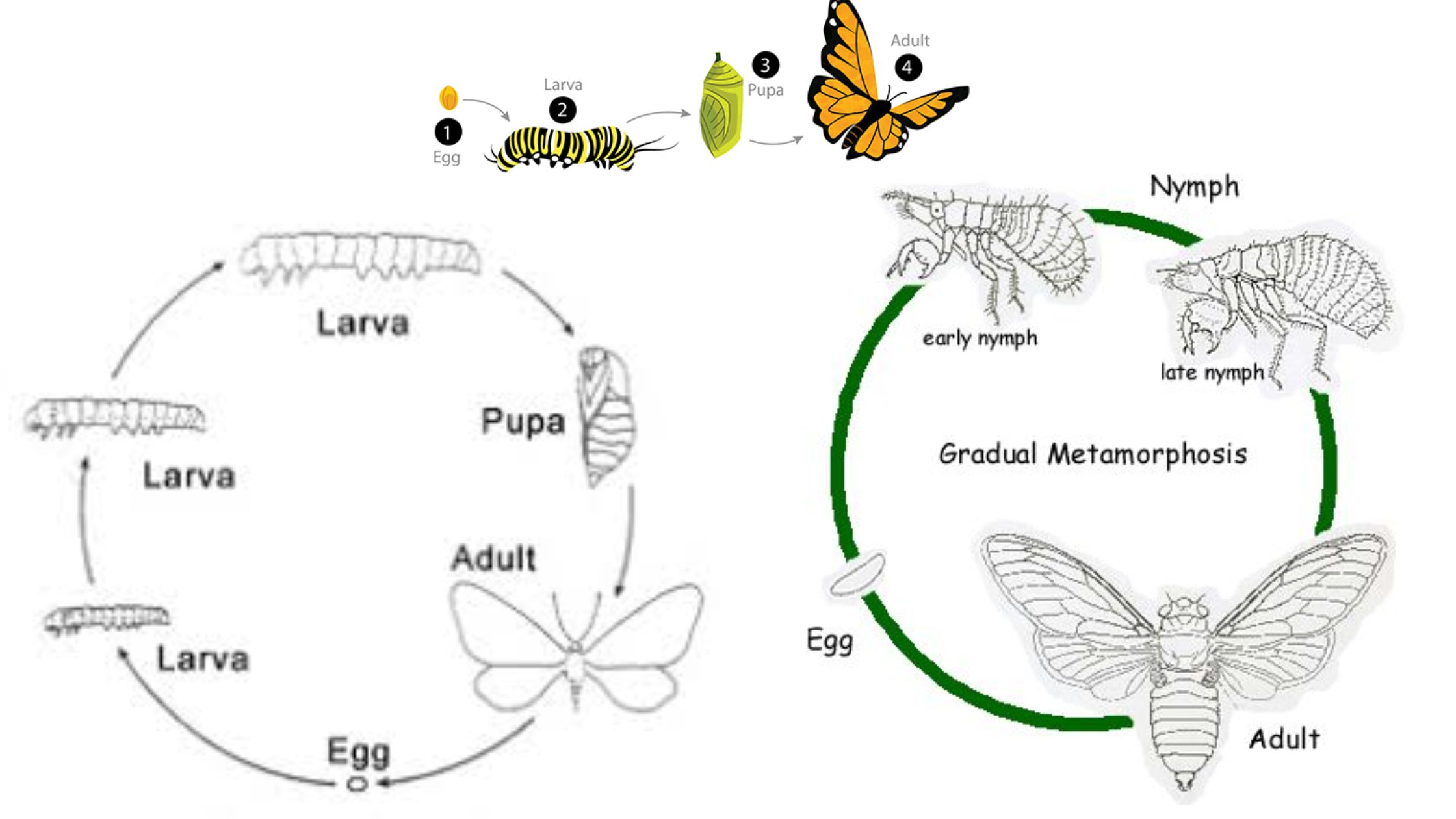
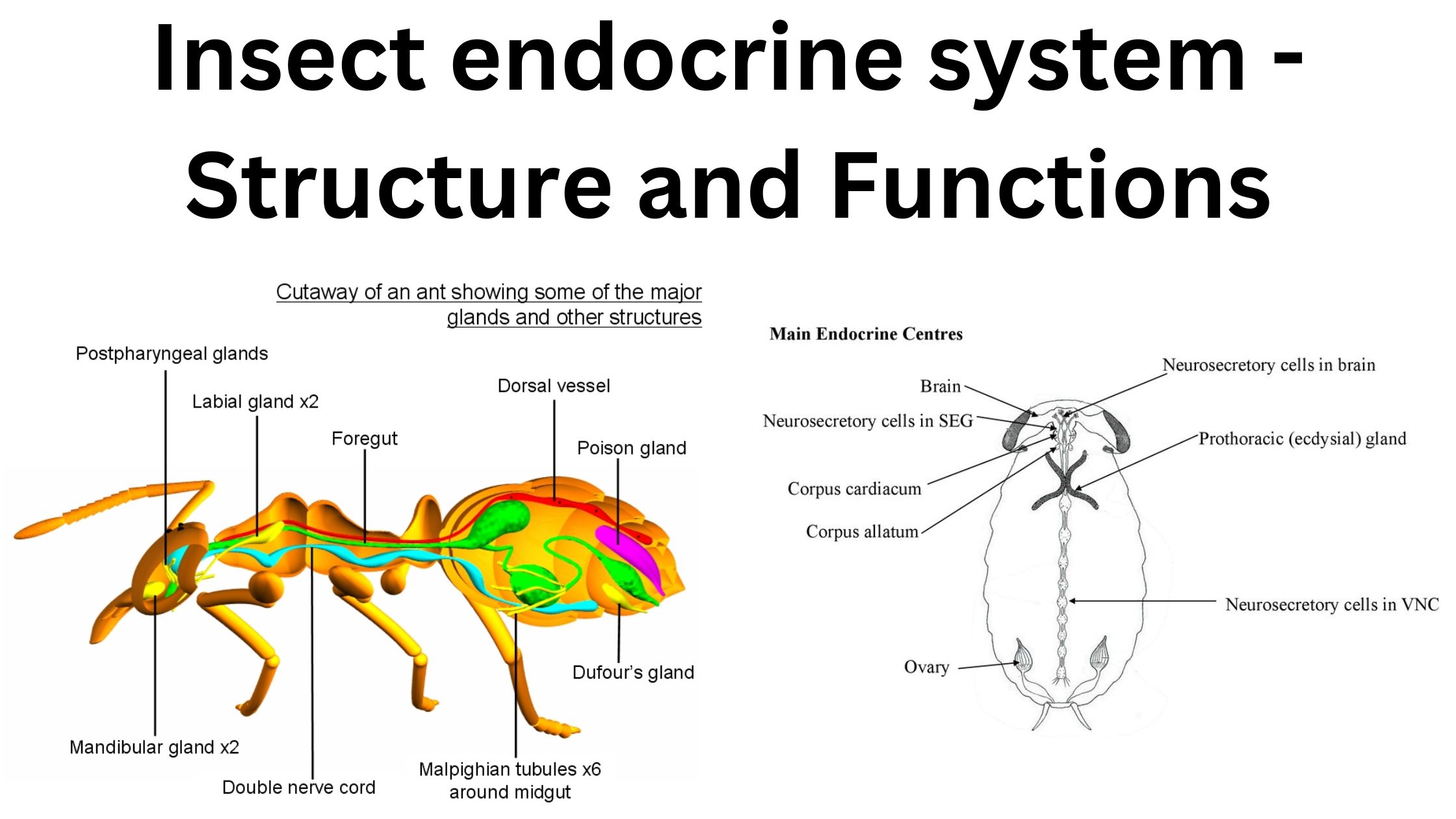
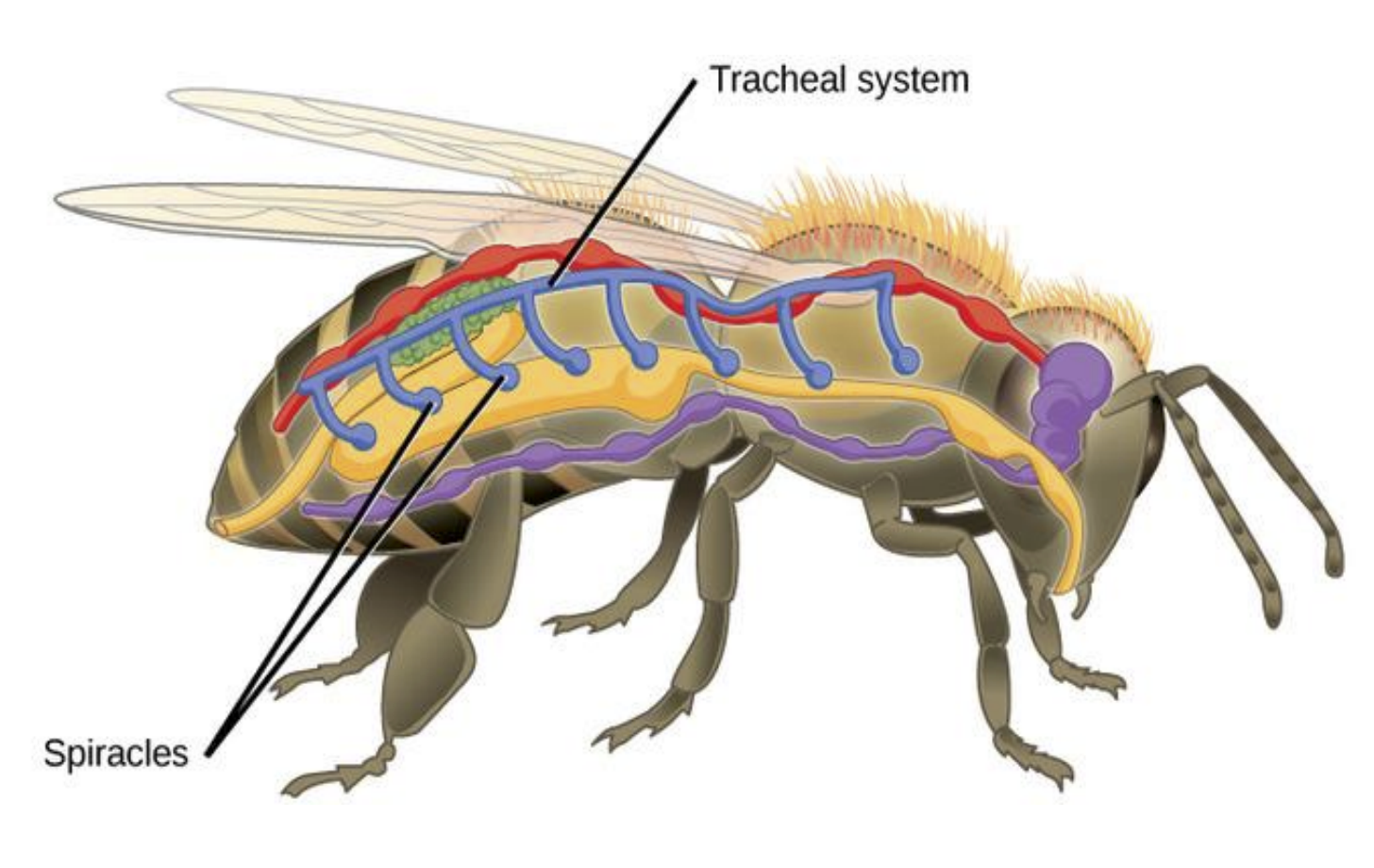
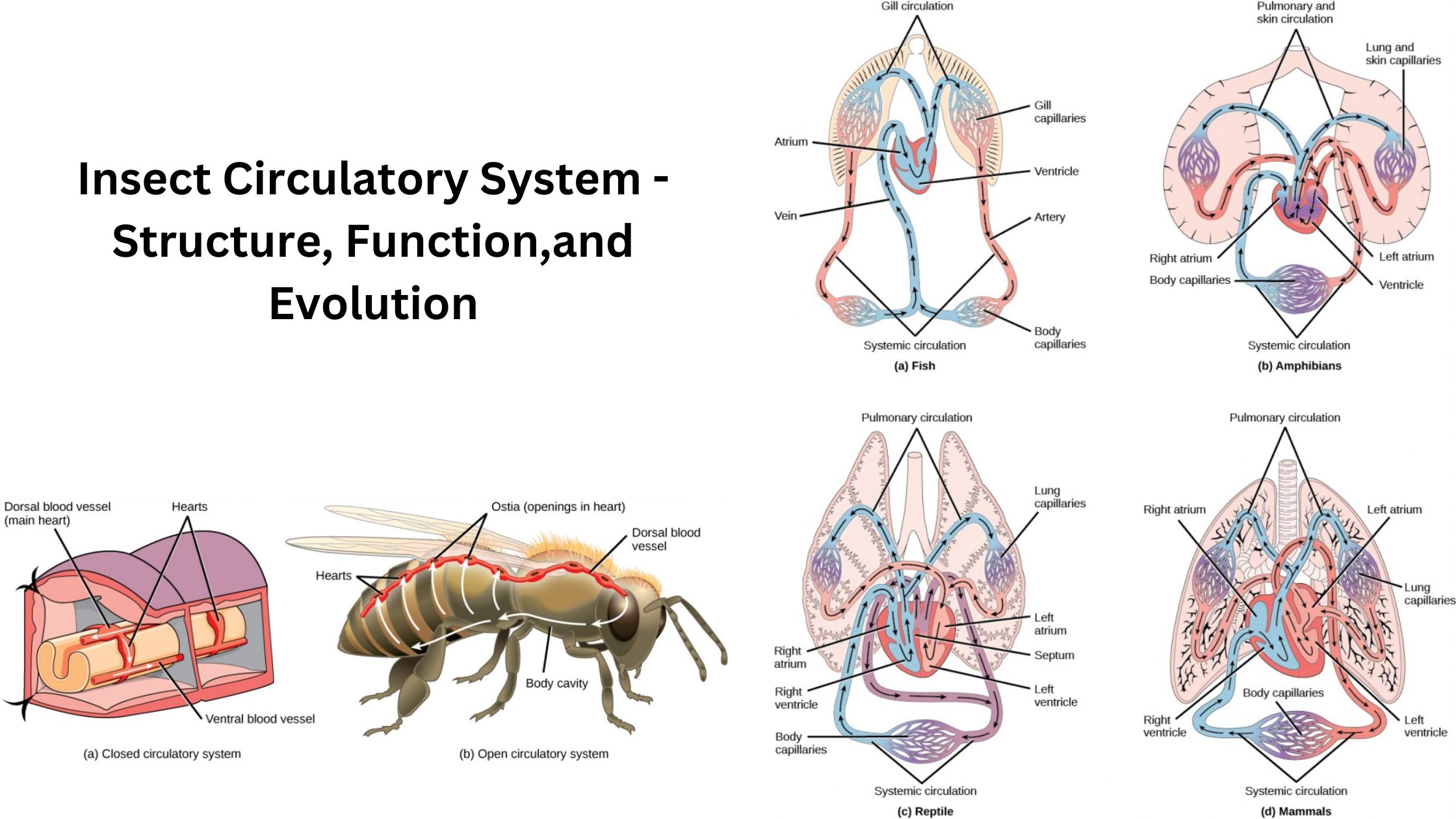
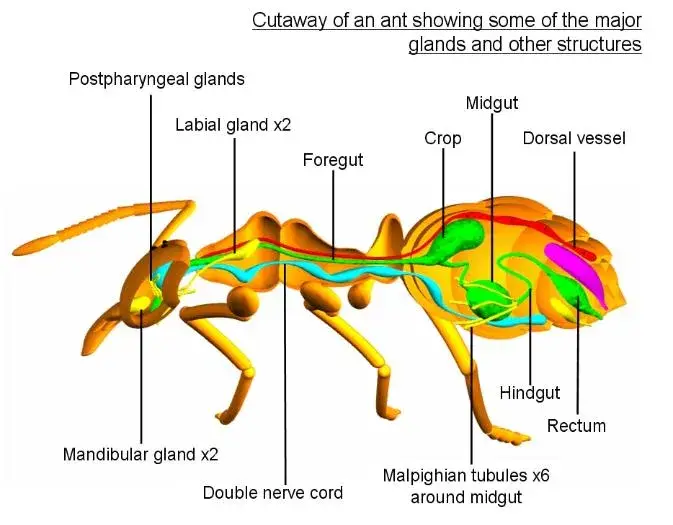
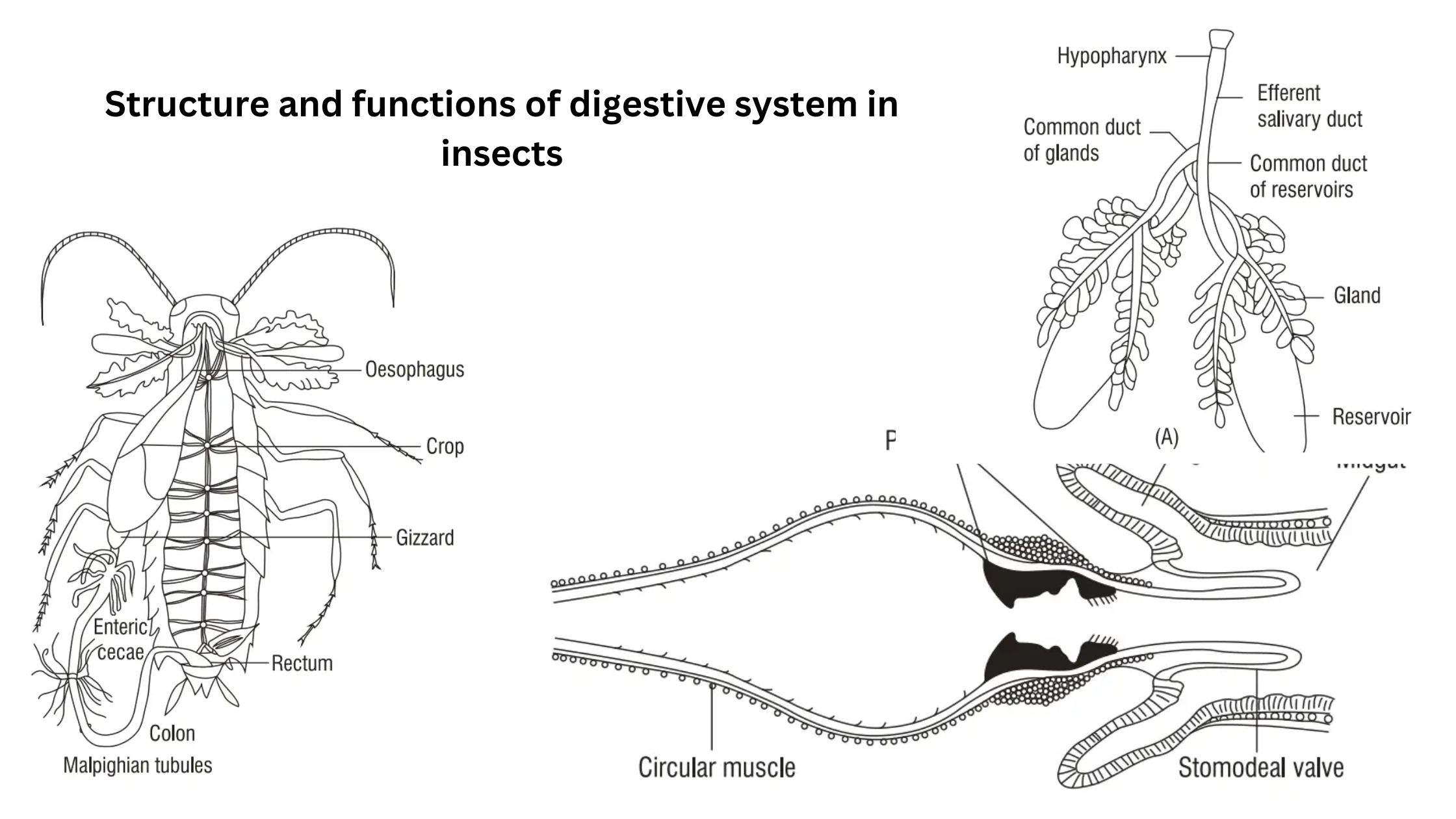
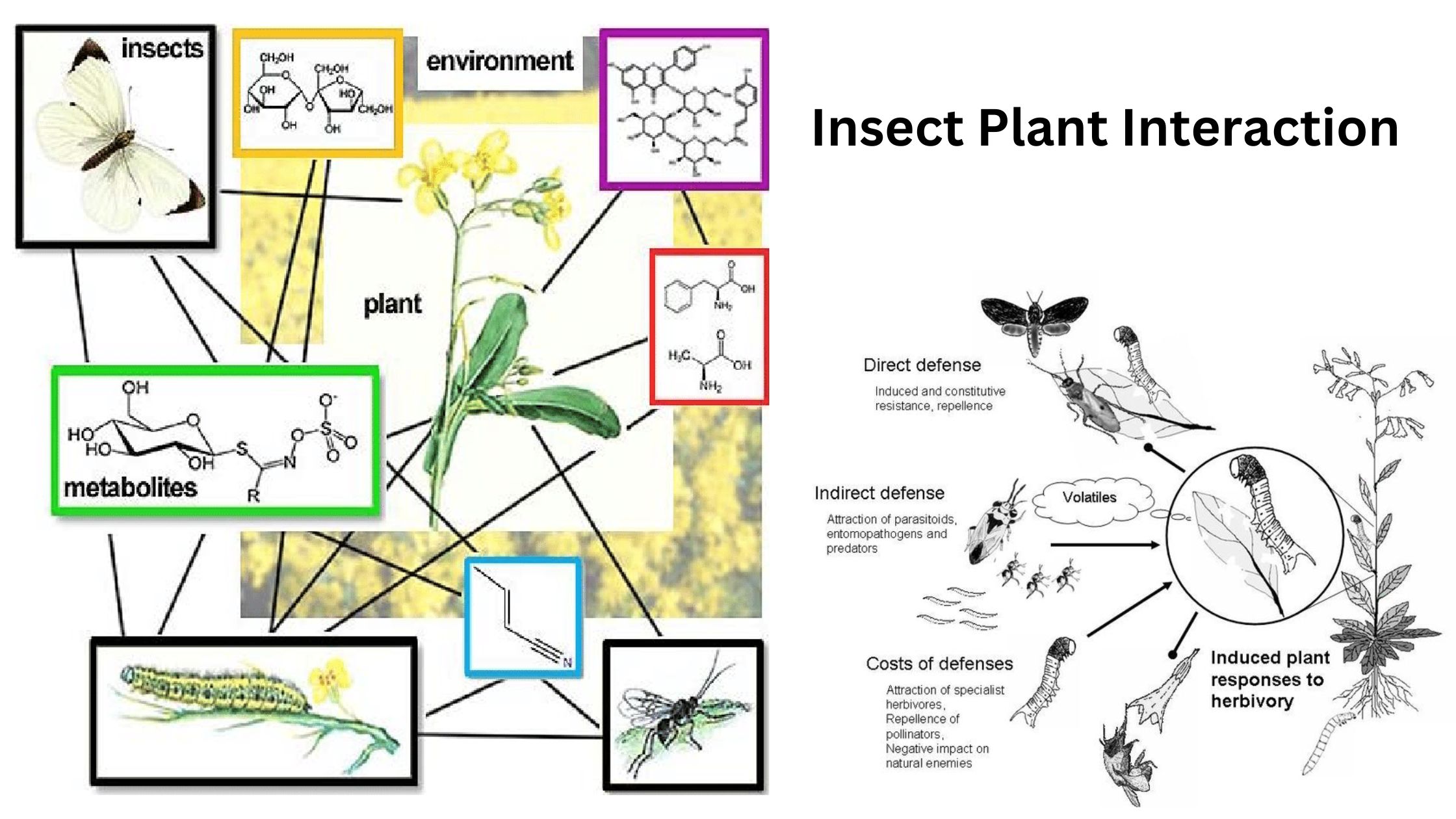
Sensory Receptors of Insect – Examples and Functions
Insects possess a diverse array of sensory receptors that enable them to effectively interact with their environments and respond to various stimuli. The primary visual receptors are compound eyes, which consist of numerous individual units called ommatidia, allowing insects to detect light, motion, and color across a broad field of vision. Additionally, dorsal ocelli and … Read more