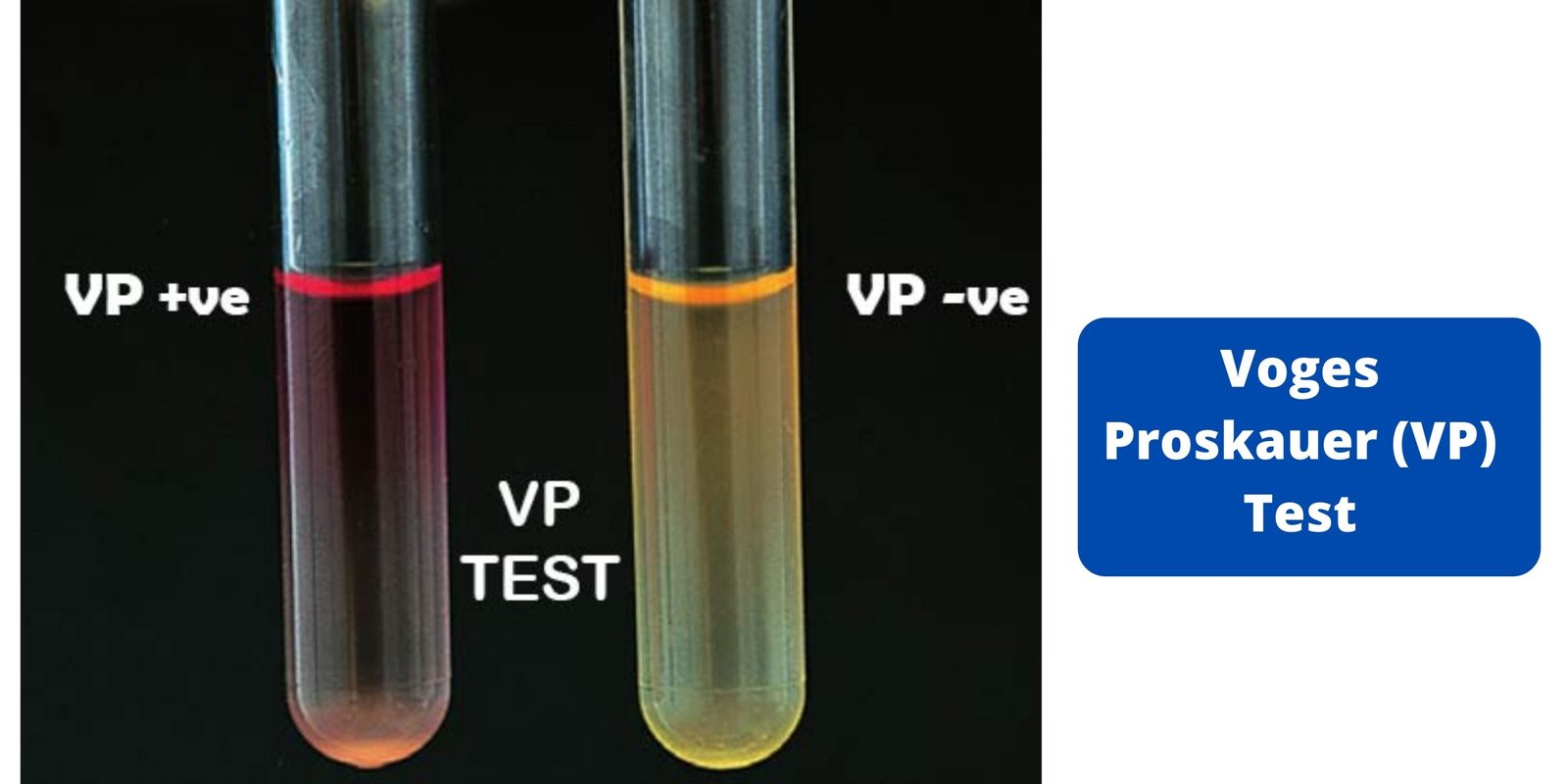
Ames Test – Principle, Procedure, Result, Limitation, Applications
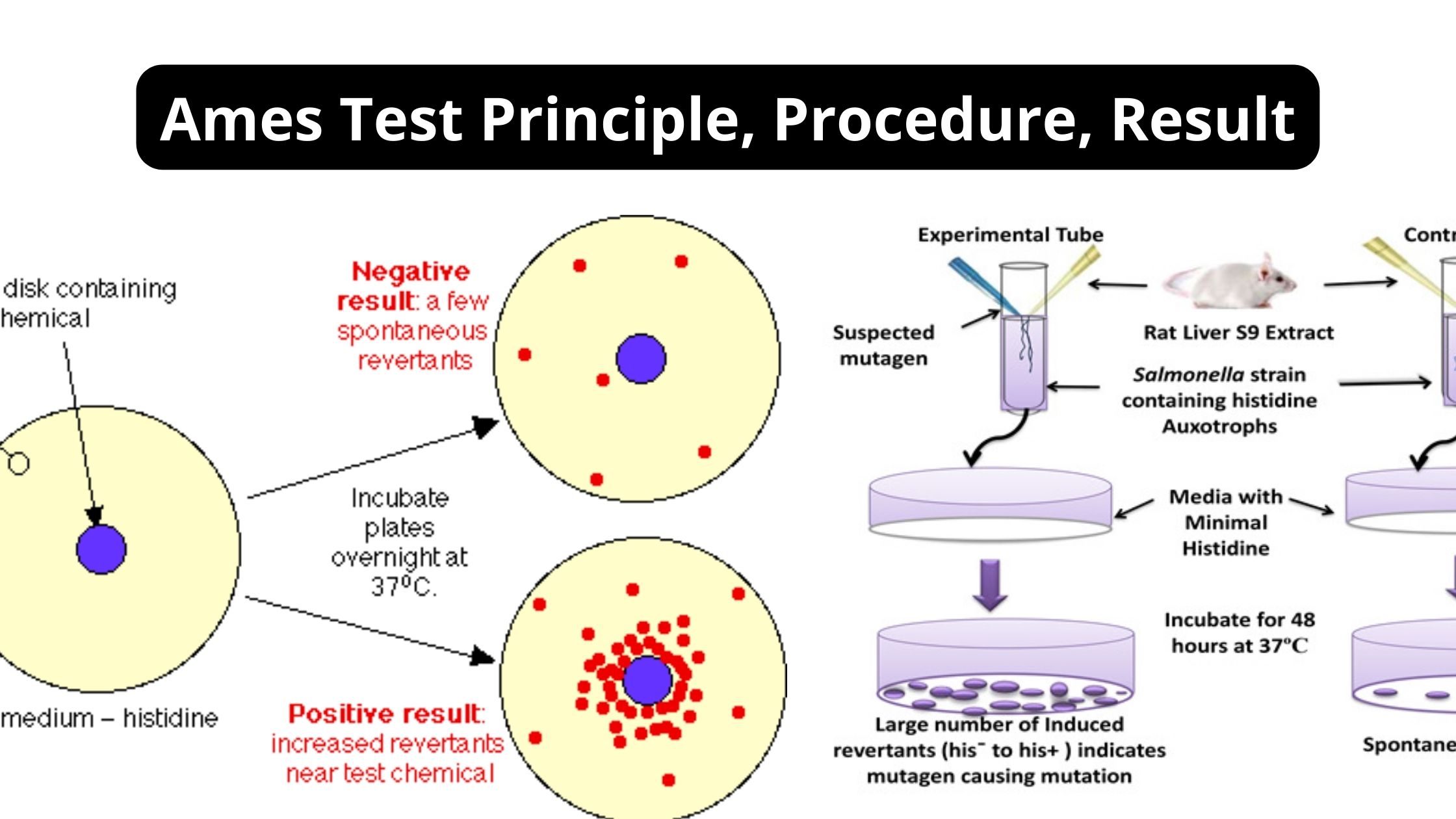
What is Ames Test? Definition of Ames Test The Ames test is a biological assay developed by Bruce Ames, used to assess the mutagenic potential of chemical compounds by observing their ability to induce mutations in specific strains of bacteria, primarily Salmonella typhimurium. A positive result indicates that the chemical may be mutagenic and potentially … Read more