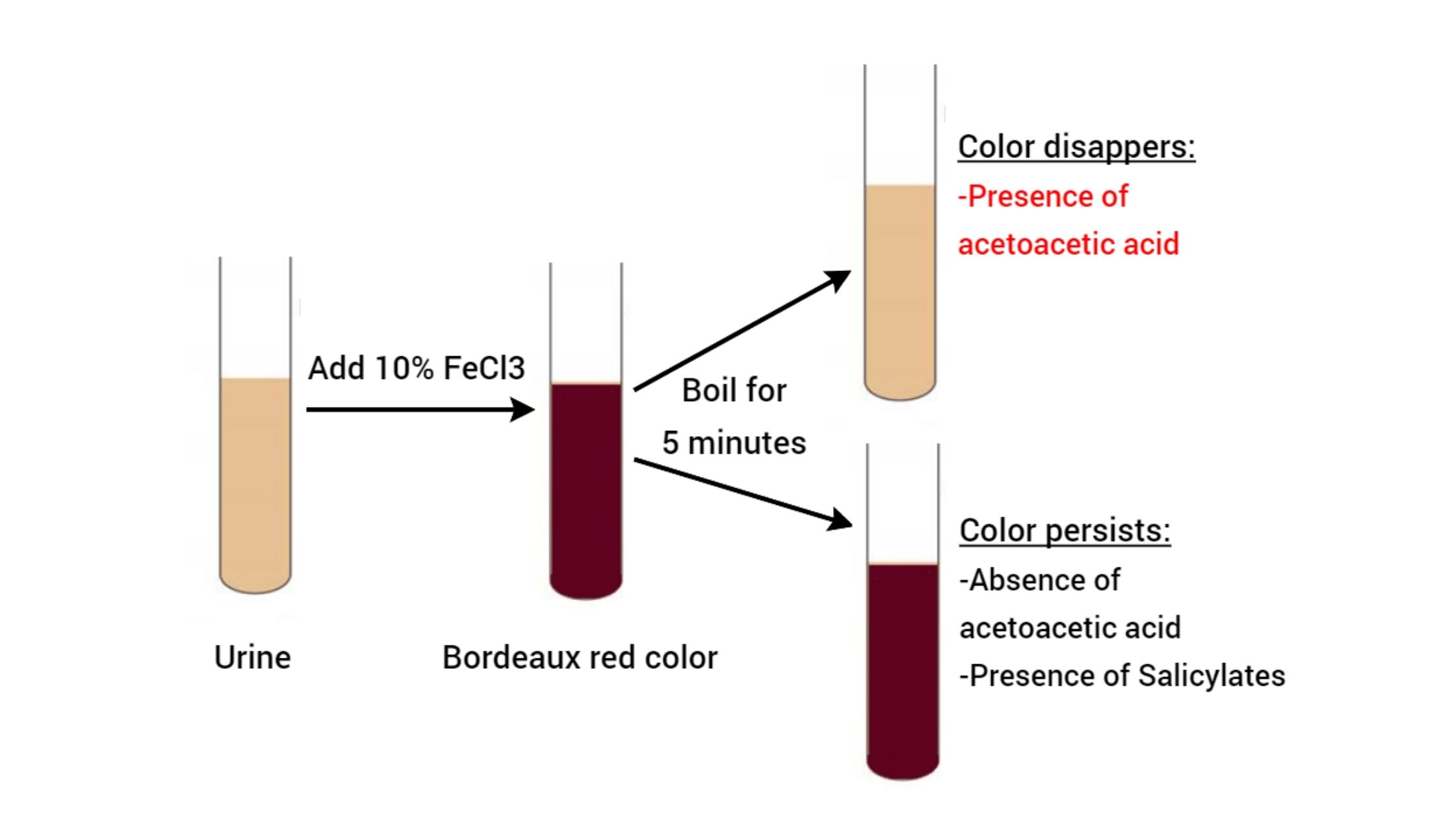
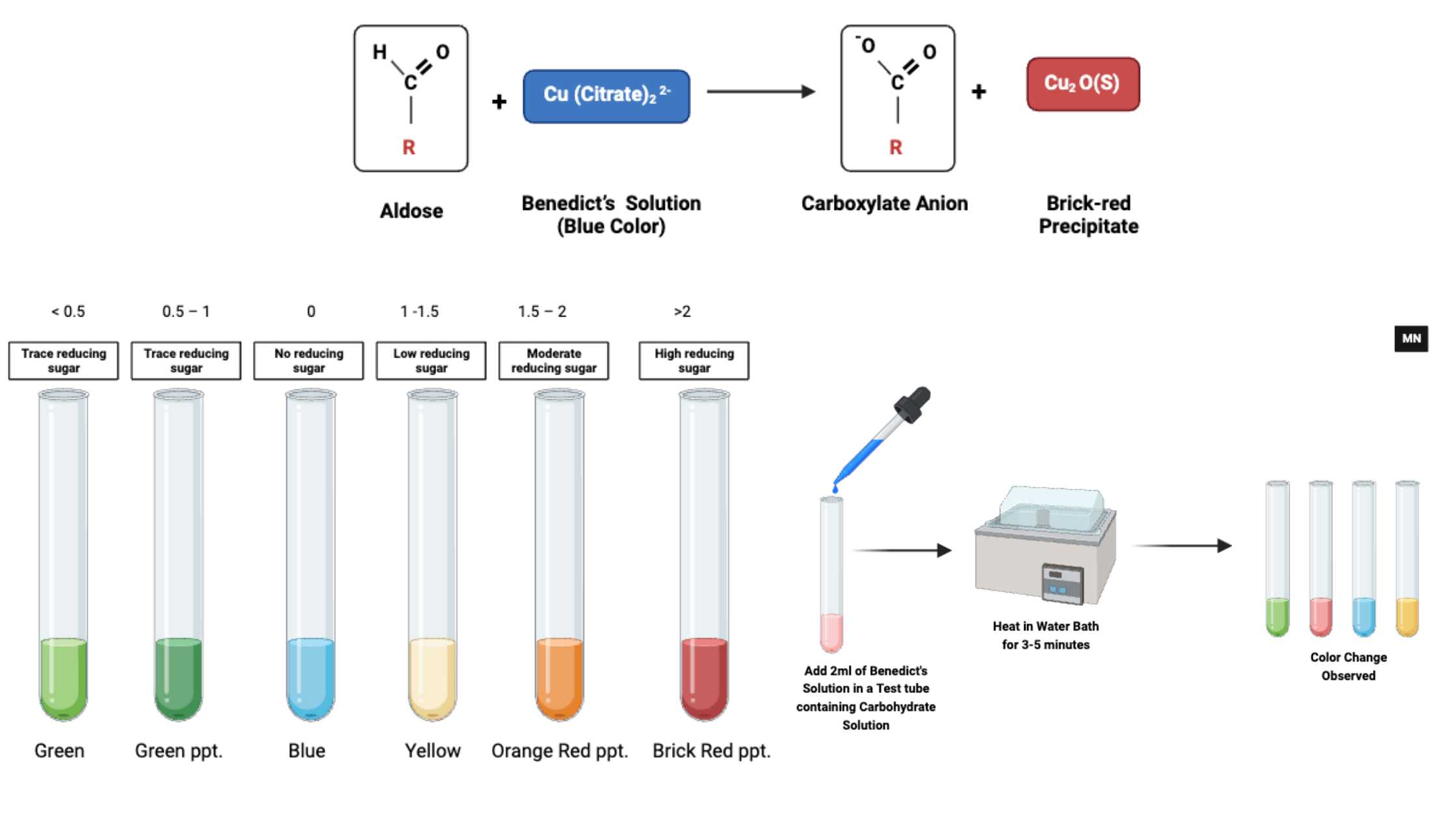
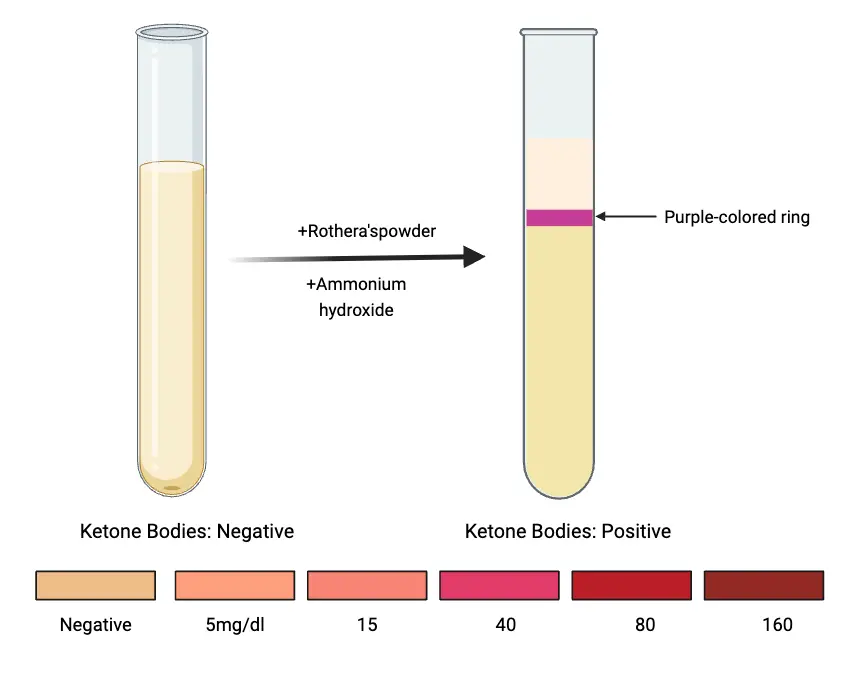
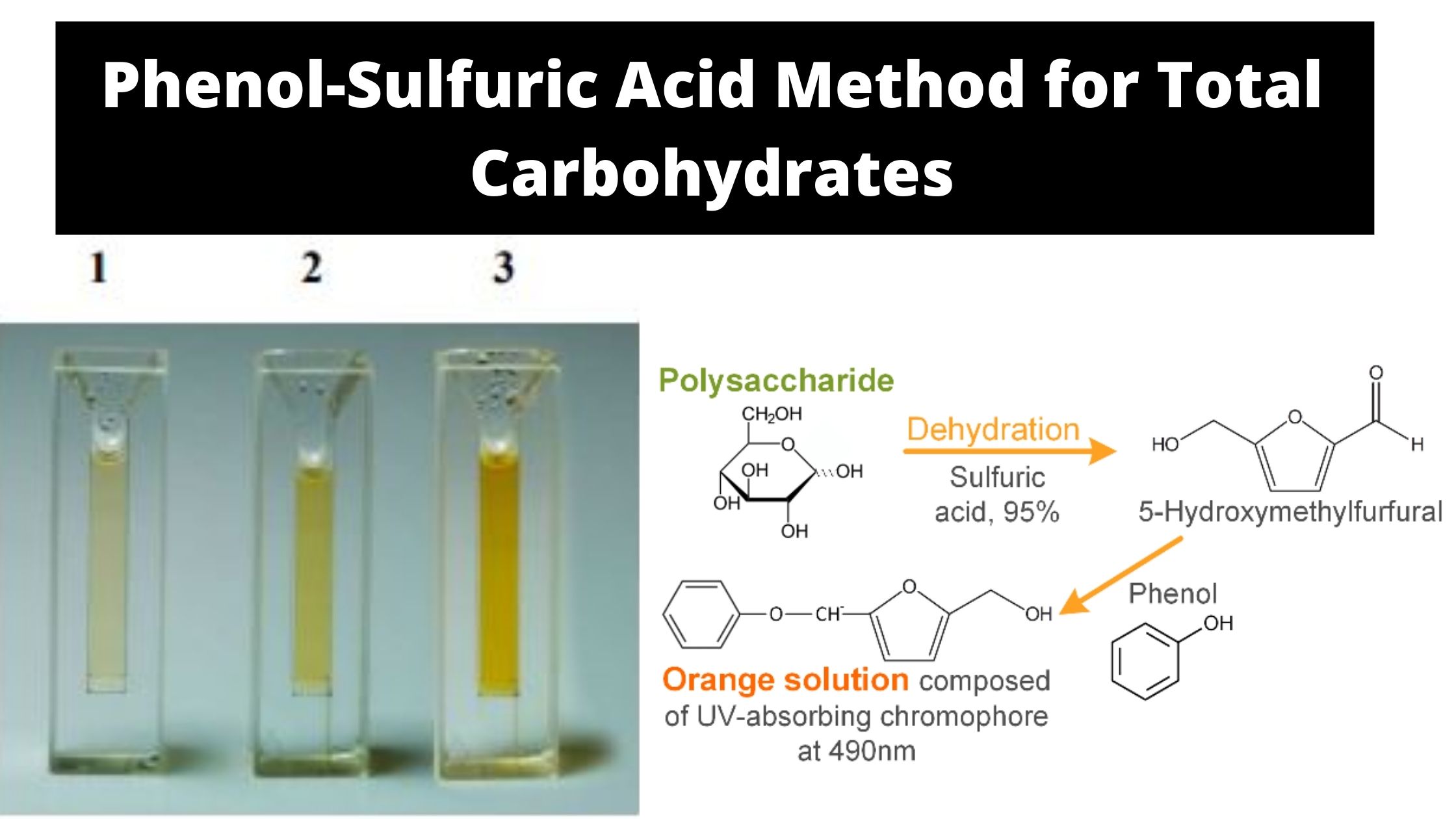
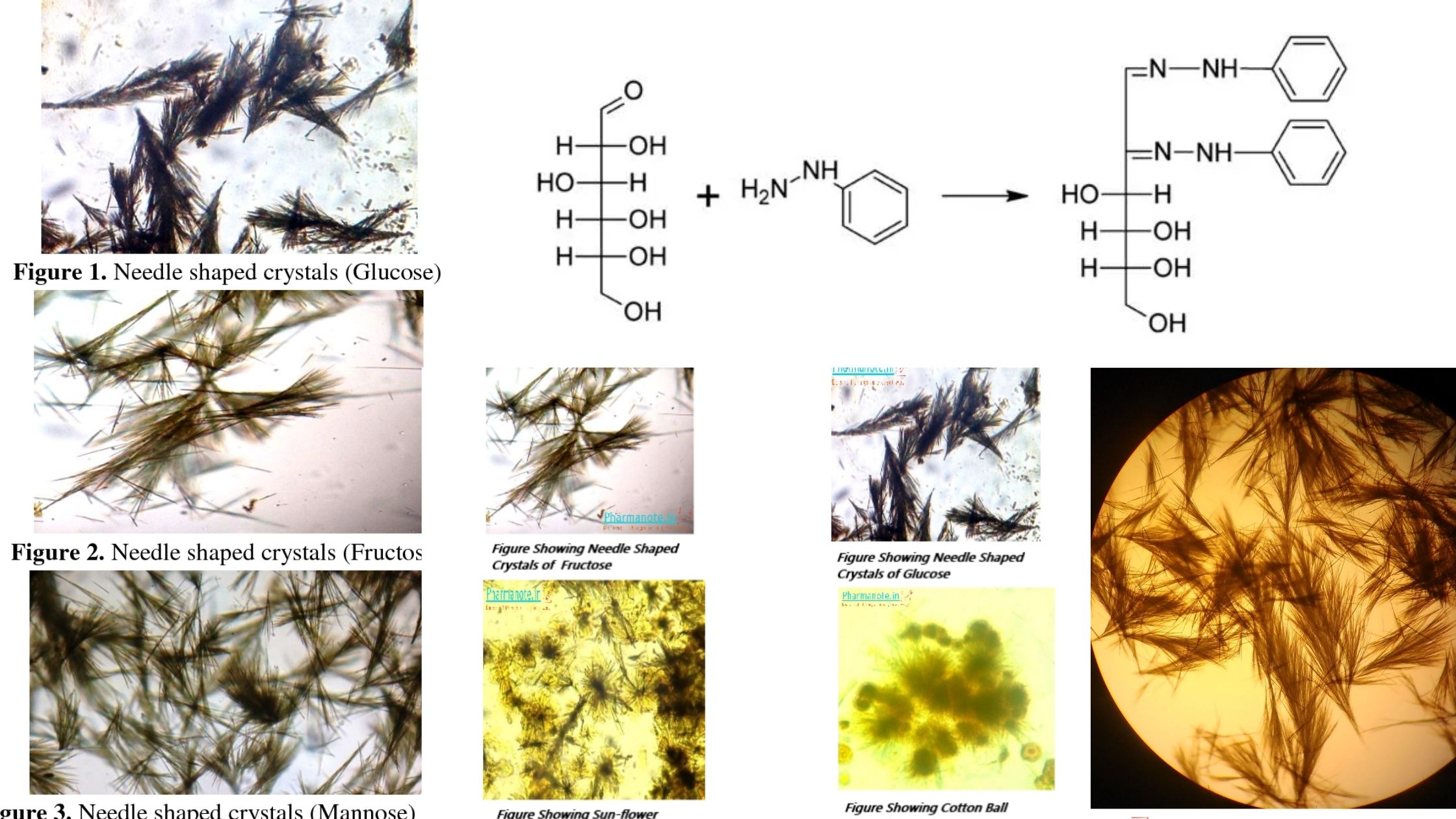
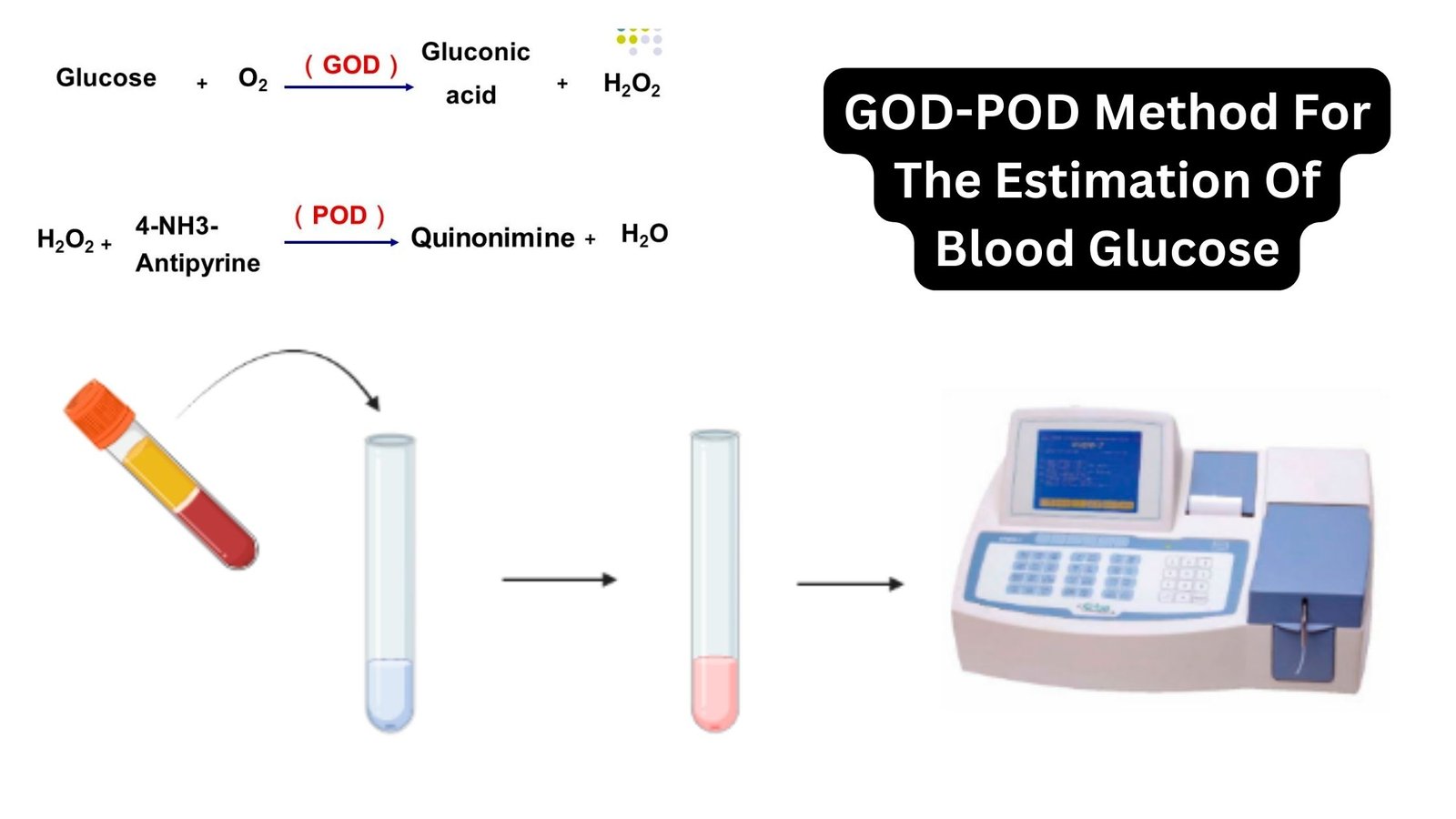
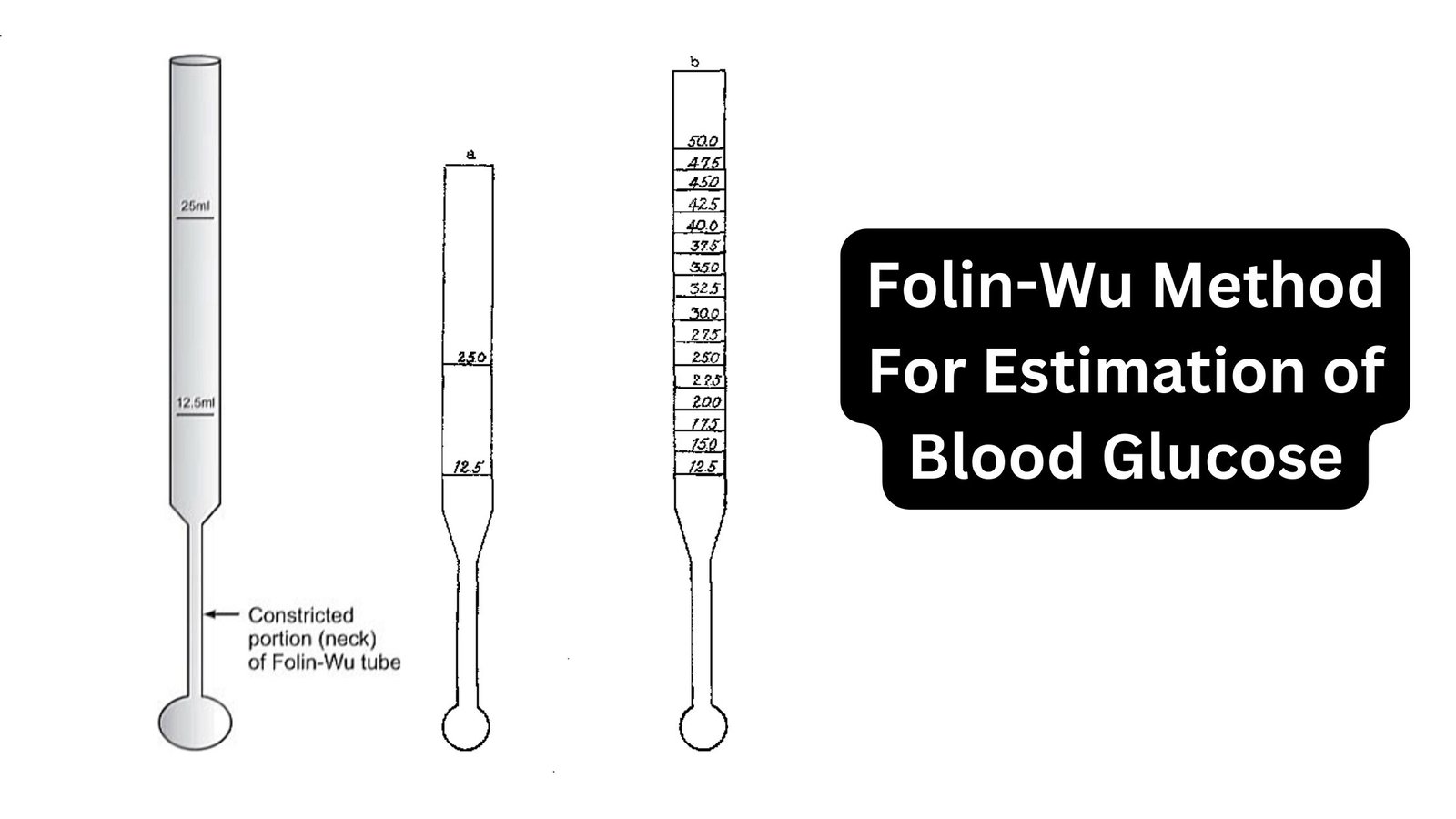
Determination of Lactose In Milk by Lane-Eynon Method
What is Lane-Eynon Method? Principle of Lane-Eynon Method The method based on reduction of cupric ions (Cu²⁺) to cuprous oxide (Cu₂O) by the reducing sugars in alkaline condition. In the reaction, CuSO₄ from Fehling A and alkaline tartrate from Fehling B react to form a deep blue cupric–tartrate complex, which remain stable in hot solution … Read more