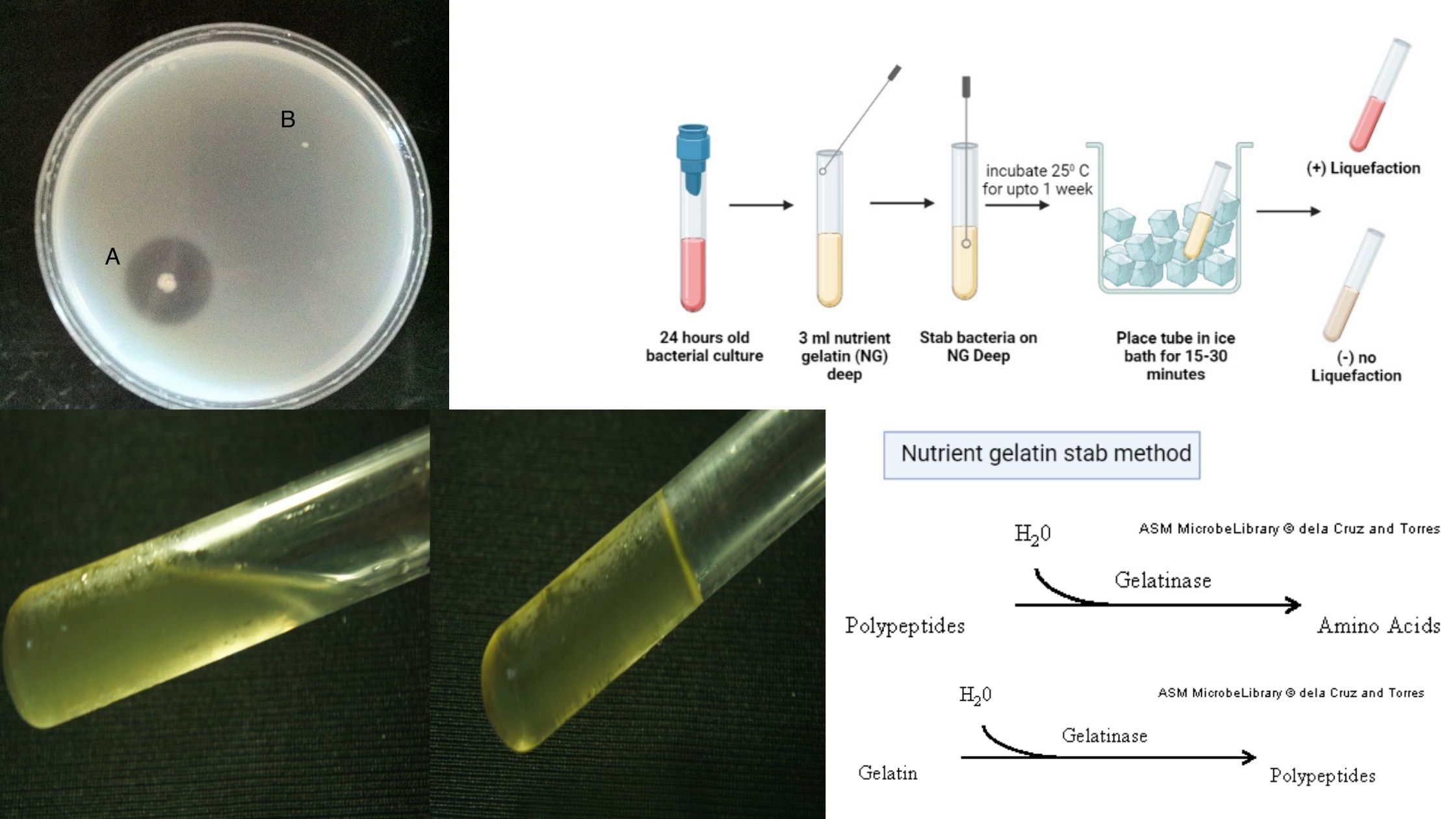
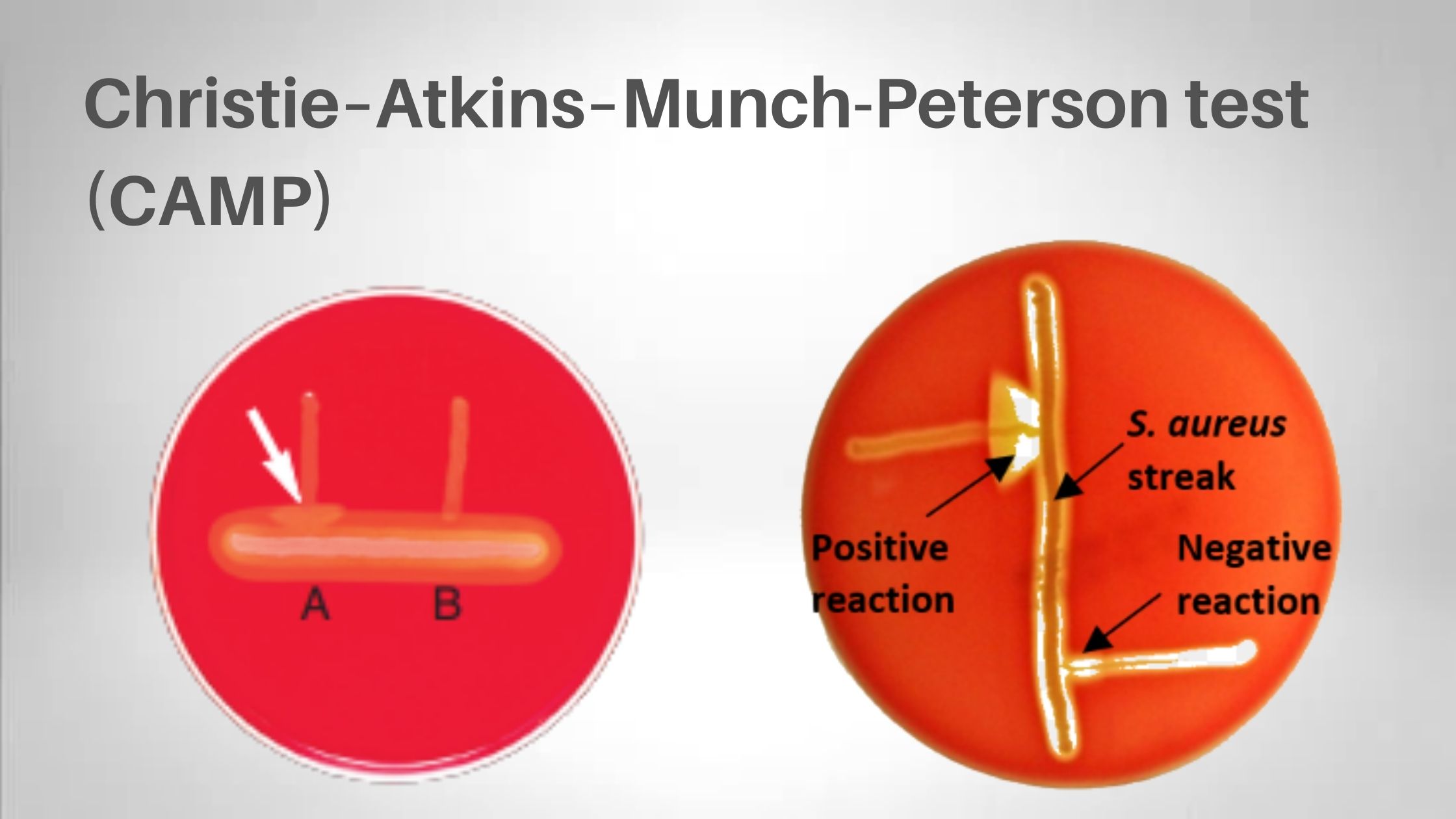
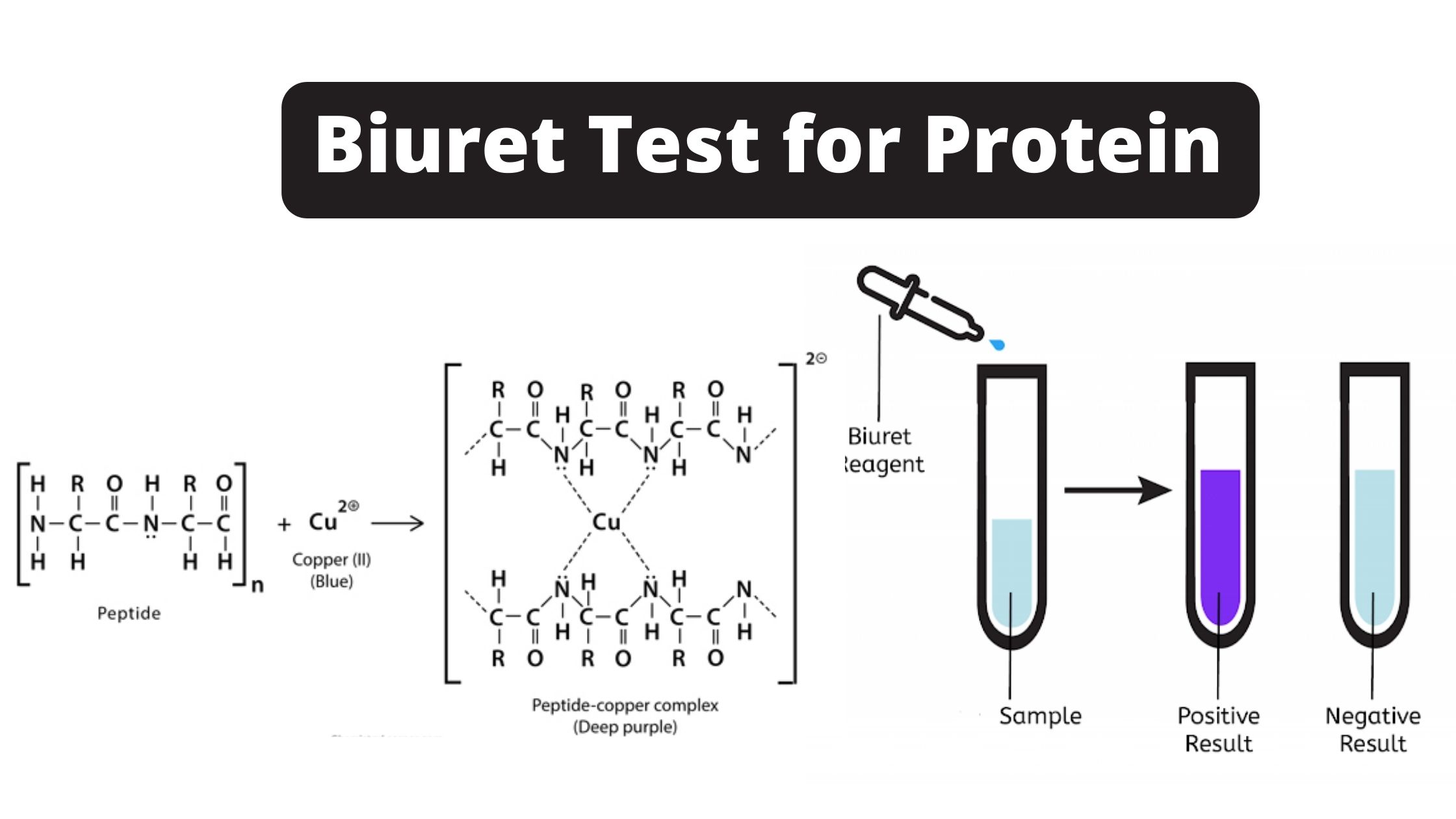
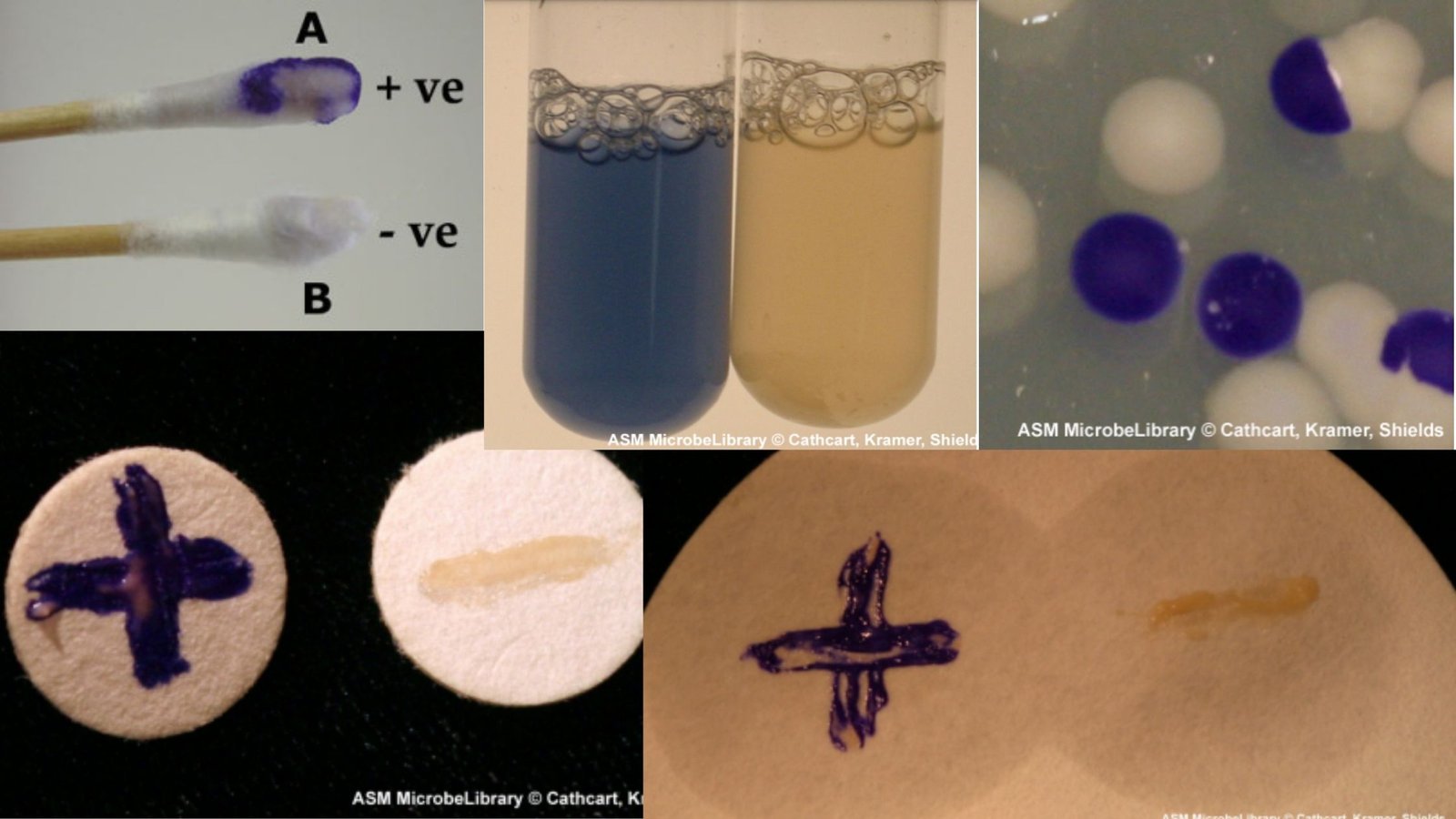
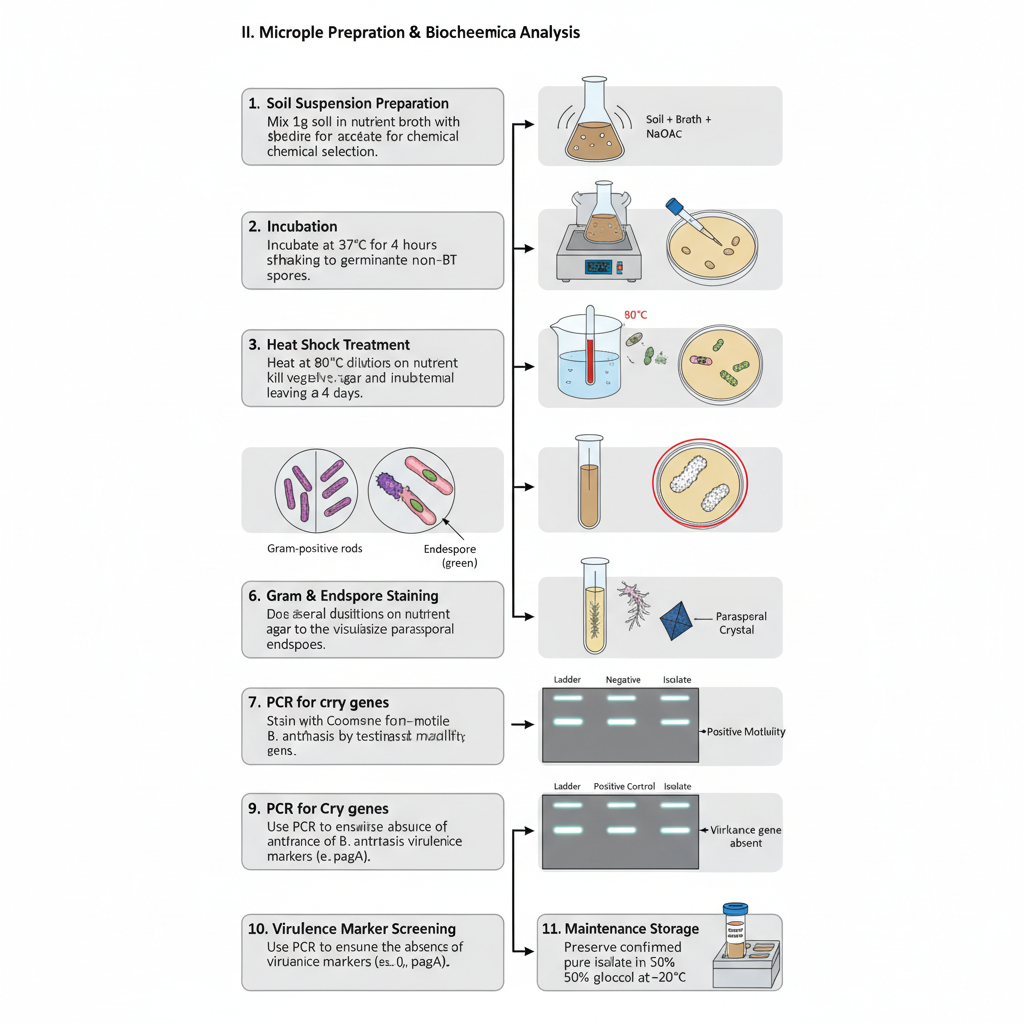
Simmons Citrate Agar – Principle, Composition, Procedure, Result, uses
Simmons Citrate Agar is a chemically defined medium in which sodium citrate act as the only carbon source and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate act as the only nitrogen source. It is the medium developed as a modification of Koser’s citrate medium and it is used mainly to differentiate members of Enterobacteriaceae. It is the process in … Read more