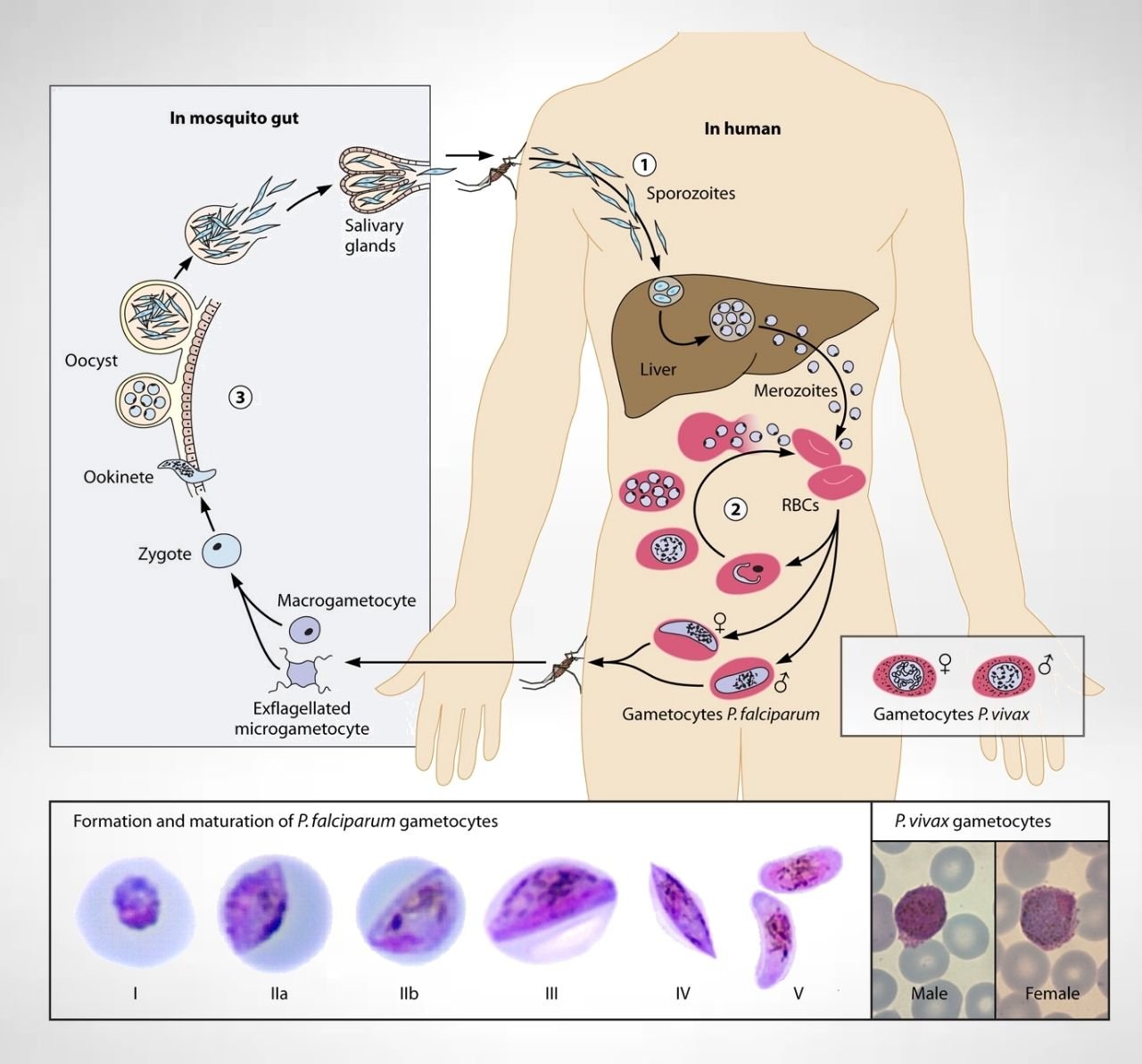
Schistosomiasis – Life cycle, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention
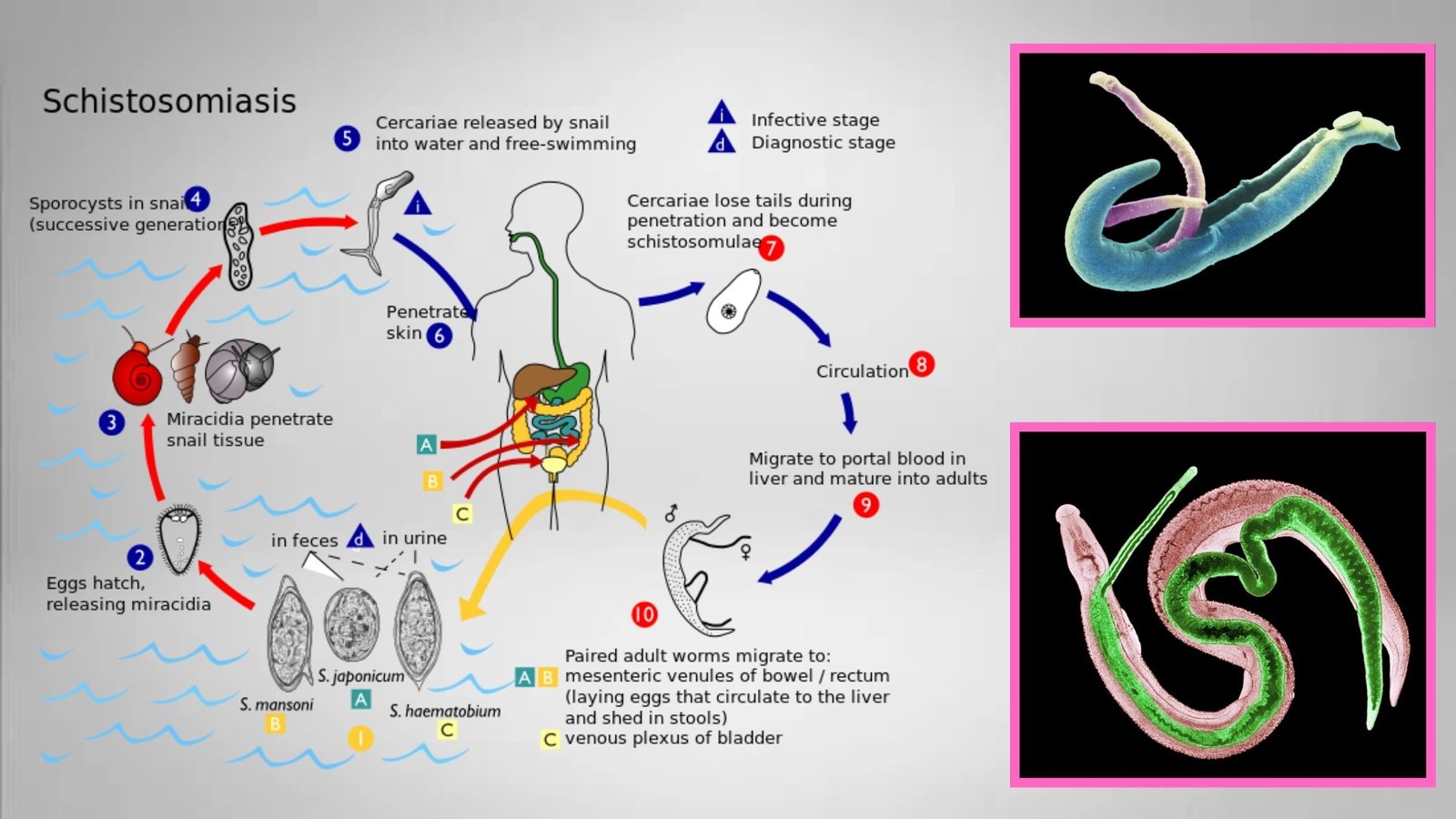
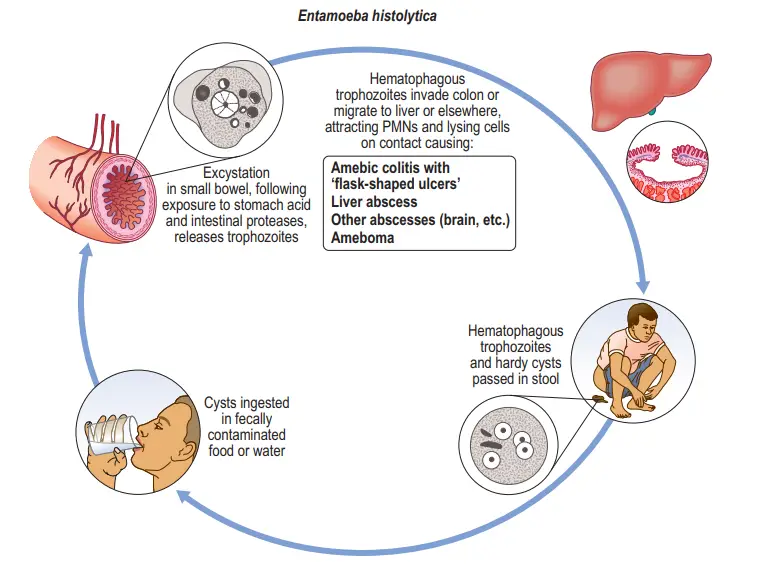
Schistosomiasis also termed snail fever or bilharzia is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. Infection with Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium, and S. japonicum causes illness in humans; less commonly, S. mekongi and S. intercalatum can cause disease.