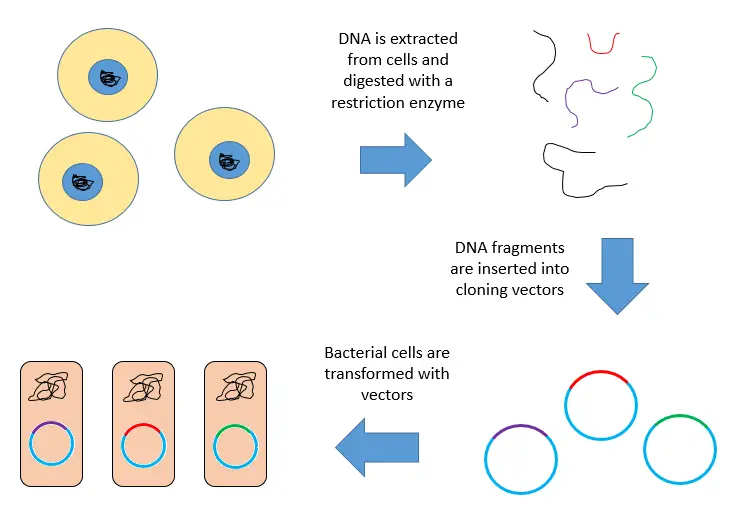
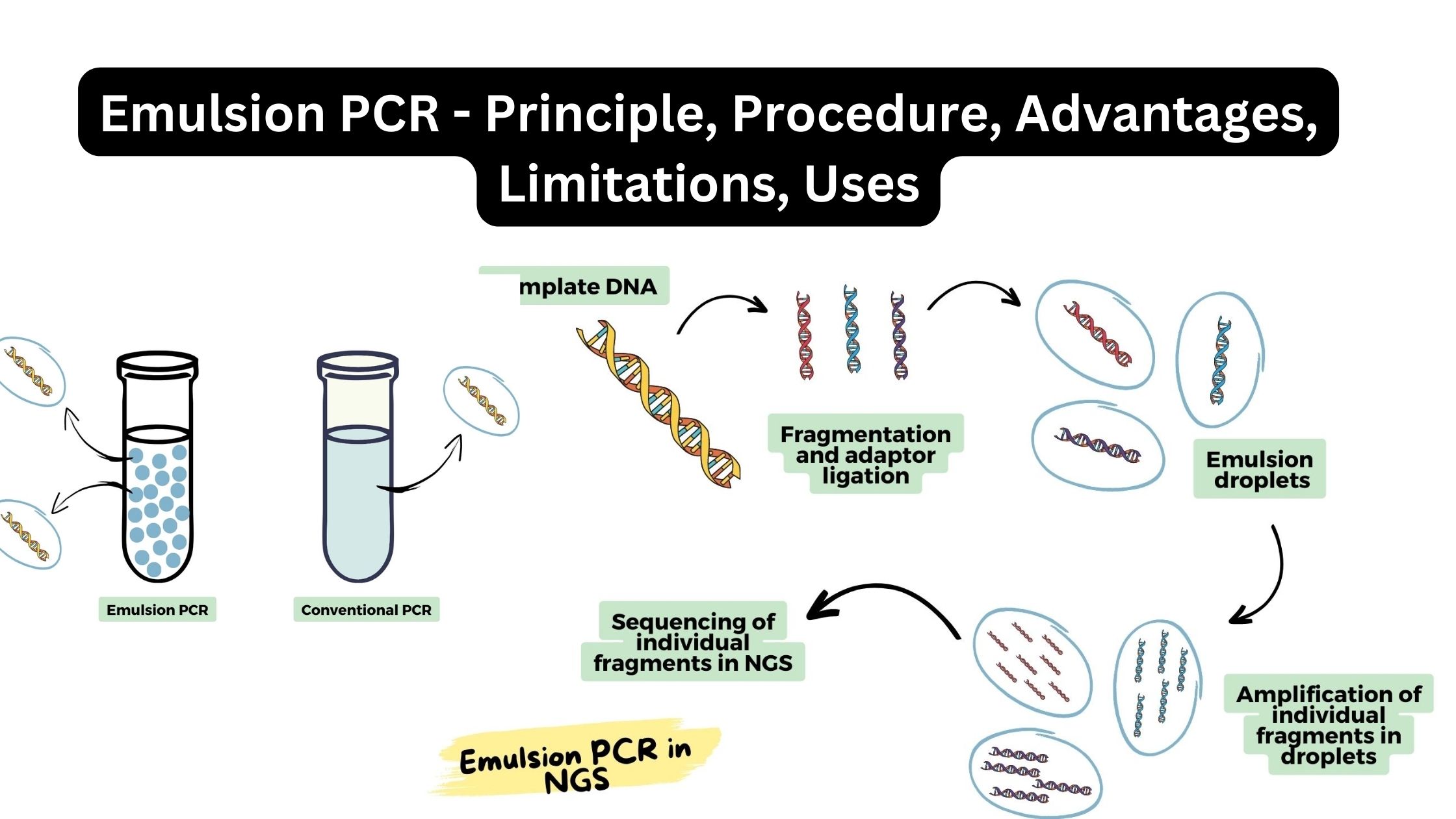
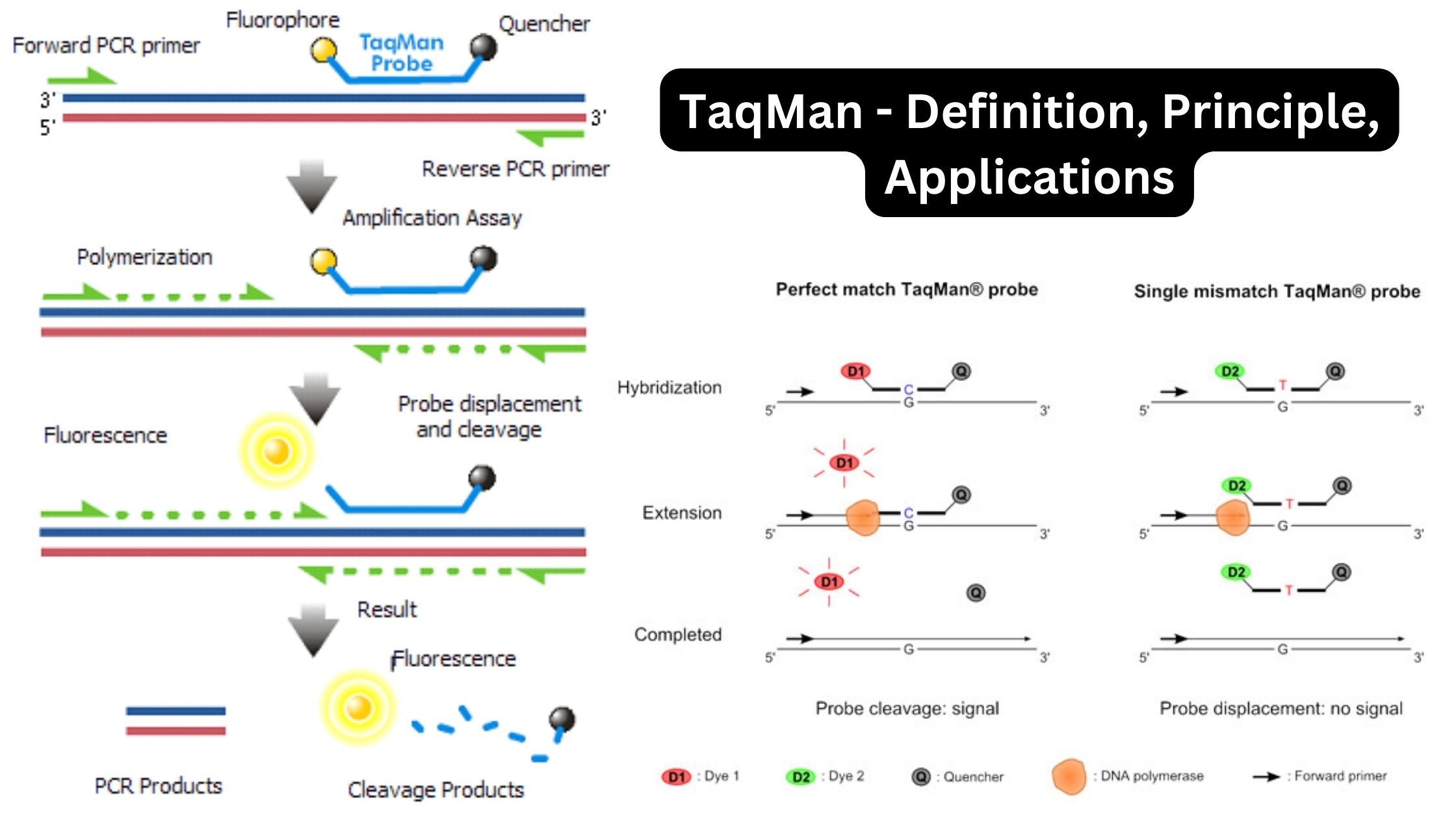
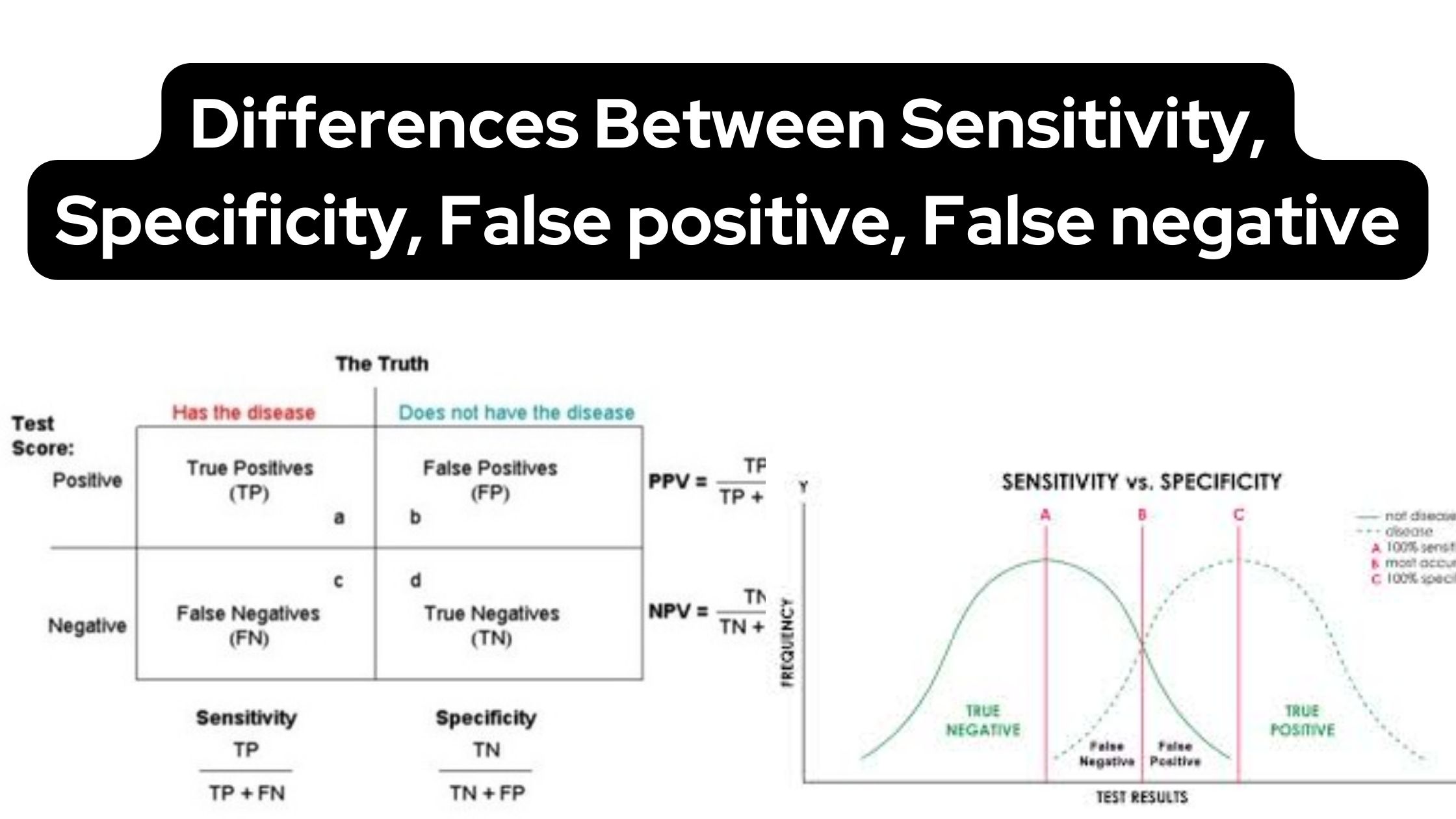
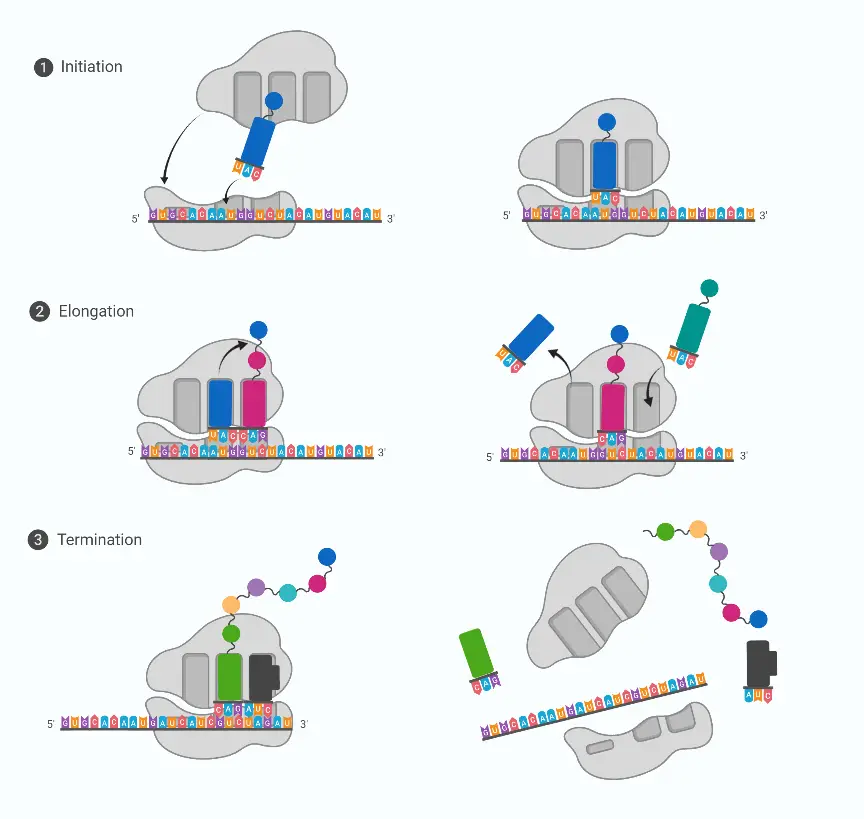
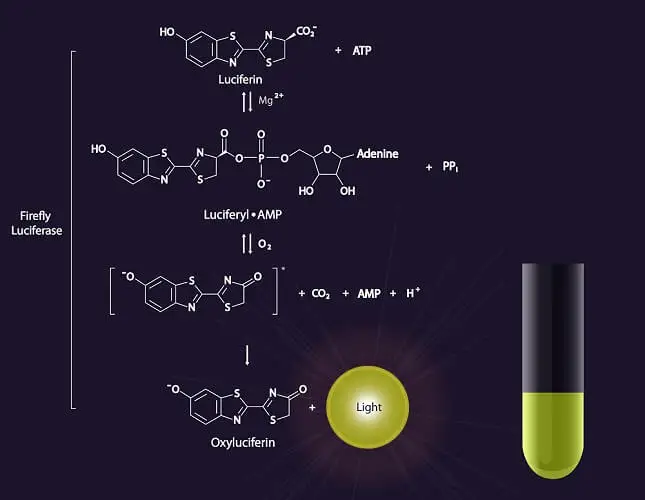
Eukaryotic DNA Replication – Definition, Steps, Singnification
Have you ever wondered how your body creates new cells? Or how genetic information is passed down from one generation to the next? The answer lies in a fascinating process called DNA replication. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of eukaryotic DNA replication, exploring its intricacies, importance, and the cutting-edge research surrounding … Read more