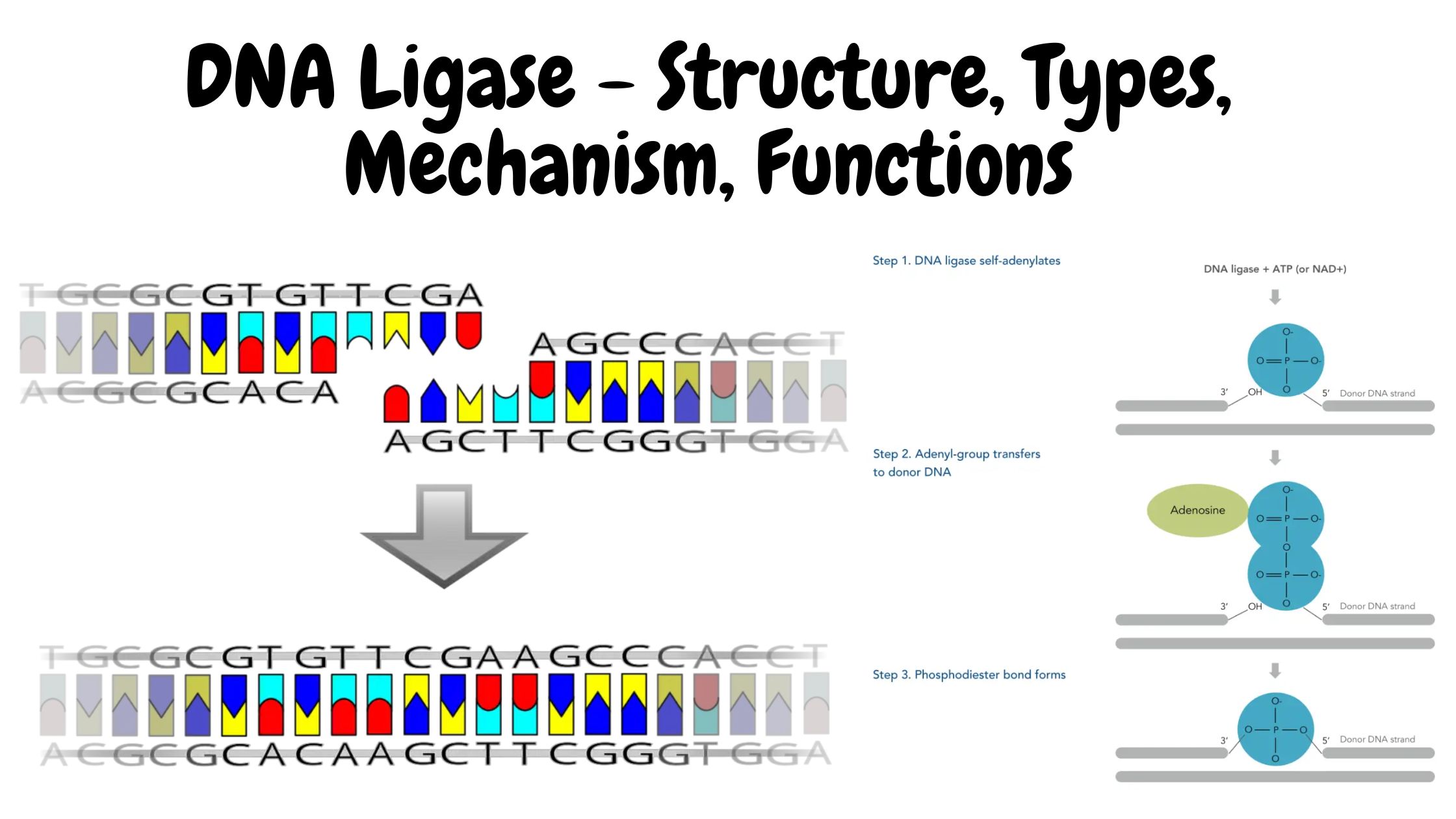
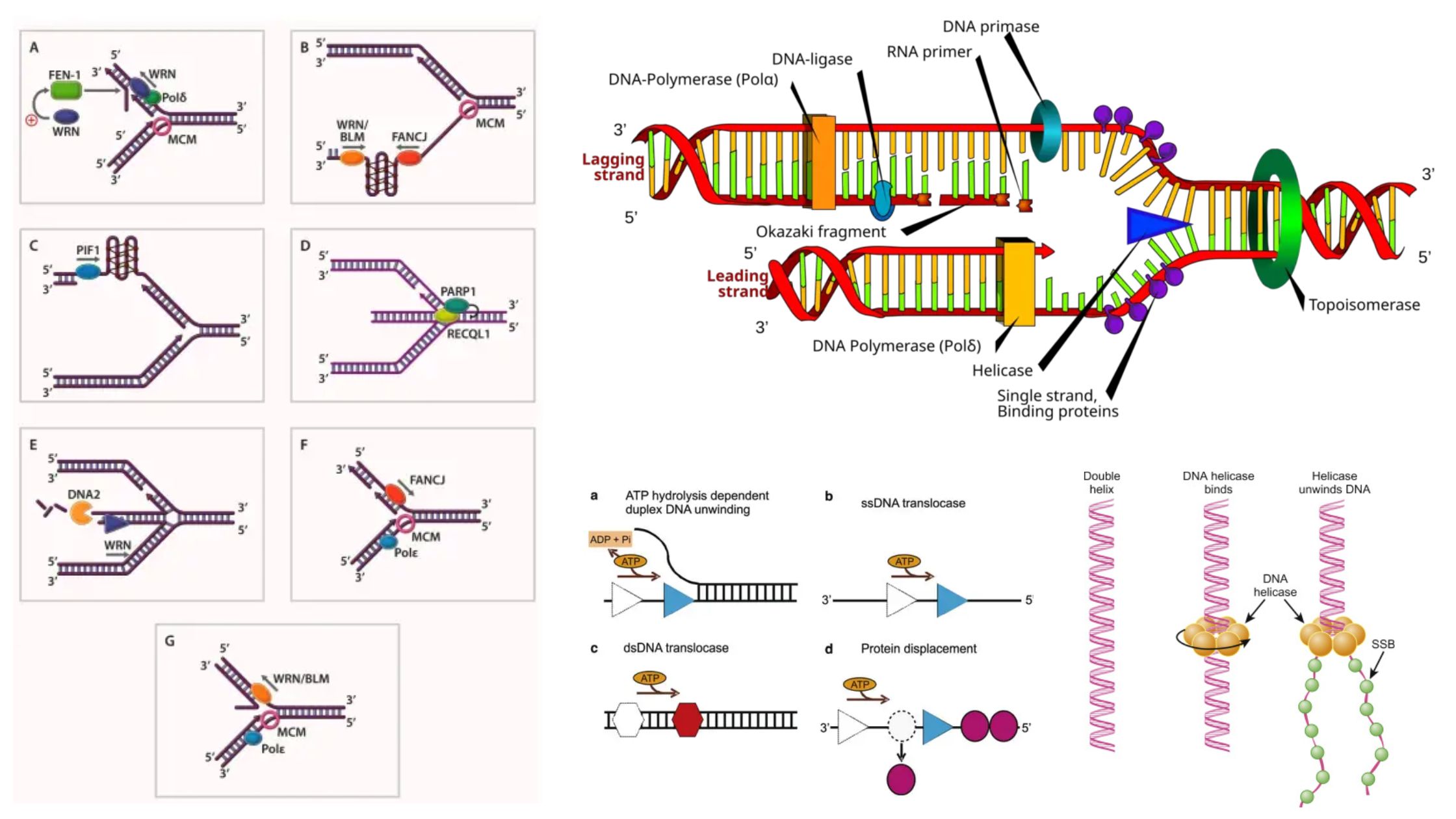
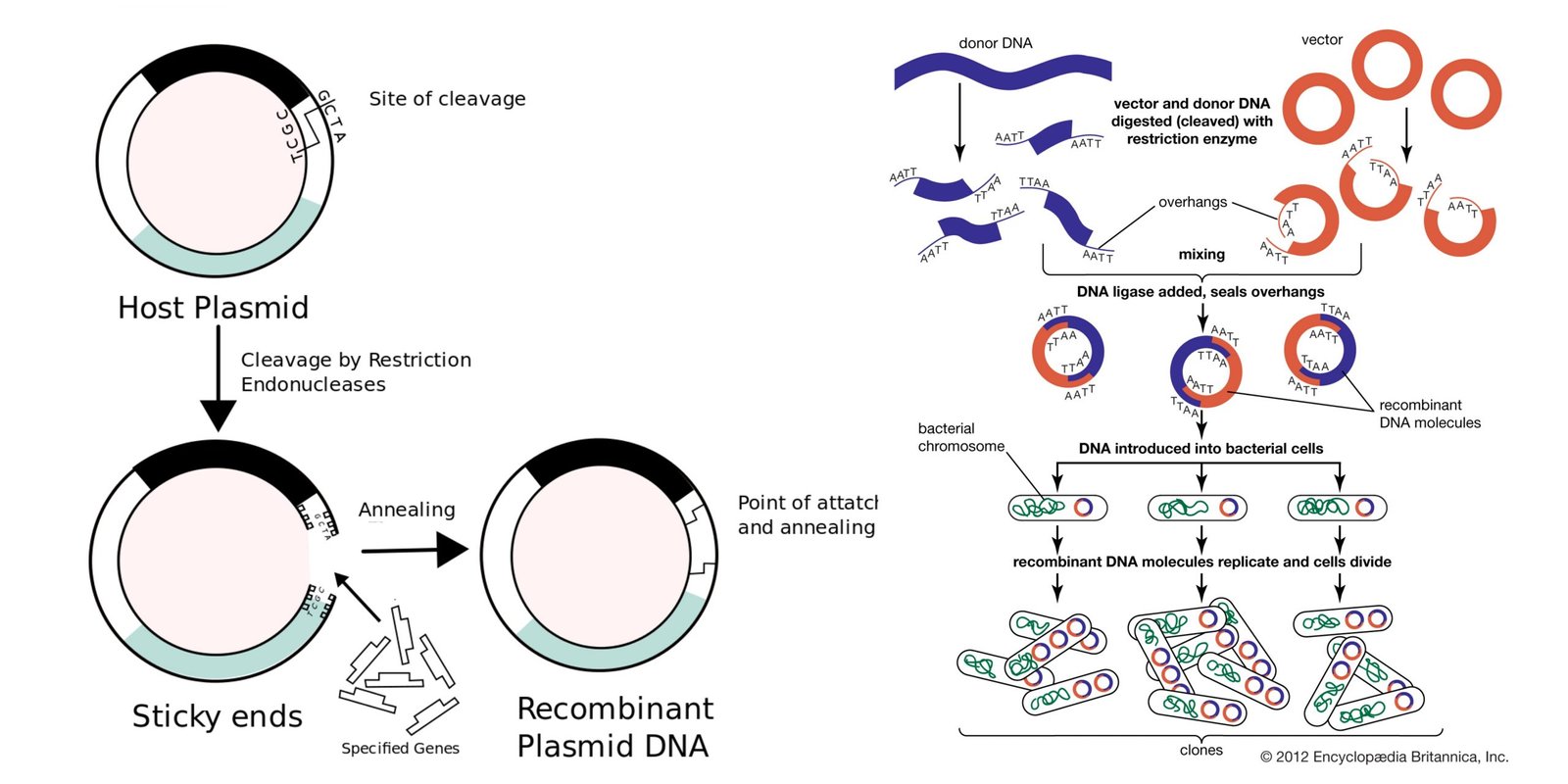
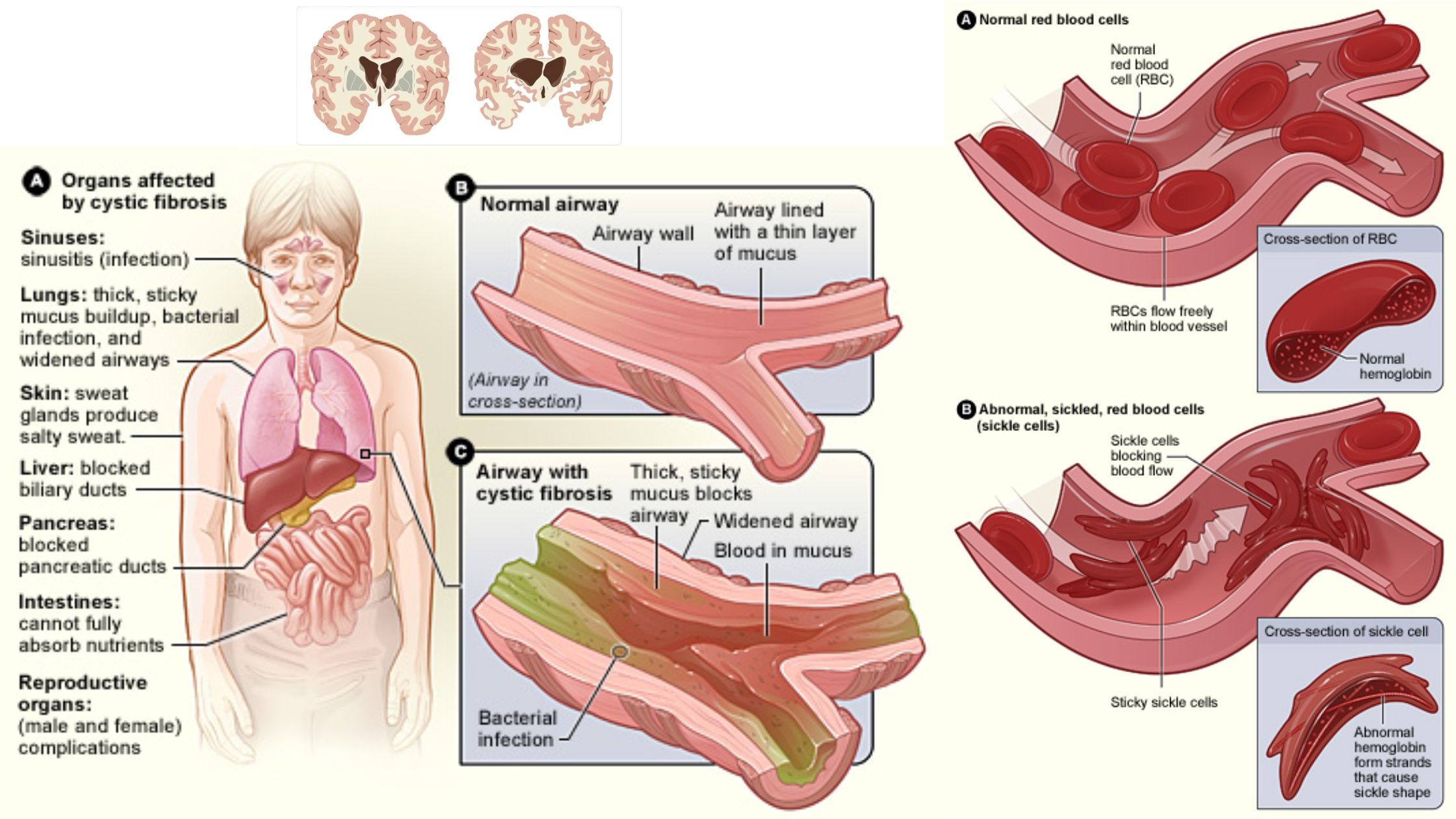
Telomeres – Structure, Aging, Shortening, Functions
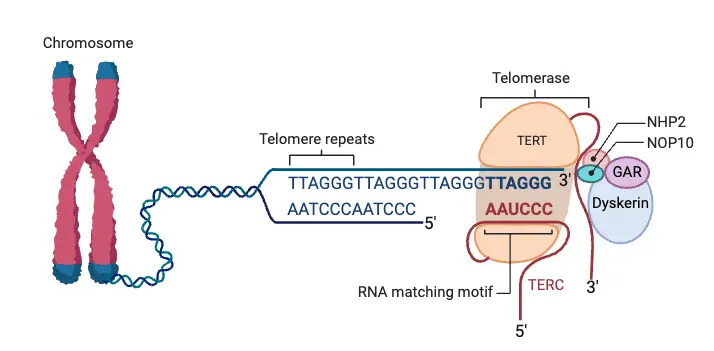
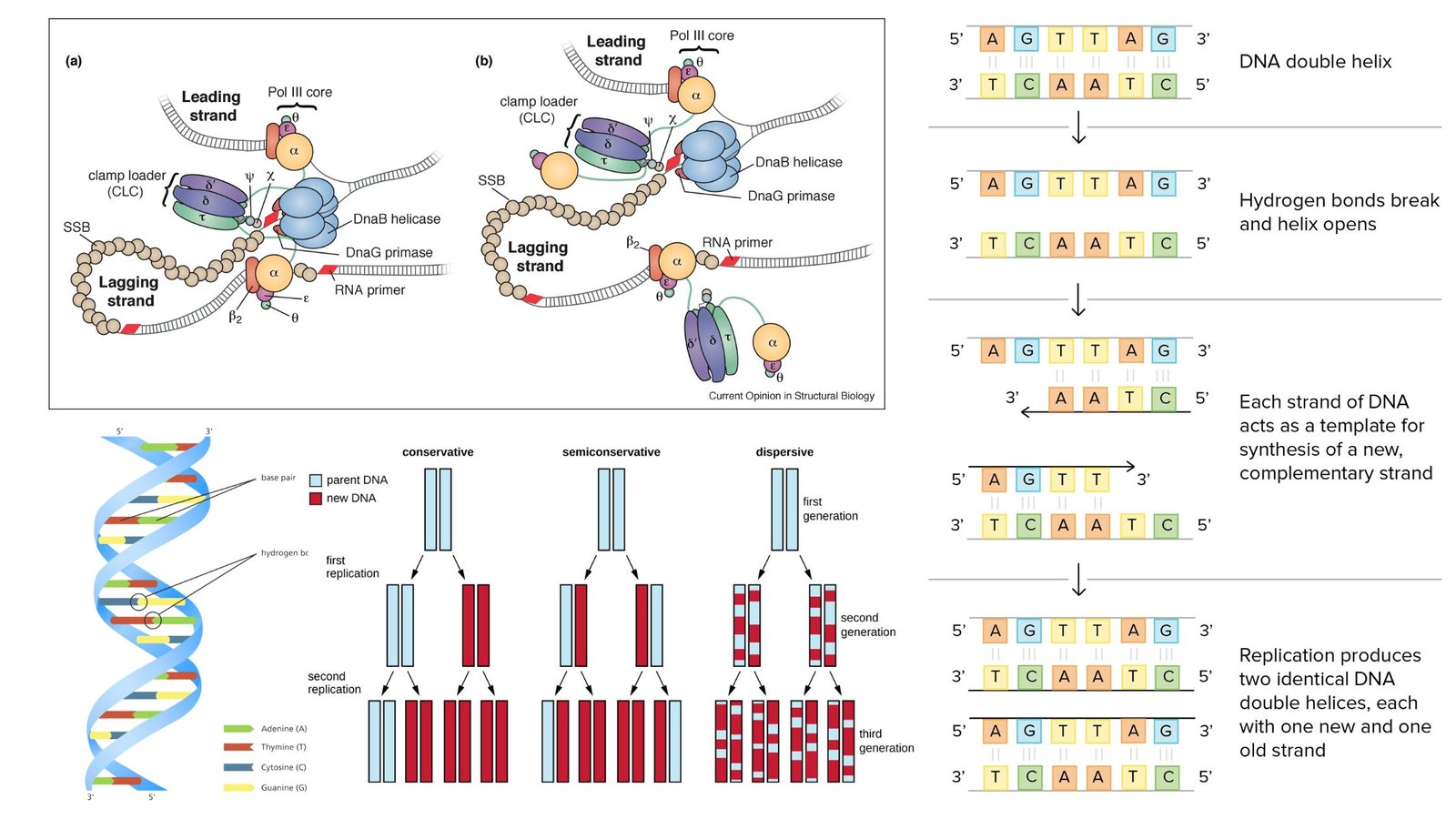
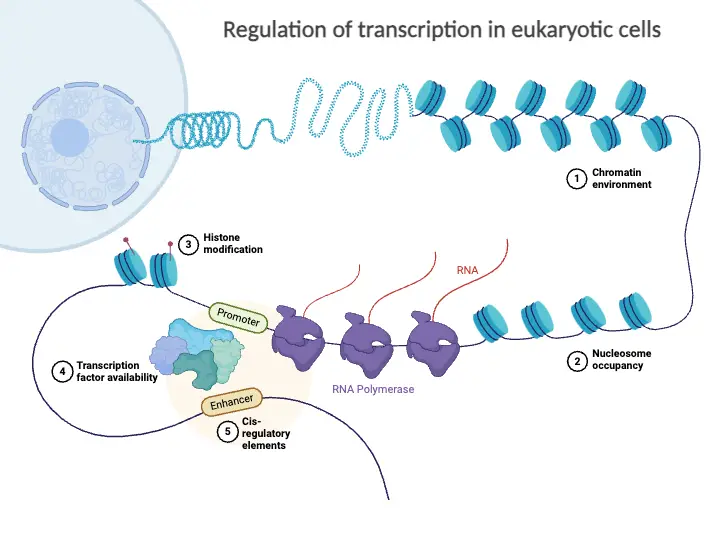
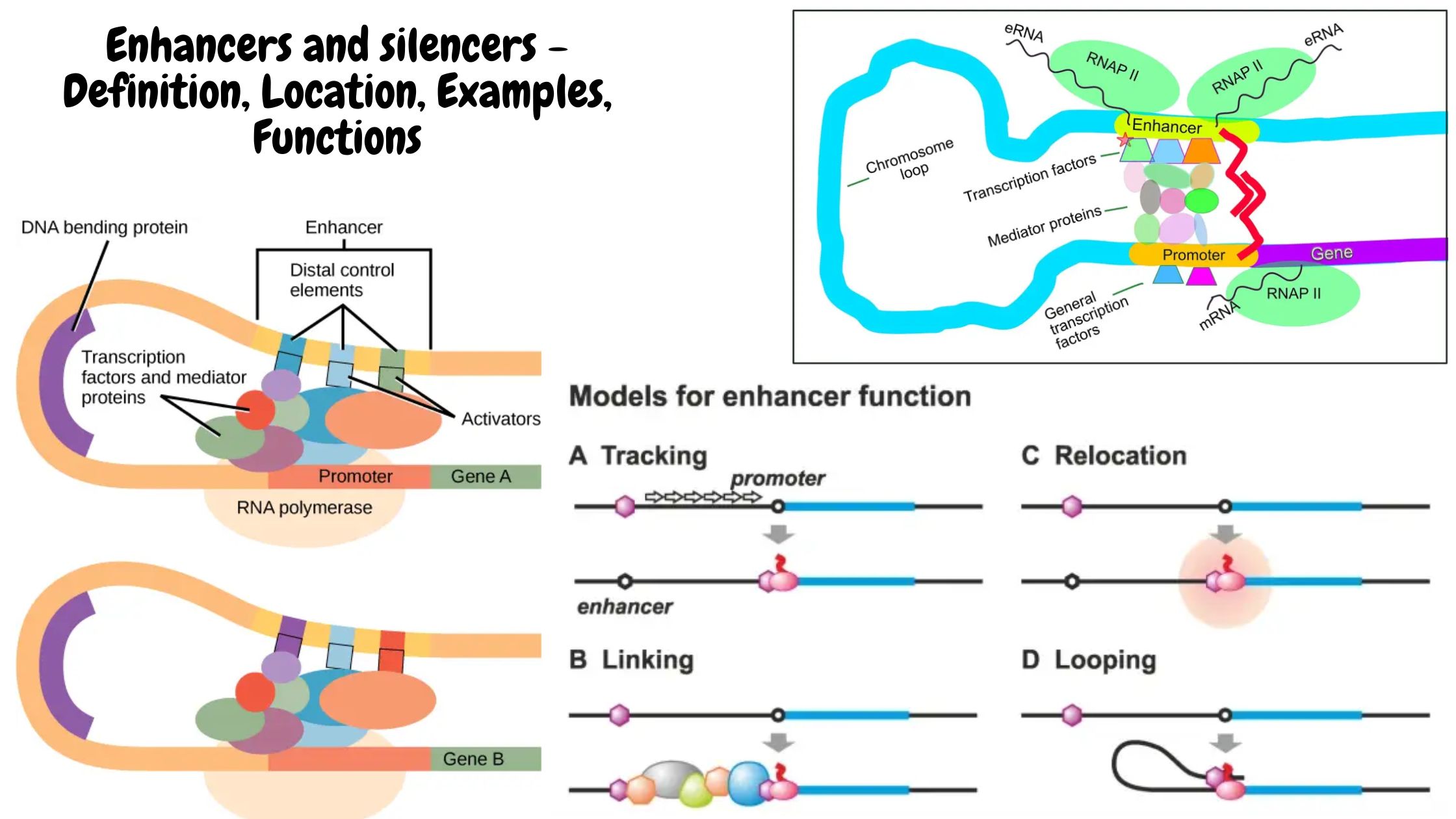
What Are Telomeres (telomere)? At the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes are specialized structures called telomeres. DNA degradation is prevented by repetitive nucleotide sequences of the telomere, which caps and so stabilizes chromosomal DNA during cell division. The termini of chromosomes not only have no translation product but instead have a highly important role in … Read more