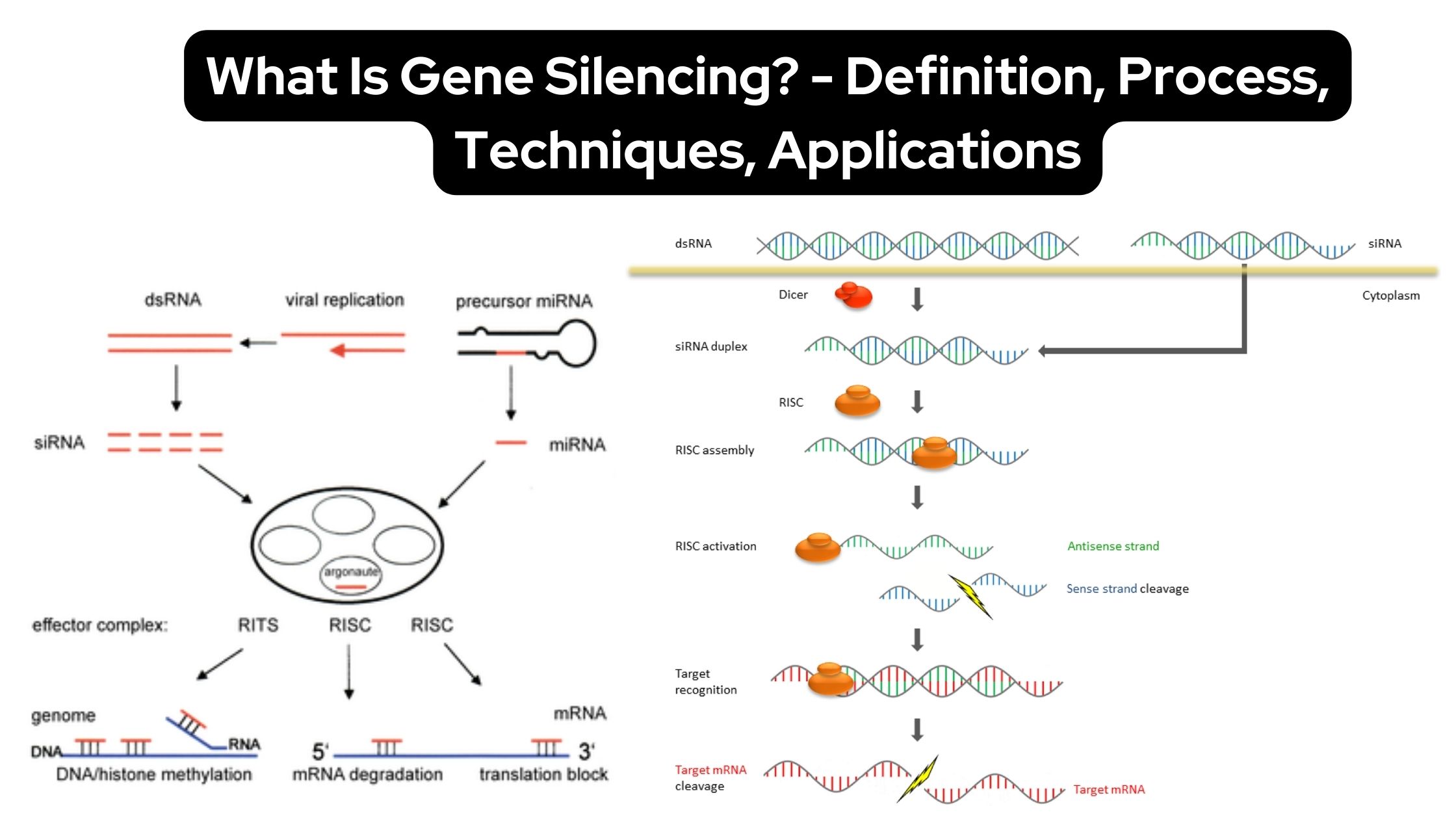
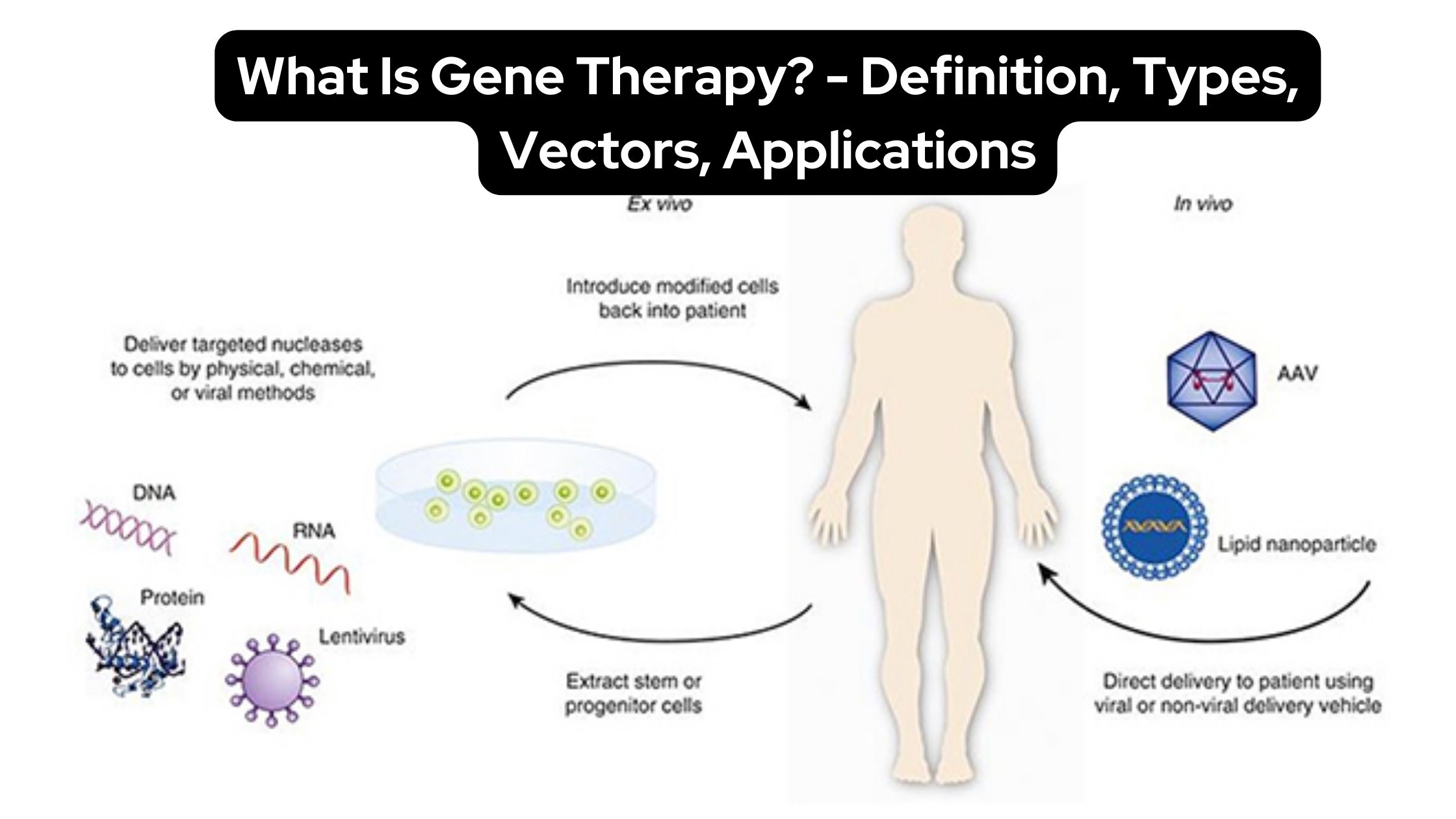
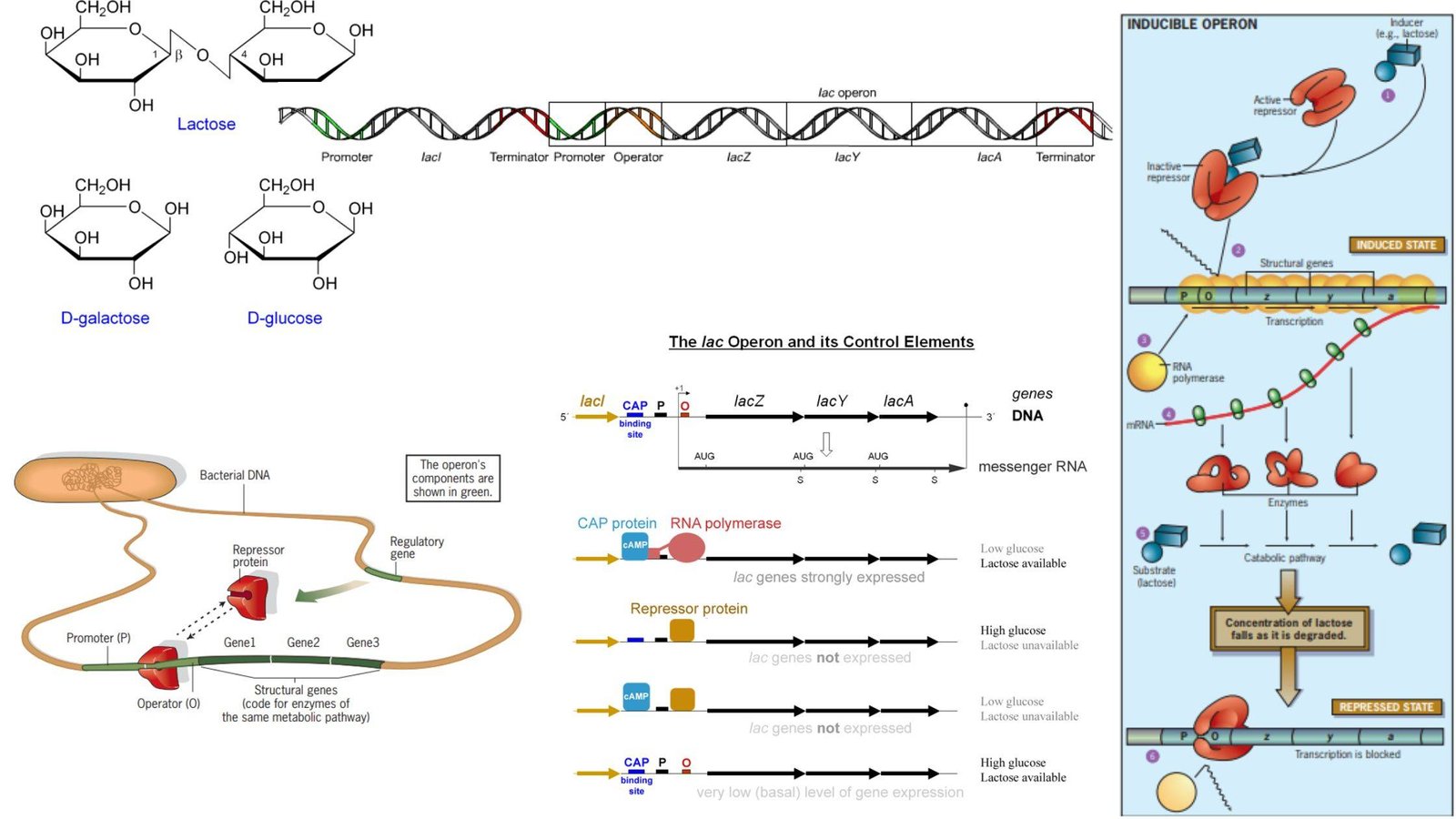
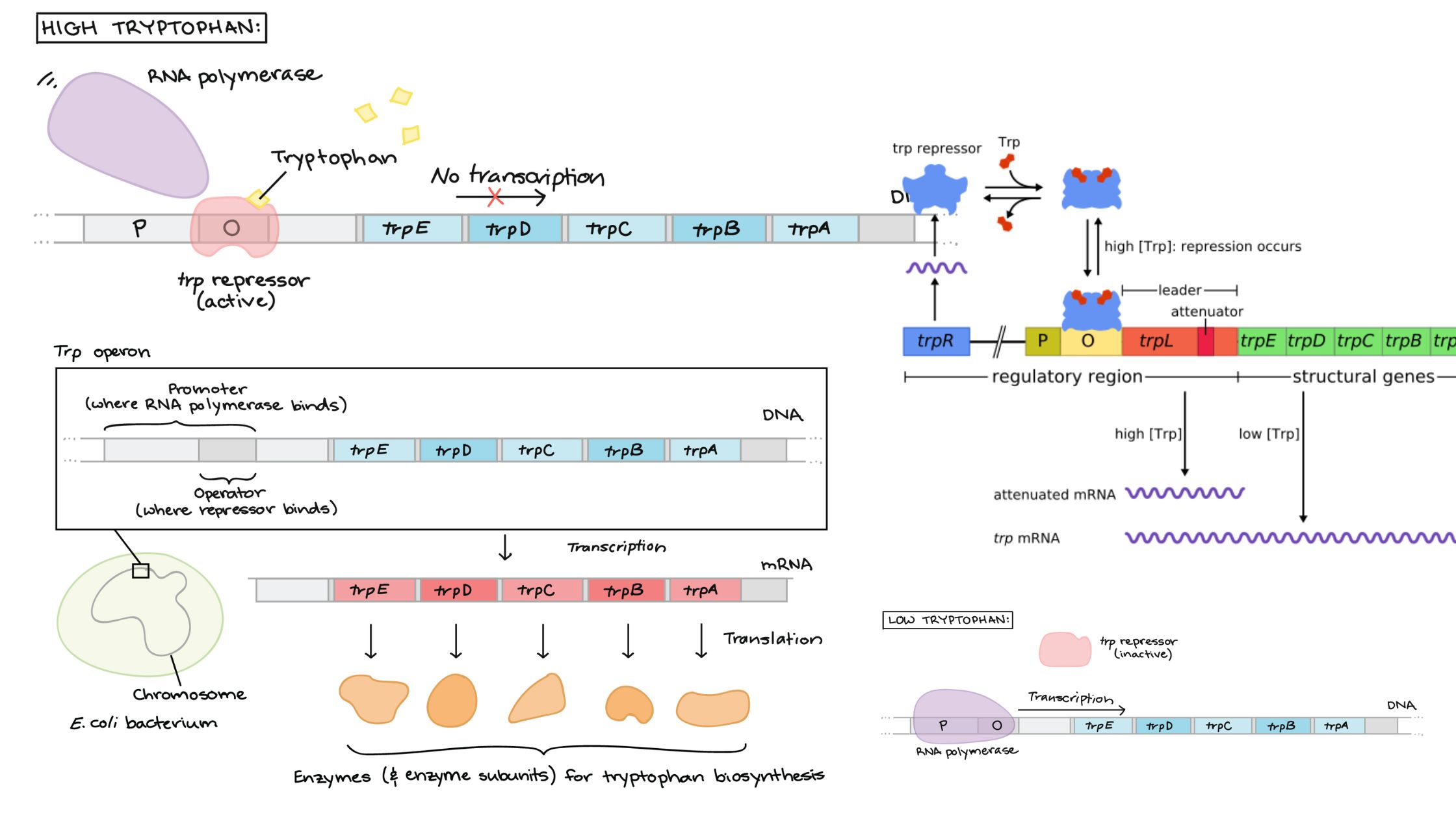
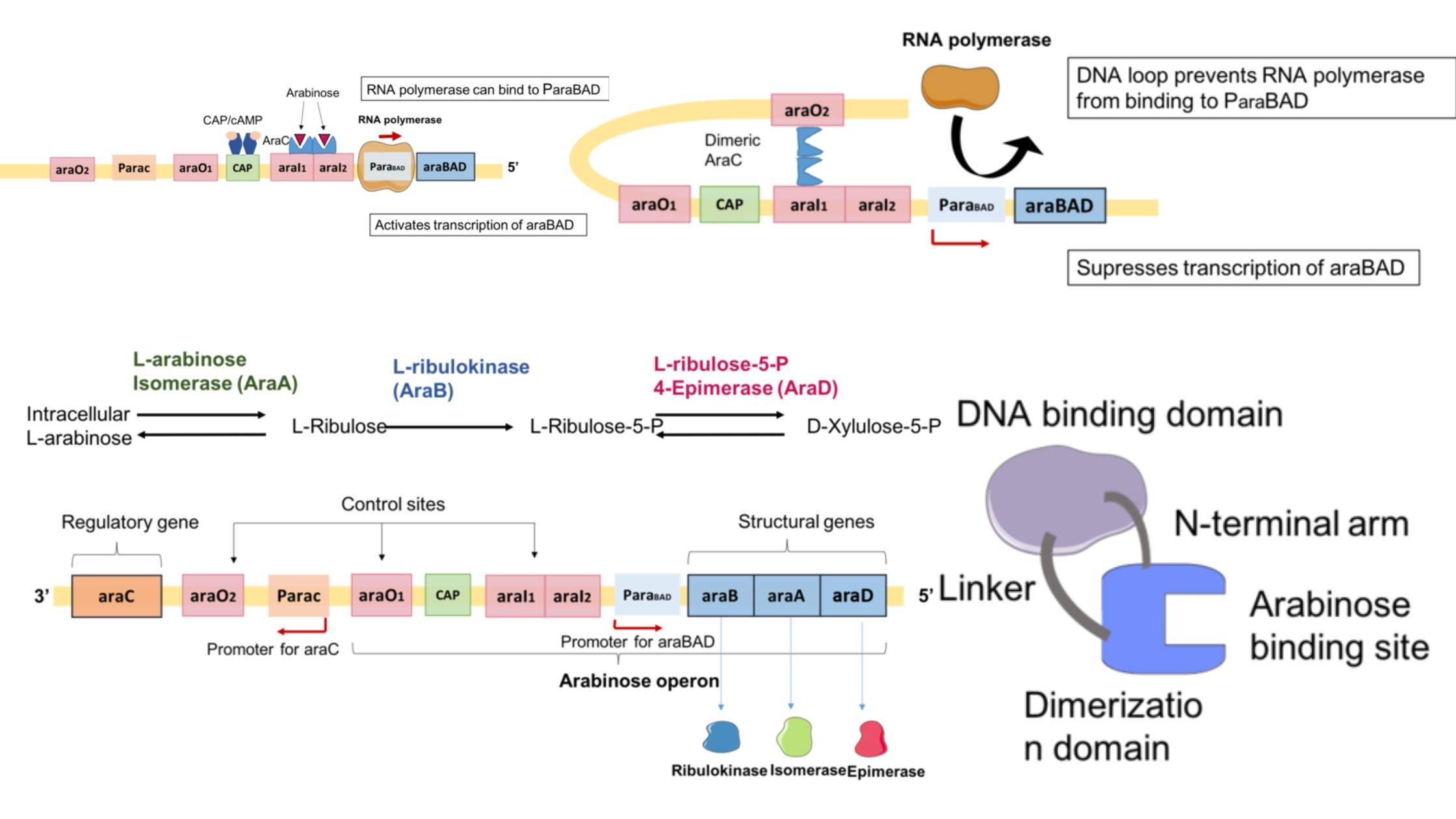
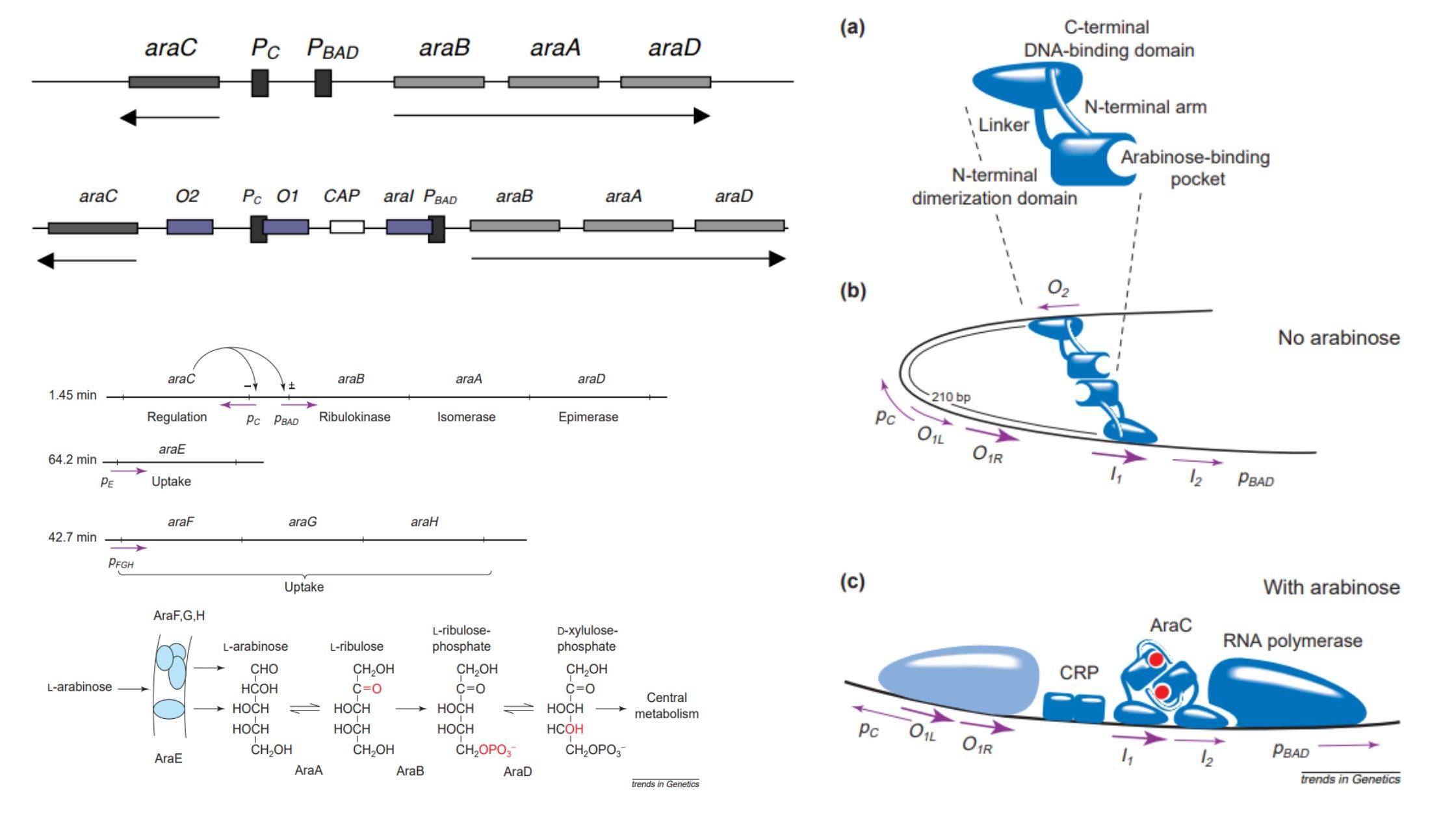
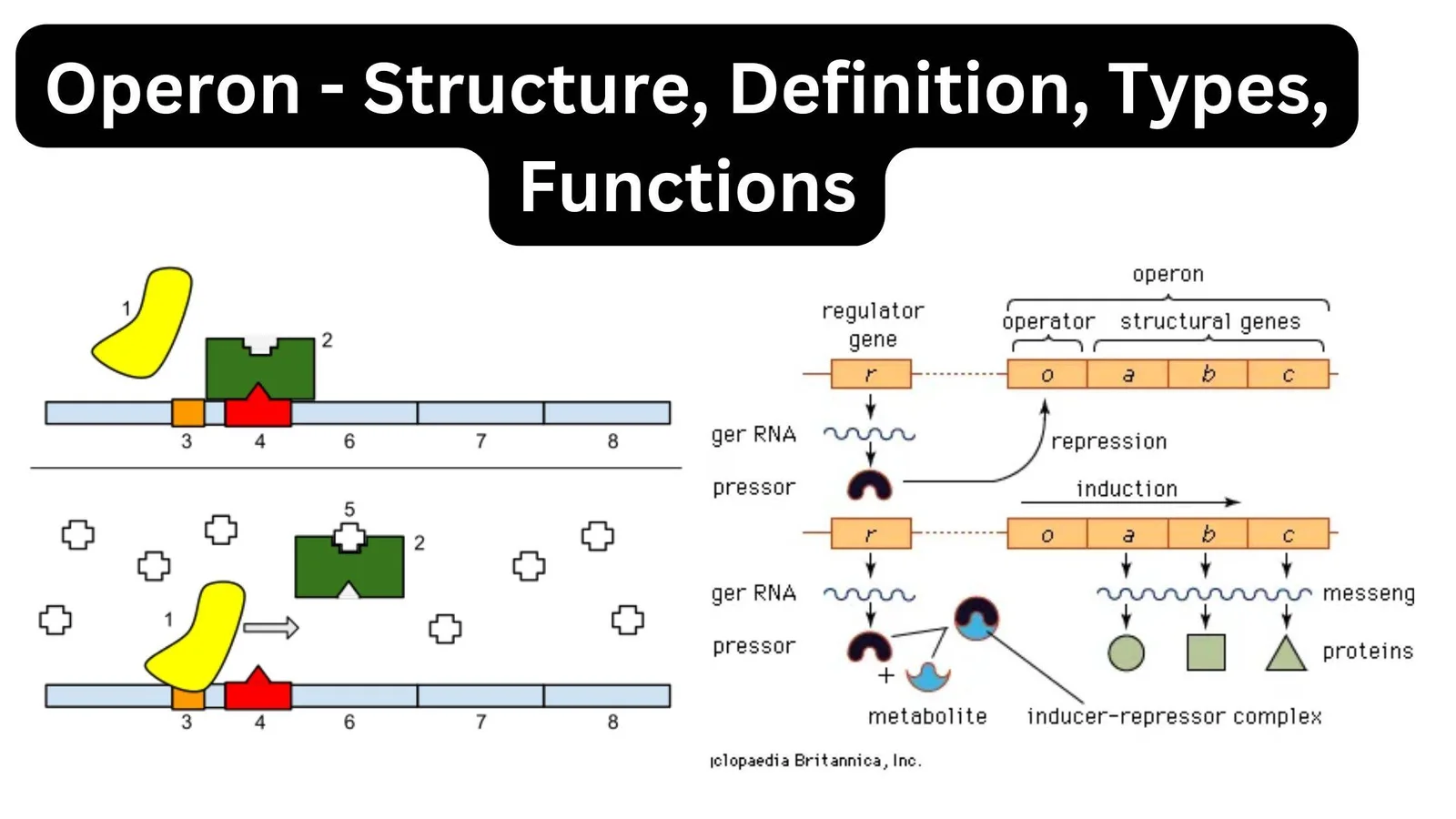
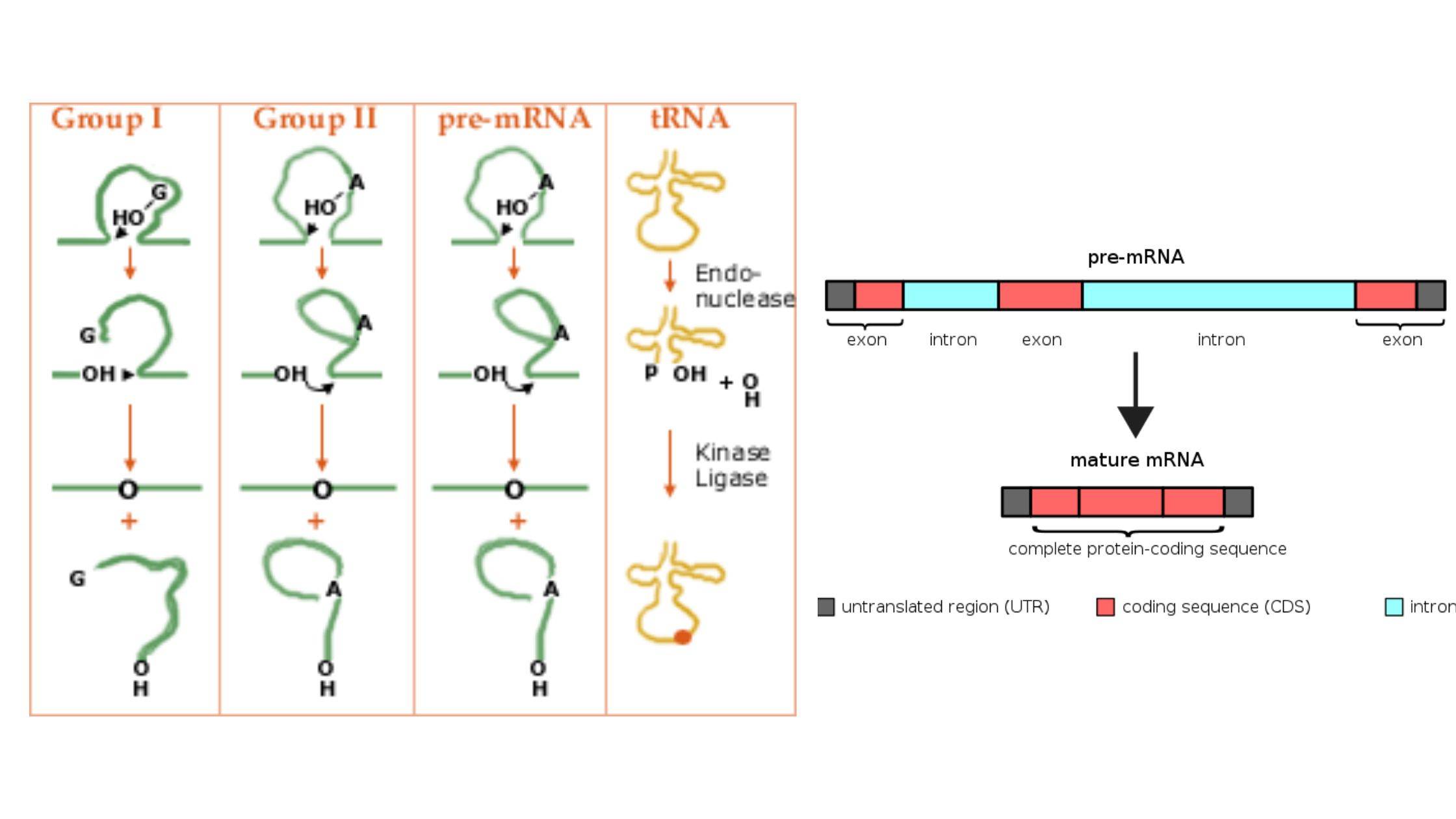
Gene Silencing – Definition, Process, Techniques, Applications
Gene silencing, a mechanism of reducing or suppressing gene expression, is critical in managing gene expression in cells. Genes, which are responsible for protein production, have distinct expression spectra that determine the amount of protein produced by a gene in a specific cell type. When the expression profile of genes is altered, however, it can … Read more