Glycoprotein – Definition, Structure, Functions, Examples
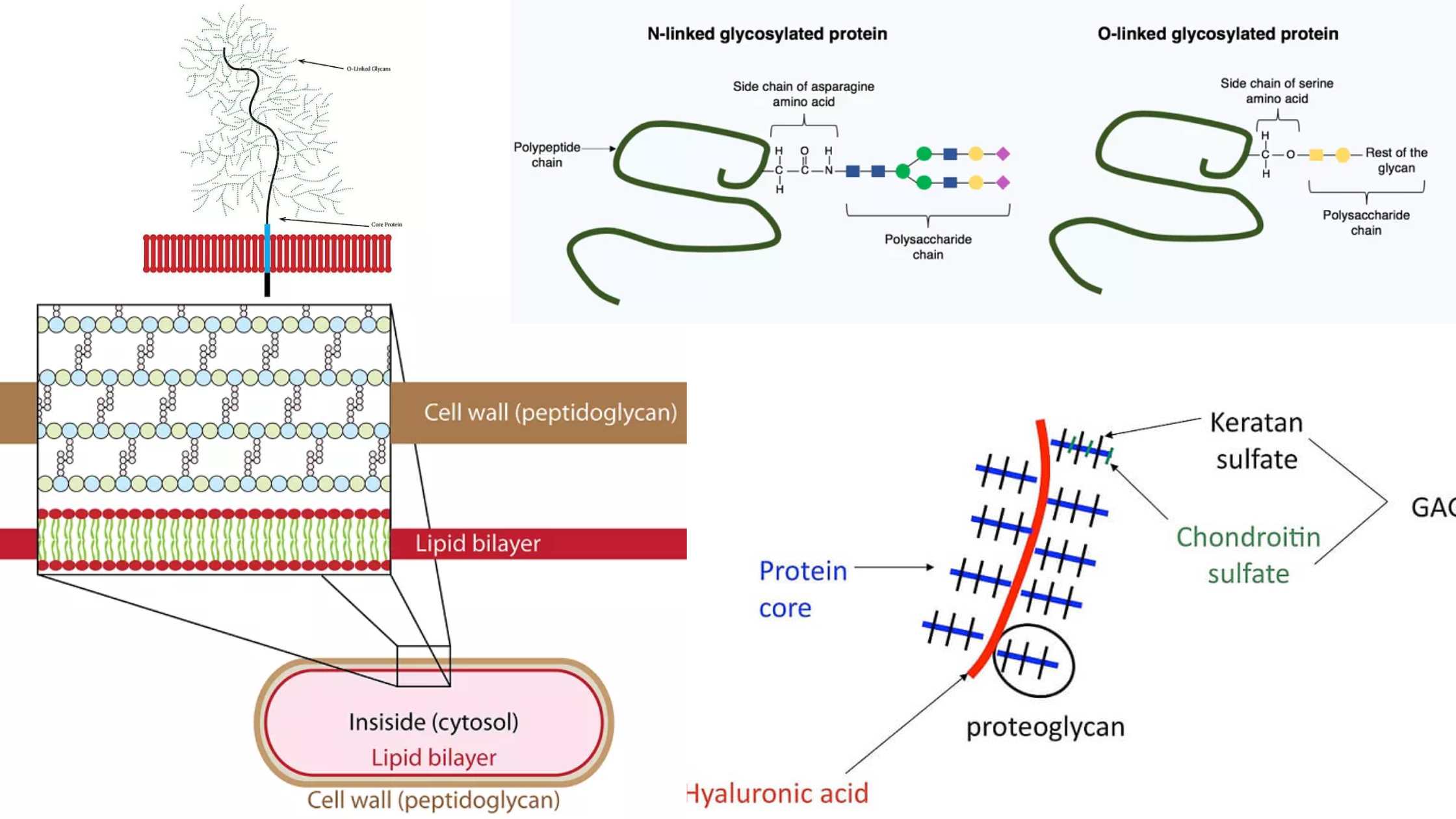
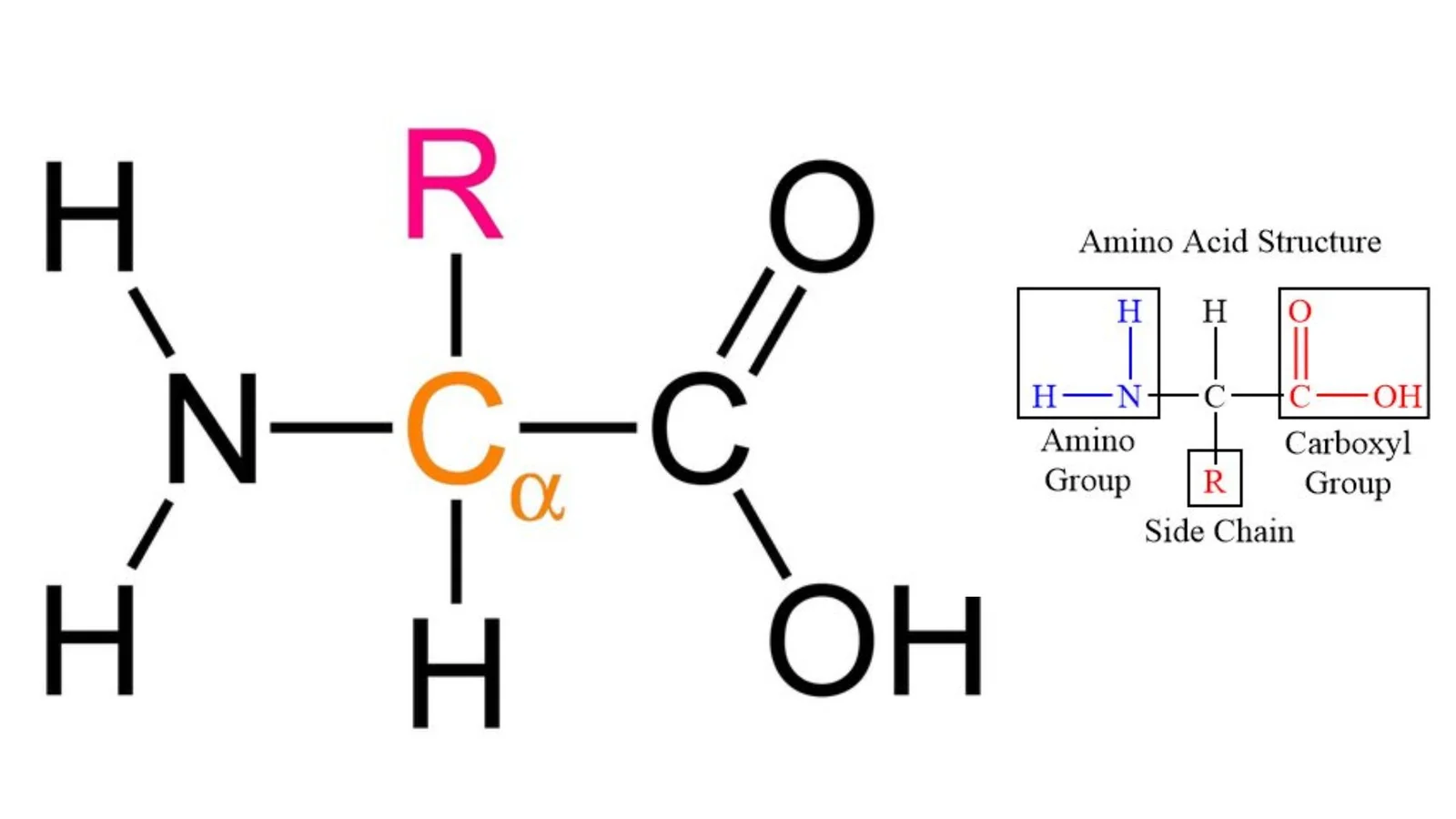
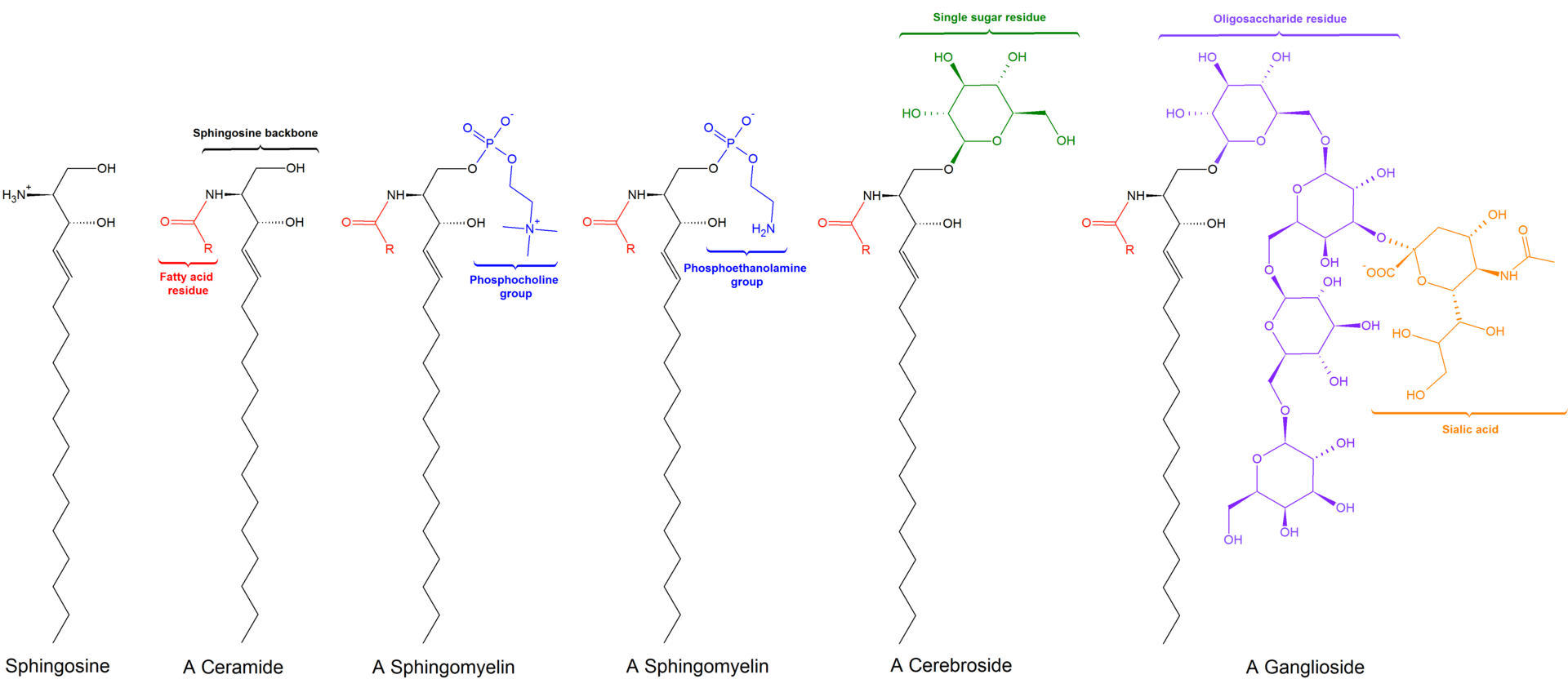
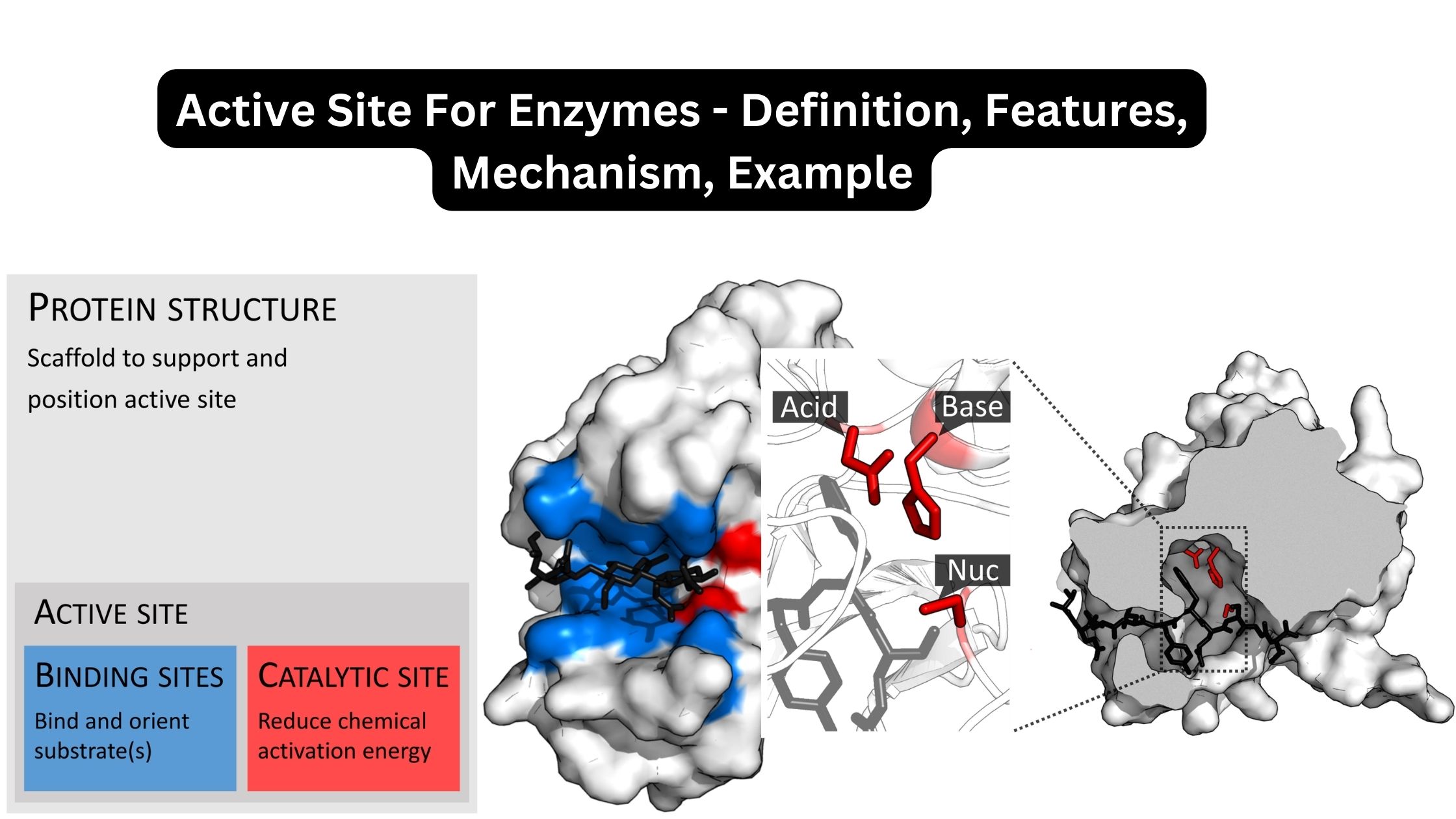
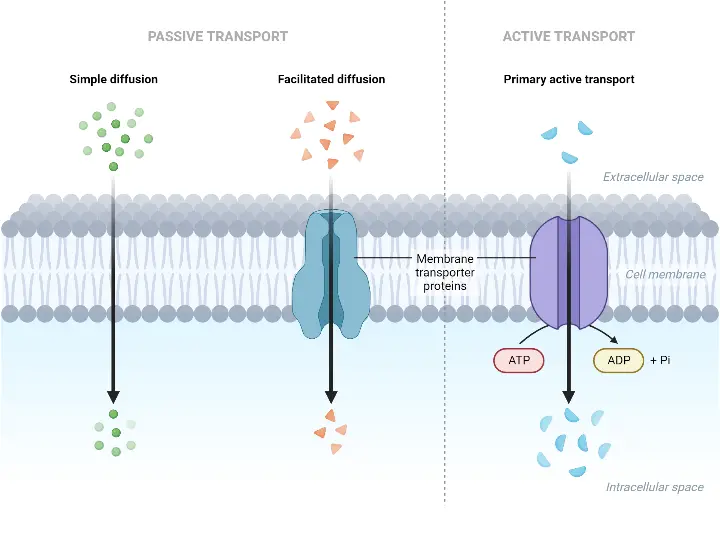
What is Glycoprotein? Definition of Glycoprotein A glycoprotein is a complex molecule composed of a protein covalently bonded to one or more carbohydrate chains, playing diverse roles in biological processes and cell-to-cell interactions. Glycoprotein Structure Methods used to study glycoproteins Glycoproteins, with their intricate structures and multifaceted roles in biological systems, necessitate advanced methodologies for … Read more