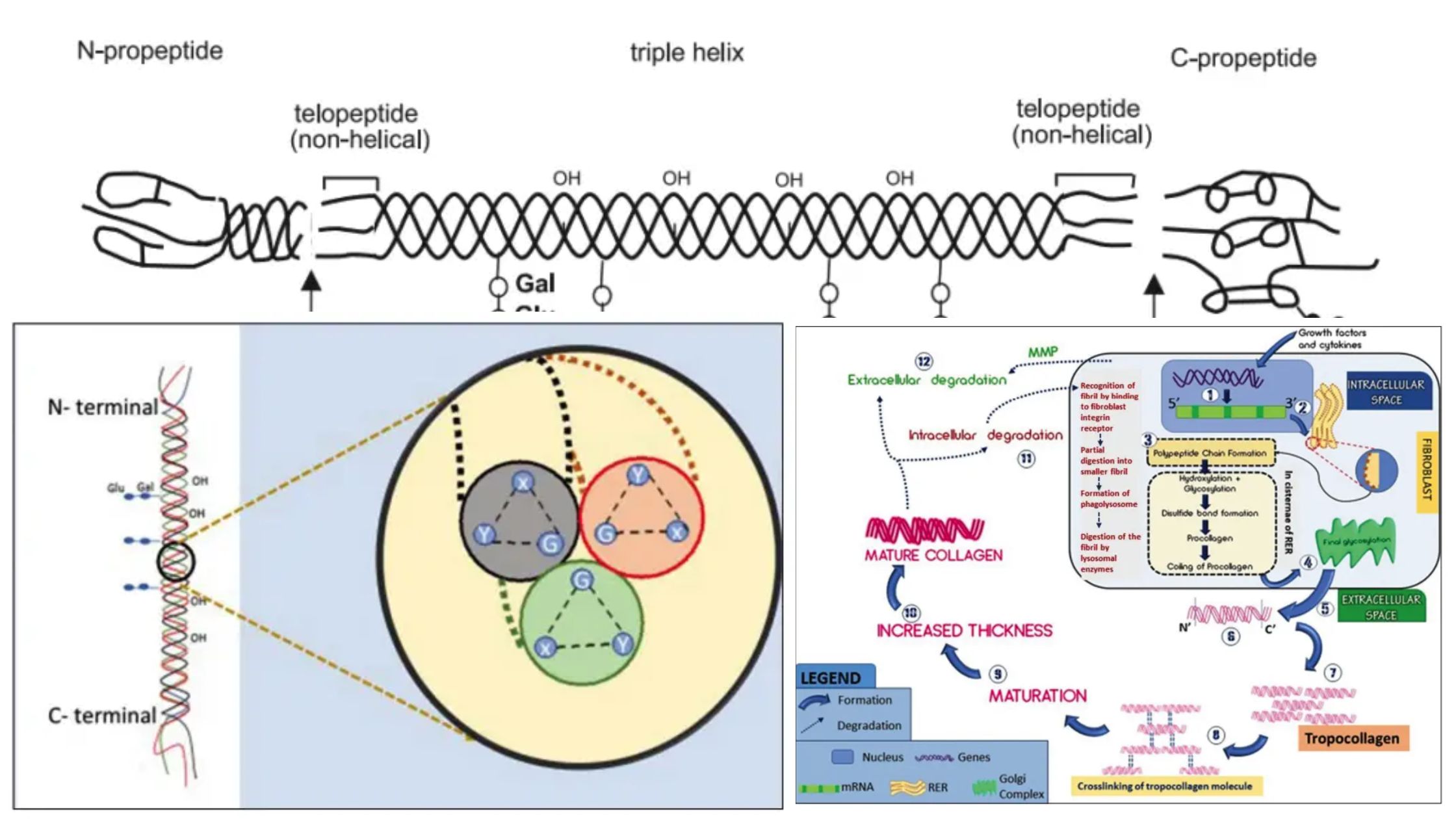
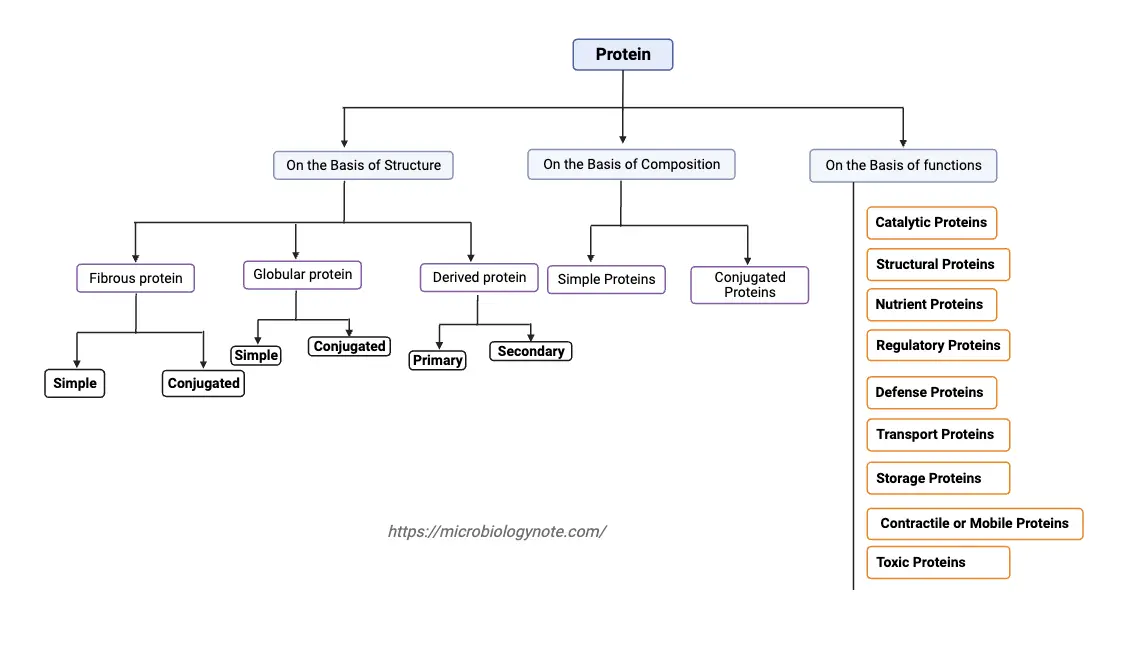
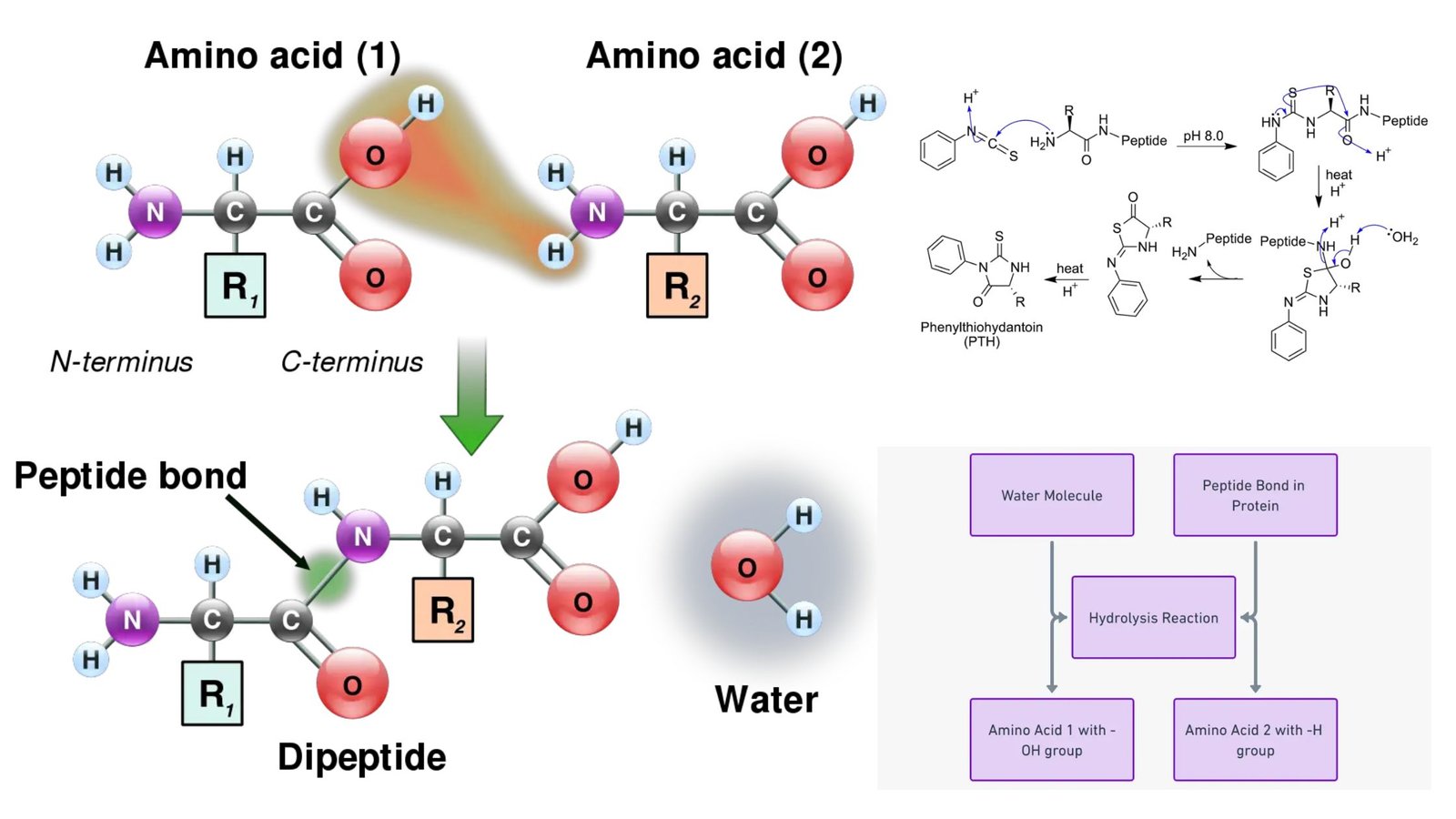
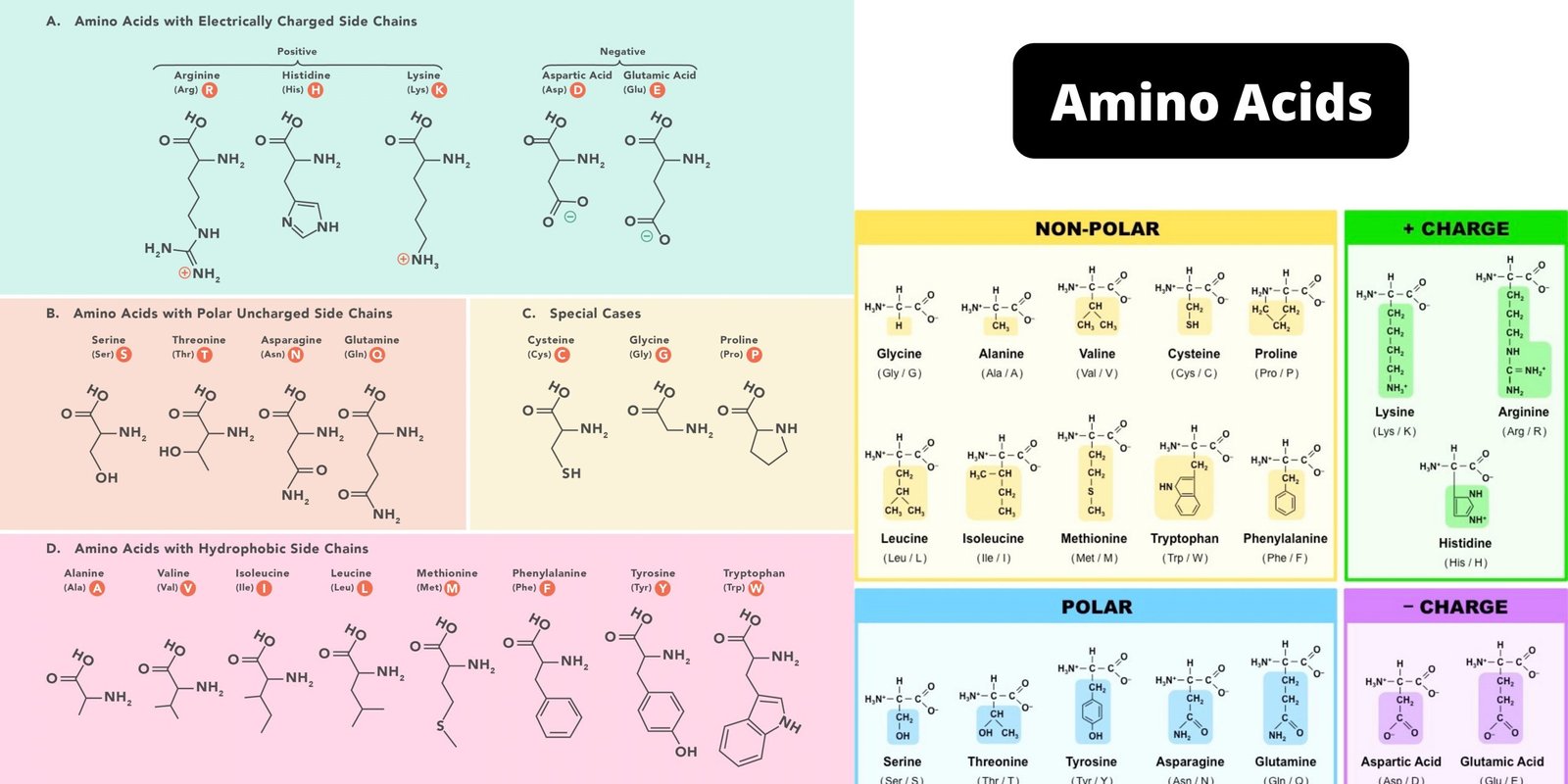
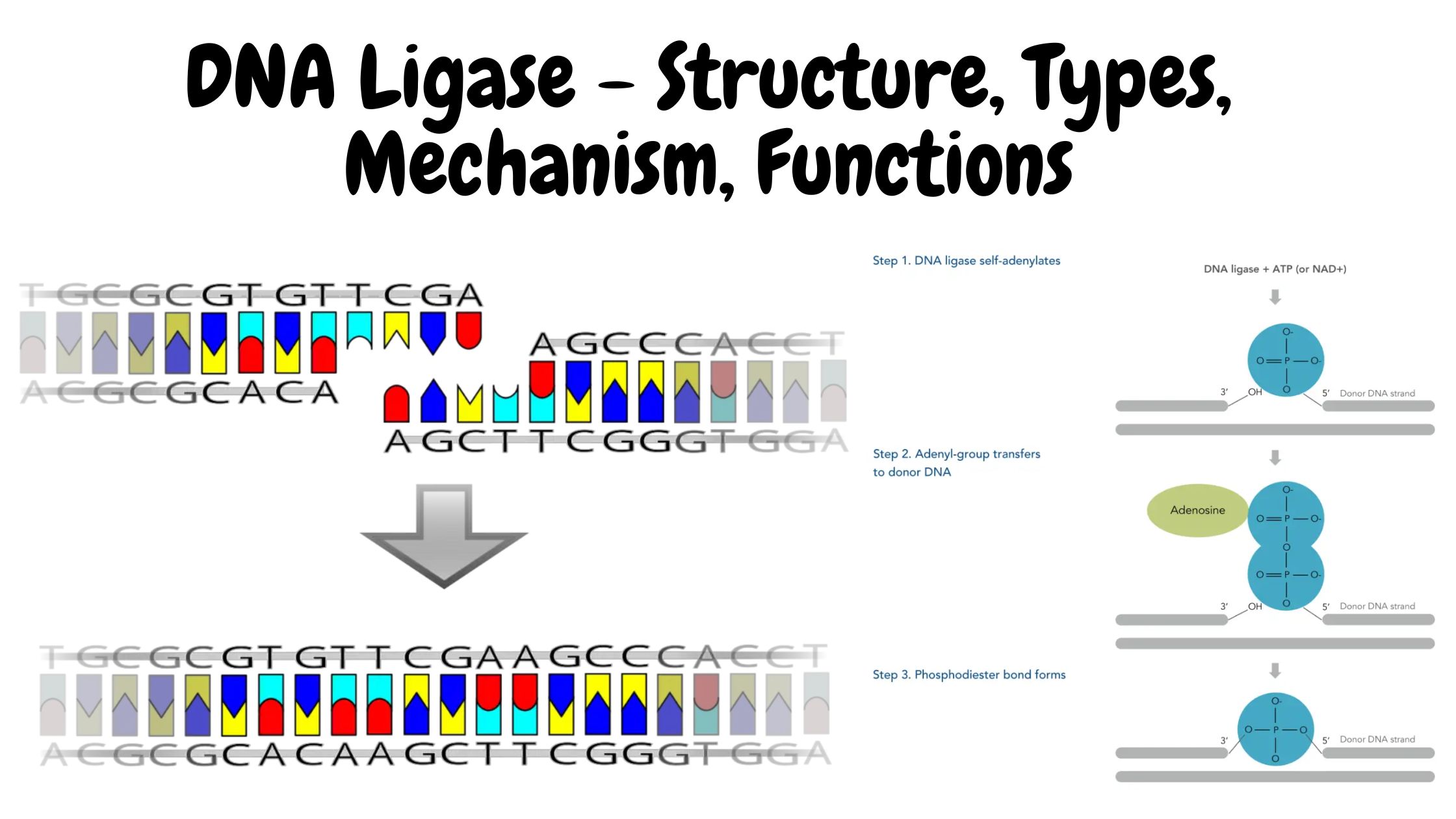
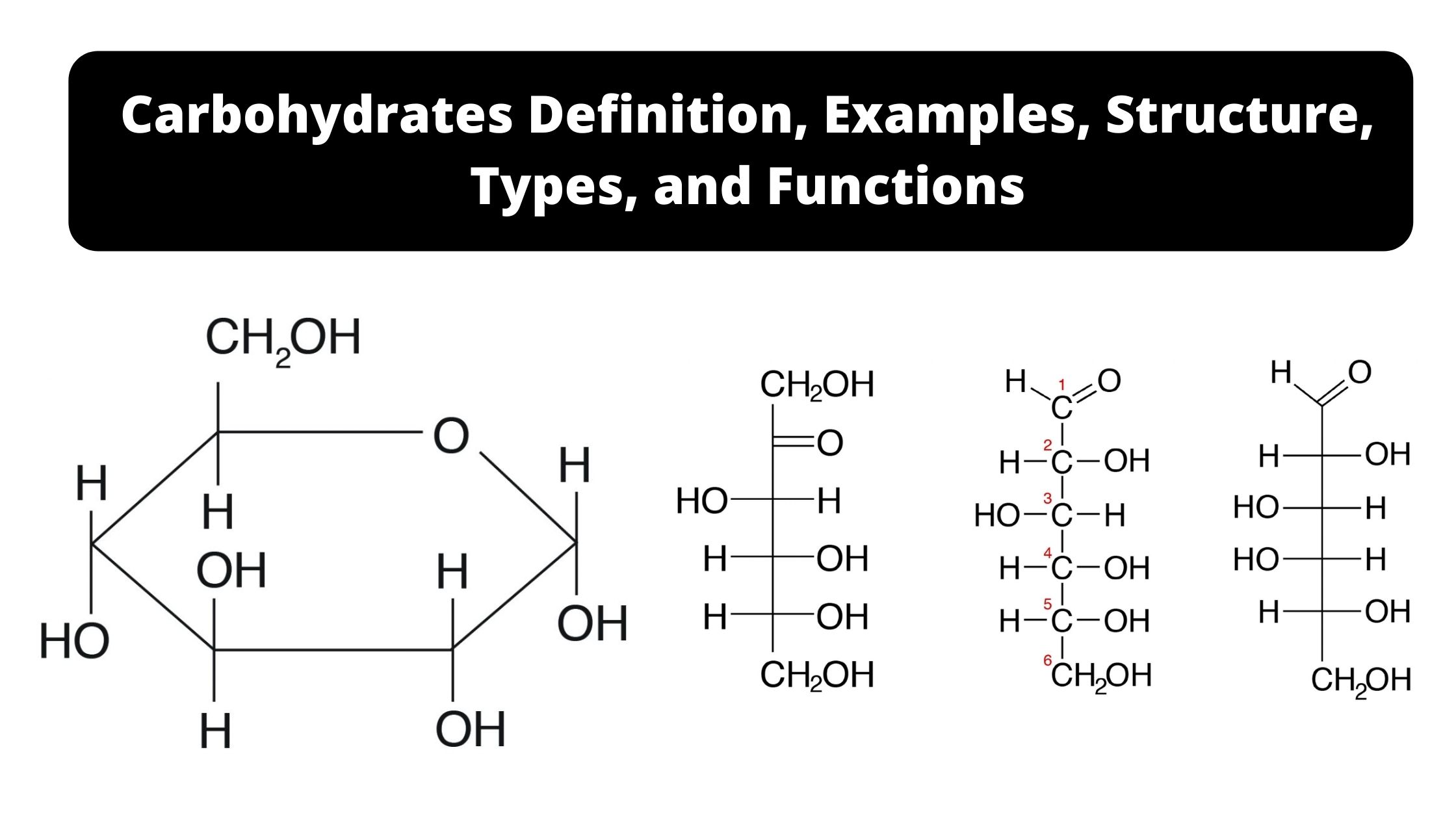
Glycolysis – Definition, Steps, Enzymes, Regulation, Result
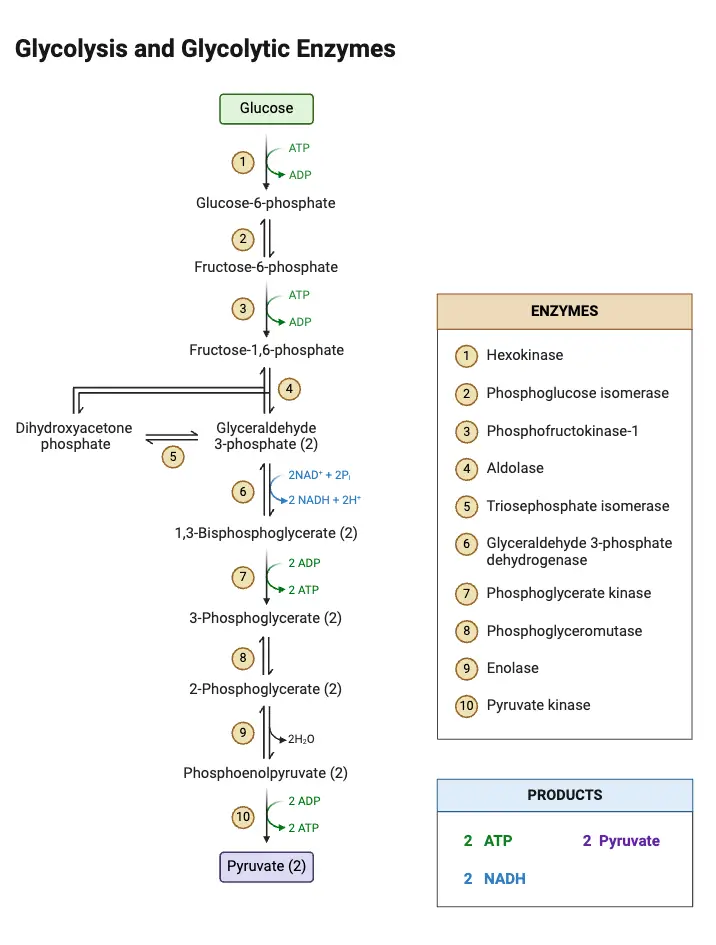
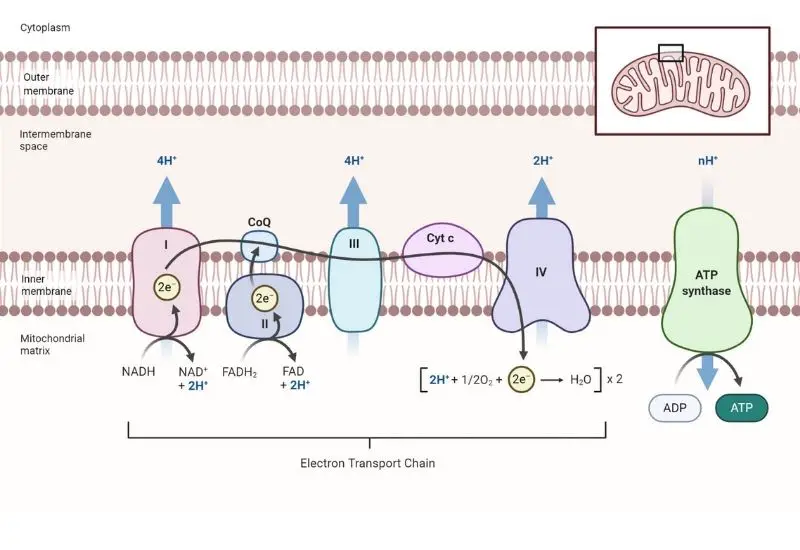
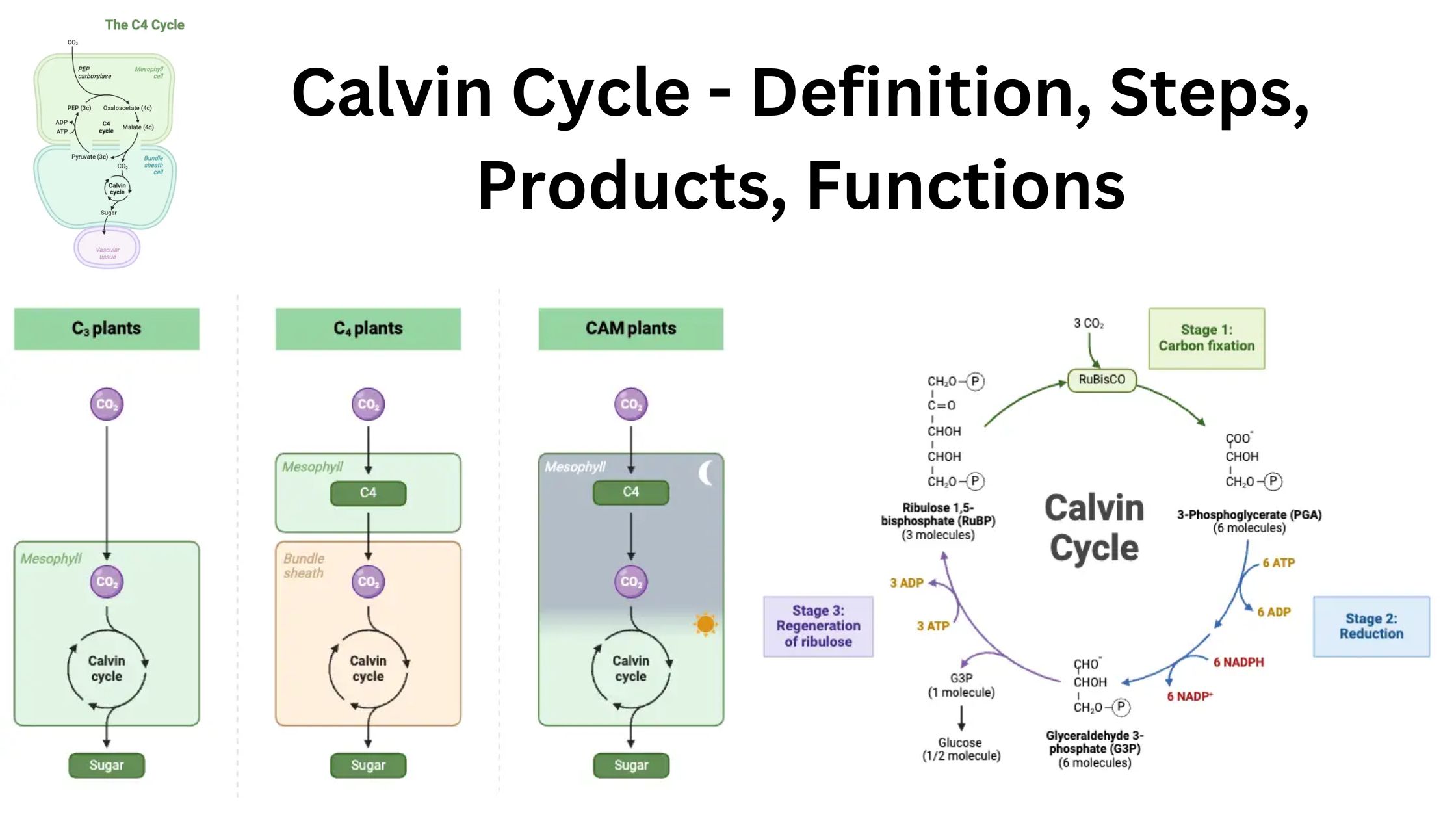
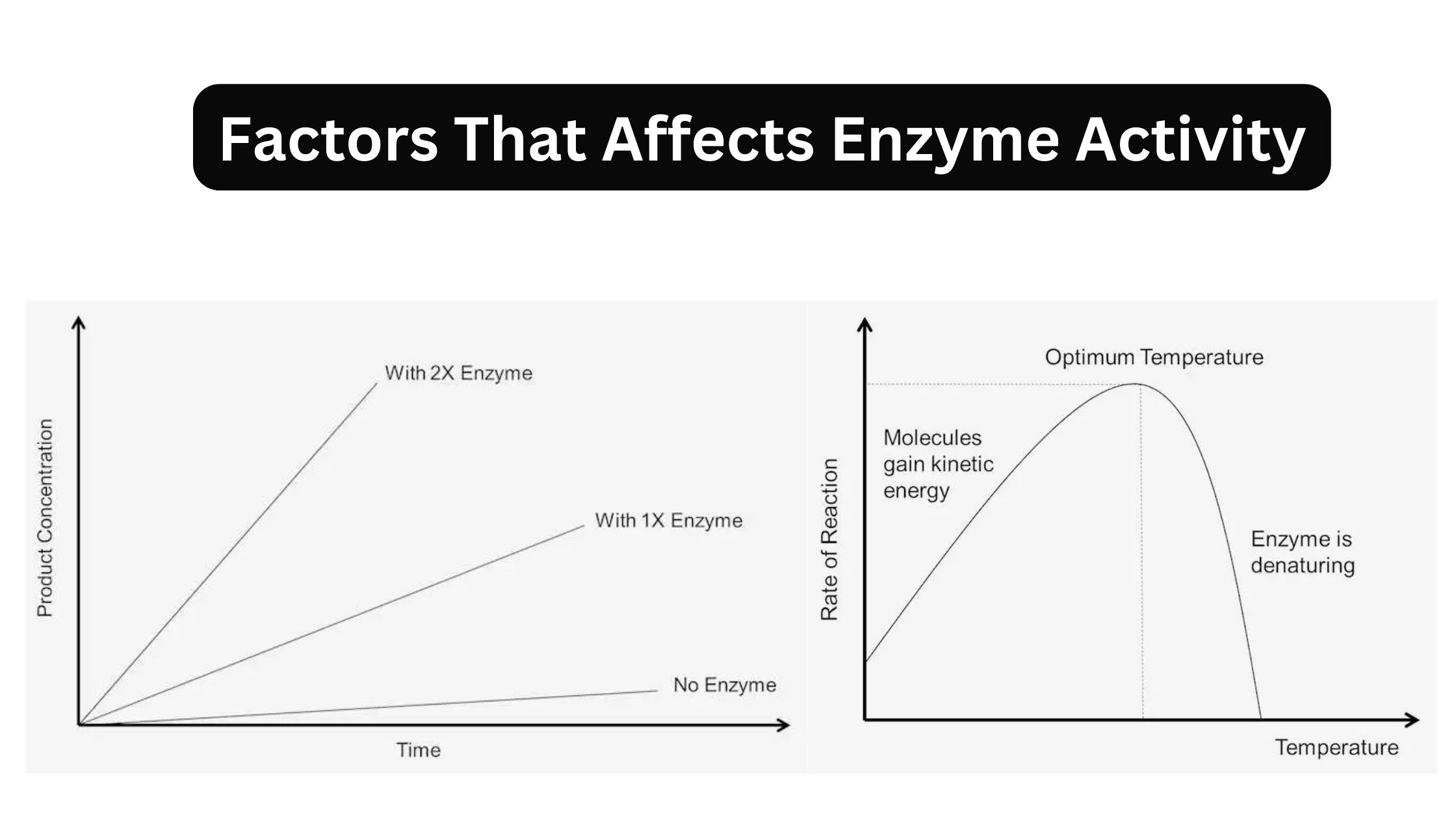
What is glycolysis? Definition of glycolysis Glycolysis is a metabolic process in which glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules, producing a net gain of two ATP and two NADH molecules. This anaerobic pathway occurs in the cytosol and is a key step in cellular energy production. Major Features of … Read more