Haworth Projection – Definition, Characterisitcs, Examples
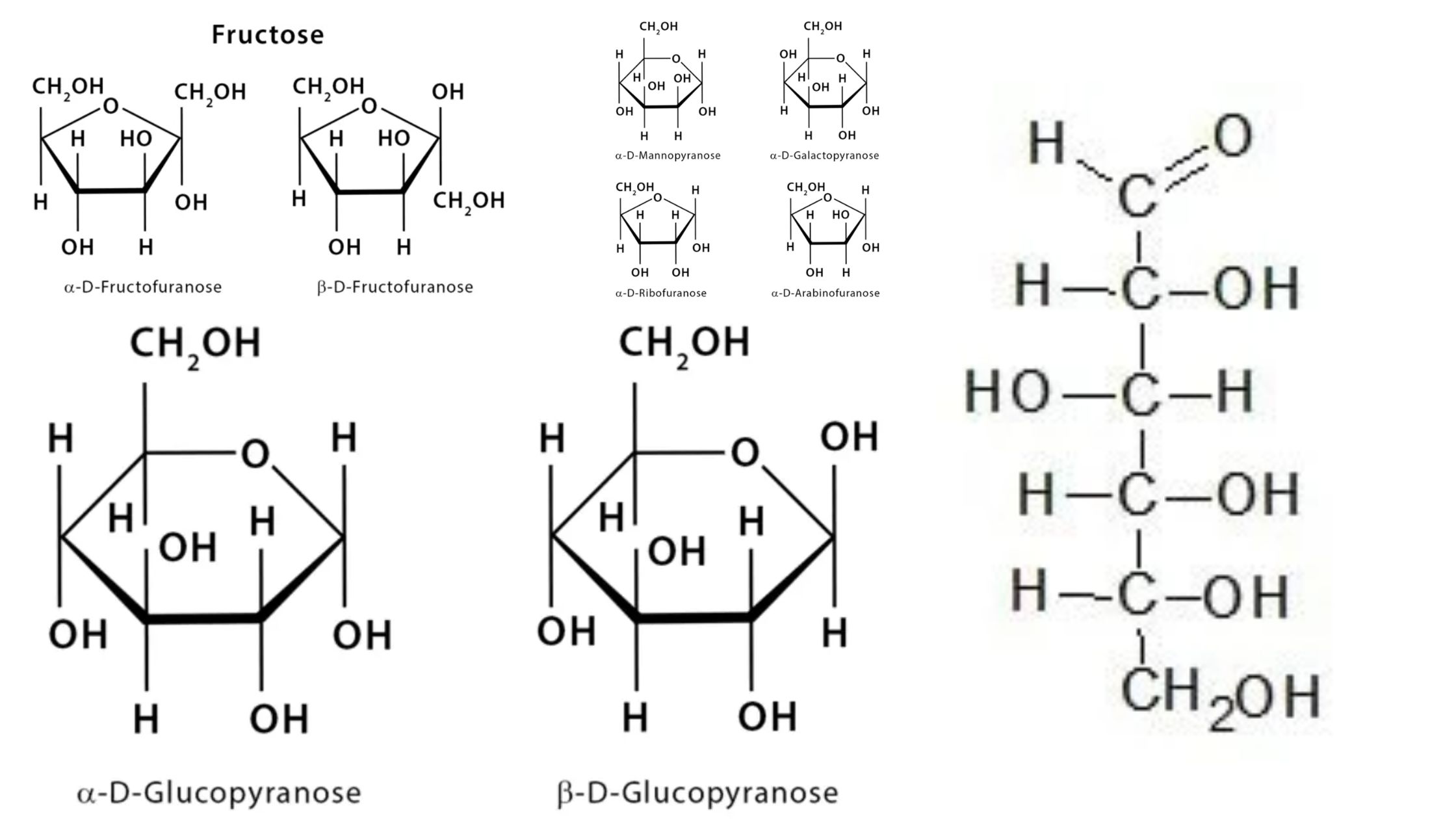
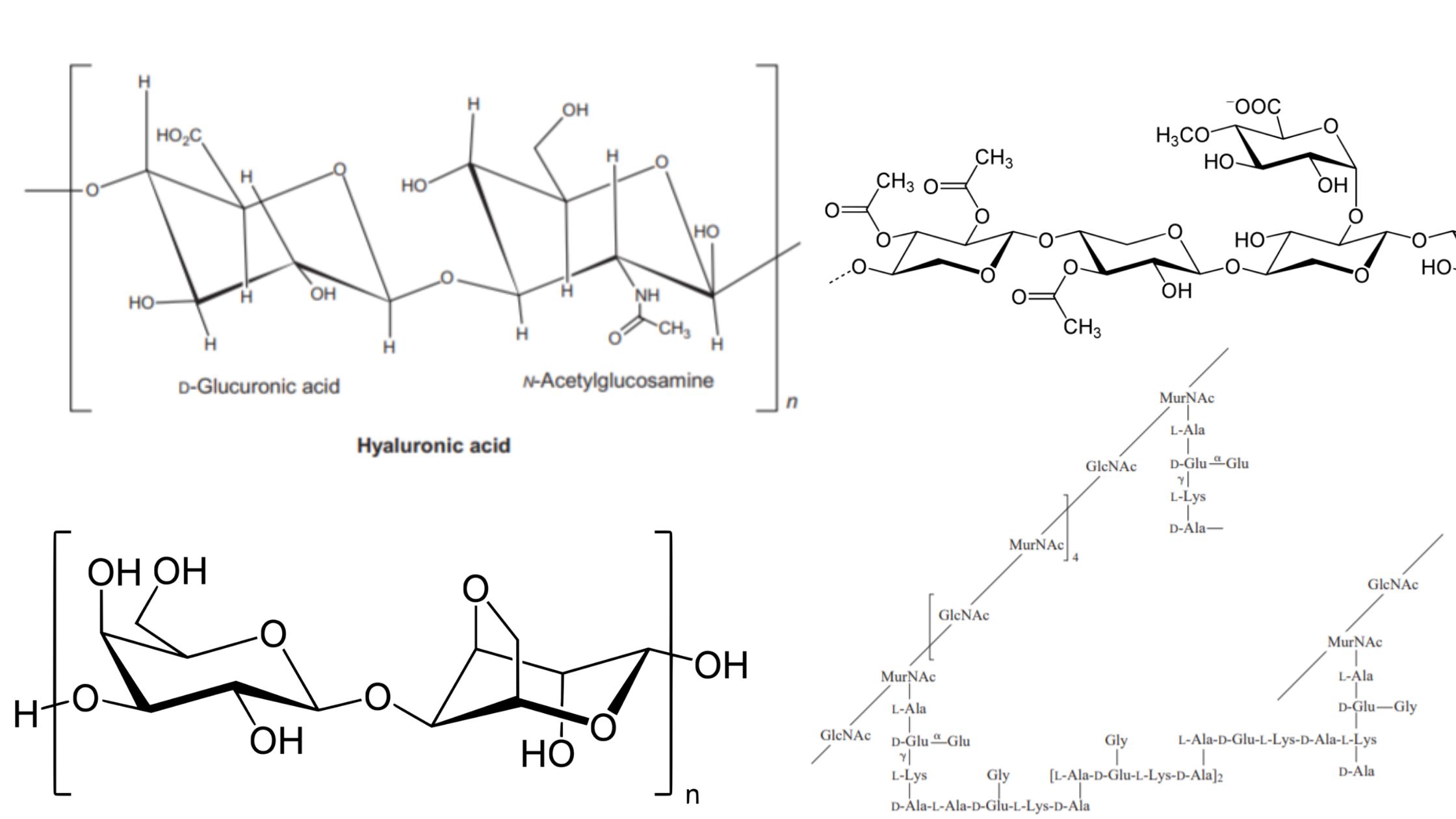
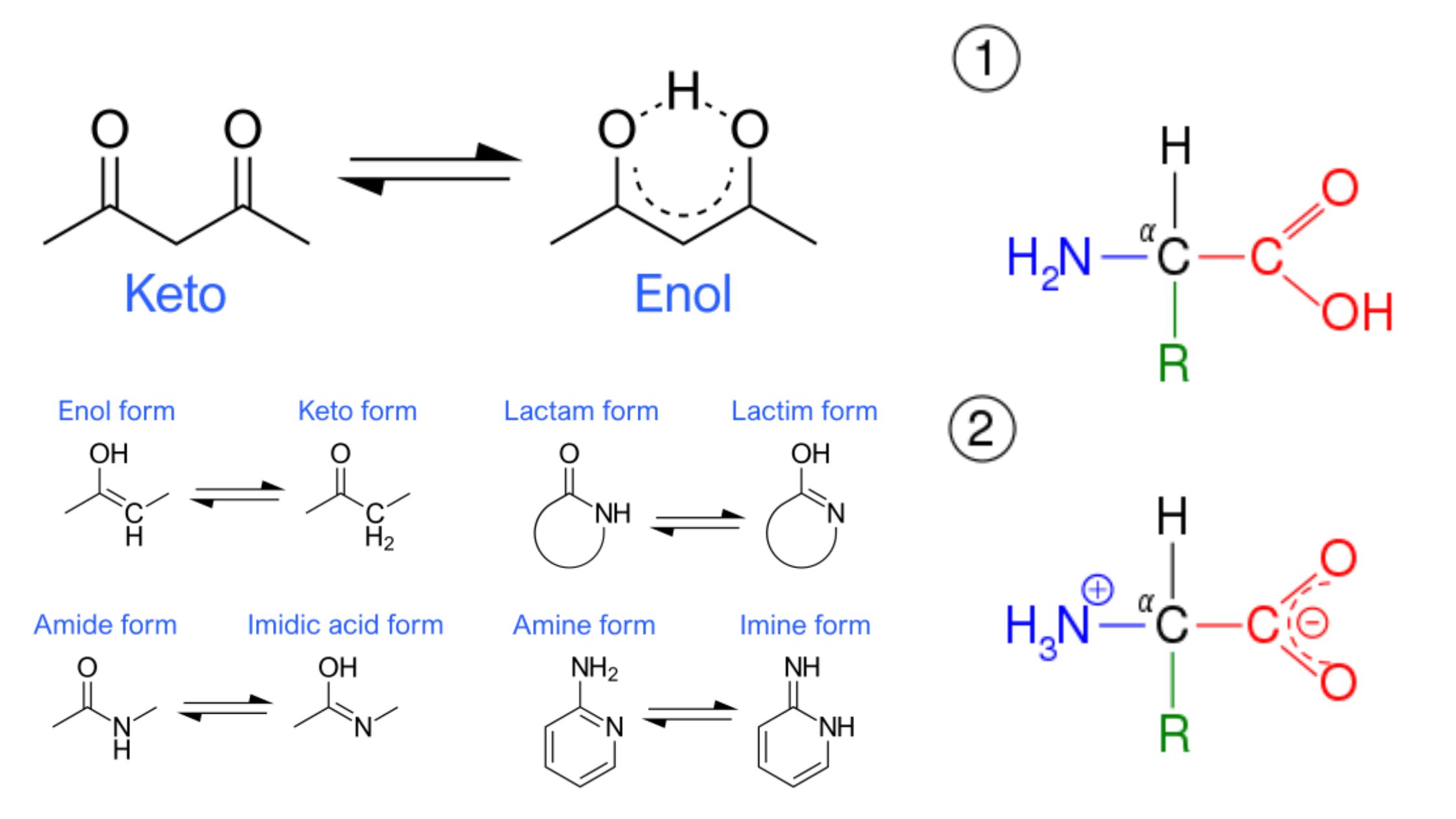
What is Haworth projection? Characteristics of Haworth projection The Haworth projection is a two-dimensional representation used to depict the three-dimensional structure of cyclic carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides and disaccharides. It provides valuable information about the arrangement of atoms and functional groups within the molecule. Here are some key characteristics of the Haworth projection: The Haworth … Read more