What are the Pathotypes of E. coli? – ETEC, EPEC, EHEC, EAEC, EIEC, DAEC
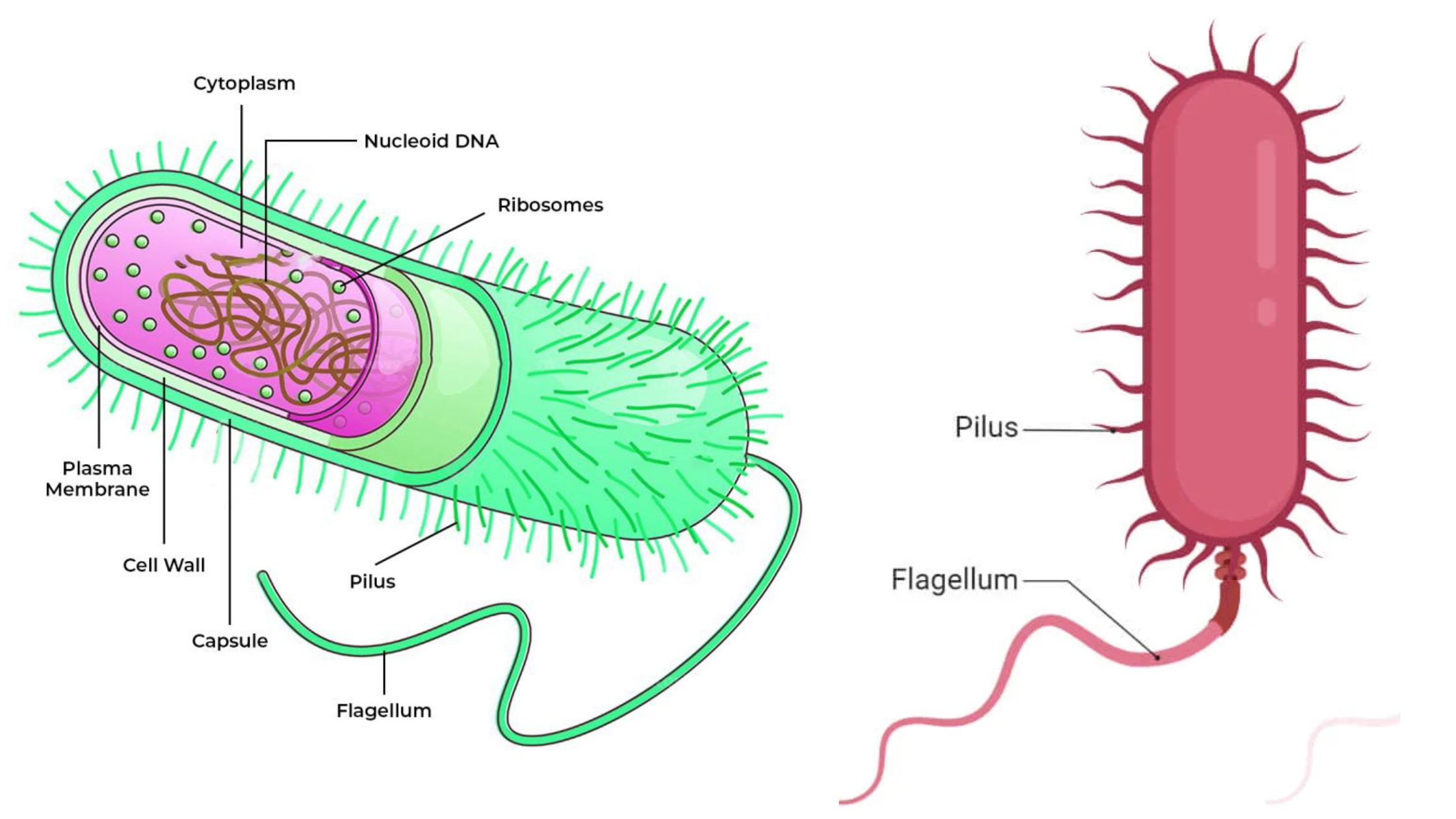
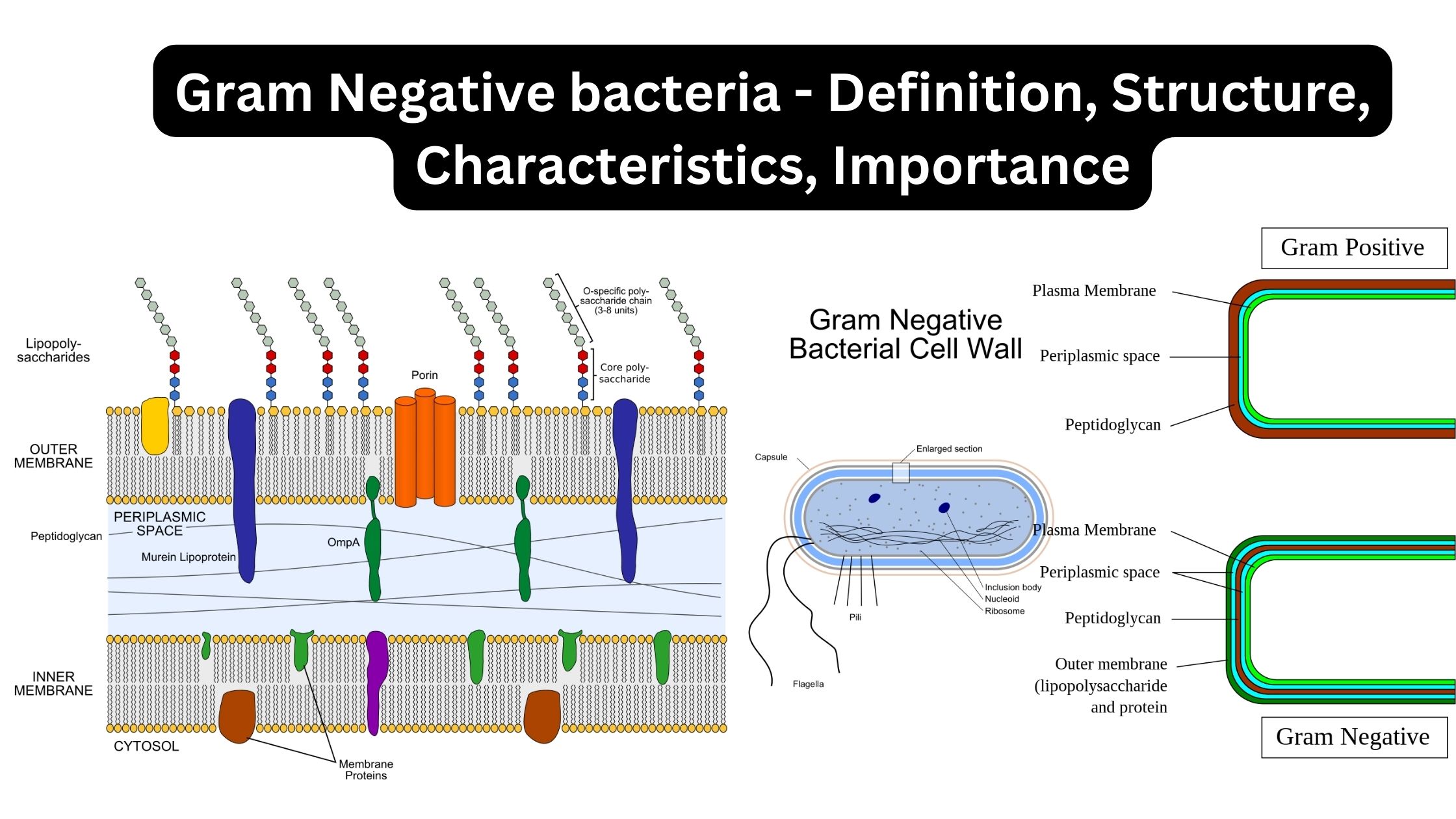
Escherichia coli, commonly referred to as E. coli, is a type of Gram-negative bacterium. It is facultative anaerobic, meaning it can survive in environments with or without oxygen, and has a rod-shaped morphology. E. coli is predominantly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms, including humans (endotherms). Human strains of E. coli can be … Read more