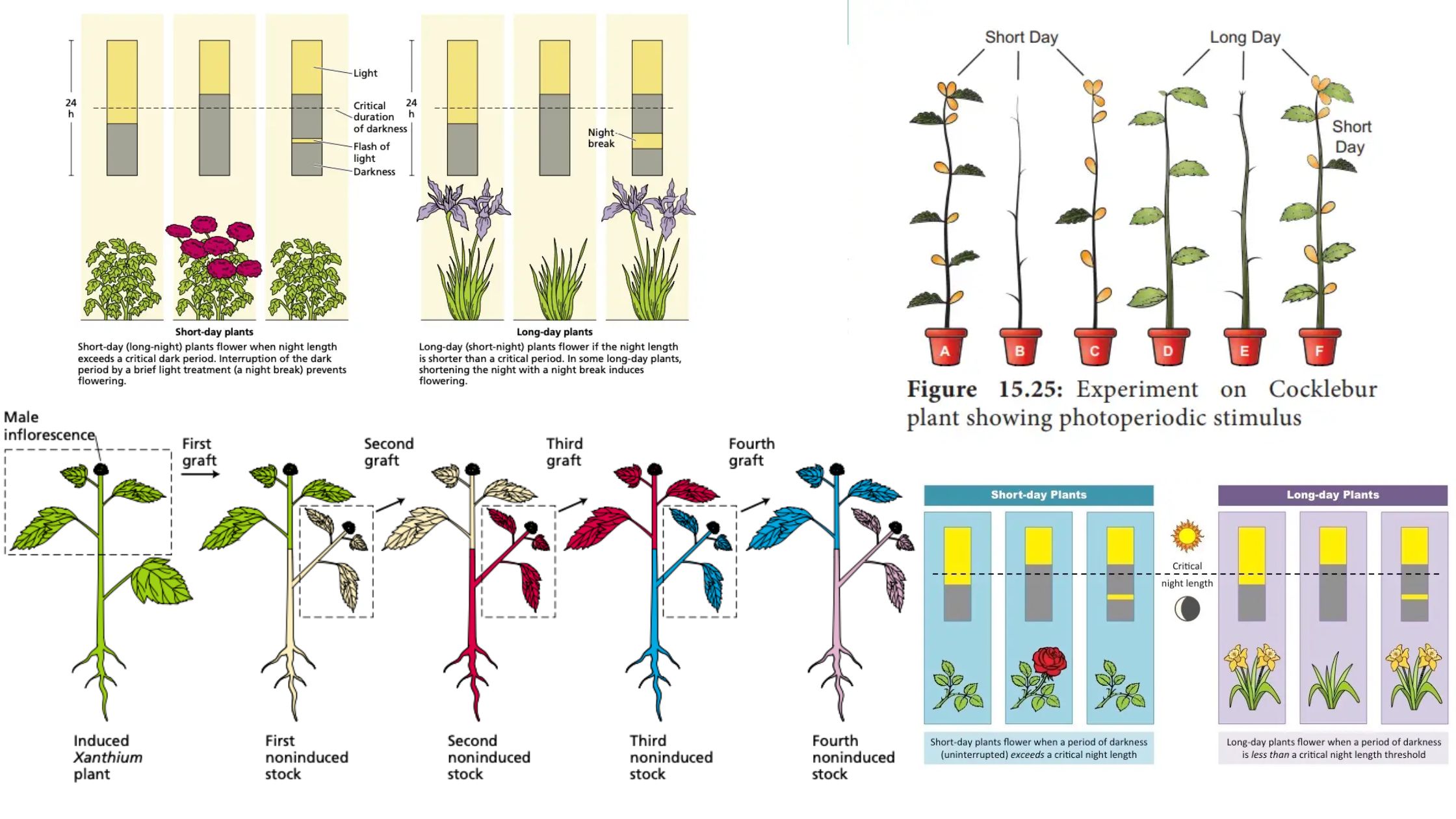
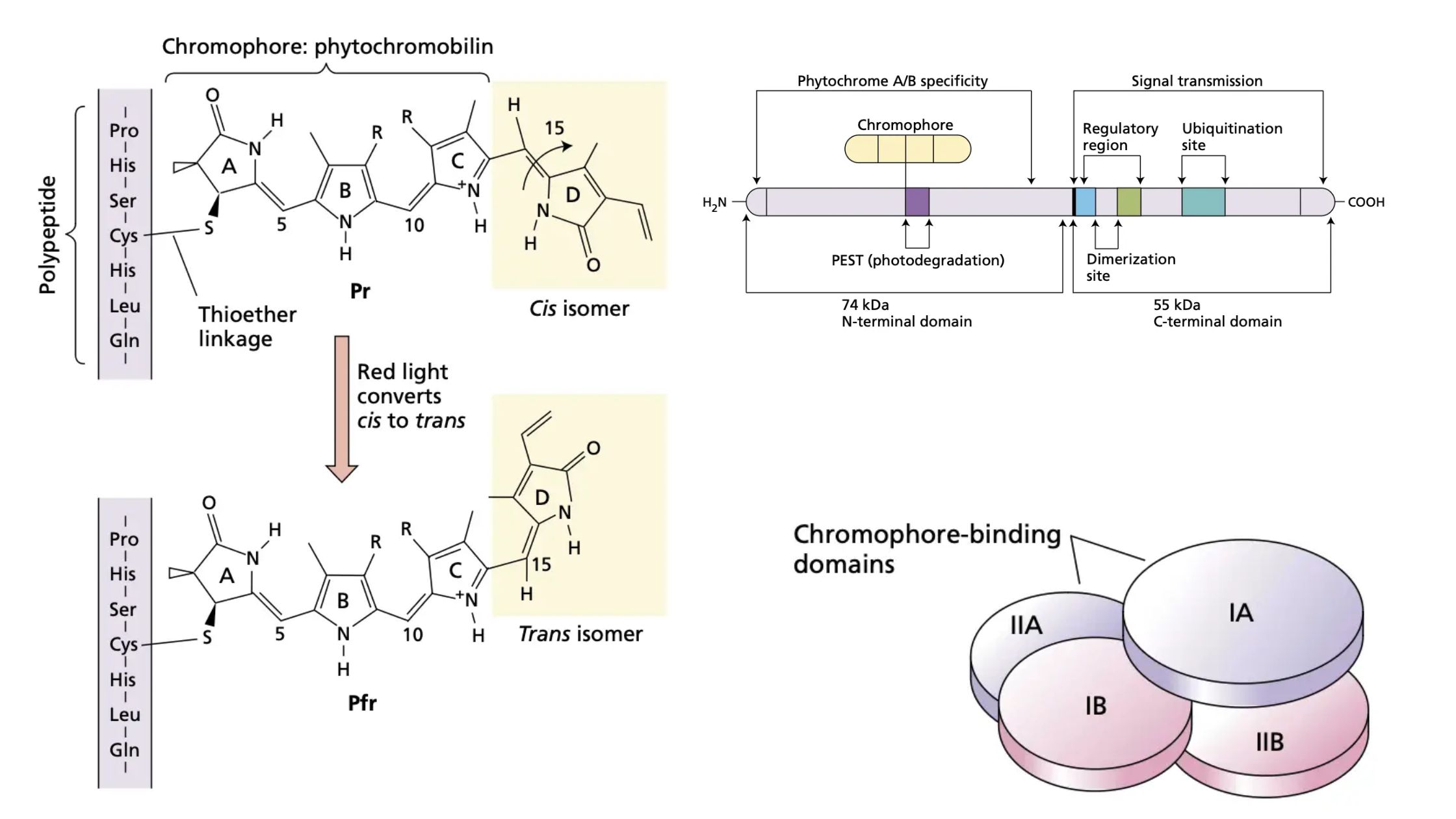
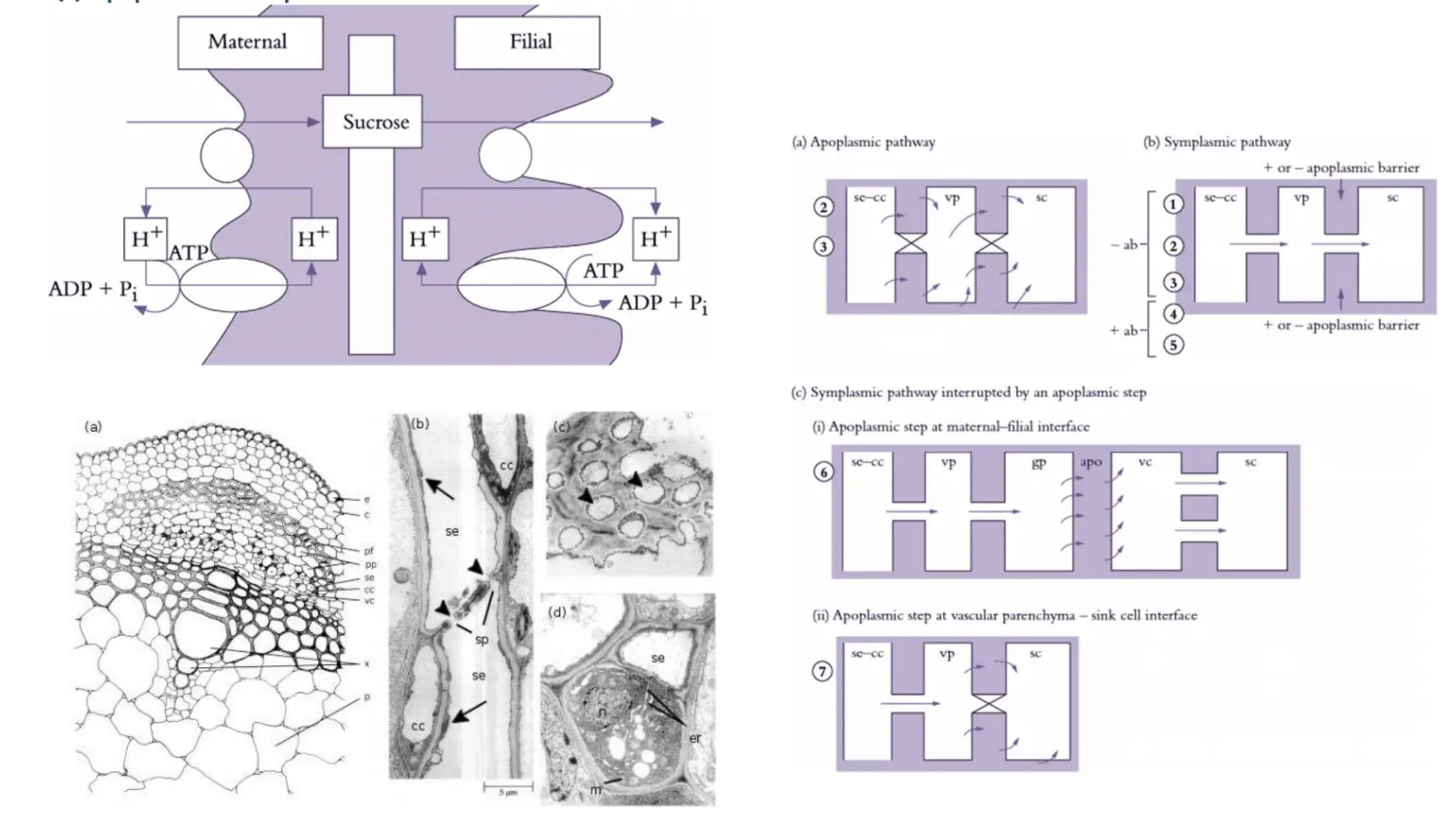
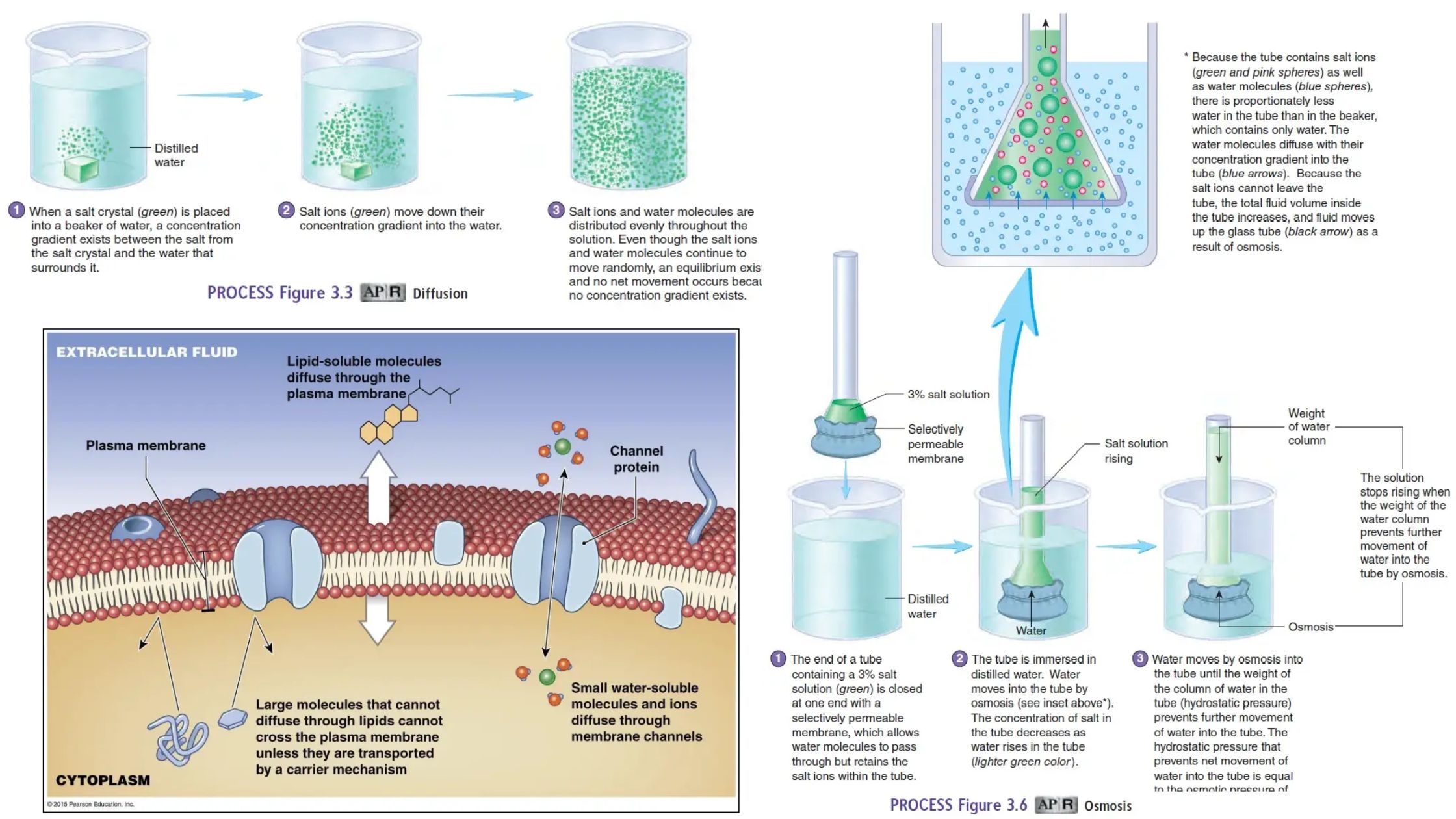
Photoperiodism – Definition, Types, Importance
What is Photoperiodism? Classification of plants based on Photoperiodism Plants are classified into several categories based on their response to the length of light and dark periods. These categories reflect how different species time their flowering and growth in accordance with seasonal day-length variations. The primary classifications include: Photoperiodic Induction Photoperiodic induction refers to the … Read more